





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (2): 814-825.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.02.030
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Jian( ), YU Zehai(
), YU Zehai( ), ZHANG Meiyu, LI Dan, WANG Jun, LIU Fangqin, ZHANG Qun, XU Shouzhen*(
), ZHANG Meiyu, LI Dan, WANG Jun, LIU Fangqin, ZHANG Qun, XU Shouzhen*( )
)
Received:2024-04-01
Online:2025-02-23
Published:2025-02-26
Contact:
XU Shouzhen
E-mail:815846879@qq.com;1062100624@qq.com;xsz2738@sina.com.cn
CLC Number:
LIU Jian, YU Zehai, ZHANG Meiyu, LI Dan, WANG Jun, LIU Fangqin, ZHANG Qun, XU Shouzhen. Full-genome Analysis of a Bovine Enterovirus Type F and the Establishment of an Indirect ELISA Method for Antibody Detection[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 814-825.
Table 1
Reference strains of bovine enterovirus"
| 毒株 Strains | 登录号 Accession numbers | 国家 Country | 分型 Species | 宿主 Host |
| HeN-YR91 | MN598018. 1 | China | F | 牛 |
| HeN-B62 | MN598011.1 | China | F | 牛 |
| BEV-261 | DQ092770.1 | USA | F | 牛 |
| BEVVG527 | D00214.1 | USA | E | 牛 |
| NX-FY40 | MN598039.1 | China | E | 牛 |
| JL-JY42 | MN598032.1 | China | E | 牛 |
| NX-b-DR47 | MN598037.1 | China | E | 牛 |
| SL305 | AF123433.1 | Australia | E | 牛 |
| E1-NSWL7 | OP020147.1 | Australia | E | 牛 |
| BEV-7414 | NC001859 | USA | E | 牛 |
| PS87F3 | DQ092794.1 | USA | F | 牛 |
| PS89F2 | DQ092795.1 | USA | F | 牛 |
| Porcine enterovirus type 9 | Y14459 | United Kingdom | G | 猪 |
| Ovine enterovirus TB4-OEV | JQ277724 | Hungary | G | 羊 |
| Human enterovirus 88 strain BAN01-10398 | AY843306 | USA | B | 人 |
| F4 | AY462106.1 | USA | F | 牛 |
| A71F5 | MG674288.1 | China | EV-A | 人 |
| BEV4 | ON986117.1 | China | F | 牛 |
| 128135 | HQ424437.2 | Greece | EV-A | 人 |
Table 2
Number and location of non-coding regions and nucleotides in coding regions of BEV isolates"
| 功能区 Function region | 位置 Position | 核酸数目/ bp Nucleotide number |
| 5’UTR | 1-822 bp | 822 |
| VP4 | 823-1 029 bp | 207 |
| VP2 | 1 030-1 767 bp | 738 |
| VP3 | 1 768-2 496 bp | 729 |
| VP1 | 2 497-3 321 bp | 825 |
| 2A | 3 322-3 822 bp | 501 |
| 2B | 3 723-4 119 bp | 297 |
| 2C | 4 120-5 106 bp | 987 |
| 3A | 5 107-5 373 bp | 267 |
| 3B | 5 374-5 442 bp | 69 |
| 3C | 5 443-5 991 bp | 549 |
| 3D | 5 992-7 326 bp | 1 335 |
| 3’UTR | 7 327-7 439bp | 113 |
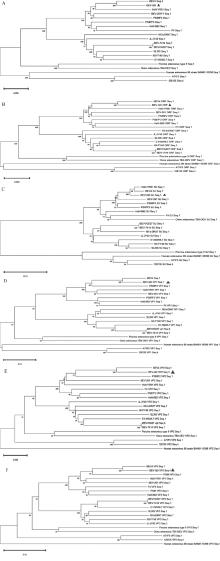
Fig. 3
Genetic evolution of BEV isolates of whole genes, ORF, 5′ UTR, VP1, VP2, VP3 genes A. Genetic evolutionary tree of the whole gene sequence of BEV isolates; B. Genetic evolutionary tree of ORF gene of BEV isolates; C. Genetic evolutionary tree of 5′-UTR fragment of BEV isolates; D. Genetic evolutionary tree of VP1 fragment of BEV isolates; E. Genetic evolutionary tree of VP2 fragment of BEV isolates; F. Genetic evolutionary tree of VP3 fragment of BEV isolates"

Table 3
Nucleotide homology analysis of BEV-QD strain with other EV strains %"
| 毒株Strain | 全基因组 Whole genome | ORF | 5’UTR | VP1 | VP2 | VP3 |
| HeN-YR91 | 81.0 | 78.9 | 95.6 | 72.5 | 73.3 | 72.7 |
| HeN-B62 | 79.0 | 77.8 | 85.9 | 66.8 | 71.5 | 70.6 |
