





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 2312-2324.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.05.029
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIA Chaoying1( ), ZHANG Huawei2, LUO Xiuxin2, LIU Qingyun1, WANG Xiangru1,*(
), ZHANG Huawei2, LUO Xiuxin2, LIU Qingyun1, WANG Xiangru1,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-24
Online:2025-05-23
Published:2025-05-27
Contact:
WANG Xiangru
E-mail:13752871611@163.com;wangxr228@mail.hzau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
JIA Chaoying, ZHANG Huawei, LUO Xiuxin, LIU Qingyun, WANG Xiangru. Establishment of Mice Model Infected by Bovine Mannheimia haemolytica and the Immunogenicity of Inactivated Vaccine[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2312-2324.
Table 2
Results of drug sensitivity test of isolated strain KQ-Mh-1"
| 抗生素 Antibiotic | 含量/(μg·片-1) Content | 判定标准 Standard of criterion | 抑菌圈直径/mm Diameter of inhibition zone | 判定 Judgement | ||
| 耐药 | 中介 | 敏感 | ||||
| 头孢噻肟 Cefotaxime | 30 | ≤25 | >25~<33 | ≥33 | 35 | 敏感 |
| 诺氟沙星 Norfloxacin | 10 | ≤15 | >15~<21 | ≥21 | 22 | 敏感 |
| 头孢哌酮 Cefoperazone | 75 | ≤12 | >12~<17 | ≥17 | 21 | 敏感 |
| 左氧氟沙星 Levofloxacin | 5 | ≤19 | >19~<26 | ≥26 | 23 | 中介 |
| 阿米卡星 Amikacin | 30 | ≤19 | >19~<26 | ≥26 | 11 | 耐药 |
| 美洛西林 Mezlocillin | 75 | ≤17 | >17~<21 | ≥21 | 0 | 耐药 |
| 妥布霉素 Tobramycin | 10 | ≤12 | >12~<17 | ≥17 | 14 | 中介 |
| 庆大霉素 Gentamycin | 10 | ≤19 | >19~<26 | ≥26 | 12 | 耐药 |
| 环丙沙星 Ciprofloxacin | 5 | ≤15 | >15~<21 | ≥21 | 22 | 敏感 |
| 多黏菌素 Polymyxin | 300 | ≤13 | >13~<19 | ≥19 | 20 | 敏感 |
| 新霉素 Neomycin | 30 | ≤12 | >12~<17 | ≥17 | 19 | 敏感 |
| 链霉素 Streptomycin | 10 | ≤12 | >12~<17 | ≥20 | 0 | 耐药 |
| 多西环素 Doxycycline | 30 | ≤18 | >18~<24 | ≥24 | 26 | 敏感 |
| 阿莫西林 Amoxicillin | 20 | ≤13 | >13~<21 | ≥21 | 0 | 耐药 |
| 磺胺异恶唑 Sulfisoxazole | 250 | ≤15 | >15~<23 | ≥23 | 0 | 耐药 |
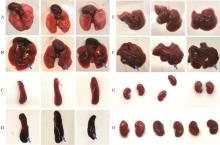
Fig. 6
Anatomical results of infected and uninfected mice A. Autopsy of the hearts and lungs of healthy mice; B. Autopsy of the hearts and lungs of infected dead mice; C. Autopsy of spleens of healthy mice; D. Autopsy of spleens of infected dead mice; E. Autopsy of livers of healthy mice; F. Autopsy of livers of infected dead mice; G. Autopsy of kidneys of healthy mice; H. Autopsy of kidneys of dead mice"
Table 4
Vaccine protection rate with different antigen content"
| 组别 Group | 抗原含量/(CFU·mL-1) Antigenic content | 免疫剂量/mL Immunizing dose | 攻毒菌量/(CFU·只-1) Challenged bacteria amount | 保护率 Protective rate |
| 免疫组 | 2.5×1010 | 0.2 | 1.56×1010 | 7/10 |
| Immunized group | 1.0×1010 | 0.2 | 1.56×1010 | 5/10 |
| 5.0×109 | 0.2 | 1.56×1010 | 1/10 | |
| 未免疫组 Non immunized group | 0 | 0.2 | 1.56×1010 | 0/10 |
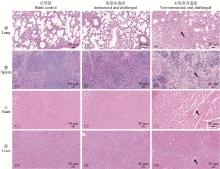
Fig. 10
Histopathological observation of lung, spleen, heart and liver in blank control group, immune group and non-immune group A1-D1. Structure of lung, spleen, heart, and liver tissue in healthy mice; A2-D2. Tissue structure of lung, spleen, heart, and liver of surviving micein immune group after challenge; A3-D3. Tissue structure of lung, spleen, heart, and liver in non-immunized mice after challenge"

| 1 |
CROUCHC F,LAFLEURR,RAMAGEC,et al.Cross protection of a Mannheimia haemolytica A1 Lkt-/Pasteurella multocida ΔhyaE bovine respiratory disease vaccine against experimental challenge with Mannheimia haemolytica A6 in calves[J].Vaccine,2012,30(13):2320-2328.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.01.063 |
| 2 |
CHAIJ M,CAPIKS F,KEGLEYB,et al.Bovine respiratory microbiota of feedlot cattle and its association with disease[J].Vet Res,2022,53(1):4.
doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-01020-x |
| 3 |
VALERIS-CHACINR,POWLEDGES,MCATEET,et al.Mycoplasma bovis is associated with Mannheimia haemolytica during acute bovine respiratory disease in feedlot cattle[J].Front Microbiol,2022,13,946792.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.946792 |
| 4 |
CONFERA W,AYALEWS.Mannheimia haemolytica in bovine respiratory disease: immunogens, potential immunogens, and vaccines[J].Anim Health Res Rev,2018,19(2):79-99.
doi: 10.1017/S1466252318000142 |
| 5 |
RICEJ A,CARRASCO-MEDINAL,HODGINSD C,et al.Mannheimia haemolytica and bovine respiratory disease[J].Anim Health Res Rev,2007,8(2):117-128.
doi: 10.1017/S1466252307001375 |
| 6 |
MASONC,ERRINGTONJ,FOSTERG,et al.Mannheimia haemolytica serovars associated with respiratory disease in cattle in Great Britain[J].BMC Vet Res,2022,18(1):5.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-03121-3 |
| 7 | 贾开文,操义恒,王子杰,等.新疆牛源溶血性曼氏杆菌和多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定及耐药性和毒力分析[J].中国预防兽医学报,2023,45(2):201-206. |
| JIAK W,CAOY H,WANGZ J,et al.Isolation, identification, drug resistance and virulence analysis of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida from a cattle farm in Xinjiang[J].Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine,2023,45(2):201-206. | |
| 8 |
MCGILLJ L,SACCOR E.The immunology of bovine respiratory disease: recent advancements[J].Vet Clin North Am: Food Anim Pract,2020,36(2):333-348.
doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2020.03.002 |
| 9 |
TUCCIP,ESTEVEZV,BECCOL,et al.Identification of Leukotoxin and other vaccine candidate proteins in a Mannheimia haemolytica commercial antigen[J].Heliyon,2016,2(9):e00158.
doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2016.e00158 |
| 10 | 谢艺萌,刘珊珊,苏思雨,等.牛溶血性曼氏杆菌对BT细胞炎症因子及其TLR4/NF-κB信号通路影响的研究[J].中国预防兽医学报,2023,45(10):1061-1065. |
| XIEY M,LIUS S,SUS Y,et al.Effects of bovine Mannheimia hemolytica on cytokines and its TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in BT cells[J].Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine,2023,45(10):1061-1065. | |
| 11 |
FIGUEROA-VALENZUELAC,MONTES-GARCÍAJ F,VAZQUEZ-CRUZC,et al.Mannheimia haemolytica OmpH binds fibrinogen and fibronectin and participates in biofilm formation[J].Microb Pathog,2022,172,105788.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105788 |
| 12 |
RAMÍREZ-RICOG,MARTINEZ-CASTILLOM,RUIZ-MAZÓNL,et al.Identification, biochemical characterization, and in vivo detection of a Zn-Metalloprotease with collagenase activity from Mannheimia haemolytica A2[J].Int J Mol Sci,2024,25(2):1289.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25021289 |
| 13 |
MENGHWARH,TATUMF M,BRIGGSR E,et al.Enhanced phagocytosis and complement-mediated killing of Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 following in-frame CMP-sialic acid synthetase (neuA) gene deletion[J].Microbiol Spectr,2023,11(6):e0294423.
doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02944-23 |
| 14 |
AMATS,TIMSITE,BAINESD,et al.Development of bacterial therapeutics against the bovine respiratory pathogen Mannheimia haemolytica[J].Appl Environ Microb,2019,85(21):e0135919.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.01359-19 |
| 15 |
CONFERA W,AYALEWS,MONTELONGOM,et al.Immunity of cattle following vaccination with a Mannheimia haemolytica chimeric PlpE-LKT (SAC89) protein[J].Vaccine,2009,27(11):1771-1776.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.09.028 |
| 16 |
AYALEWS,SHRESTHAB,MONTELONGOM,et al.Identification and immunogenicity of Mannheimia haemolytica S1 outer membrane lipoprotein PlpF[J].Vaccine,2011,29(47):8712-8718.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.08.074 |
| 17 |
UDDINM S,KALDISA,MENASSAR,et al.Mucosal immunization with spore-based vaccines against Mannheimia haemolytica enhances antigen-specific immunity[J].Vaccines,2024,12(4):375.
