





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 3188-3198.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.07.014
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Tong1( ), WANG Yahui2, WU Tianyi2, GAO Chen2, GAO Xiaoxiao1, ZHANG Lupei2,*(
), WANG Yahui2, WU Tianyi2, GAO Chen2, GAO Xiaoxiao1, ZHANG Lupei2,*( ), GAO Huijiang2, LI Junya2
), GAO Huijiang2, LI Junya2
Received:2025-01-21
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
ZHANG Lupei
E-mail:zhaotong1204@163.com;zhanglupei@caas.cn
CLC Number:
ZHAO Tong, WANG Yahui, WU Tianyi, GAO Chen, GAO Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Lupei, GAO Huijiang, LI Junya. Effects of Overexpression and Interference of PRKD1 Gene on Osteogenic Differentiation of Bovine Osteoblasts[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3188-3198.
Table 2
Primer sequences for PRKD1 RT-qPCR amplification"
| 基因Gene | 上游引物(5′→3′) Forward primer sequence | 下游引物(5′→3′) Reverse primer sequence |
| PRKD1 | AGACTTTCAGATTCGCCCCC | TCAGCCCACATCCTTCACAT |
| RUNX2 | CGGAGTGGAAGAGGCAAGAG | TGGATGGACGGAGGAGTCAT |
| COL I | AGGCCAAGAAGAAGACATCCC | GGGACTTTGGCGTTAGGACA |
| SPP1 | GCTAAAGCCTGACCCATCTCA | GGACTTACTTGGGAGGGTATTTTG |
| SP7 | TGGCACACGGGCGAGAGG | TGGAGCAGAGTAGGCAGGTGAAC |
| GAPDH | AGGTCGGAGTGAACGGATTC | CCAGCATCACCCCACTTGAT |
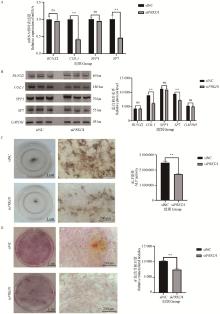
Fig. 3
PRKD1 knockdown inhibited the osteogenic differentiation of bovine osteoblasts A. mRNA expression levels of RUNX2, SP7, COL I and SPP1 were detected by RT-qPCR; B.Protein expression levels of RUNX2, SP7, COL I and SPP1 were detected by Western blot; C.ALP staining and quantification of bovine osteoblasts on the 7 day after transfection induced osteogenesis; D.Staining and quantification of Alizarin Red calcium nodules in bovine osteoblasts induced by osteogenesis after transfection on day 21"
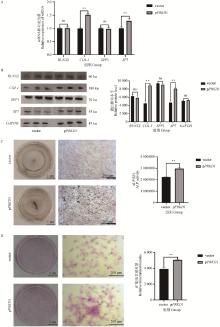
Fig. 5
Overexpression of PRKD1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of bovine osteoblasts A. mRNA expression levels of RUNX2, SP7, COL I and SPP1 were detected by RT-qPCR; B.Protein expression levels of RUNX2, SP7, COL I and SPP1 were detected by Western blot; C.ALP staining and quantification of bovine osteoblasts on the 7 day after transfection induced osteogenesis; D.Staining and quantification of Alizarin Red calcium nodules in bovine osteoblasts induced by osteogenesis after transfection on day 21"
| 1 | 邱怀, 常智杰, 昝林森. 秦川牛及其杂种后代胴体评定标准(试行)[J]. 黄牛杂志, 1997 (2): 11- 12. |
| QIU H , CHANG Z J , ZAN L S . Performance evaluation of Qinchuan cattle and its crossbreeding progeny[J]. China Cattle Science, 1997 (2): 11- 12. | |
| 2 | CAI W T , ZHANG Y P , CHANG T P , et al. The eQTL colocalization and transcriptome-wide association study identify potentially causal genes responsible for economic traits in Simmental beef cattle[J]. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2023, 14 (1): 78. |
| 3 | ZHU S Y , CHEN W , MASSON A , et al. Cell signaling and transcriptional regulation of osteoblast lineage commitment, differentiation, bone formation, and homeostasis[J]. Cell Discov, 2024, 10 (1): 71. |
| 4 | KANG Z Y , WU B , ZHANG L H , et al. Metabolic regulation by biomaterials in osteoblast[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2023, 11, 1184463. |
| 5 | NING K T , LIU S Q , YANG B Q , et al. Update on the effects of energy metabolism in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation[J]. Mol Metab, 2022, 58, 101450. |