| BEV-261 | 79.4 | 78.0 | 89.2 | 70.3 | 72.9 | 74.5 |
| BEVVG527 | 68.5 | 67.2 | 79.0 | 54.9 | 67.3 | 60.7 |
| NX-FY40 | 69.3 | 67.9 | 77.8 | 55.6 | 66.3 | 64.0 |
| JL-JY42 | 70.2 | 68.6 | 80.6 | 53.0 | 65.4 | 64.3 |
| NX-b-DR47 | 68.8 | 67.3 | 75.4 | 55.2 | 68.4 | 62.9 |
| SL305 | 68.7 | 67.6 | 76.6 | 60.1 | 66.0 | 63.5 |
| E1-NSWL7 | 68.8 | 67.5 | 78.7 | 54.7 | 64.9 | 62.1 |
| BEV-7414 | 68.5 | 67.2 | 79.0 | 54.9 | 67.3 | 60.7 |
| PS87 | 78.3 | 76.6 | 89.8 | 65.8 | 69.5 | 69.7 |
| PS89 | 80.0 | 78.8 | 88.0 | 74.5 | 74.1 | 73.3 |
| Porcine enterovirus type 9 | 62.8 | 63.4 | 45.2 | 54.4 | 62.6 | 60.2 |
| Ovine enterovirus TB4-OEV | 65.3 | 63.5 | 78.0 | 51.8 | 63.1 | 63.2 |
| Human enterovirus 88 strain BAN01-10398 | 59.0 | 60.8 | 47.8 | 20.1 | 60.0 | 54.8 |
| F4 | 75.1 | 74.3 | 76.7 | 60.2 | 70.2 | 68.2 |
| A71F5 | 58.8 | 59.5 | 44.0 | 36.7 | 62.3 | 51.2 |
| BEV4 | 88.4 | 87.6 | 94.7 | 87.5 | 86.9 | 89.0 |
| 128135 | 59.1 | 60.7 | 48.8 | 44.7 | 62.5 | 59.2 |
Table 4
Amino acid sequence site variation of BEV isolates"
| 区域 Area | 功能区 Function region | 氨基酸突变位置 Amino acid mutation location | 氨基酸Amino acid | |
| 突变前Before mutation | 突变后After mutation | |||
| P1区 | VP2 | 167 | F | Y |
| 224 | P | N | ||
| VP3 | 375 | N/S | A | |
| VP1 | 616 | T | L | |
| 640 | D/N | T | ||
| P2区 | 2A | 902 | M/N | S |
| 922 | L | I | ||
| 964 | P/F | L | ||
| 2B | 1 054 | L | V | |
| 2C | 1 308 | P | S | |
| 1 320 | P/T | I | ||
| P3区 | 3C | 1 541 | C | S |
| 1 626 | H/D | Y | ||
| 3D | 1 844 | C | R | |
| 1 911 | P/S | L | ||
| 1 935 | A | V | ||
| 1 955 | P | L | ||
| 1 957 | P | L | ||
Table 6
Sensitivity test results"
| 稀释度 dilutability | 阳性OD450(${\bar x}$ ± s) OD450 P | 变异系数/% CV |
| 1∶10 | 1.884±0.189 | 9.967 |
| 1∶40 | 1.227±0.080 | 6.531 |
| 1∶80 | 1.006±0.118 | 11.756 |
| 1∶100 | 0.993±0.075 | 7.598 |
| 1∶200 | 0.921±0.026 | 2.783 |
| 1∶400 | 0.842±0.048 | 5.688 |
| 1∶800 | 0.804±0.029 | 3.714 |
| 1∶1 600 | 0.691±0.073 | 10.617 |
| 1∶3 200 | 0.455±0.043 | 9.425 |
| 1 | 朱利塞. E种肠道病毒HY12准种与进化及VP1基因突变对病毒复制的影响[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017. |
| ZHU L S. Quasispecies and evolution of enterovirus HY12 and the effect of VP1 mutation on viral replication[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017. | |
| 2 | 朱彤, 赵贵民, 沈付娆, 等. 牛肠道病毒SYBR Green Ⅰ实时荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立及初步应用[J]. 病毒学报, 2015, 31 (5): 488- 493. |
| ZHU T , ZHAO G M , SHEN F Y , et al. Establishment and preliminary application of the SYBR green I real-time PCR assay for detection of the bovine enterovirus[J]. Chinese Journal of Virology, 2015, 31 (5): 488- 493. | |
| 3 |
LIU D , LIU C M , LIU X , et al. Rescue and characterization of a recombinant HY12 bovine enterovirus carrying a foreign HA epitope in the 3A nonstructural protein[J]. Arch Virol, 2019, 164 (5): 1309- 1321.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-019-04178-0 |
| 4 |
DOEDENS J R , KIRKEGAARD K . Inhibition of cellular protein secretion by poliovirus proteins 2B and 3A[J]. EMBO J, 1995, 14 (5): 894- 907.
doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07071.x |
| 5 | GEAR J H . Nonpolio causes of polio-like paralytic syndromes[J]. Rev Infect Dis, 1984, 6 Suppl 2, S379- S384. |
| 6 |
HUANG H I , SHIH S R . Neurotropic enterovirus infections in the central nervous system[J]. Viruses, 2015, 7 (11): 6051- 6066.
doi: 10.3390/v7112920 |
| 7 |
LEY V , HIGGINS J , FAYER R . Bovine enteroviruses as indicators of fecal contamination[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2002, 68 (7): 3455- 3461.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.7.3455-3461.2002 |
| 8 | MOSCOVICI C , LA PLACA M . Further studies of bovine enteroviruses--tentative scheme of classification[J]. Am J Vet Res, 1962, 23, 645- 648. |
| 9 |
PAUL A V , PETERS J , MUGAVERO J , et al. Biochemical and genetic studies of the VPg uridylylation reaction catalyzed by the RNA polymerase of poliovirus[J]. J Virol, 2003, 77 (2): 891- 904.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.2.891-904.2003 |
| 10 |
ZELL R , SIDIGI K , HENKE A , et al. Functional features of the bovine enterovirus 5'-non-translated region[J]. J Gene Virol, 1999, 80 (9): 2299- 2309.
doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-80-9-2299 |
| 11 | 季程远, 张瑶, 姚火春. 基于牛肠道病毒重组VP2蛋白间接ELISA抗体检测方法的建立与应用[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2023, 55 (7): 95- 99. |
| JI C Y , ZHANG Y , YAO H C . Establishment and application of an indirect ELISA based on recombinant VP2 protein of bovine enterovirus[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 55 (7): 95- 99. | |
| 12 | 周世力, 李琳琳. 肠道病毒71型外壳蛋白VP3在Pichia. pastoris酵母中的表达[J]. 江汉大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 34 (3): 41-43, 52. |
| ZHOU S L , LI L L . Expression antigen VP3 of enterovirus 71 in Pichia. pastoris[J]. Journal of Jianghan University (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 34 (3): 41-43, 52. | |
| 13 | 张海丽. 牛肠道病毒的分离鉴定及HLJ-3531株感染性分子克隆的建立[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2015. |
| ZHANG H L. Isolation and identification of bovine enterovirus and constrution of infectious cDNA of HLJ-3531 strain[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| 14 | 张姗. 牛肠道病毒BJ101株感染性cDNA克隆的构建及病毒拯救[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2018. |
| ZHANG S. Construction and rescue of bovine enterovirus strain BJ101 infectious clone[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 15 | 王刚. 牛肠道病毒的分离鉴定及二价灭活疫苗研制[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2021. |
| WANG G. Isolation and identification of bovine enterovirus and development of bivalent inactivated vaccine[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 16 | 郭金玉, 高志强, 张鹤晓, 等. 牛肠道病毒2型VP1+表达和间接ELISA方法的建立与应用[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2014, 50 (11): 40- 43. |
| GUO J Y , GAO Z Q , ZHANG H X , et al. Development and application of indirect ELISA for the detection of antibodies against bovine enterovirus type 2 based on VP1+ protein expression[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2014, 50 (11): 40- 43. |
| [1] | SHAO Yongheng, NI Minting, GAO Mengling, TANG Jiao, ZHANG Gengxin, LIN Shengyu, LIU Guangliang, CHEN Jianing, WANG Wenhui. Prokaryotic Expression of VP1 Protein to Porcine Teschovirus Type 5 and the Establishment of an Indirect ELISA Detection Method [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 883-889. |
| [2] | DU Qingjie, WU Liping, ZHANG Fan, DAI Pengxiu, FENG Xiancheng, ZHANG Xinke. Difference Analysis of Oral Flora in Dogs with Periodontitis and Drug Resistance of Oral Porphyromonas [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 934-942. |
