





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 3474-3483.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.07.039
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Yuze( ), YU Zhuoya(
), YU Zhuoya( ), GONG Zhiguo, REN Peipei, ZHAO Jiamin, MAO Wei, ZHANG Shuangyi*(
), GONG Zhiguo, REN Peipei, ZHAO Jiamin, MAO Wei, ZHANG Shuangyi*( ), FENG Shuang*(
), FENG Shuang*( )
)
Received:2024-09-12
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
ZHANG Shuangyi, FENG Shuang
E-mail:2516758527@qq.com;17704884830@163.com;shuangyisyau@163.com;fairysshuang@163.com
CLC Number:
LIU Yuze, YU Zhuoya, GONG Zhiguo, REN Peipei, ZHAO Jiamin, MAO Wei, ZHANG Shuangyi, FENG Shuang. The Impact of Lipoprotein on the Secretion of Inflammatory Mediators and the Synthesis of Prostaglandin E2 in Bovine Bone Marrow-derived Macrophages Infected with Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3474-3483.
Table 1
Real-time PCR primer"
| 引物名称 Primer name | GenBank登录号 GenBank accession No | 引物序列 Primer sequences |
| β-actin | NM_173979.3 | Forward 5′-TCACCAACTGGGACGACA-3′ |
| Reverse 5′-GCATACAGGGACAGCACA-3′ | ||
| TLR2 | NM_174197.2 | Forward 5′-CGATGACTACCGCTGTGACTC-3′ |
| Reverse 5′-CCTTCCTGGGCTTCCTCTT-3′ | ||
| TLR4 | NM_174198.6 | Forward: 5′-TGCCTTCACTACAGGGACTTT-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-TGGGACACCACGACAATAAC-3′ | ||
| NLRP3 | NM_001102219.1 | Forward: 5′-CAGATGAGCAGCAAGCAAGG-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-ACAATCCAGCAGACCAGAGG-3′ | ||
| COX-2 | XM_007115297.3 | Forward: 5′-GGTGCCTGGTCTGATGATGT-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-GATTAGCCTGCTTGTCTGGAAC-3′ | ||
| mPGES-1 | XM_027556544.1 | Forward: 5′-ATGGTACACACCGTGGCATA-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-CACAATCTCAAAGGGCCATC-3′ |
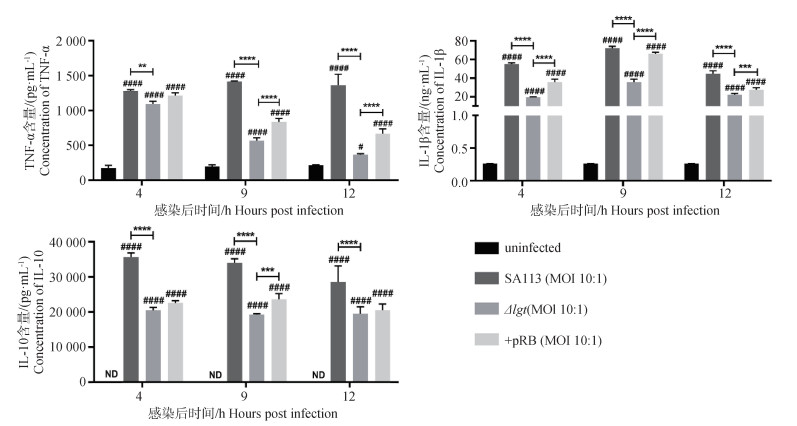
Fig. 1
Effect of lipoproteins on the secretion of inflammatory mediators in bBMMs infected with S. aureus Comparison between experimental groups, *. P < 0.05, **. P < 0.01, ***. P < 0.001, ****. P < 0.000 1;Comparison between the experimental group and the uninfected control group, #.P < 0.05, ##.P < 0.01, ###.P < 0.001, ####.P < 0.000 1. The same as below"
| 1 | ARCHER G . Staphylococcus aureus: a well-armed pathogen[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 1998, 26 (5): 1179- 1181. |
| 2 | VAUTOR E , MAGNONE V , RIOS G , et al. Genetic differences among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from dairy ruminant species: a single-dye DNA microarray approach[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2009, 133, 105- 114. |
| 3 | MOHAMMAD M , ALI A , NGUYEN M T , et al. Staphylococcus aureus lipoproteins in infectious diseases[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13, 1006765. |
| 4 | CILOGLU F U , CALISKAN A , SARIDAG A M , et al. Drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteria detection by combining surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) and deep learning techniques[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 18444. |
| 5 | LIAO Z , LIN K , LIAO W , et al. Transcriptomic analyses reveal the potential antibacterial mechanism of citral against Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Front Microbiol, 2023, 14, 1171339. |
| 6 | ULLAH N , DAR H A , NAZ K , et al. Genomic investigation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST113 strains isolated from tertiary care hospitals in Pakistan[J]. Antibiotics, 2021, 10 (9): 1121. |
| 7 | BUBECK WARDENBURG J , WILLIAMS W , MISSIAKAS D . Host defenses against Staphylococcus aureus infection require recognition of bacterial lipoproteins[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2006, 103 (37): 13831- 13836. |
| 8 | THOMAS C , LI Y , KODAMA T , et al. Protection from lethal gram-positive infection by macrophage scavenger receptor-dependent phagocytosis[J]. J Exp Med, 2000, 191 (1): 147- 156. |