| 6 | GLASS D , BIALEK P , AHN J , et al. Canonical Wnt signaling in differentiated osteoblasts controls osteoclast differentiation[J]. Dev Cell, 2005, 8 (5): 751- 764. |
| 7 | HU H H , HILTON M , TU X L , et al. Sequential roles of Hedgehog and Wnt signaling in osteoblast development[J]. Development, 2005, 132 (1): 49- 60. |
| 8 | STEGEN S , CARMELIET G . Metabolic regulation of skeletal cell fate and function[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2024, 20 (7): 399- 413. |
| 9 | BUCK H , STAINS J . Osteocyte-mediated mechanical response controls osteoblast differentiation and function[J]. Front Physiol, 2024, 15, 1364694. |
| 10 | CHEN H Y , SENDA T , KUBO K . The osteocyte plays multiple roles in bone remodeling and mineral homeostasis[J]. Med Mol Morphol, 2015, 48 (2): 61- 68. |
| 11 | BONEWALD L . The amazing osteocyte[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2011, 26 (2): 229- 238. |
| 12 | JOHANNES F , PRESTLE J , EIS S , et al. PKCu is a novel, atypical member of the protein kinase C family[J]. J Biol Chem, 1994, 269 (8): 6140- 6148. |
| 13 | HAYASHI A , SEKI N , HATTORI A , et al. PKCnu, a new member of the protein kinase C family, composes a fourth subfamily with PKCmu[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1999, 1450 (1): 99- 106. |
| 14 | STURANY S , VAN LINT J , MULLER F , et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human protein kinase D2. A novel member of the protein kinase D family of serine threonine kinases[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276 (5): 3310- 3318. |
| 15 | LEMONNIER J , GHAYOR C , GUICHEUX J , et al. Protein kinase C-independent activation of protein kinase D is involved in BMP-2-induced activation of stress mitogen-activated protein kinases JNK and p38 and osteoblastic cell differentiation[J]. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279 (1): 259- 264. |
| 16 | LI S , XU W F , XING Z , et al. A conditional knockout mouse model reveals a critical role of PKD1 in osteoblast differentiation and bone development[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7, 40505. |
| 17 | 张兴凯, 杨庆铭, 邓廉夫, 等. 成人成骨细胞体外培养[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2000, 38 (1): 51- 53. |
| ZHANG X K , YANG Q M , DENG L F , et al. In vitro culture of human osteoblasts[J]. Chinese Journal of Surgery, 2000, 38 (1): 51- 53. | |
| 18 | 李素华, 郭定宗, 黎兵, 等. 新生奶牛成骨细胞的体外培养、鉴定及生物特性[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2008 (9): 1084-1087+1100. |
| LI S H , YANG D Z , LI B , et al. Culture, idntification and biological characteristics of new born calf osteoblast[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2008 (9): 1084-1087+1100. | |
| 19 | GERBER I , GWYNN I . Influence of cell isolation, cell culture density, and cell nutrition on differentiation of rat calvarial osteoblast-like cells in vitro[J]. Eur Cell Mater, 2001, 2, 10- 20. |
| 20 | 王欢, 朱化彬, 李俊良, 等. 利用Tild-CRISPR/Cas9定点编辑荷斯坦种公牛的无角Pc位点[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2021, 48 (9): 3343- 3353. |
| WANG H , ZHU H B , LI J L , et al. Targeted Editing of Hornless Pc Site in Holstein Bulls Using Tild-CRISPR/Cas9[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 48 (9): 3343- 3353. | |
| 21 | 吴学祥, 肖传斌. 动物解剖学[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 2023. |
| WU X X , XIAO C B . Animal anatomy[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 2023. | |
