





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (2): 826-838.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.02.031
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Long1( ), LIN Jingyi1, DOU Wei1, XU Tingxuan1, GU Qingyun2, GAO Haihui1,3, LI Shengqing4,*(
), LIN Jingyi1, DOU Wei1, XU Tingxuan1, GU Qingyun2, GAO Haihui1,3, LI Shengqing4,*( ), GUO Kangkang1,*(
), GUO Kangkang1,*( )
)
Received:2024-04-02
Online:2025-02-23
Published:2025-02-26
Contact:
LI Shengqing, GUO Kangkang
E-mail:448069517@qq.com;lsq.8008@163.com;guokk2007@nwsuaf.edu.cn
CLC Number:
ZHAO Long, LIN Jingyi, DOU Wei, XU Tingxuan, GU Qingyun, GAO Haihui, LI Shengqing, GUO Kangkang. In vitro Screening of Tibetan Medicine with Inhibitory Effects on Bovine Coronavirus Replication[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 826-838.
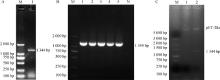
Fig. 1
BCoV N gene amplification electrophoresis and identification of pET28a-BCoV-N recombinant plasmid A. BCoV N gene amplification product electrophoresis (M. DL 2000 DNA marker; 1. BCoV N gene); B. Monoclonal positive colony PCR identification electrophoresis (M. DL 2000 DNA marker; 1-5. Positive colonies; N. Negative control); C. pET-28a-BCoV-N vector double enzyme digestion identification electrophoresis (M. DL 5000 DNA marker; 1. Undigested pET-28a-BCoV-N vector; 2. pET-28a-BCoV-N vector after enzyme digestion)"
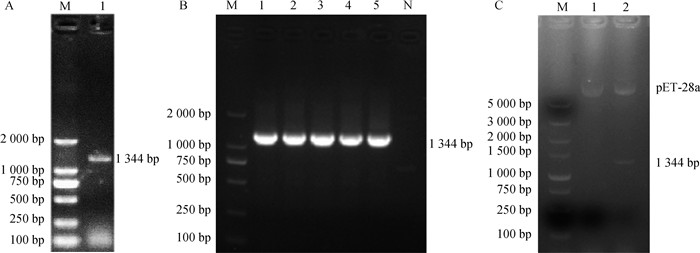
Fig. 2
Induced expression of recombinant N protein and identification of reactivity of polyclonal antibody with native N protein A. Identification of recombinant N protein expression (M. Protein marker; 1. Ultrasonic lysis of cell supernatant; 2. Ultrasonic lysis of cell precipitate); B. Purification of recombinant N protein (M. Protein marker; 1-4. Washing liquor; 5-8. Different concentrations of imidazole eluent); C. Western blot identification; D. IFA identification(bar=50 μm)"
Table 1
The safe concentration of 21 kinds of Tibetan medicine water extract in HCT-8 cells"
| 药物名称 Name of medicine | 干粉质量/g Weight of dry powder | 药物初始浓度/(mg·mL-1) Initial drug concentration | 最大安全浓度/(mg·mL-1) Maximum safe concentration |
| 独一味 | 13.22 | 55.80 | 3.49 |
| 蓝花荆芥 | 9.32 | 38.75 | 4.84 |
| 绿萝花 | 11.35 | 91.91 | 11.49 |
| 藏木香 | 14.66 | 41.12 | 20.56 |
| 盘花垂头菊 | 17.11 | 45.96 | 1.44 |
| 诃子 | 14.90 | 1.30 | 0.16 |
| 青藏大戟 | 18.38 | 3.95 | 0.12 |
| 乌奴龙胆 | 12.72 | 223.21 | 111.61 |
| 短穗兔耳草 | 15.35 | 1.30 | 0.33 |
| 五脉绿绒蒿 | 9.88 | 208.64 | 6.52 |
| 长松萝 | 17.26 | 11.88 | 1.48 |
| 余甘子 | 15.77 | 4.88 | 0.31 |
| 蒺藜 | 10.62 | 71.25 | 17.81 |
| 铁棒锤 | 18.39 | 15.63 | 0.98 |
| 螃蟹甲 | 16.715 | 7.42 | 1.86 |
| 甘青青兰 | 13.99 | 39.06 | 4.88 |
| 川西獐牙菜 | 13.24 | 39.06 | 9.77 |
| 甘青乌头 | 16.71 | 14.47 | 3.67 |
| 矮紫堇 | 17.23 | 82.25 | 2.57 |
| 瑞香狼毒 | 15.12 | 56.88 | 7.17 |
| 虎耳草 | 12.73 | 18.59 | 1.16 |
| 利巴韦林 | 0.10 | 0.38 | 0.024 |
| 1 | 刘蓉菁, 张志平, 王谢忠, 等. 我国牦牛源冠状病毒流行现状分析[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2020, 37 (3): 13- 16. |
| LIU R J , ZHANG Z P , WANG X Z , et al. Analysis on the prevalence status of yak-derived bovine coronavirus in China[J]. China Animal Health Inspection, 2020, 37 (3): 13- 16. | |
| 2 |
KEHA A , XUE L , YAN S , et al. Prevalence of a novel bovine coronavirus strain with a recombinant hemagglutinin/esterase gene in dairy calves in China[J]. Transbound Emerg Dis, 2019, 66 (5): 1971- 1981.