| 9 | KAWAI T , AKIRA S . The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors[J]. Nat Immunol, 2010, 11 (5): 373- 384. |
| 10 | AKIRA S , TAKEDA K . Toll-like receptor signalling[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2004, 4 (7): 499- 511. |
| 11 | DÍAZ-MUÑOZ M , OSMA-GARCÍA I , FRESNO M , et al. Involvement of PGE2 and the cAMP signalling pathway in the up-regulation of COX-2 and mPGES-1 expression in LPS-activated macrophages[J]. Biochem J, 2012, 443 (2): 451- 461. |
| 12 | WåNGGREN K , LALITKUMAR P , STAVREUS-EVERS A , et al. Prostaglandin E2 and F2alpha receptors in the human Fallopian tube before and after mifepristone treatment[J]. Mol Hum Reproduct, 2006, 12 (9): 577- 585. |
| 13 | SERHAN C , LEVY B . Success of prostaglandin E2 in structure-function is a challenge for structure-based therapeutics[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2003, 100 (15): 8609- 8611. |
| 14 | PARK J Y , PILLINGER M H , ABRAMSON S B . Prostaglandin E2 synthesis and secretion: the role of PGE2 synthases[J]. Clin Immunol, 2006, 119 (3): 229- 240. |
| 15 | VANE J R , BOTTING R M . The mechanism of action of aspirin[J]. Thromb Res, 2003, 110 (5-6): 255- 258. |
| 16 | 刘博, 巩志国, 赵佳敏, 等. MLKL对金黄色葡萄球菌感染所致小鼠肝脏和肾脏损伤的调控作用[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2024, 44 (4): 670- 676. |
| LIU B , GONG Z , ZHAO J , et al. MLKL-mediated regulation against Staphylococcus aureus infection-induced liver and kidney damage in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2024, 44 (4): 670- 676. | |
| 17 | 吴金迪. 金黄色葡萄球菌感染小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞的分子机制及前列腺素E2对其影响的研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019. |
| WU J. Molecular mechanism and the effect of prostaglandin E2 regulate activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages by Staphylococcus aureus [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese) | |
| 18 | WU J , LIU B , MAO W , et al. Prostaglandin E2 regulates activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages by Staphylococcus aureus through toll-like receptor 2, toll-like receptor 4, and NLRP3 inflammasome signaling[J]. J Innate Immun, 2020, 12 (2): 154- 169. |
| 19 | WANG M , FAN Z , HAN H . Autophagy in Staphylococcus aureus infection[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11, 750222. |
| 20 | MCADOW M , DEDENT A C , EMOLO C , et al. Coagulases as determinants of protective immune responses against Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Infect Immun, 2012, 80 (10): 3389- 3398. |
| 21 | FOSTER T J , GEOGHEGAN J A , GANESH V K , et al. Adhesion, invasion and evasion: the many functions of the surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2013, 12 (1): 49- 62. |
| 22 | KIELIAN T , MOHAMMAD M , NGUYEN M-T , et al. The YIN and YANG of lipoproteins in developing and preventing infectious arthritis by Staphylococcus aureus[J]. PLOS Pathog, 2019, 15 (6): e1007877. |
| 23 | ZLOTNIK A , YOSHIE O . The chemokine superfamily revisited[J]. Immunity, 2012, 36 (5): 705- 716. |
| 24 | GEERT V L , MATHIEU J M B . Death by TNF: a road to inflammation[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2022, 23 (5): 289- 303. |
| 25 | SARAIVA M , O 'GARRA A . The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2010, 10 (3): 170- 181. |
| 26 | SCHMALER M , JANN N J , GÖTZ F , et al. Staphylococcal lipoproteins and their role in bacterial survival in mice[J]. Int J Med Microbiol, 2010, 300 (2-3): 155- 160. |
| 27 | MOHAMMAD M , NA M , HU Z , et al. Staphylococcus aureus lipoproteins promote abscess formation in mice, shielding bacteria from immune killing[J]. Commun Biol, 2021, 4 (1): 432. |
| 28 | VIOLA A , MUNARI F , SÁNCHEZ-RODRÍGUEZ R , et al. The Metabolic Signature of Macrophage Responses[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10, 1462. |
| 29 | MAMILOS A , WINTER L , SCHMITT V H , et al. Macrophages: From simple phagocyte to an integrative regulatory cell for inflammation and tissue regeneration-A review of the literature[J]. Cells, 2023, 12 (2): 276. |