| 22 | LEDUC F , SMOL T , CATTEAU B , et al. PRKD1-related telangiectasia-ectodermal dysplasia-brachydactyly-cardiac anomaly syndrome: Case report and review of the literature[J]. Eur J Med Genet, 2024, 69, 104942. |
| 23 | CHALFANT V , RIVEROS C , SINGH P , et al. Potential role for protein kinase D inhibitors in prostate cancer[J]. J Mol Med (Berl), 2023, 101 (4): 341- 349. |
| 24 | BOLLAG W , CHOUDHARY V , ZHONG Q , et al. Deletion of protein kinase D1 in osteoprogenitor cells results in decreased osteogenesis in vitro and reduced bone mineral density in vivo[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2018, 461, 22- 31. |
| 25 | TULADHAR A , SHAVER J , MCGEE W A , et al. Prkd1 regulates the formation and repair of plasma membrane disruptions (PMD) in osteocytes[J]. Bone, 2024, 186, 117147. |
| 26 | ARYA P , SARANYA I , SELVAMURUGAN N . RUNX2 regulation in osteoblast differentiation: A possible therapeutic function of the lncRNA and miRNA-mediated network[J]. Differentiation, 2024, 140, 100803. |
| 27 | KOMORI T . Bone development by Hedgehog and Wnt signaling, Runx2, and Sp7[J]. J Bone Miner Metab, 2025, 43 (1): 33- 38. |
| 28 | KOMORI T . Whole aspect of Runx2 functions in skeletal development[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (10): 5776. |
| 29 | SELVARAJ V , SEKARAN S , DHANASEKARAN A , et al. Type 1 collagen: Synthesis, structure and key functions in bone mineralization[J]. Differentiation, 2024, 136, 100757. |
| 30 | WANG J L , TOKAVANICH N , WEIN M . SP7: from bone development to skeletal disease[J]. Curr Osteoporos Rep, 2023, 21 (2): 241- 252. |
| 31 | JENSEN E , SCHROEDER T , BAILEY J , et al. Histone deacetylase 7 associates with Runx2 and represses its activity during osteoblast maturation in a deacetylation-independent manner[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2008, 23 (3): 361- 372. |
| 32 | JENSEN E , GOPALAKRISHNAN R , WESTENDORF J . Bone morphogenic protein 2 activates protein kinase D to regulate histone deacetylase 7 localization and repression of Runx2[J]. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284 (4): 2225- 2234. |
| 33 | BARRIO-HERNANDEZ I , JAFARI A , RIGBOLT K , et al. Phosphoproteomic profiling reveals a defined genetic program for osteoblastic lineage commitment of human bone marrow-derived stromal stem cells[J]. Genome Res, 2020, 30 (1): 127- 137. |
| 34 | CHUNG R , FOSTER B , XIAN C . Inhibition of protein kinase-D promotes cartilage repair at injured growth plate in rats[J]. Injury, 2013, 44 (7): 914- 922. |
| 35 | KOMORI T . Regulation of skeletal development and maintenance by Runx2 and Sp7[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (18): 10102. |
| 36 | CIANFEROTTI L . Osteomalacia is not a single disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (23): 14896. |
| 37 | YU H J , LI C R , WU H X , et al. Pathogenic mechanisms of osteogenesis imperfecta, evidence for classification[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2023, 18 (1): 234. |
| [1] | LIU Yuze, YU Zhuoya, GONG Zhiguo, REN Peipei, ZHAO Jiamin, MAO Wei, ZHANG Shuangyi,FENG Shuang. The Impact of Lipoprotein on the Secretion of Inflammatory Mediators and the Synthesis of Prostaglandin E2 in Bovine Bone Marrow-derived Macrophages Infected with Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3474-3483. |
| [2] | GAO Linna, JIANG Yingying, WANG Yue, SHI Qianqian, AN Zhenjiang, WANG Huili, SHEN Yangyang, CHEN Kunlin, ZHANG Leying. Construction of a Whole Genome Knockout Library of bMECs Based on CRISPR/Cas9 Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2711-2723. |