doi: 10.1111/tbed.13228 |
| 3 |
VLASOVA A N , SAIF L J . Bovine coronavirus and the associated diseases[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2021, 8, 643220.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.643220 |
| 4 | 李晨露, 吴发兴, 徐海玲, 等. 基于N蛋白的牛冠状病毒抗体间接ELISA检测方法的建立与应用[J]. 动物医学进展, 2022, 43 (5): 1- 5. |
| LI C L , WU F X , XU H L , et al. Establishment and application of indirect ELISA detection method for bovine coronavirus antibody based on N protein[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 43 (5): 1- 5. | |
| 5 | CHOULJENKO V N , LIN X Q , STORZ J , et al. Comparison of genomic and predicted amino acid sequences of respiratory and enteric bovine coronaviruses isolated from the same animal with fatal shipping pneumonia[J]. J Gen Virol, 2001, 82 (Pt 12): 2927- 2933. |
| 6 |
MURADYAN N , ARAKELOV V , SARGSYAN A , et al. Impact of mutations on the stability of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein structure[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14 (1): 5870.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55157-8 |
| 7 |
PENG Y , DU N , LEI Y Q , et al. Structures of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid and their perspectives for drug design[J]. EMBO J, 2020, 39 (20): e105938.
doi: 10.15252/embj.2020105938 |
| 8 | 梁彤, 曹存, 王芳, 等. 牛冠状病毒N蛋白的原核表达及其单克隆抗体的制备[J/OL]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2022, doi: 10.19958/j. |
| cnki. cn31-2031/s. 20221123. 002. LIANG T, CAO C, WANG F, et al. Prokaryotic expression of N protein of bovine coronavirus and preparation of its monoclonal antibody[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2022, doi: 10.19958/j.(inChinese) | |
| 9 |
DAI L P , GAO G F . Viral targets for vaccines against COVID-19[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2021, 21 (2): 73- 82.
doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-00480-0 |
| 10 |
刘冬涵, 钟宛凌, 竺楹银, 等. 藏药治疗新型冠状病毒肺炎高频药物的药理作用研究进展[J]. 中成药, 2022, 44 (7): 2249- 2256.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2022.07.031 |
|
LIU D H , ZHONG W L , ZHU Y Y , et al. Research progress on pharmacological effects of high-frequency drugs for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 in Tibetan medicine[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2022, 44 (7): 2249- 2256.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2022.07.031 |
|
| 11 |
JOKAR A , MASOOMI F , SADEGHPOUR O , et al. Potential therapeutic applications for Terminalia chebula in Iranian traditional medicine[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2016, 36 (2): 250- 254.