| [3] | ZENG Miaomiao, YANG Xiaoman, ZHANG Xin, LIU Dakai, SHI Hongyan, ZHANG Jiyu, ZHANG Liaoyuan, CHEN Jianfei, FENG Tingshuai, LI Xiuwen, SHI Da, FENG Li. Establishment and Preliminary Application of an Indirect ELISA for Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus N Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 319-326. |
| [4] | Huancheng LIAO, Zhengwang SHI, Juncong LUO, Wanying WANG, Lu FENG, Jing ZHOU, Fan ZHANG, Xintai SHI, Hong TIAN. Preparation of Monoclonal Antibody against Cathay Topotype of FMDV Type O and Development of Double Antibody Sandwich ELISA for Cathay Topotype of FMDV Type O [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4012-4020. |
| [5] | Liguo GAO, Hanqin SHEN, Yiquan CHEN, Sheng CHEN, Wencheng LIN, Feng CHEN. Prokaryotic Expression of Recombinant VP6* Protein of Porcine Rotavirus and Establishment of Indirect ELISA Detection Method [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4021-4028. |
| [6] | Shan ZHANG, Dahu LIU, Baojing LIU, Lin LIANG, Ruiying LIANG, Xinming TANG, Xusheng QIU, Chan DING, Jiabo DING, Shaohua HOU. Isolation, Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of a Pigeon Paramyxovirus-1 Strain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4051-4060. |
| [7] | Cheng YANG, Ye LIU, Ning CHENG, Kaiyue WANG, Xinlei LI, Jiuying SUN, Junping HAN, Wenjun LI, Huanhuan WANG, Xiao SHAO, Xuejiao CHENG, Yingfeng SUN. Genomic Characterization of a Recombinant Strain of PRRSV-2 between Lineages 1.8 and 1.5 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3570-3578. |
| [8] | Huanqin ZHENG, Xiaomin JIANG, Hong YUE, Baoyan WANG, Yang LIU, Xingxiao ZHANG, Jianlong ZHANG, Hongwei ZHU. Isolation, Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics Analysis of Feline Herpesvirus-1 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3040-3048. |
| [9] | Jitong LI, Tong ZHU, Junfeng LÜ, Yuehua GAO, Feng HU, Kexiang YU, Minxun SONG, Jianlin WANG, Yufeng LI. Isolation and Identification of Novel Picornavirus from Ducks and Whole Genome Sequence Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3075-3084. |
| [10] | Bohua LIU, Hanyu FU, Yuheng WANG, Suolangsizhu, Jiaqiang NIU, Yuhua BAO, Jiakui LI, Yefen XU. Isolation, Identification and Genome Analysis of Type B Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Yak in Tibetan Nakchu City [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3105-3118. |
| [11] | HUANG Jin, LI Siyuan, MAO Li, CAI Xuhang, XIE Lingling, WANG Fu, ZHOU Hua, LI Jizong, LI Bin. Eukaryotic Expression of Bovine Coronavirus S1 Protein and Establishment and Application of Indirect ELISA [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2050-2060. |
| [12] | SONG Xiaoqing, DENG Ruide, LI Xin, LI Jiao, LI Runcheng, DU Lifei, DONG Wei, GE Meng. Establishment of ELISA for Detection of PCV4-Cap Antibody and Sero-epidemiological Survey [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2072-2079. |
| [13] | ZHAO Canqi, FENG Yu, LÜ Lang, LI Yanjun, WEI Yulei, DING Jiabo, CHEN Xiang, JIANG Hui. Study on Purification of Bovine Brucellosis by Competitive ELISA and Indirect ELISA [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2146-2153. |
| [14] | ZHENG Rui, LIU Zishi, ZHANG Kangyou, YAN Yong, WEI Ling, ZEREN Wengmu, DINGZE Demi, HUANG Jianjun, WANG Li, WEI Yong. Isolation, Identification and Biological Characterization of Colletotrichum jasminigenum in Stems of Peanuts [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2206-2213. |
| [15] | TIAN Rui, XU Sixiang, XIE Feng, LIU Guangjin, WANG Gang, LI Qingxia, DAI Lei, XIE Guoxin, ZHANG Qiongwen, LU Yajing, WANG Guangwen, WANG Jinxiu, ZHANG Wei. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Genome of Clostridium perfringens Isolated from Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1707-1715. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||