| [3] | HAN Xitong, ZHANG Nan, ZHANG Ning, ZHANG Jiaxin. FLI Promotes in Vitro Maturation of Bovine Oocytes by Increasing the Glucose Metabolism Pathway [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2778-2789. |
| [4] | JIA Chaoying, ZHANG Huawei, LUO Xiuxin, LIU Qingyun, WANG Xiangru. Establishment of Mice Model Infected by Bovine Mannheimia haemolytica and the Immunogenicity of Inactivated Vaccine [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2312-2324. |
| [5] | ZHAO Ying, WANG Jinglei, WANG Meng, WANG Libin, ZHANG Qian, LI Zhijie, MA Xin, YU Sijiu, PAN Yangyang. Preparation and Characterization of Forsythiaside A and Kaempferol Encapsulated in Milk-derived Exosomes and Evaluation of Anti-inflammatory Effects in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2481-2495. |
| [6] | XIONG Keng, FAN Haojie, WANG Jie, ZHAO Shanjiang, ZHU Qingli, HU Zhihui, LUO Haoshu, ZHU Huabin. Recent Advances and Applications of Recombinant Follicle-Stimulating Hormone in Bovine Superovulation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2047-2055. |
| [7] | ZHAO Wanyue, XU Xiaowen, CHANG Shushu, XIANG Zhijie, GUO Aizhen, CHEN Yingyu. Epidemiologic Investigation of the Major Viruses of the Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1324-1335. |
| [8] | JIANG Huihua, ZHAO Long, GUO Kangkang. Effect of HE Gene Receptor Binding Domain Variation on Bovine Coronavirus Infection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1336-1343. |
| [9] | ZHAO Wenyue, YANG Jing, SHAO Yilan, LI Jiaxuan, JIANG Yanping, CUI Wen, WANG Xiaona, TANG Lijie. Screening and Identification of Secretory Signal Peptide of Lactobacillus reuteri Expressing Lactoferrin Peptide [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1431-1440. |
| [10] | ZHANG Zhengyu, YANG Peihong, GUO Hong, LI Xin, ZHANG Linlin, GUO Yiwen, HU Debao, DING Xiangbin. Effects of Sirt1 Deacetylase on Proliferation and Differentiation of Bovine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 603-610. |
| [11] | LIANG Entang, LI Huaxuan, CHEN Shuaicheng, LI Guo, SUN Gege, ZAN Linsen. Effect of Genistein on Semen Cryopreservation of Bull [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 700-710. |
| [12] | LIU Jian, YU Zehai, ZHANG Meiyu, LI Dan, WANG Jun, LIU Fangqin, ZHANG Qun, XU Shouzhen. Full-genome Analysis of a Bovine Enterovirus Type F and the Establishment of an Indirect ELISA Method for Antibody Detection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 814-825. |
| [13] | ZHAO Long, LIN Jingyi, DOU Wei, XU Tingxuan, GU Qingyun, GAO Haihui, LI Shengqing, GUO Kangkang. In vitro Screening of Tibetan Medicine with Inhibitory Effects on Bovine Coronavirus Replication [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 826-838. |
| [14] | WANG Haolei, LIU Mengyan, LONG Quan, LI Manman, LÜ Xiang, LIN Tao, JIANG Caode. Inhibition of Epicatechin Gallate on Inflammation and Pyroptosis as Well as NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome in MAC-T Cells and Mouse Mammary Glands [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 430-441. |
| [15] | Yi WANG, Jianfei GONG, Nuo HENG, Yingfan HU, Rui WANG, Huan WANG, Ni ZHU, Wei HE, Zhihui HU, Haisheng HAO, Huabin ZHU, Shanjiang ZHAO. Melatonin Alleviates Palmitic Acid-induced Damage in Bovine Endometrial Epithelial Cells by Improving Mitochondrial Dynamics [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3978-3987. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||