doi: 10.1016/S0254-6272(16)30035-8 |
| 12 |
王丹阳, 张康, 王旭荣, 等. 诃子、矮紫堇、甘青乌头提取物对牛病毒性腹泻病毒的体外抑制作用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2018, 49 (9): 2036- 2043.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2018.09.025 |
|
WANG D Y , ZHANG K , WANG X R , et al. Inhibitory effects of extracts from Terminalia chebula, Corydalis hendersonii, Aconitum tanguticum on bovine viral diarrhea virus in vitro[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2018, 49 (9): 2036- 2043.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2018.09.025 |
|
| 13 | 张媛媛, 曾慧婷, 袁源见, 等. 藏药诃子的化学成分与药理活性研究进展[J]. 中国药房, 2018, 29 (14): 2002- 2006. |
| ZHANG Y Y , ZENG H T , YUAN Y J , et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Tibetan medicine Terminalia chebula Retz[J]. China Pharmacy, 2018, 29 (14): 2002- 2006. | |
| 14 | 张春江, 李薇, 孙振鹏, 等. 藏药甘青乌头抗单纯疱疹病毒Ⅱ型体内外作用研究[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2009, 44 (1): 26- 31. |
| ZHANG C J , LI W , SUN Z P , et al. Evaluation of antiviral activity of Tibetan medicine Aconitum tanguticum against herpes simplex virus type Ⅱ in vitro and in vivo[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal, 2009, 44 (1): 26- 31. | |
| 15 |
李爱科, 王薇薇, 王永伟, 等. 生物饲料及其替代和减少抗生素使用技术研究进展[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32 (10): 4793- 4806.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.10.031 |
|
LI A K , WANG W W , WANG Y W , et al. Research progress of biological feed and its use technology in substitution and reduction of antibiotics[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32 (10): 4793- 4806.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.10.031 |
|
| 16 |
BAIG T A , ZHANG M Y , SMITH B L , et al. Environmental effects on viable virus transport and resuspension in ventilation airflow[J]. Viruses, 2022, 14 (3): 616.
doi: 10.3390/v14030616 |
| 17 |
ZAHARIEVA M M , FOKA P , KARAMICHALI E , et al. Photodynamic inactivation of bovine coronavirus with the photosensitizer toluidine blue O[J]. Viruses, 2023, 16 (1): 48.
doi: 10.3390/v16010048 |
| 18 |
SINIAVIN A E , GUSHCHIN V A , SHASTINA N S , et al. New conjugates based on N4-hydroxycytidine with more potent antiviral efficacy in vitro than EIDD-2801 against SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses[J]. Antiviral Res, 2024, 225, 105871.
doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105871 |
| 19 | 黄名英, 傅安静, 田润. 鼠源和兔源多克隆抗体的比较试验[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2017, (3): 175- 177. |
| HUANG M Y , FU A J , TIAN R . Comparative test of mouse and rabbit polyclonal antibodies[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2017, (3): 175- 177. | |
| 20 | SAIF L J , JUNG K . Comparative pathogenesis of bovine and porcine respiratory coronaviruses in the animal host species and SARS-CoV-2 in humans[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2020, 58 (8): e01355- 20. |
| 21 | LI Z Y , CHEN W X , QIU Z L , et al. African swine fever virus: a review[J]. Life (Basel), 2022, 12 (8): 1255. |
| 22 | KAUSAR S , KHAN F S , UR REHMAN M I M , et al. A review: mechanism of action of antiviral drugs[J]. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, 2021, 35, 20587384211002621. |
| 23 | YIN H , JIANG N , SHI W H , et al. Development and effects of influenza antiviral drugs[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26 (4): 810. |
| 24 | 林志达, 黄晶, 蔡杰, 等. 兽药残留种类及检测方法[J]. 中国动物保健, 2022, 24 (1): 1. |
| LIN Z D , HUANG J , CAI J , et al. Veterinary drug residue types and detection methods[J]. China Animal Health, 2022, 24 (1): 1. | |
| 25 | 吉守祥, 鞠怀强, 向阳飞, 等. 余甘子等28种藏药提取物体外抗乙型肝炎病毒的实验研究[J]. 中药材, 2011, 34 (3): 438- 440. |
| JI S X , JU H Q , XIANG Y F , et al. Anti-in vitro of 28 kinds of Tibetan medicine extracts such as Phyllanthus emblica[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2011, 34 (3): 438- 440. | |
| 26 | 种新禄, 侯晓林, 陈佳佳, 等. 诃子中总多酚粗提取工艺及药理作用研究[J]. 北京农学院学报, 2014, 29 (3): 64- 67. |
| CHONG X L , HOU X L , CHEN J J , et al. Research on the process of polyphenols crude extract from terminalia and its pharmacological effect[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Agriculture, 2014, 29 (3): 64- 67. | |
| 27 | 杨红霞, 马芳, 杜玉枝, 等. 藏药川西獐牙菜及其不同提取物的红外光谱分析[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2014, 34 (11): 2973- 2977. |