| 30 | IKUO M . Distinct functions of COX-1 and COX-2[J]. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat, 2002, 68-69, 165- 175. |
| [1] | ZHANG Manqi, ZHAO Bingyu, WEN Ruru, ZHANG Jingwen, SUN Mengran, ZHAN Leyang, GOU Jingxuan, SONG Xiangjun. Prokaryotic Expression of the T6SS Effector Protein Tse1 and Its inhibitory Effect on Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2917-2926. |
| [2] | JI Xing, LI Jun, WANG Ran, HE Tao. Research Progress on Virulence Regulation and Antivirulence Drugs of Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1594-1607. |
| [3] | Yiqian FU, Dongge LIANG, Mingyang WANG, Jiajia PAN, Yanbin YANG, Lei ZENG, Xiangtao KANG. Construction of Interferon Regulatory Factor Knockdown Cell Line and Its Effect on Pseudorabies Virus Proliferation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4100-4109. |
| [4] | Tong ZHAO, Wenzhe YANG, Feilong PAN, Shuchen ZHAO, Kexiang LIU, Zhanjun LÜ, Lijia ZHAO. Bisphenol A Inhibits Testosterone Synthesis in TM3 Cells by Upregulating Apoa1 Gene Expression [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3516-3525. |
| [5] | Hengjie CUI, Jinlong QIN, Zhihao ZHU, Xue BAO, Shaowen LI, Xianrong MENG. Correlation Analysis of Benzalkonium Bromide Sensitivity and Biofilm Formation Ability in Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3669-3677. |
| [6] | Tingting XIAN, Yan LIU, Xin CAO, Tao FENG. Analysis of the Changes of Vaginal Microflora and Serum Pro-inflammatory Cytokines and Their Correlation in Sows with Endometritis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3688-3698. |
| [7] | HE Xiaolan, ZHAO Yankun, MENG Lu, LIU Huimin, GAO Jiaojiao, ZHENG Nan. Research Progress in Heteroresistance of Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1432-1445. |
| [8] | LUO Chenghui, GAO Jiangrui, CHEN Junwei, WEI Chunjie, WEI Shuangshuang, PEI Yechun. Construction of Mouse Model of Dust Mite Induced Atopic Dermatitis and Asthma [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1257-1267. |
| [9] | WU Zihao, CAI Yilong, TUO Haixin, CHEN Wei. Pathogenicity Analysis of a PVL+ ST22 Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Equine Raw Milk [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 718-726. |
| [10] | ZHANG Zixuan, ZHANG Ying, LI Zhijun, YANG Jingling, JIANG Zihao, HUANG Huamin, QI Xuefeng. The Effects of Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus (BVDV)-induced Ferroptosis on Virus Replication [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5716-5724. |
| [11] | ZHANG Meiwen, WANG Chenglong, LIU Yuzhen, ZHAO Yutong, ZHU Jiping, LI Yi. Analysis of the Inhibitory Effect of Salidroside on Canine Parvovirus Replication in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5738-5750. |
| [12] | Kexin WANG, Xian WU, Haizhou GONG, Qiaoyu FANG, Xiangchen LI, Yanan ZHANG. Effects of Co-Treatment of Sodium Butyrate and Indole-3-Propionic Acid on Tight Junctions and Inflammatory Cytokines in Caco-2 Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5124-5134. |
| [13] | XING Baorui, LIU Zhen, ZHAO Haiping, MA Zefang, LI Xunsheng, ZHOU Jue, SUN Hongmei. Research Progress in Reverse Osteogenesis of Deer Antler [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2231-2240. |
| [14] | CHEN Yang, MENG Linchun, GUO Mengjiao, ZHANG Chengcheng, BO Zongyi, CHU Dianfeng, CAO Yongzhong, WU Yantao, ZHANG Xiaorong. Establishment and Preliminary Application of Indirect ELISA Method and HI Test for Detection of Mycoplasma Gallisepticum Antibody [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 2062-2072. |
| [15] | LIU Yankun, LUO Runbo, LIN Yan, ZHU Weiyun. Effects of Phage Cocktail on Growth Performance, Blood Parameters and Fecal Microbiota of Weaned Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(4): 1555-1567. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||