doi: 10.3390/vaccines12040375 |
| 18 |
KALDISA,UDDINM S,GULUARTEJ O,et al.Development of a plant-based oral vaccine candidate against the bovine respiratory pathogen Mannheimia haemolytica[J].Front Plant Sci,2023,14,1251046.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1251046 |
| 19 | 高佳滨,陈为宏,尹辉,等.牛溶血性曼氏杆菌灭活疫苗的制备与检定[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2014,27(8):990-993. |
| GAOJ B,CHENW H,YIH,et al.Preparation and quality control of inactivated bovine Mannheimia haemolytica vaccine[J].Chinese Journal of Biologicals,2014,27(8):990-993. | |
| 20 | 韩小丽,任静静,杨铭伟,等.致肉牛运输热溶血曼氏杆菌的分离鉴定及部分生物学特性研究[J].中国畜牧兽医,2019,46(2):548-556. |
| HANX L,RENJ J,YANGM W,et al.Isolation, identification and partial biological characteristics of Mannheimia haemolytica in shipping fever of beef cattle[J].China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2019,46(2):548-556. | |
| 21 | YEKTASERESHTA,HEMATIZ,SABET SARVESTANIF,et al.Immunization with recombinant PlpE of ovine Mannheimia haemolytica isolate provides protection against lethal challenge in mice[J].Iran J Vet Res,2021,22(4):272-276. |
| 22 | CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed[R]. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 2020. |
| 23 | 韩瑞,郝成武,马长宾,等.牛源溶血性曼氏杆菌新疆株的分离鉴定和生物学特性[J].中国兽医杂志,2023,59(10):70-75. |
| HANR,HAOC W,MAC B,et al.Isolation, identification and biological characteristics of Mannheimia hacmolytica strains from bovine sources in Xinjiang[J].Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine,2023,59(10):70-75. | |
| 24 |
HOLSCHBACHC L,AULIKN,POULSENK,et al.Prevalence and temporal trends in antimicrobial resistance of bovine respiratory disease pathogen isolates submitted to the Wisconsin Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory: 2008-2017[J].J Dairy Sci,2020,103(10):9464-9472.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-17570 |
| 25 | 朱杰,赵旭,东笑,等.牛多杀性巴氏杆菌和溶血性曼氏杆菌的分离鉴定及致病力评估[J].中国兽医学报,2024,44(1):80-87. |
| ZHUJ,ZHAOX,DONGX,et al.Isolation, identification, and pathogenicity evaluation of Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolytica[J].Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science,2024,44(1):80-87. | |
| 26 | 高磊,李旭雯,宫枫举,等.牛源溶血性曼氏杆菌的分离鉴定及其生物学特性分析[J].畜牧与兽医,2023,55(8):57-63. |
| GAOL,LIX W,GONGF J,et al.Isolation, identification and biological characterization of Mannheimia haemolytica from cattle[J].Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2023,55(8):57-63. | |
| 27 |
ANDRÉS-LASHERASS,ZAHEERR,KLIMAC,et al.Serotyping and antimicrobial resistance of Mannheimia haemolytica strains from European cattle with bovine respiratory disease[J].Res Vet Sci,2019,124,10-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2018.12.021 |
| 28 |
ALHAJIN B,ODETOKUNI A,ADAMUA M,et al.Antimicrobial usage and associated residues and resistance emergence in smallholder beef cattle production systems in Nigeria: a One Health challenge[J].Vet Res Commun,2023,47(1):233-245.
doi: 10.1007/s11259-022-09944-1 |
| 29 |
TIMSITE,HALLEWELLJ,BOOKERC,et al.Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, and Histophilus somni isolated from the lower respiratory tract of healthy feedlot cattle and those diagnosed with bovine respiratory disease[J].Vet Microbiol,2017,208,118-125.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.07.013 |
| 30 |
KOSTOVAV,HANKED,KASPARH,et al.Macrolide resistance in Mannheimia haemolytica isolates associated with bovine respiratory disease from the German national resistance monitoring program GERM-Vet 2009 to 2020[J].Front Microbiol,2024,15,1356208.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1356208 |
| 31 |
BACANLIM,BAŞARANN.Importance of antibiotic residues in animal food[J].Food Chem Toxicol,2019,125,462-466.
doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2019.01.033 |
| 32 |
ROIERS,FENNINGERJ C,LEITNERD R,et al.Immunogenicity of Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolytica outer membrane vesicles[J].Int J Med Microbiol,2013,303(5):247-256.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.05.001 |
| 33 |
李甜,杨洋,谢黎卿,等.牛溶血性曼氏杆菌及牛荚膜A型多杀性巴氏杆菌灭活疫苗对小鼠的保护性研究[J].畜牧兽医学报,2021,52(9):2579-2588.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.09.021 |
|
LIT,YANGY,XIEL Q,et al.Study on the Immunoprotection of inactivated vaccine of bovine Mannheimia haemolytica and bovine Pasteurella multocida capsular serotype a in mouse model[J].Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2021,52(9):2579-2588.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.09.021 |
|
| 34 | 周金玲. 牛溶血性曼氏杆菌小鼠感染模型建立及灭活疫苗免疫原性研究[D]. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2018. |
| ZHOU J L. Establishment of mice model infected by bovine Mannheimia haemolytica and the immunogenicity of inactivated vaccine[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese) | |
| 35 | 张继鑫,彭远义,李能章.溶血性曼氏杆菌白细胞毒素研究进展[J].中国预防兽医学报,2019,41(11):1178-1182. |
| ZHANGJ X,PENGY Y,LIN Z.The immunogenicity of leukotoxin, PlpE and OmpA of bovine Mannheimia haemolytica[J].Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine,2019,41(11):1178-1182. | |
| 36 |
CONLONJ A,SHEWENP E,LOR Y.Efficacy of recombinant leukotoxin in protection against pneumonic challenge with live Pasteurella haemolytica A1[J].Infect Immun,1991,59(2):587-591.
doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.587-591.1991 |
| 37 |
GUZMÁN-BRAMBILAC,QUINTERO-FABIÁNS,GONZÁLEZ-CASTILLOC,et al.LKTA and PlpE small fragments fusion protein protect against Mannheimia haemolytica challenge[J].Res Vet Sci,2012,93(3):1293-1300.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2012.07.004 |
| 38 |
MOLAEEH,TAHAMTANY,SAEEDNEZHADE,et al.Isolation of the various serotypes of Mannheimia haemolytica and preparation of the first vaccine candidate in Iran[J].Mol Biol Rep,2022,49(11):10367-10375.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07890-4 |
| 39 |
BOOKERC W,LUBBERSB V.Bovine respiratory disease treatment failure: impact and potential causes[J].Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract,2020,36(2):487-496.
doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2020.03.007 |
| 40 |
PILLAID K,CHAE,MOSIERD.Role of the stress-associated chemicals norepinephrine, epinephrine and substance P in dispersal of Mannheimia haemolytica from biofilms[J].Vet Microbiol,2018,215,11-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.11.025 |
| 41 | 陈平,王斐,何振富,等.牛呼吸道疾病综合征防治研究进展[J].中国兽医学报,2021,41(10):2064-2068. |
| CHENP,WANGF,HEZ F,et al.Research advances on prophylaxis and treatment for bovine respiratory disease complex[J].Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science,2021,41(10):2064-2068. | |
| 42 | 陶乔孝慈,马雪,张丽媛,等.牛呼吸道疾病两种细菌性病原研究进展[J].动物医学进展,2021,42(9):96-102. |
| TAOQ X C,MAX,ZHANGL Y,et al.Progress on two bacterial bovine respiratory pathogens[J].Progress in Veterinary Medicine,2021,42(9):96-102. | |
| 43 |
CUEVAS-GÓMEZI,MCGEEM,SÁNCHEZJ M,et al.Association between clinical respiratory signs, lung lesions detected by thoracic ultrasonography and growth performance in pre-weaned dairy calves[J].Irish Vet J,2021,74(1):7.
doi: 10.1186/s13620-021-00187-1 |
| 44 |
KAMELM S,DAVIDSONJ L,VERMAM S.Strategies for bovine respiratory disease (BRD) diagnosis and prognosis: a comprehensive overview[J].Animals,2024,14(4):627.