| YANG H X , MA F , DU Y Z , et al. Study on the Tibetan medicine Swertia mussotii franch and its extracts by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2014, 34 (11): 2973- 2977. |
| [1] | ZENG Miaomiao, YANG Xiaoman, ZHANG Xin, LIU Dakai, SHI Hongyan, ZHANG Jiyu, ZHANG Liaoyuan, CHEN Jianfei, FENG Tingshuai, LI Xiuwen, SHI Da, FENG Li. Establishment and Preliminary Application of an Indirect ELISA for Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus N Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 319-326. |
| [2] | HUANG Jin, LI Siyuan, MAO Li, CAI Xuhang, XIE Lingling, WANG Fu, ZHOU Hua, LI Jizong, LI Bin. Eukaryotic Expression of Bovine Coronavirus S1 Protein and Establishment and Application of Indirect ELISA [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2050-2060. |
| [3] | GUO Xuelian, LI Yongqin, LI Ruiqian, LI Hao, JIN Shuangyuan, WANG Xueyan, DU Jiawei, XU Lihua. Biological Functions of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus G and F Proteins [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1478-1487. |
| [4] | LUO Xiaofen, XIE Xiaodong, ZHAO Chao, HU Qian, WANG Yongxuan, RAN Fangfei, HU Pengfei, WEN Ming, ZHU Erpeng, CHENG Zhentao. Initial Identification of Adhesion-related Proteins of Mycoplasma bovis of Guizhou Strains [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1672-1683. |
| [5] | LIU Qiang, NIU Xiaoxia, FANG Min, LIU Yanling, GAO Hui, CHEN Jixiang, JIAHUA Cairang, ZHANG Sinong, LI Yong. Research Progress of Bovine Coronavirus Spike Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 944-956. |
| [6] | YU Qisheng, ZHU Qing, ZHOU Qun, SONG Xin, ZHANG Jiaqi, CHEN Taoyun, XU Lin, ZHANG Chaohui, ZHANG Bin. Expression of BCoV Spike Protein by Baculovirus Expression System and Its Immunogenicity in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 640-648. |
| [7] | LI Siyuan, FU Xincheng, YUAN Xuesong, MAO Li, CAI Xuhang, SUN Xinru, HUANG Jin, XIE Lingling, WANG Fu, ZHOU Hua, ZHANG Qi, LI Jizong, LI Bin. Detection of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Pathogens and Evolution Analysis of Bovine Coronavirus in Langfang, Hebei [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 649-659. |
| [8] | Qiuyuan FENG, Hanwei YU, Yunfeng YANG, Hui ZHANG, Weiyi HANWU, Xintong SUN, Xiaolong SHAO, Junlin LIU, Guohua CHEN, Zhizhong JING, Yixia CHEN. Regulation of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway by Goat Poxvirus Ankyin Protein ORF140 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5191-5199. |
| [9] | Fukang LIU, Ligang YUAN, Da ZHANG, Aoxing TANG, Guangqing LIU, Jie ZHU. Preparation and Application of N Protein Polyclonal Antibody of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus SH2021 Strain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4773-4778. |
| [10] | XIE Qingyun, XING Huixuan, YU Yanfei, YUAN Ting, XIONG Qiyan, XIONG Fuqiang, FENG Zhixin. Prokaryotic Expression, Polyclonal Antibody Preparation and Activity Identification of Helicase RuvA from Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 271-281. |
| [11] | WANG Jingyu, PAN Yangyang, XU Gengquan, ZHANG Rui, ZHANG Wenlan, WANG Xiaoshan, WU Rentaodi, ZHAO Rigetu, CUI Yan, YU Sijiu. Preparation and Preliminary Application of Yak (Bos Grunniens) Fas-associated Factor 1 Polyclonal Antibody [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3369-3382. |
| [12] | JIAO Zhengxing, PAN Yangyang, WANG Meng, WANG Jinglei, MA Wenbin, GAO Xiang, ZHANG Hui, CUI Yan, YU Sijiu, WANG Libin. Preparation of Polyclonal Antibody against Yak LC3B Protein and Its Application in Detection of Expression in Reproductive Organs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2436-2447. |
| [13] | GAO Zhenzhen, MENG Zejing, HE Xiaobing, FANG Yongxiang, TIAN Huihui, CHEN Guohua, JING Zhizhong. Identification of Immunogenicity and Neutralizing Activity of Ectromelia Virus EVM135 and EVM085 Proteins [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2468-2477. |
| [14] | WANG Bingnan, SUN Xue, JIA Hongguo, TAN Chun, MEI Sipeng, ZHOU Rongqiong. Prokaryotic Expression and Tissue Localization of C-type Lectin 4 from Toxocara canis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(4): 1641-1651. |
| [15] | WANG Lan, HE Mingyu, ZHANG Min, DING Juntao. MicroRNAs Regulate Antiviral Immunity and Viral Replication [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(2): 463-472. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||