doi: 10.3390/ani14040627 |
| 45 |
UDDINM S,GULUARTEJ O,ABBOTTD W,et al.Development of a spore-based mucosal vaccine against the bovine respiratory pathogen Mannheimia haemolytica[J].Sci Rep,2023,13(1):12981.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29732-4 |
| [1] | HU Mi, SHEN Yaoxin, FAN Baochao, SUN Min, ZHOU Jinzhu, GUO Rongli, LI Bin. Evaluation of the Characteristics of Eudragit L100-Modified Aluminum-Manganese Metal-Organic Framework as an Oral Delivery Vehicle for Inactivated Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Vaccine [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2292-2230. |
| [2] | WU Peiling, LI Yixuan, WANG Haojie, LI Yafei, LIU Shaomeng, LIU Qingyun, WANG Xiangru. Research Progress of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Vaccine for Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1042-1058. |
| [3] | ZHAO Wanyue, XU Xiaowen, CHANG Shushu, XIANG Zhijie, GUO Aizhen, CHEN Yingyu. Epidemiologic Investigation of the Major Viruses of the Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1324-1335. |
| [4] | Lu PENG, Heng ZHANG, Siqi PANG, Zhulin QIAO, Xiaofen ZHANG, Chen TAN, Yunfeng SONG, Rui ZHOU, Lu LI. Screening of Trivalent Inactivated Vaccine Candidate Strains of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2, 3 and 9 Using Galleria mellonella and Mice Infection Models [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4077-4090. |
| [5] | MENG Lingzhai, CHEN Chunli, YU Mengmeng, WANG Zhanxin, WANG Suyan, LIU Peng, HE Tana, GUO Ru, CHEN Yuntong, LIU Changjun, QI Xiaole, WU Zhiqiang, GAO Yulong. Pathogenicity of Avian Metapneumovirus Subtype B on Yellow Feather Broilers and Evaluation on Immune Effect of Inactivated Vaccine [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5154-5161. |
| [6] | HE Chenxiang, GAO Shandian, TIAN Zhancheng, DU Junzheng, WANG Jinming, GUAN Guiquan, YIN Hong. Development of a Differential Diagnostic ELISA Based on GNS Protein to Distinguish BEFV Infected and Vaccinated Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4320-4326. |
| [7] | HAO Jianwei, XUE Chunyi, CAO Yongchang. The Dose-titration Study of Inactivated Vaccine of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 1536-1543. |
| [8] | HE Shufan, YUE Hua, TANG Cheng, LIU Jie. Research Advances in Bovine Adenovirus Type 3 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(4): 1030-1040. |
| [9] | LI Tian, YANG Yang, XIE Liqing, WANG Yuanlan, LI Pan, PENG Yuanyi, LI Nengzhang. Study on the Immunoprotection of Inactivated Vaccine of Bovine Mannheimia haemolytica and Bovine Pasteurella multocida Capsular Serotype A in Mouse Model [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(9): 2579-2588. |
| [10] | WANG Guoliao, ZHANG Jie, RAO Jiarong, MO Ruiwen, YUAN Liguo. Establishment of a Mouse Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis Induced by Bleomycin and Screening of Biomarkers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(4): 1134-1140. |
| [11] | LÜ Fenfen, MA Xiaohui, WANG Li, MA Chen, ZHANG Baojiang, SU Yan. Immunogenicity Analysis of Three Different Antigen Proteins of Streptococcus equi in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(3): 752-762. |
| [12] | SUN Pu, HE Wei, FU Yuanfang, LI Dong, YANG Lin, WEI Delong, CAO Yimei, LI Pinghua, BAI Xingwen, MA Xueqing, LI Kun, BAO Huifang, ZHANG Jing, ZHU Xinrong, LIU Zaixin, LU Zengjun. Immune Effect of Inactivated Vaccines against Foot-and-Mouth Disease and Their Interference on Differential Diagnosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(10): 2481-2489. |
| [13] | HE Qi-fu, GUO Zi-jing, LI Ran, ZHOU Jun, YUE Hua, ZHANG Bin, TANG Cheng. Establishment and Application of a RT-PCR Assay for Detecting Bovine Coronavirus [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(10): 2292-2298. |
| [14] | FENG Yao, YUE Hui-xi, LIU Hong-ming, CAO San-jie, WU Rui, HUANG Xiao-bo, WEN Yi-ping, ZHAO Qin, WEN Xin-tian. The Immunogenicity Evaluation of Inactivated Vaccines of Swine Japanese Encephalitis Virus Genetype Ⅰ [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2017, 48(5): 889-895. |
| [15] | XIE Hai-dong,XIONG Qi-yan,LIU Mao-jun,WEI Yan-na,WANG Jia,NING Guan-bao,SHAO Guo-qing. Study on Immune Enhancement Effect of Different Aqueous and Oil-in-water Adjuvants to the Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Inactivated Vaccine [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2014, 45(12): 2028-2033. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||