





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (10): 5170-5179.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.10.036
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Wei1( ), LIU Shanshan1(
), LIU Shanshan1( ), FAN Yu1, DENG Shengqing1, WANG Qingyan2,*(
), FAN Yu1, DENG Shengqing1, WANG Qingyan2,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-16
Online:2025-10-23
Published:2025-11-01
Contact:
WANG Qingyan
E-mail:sunwei_223@163.com;huojianbaifenbai@163.com;99634964@qq.com
CLC Number:
SUN Wei, LIU Shanshan, FAN Yu, DENG Shengqing, WANG Qingyan. Transcriptomic Differential Analysis of Brain Tissues in Jiangkou Radish Piglets Experimentally Infected with Pseudorabies Virus[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 5170-5179.
Table 1
Primer information for qRT-PCR"
| 基因名称 Gene name | GenBank登录号 GenBank accession number | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5→3′) Sequence | 通路名称 Pathway name |
| LPAR3 | NM_001162402.1 | LPAR3-F LPAR3-R | CATGTCAGTCACGAGTATGCGGATC AGAGCAGGAAGAGATGTCACAGAGG | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
| GZMA | NM_001143709.1 | GZMA-F GZMA-R | TGCTTTGACCAGGACACACATGAG CCACTTTAGGGAGATGAAGGACAGC | |
| P2RY2 | NM_001006591.1 | P2RY2-F P2RY2-R | CGCTCTACTTCATCACCACCACTG AGACCAGGATGACGGCGAAGG | |
| NMB | XM_021097907.1 | NMB-F NMB-R | GGACAACGCACCACATCTCTCTG ACCAGCAGCCTCCTGTACGG | |
| CNR1 | XM_013992675.2 | CNR1-F CNR1-R | GGTACTGTGCGTTATCCTCCATTCC CGACGAAGCTGTAGACGAAGATGAC | |
| NTSR1 | XM_021078238.1 | NTSR1-F NTSR1-R | GTGGTGTCCGTGTTCGCTGAG TGGCATGAGCAGTAGTTGGAATCAG | |
| CALCR | NM_214354.2 | CALCR-F CALCR-R | GTGGTGTCCGTGTTCGCTGAG TGGCATGAGCAGTAGTTGGAATCAG | |
| SLC7A11 | XM_021101587.1 | SLC7A11-F SLC7A11-R | TCTTTGTTGCCCTCTCCTGCTTTG GTGTGTTTGCGGATGTGAATCATGG | Ferroptosis |
| TF | NM_001244653.1 | TF-F TF-R | TCTAAGATGGACTCCTCGCTGTACC GGCACACCACCTCACCTTCTTG | |
| SLC40A1 | XM_013984335.2 | SLC40A1-F SLC40A1-R | TGTCCCTGAGATGAGCCCTAAACC AAGACCGATTCTAGCAGCAATGACG | |
| FOS | NM_001123113.1 | FOS-F FOS-R | CTGAGATCGCCAACCTGCTGAAG CAGATCAAGGGAAGCCACAGACATC | IL-17 signaling pathway |
| FOSB | XM_063252899.1 | FOSB-F FOSB-R | ACCCCTACGACATGCCAGGAAC ACCACCGCCACTAGCTCCAC | |
| MAPK15 | XM_021090469.1 | MAPK15-F MAPK15-R | TGAGTGGACACTAGAGGCGGATG TGATAGAGGCGGCGGCGATAC | |
| β-actin | ON164673.1 | β-actin-F β-actin-R | TCGCCGACAGGATGCAGAAG CAGGATGGAGCCGCCGATC |
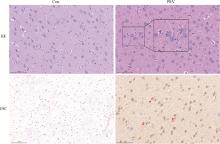
Fig. 1
Pathological changes and PEV expression in brain tissue after PRV infection (Bar=100 μm) HE. HE staining results, zoomed-in view showing increased oligodendrocytes surrounding the nerve cells; IHC. Immunohistochemical results of PRV, red arrows indicating prv-positive expression area; Con. Control group; PRV. PRV infection group"
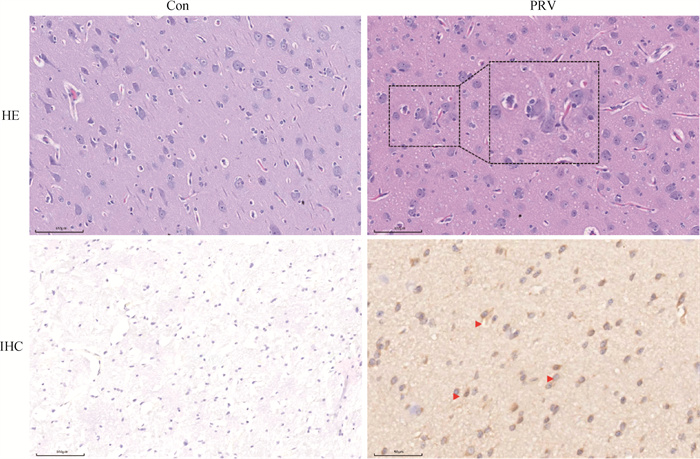
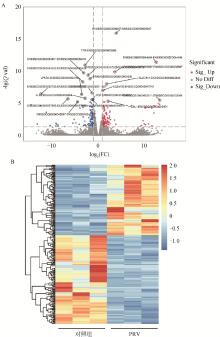
Fig. 2
Differential gene analysis of PRV infection A. The volcano plot of differential genes illustrates the differences in gene expression between the PRV-infected group and the control group (The red dots in the plot represent upregulated genes, while the blue dots indicate downregulated genes. The gray dots signify genes with insignificant changes in expression); B. The heatmap of differentially expressed genes (columns representing samples from the control group and the infected group, and rows corresponding to genes that exhibit significant differential expression during the comparison process)"
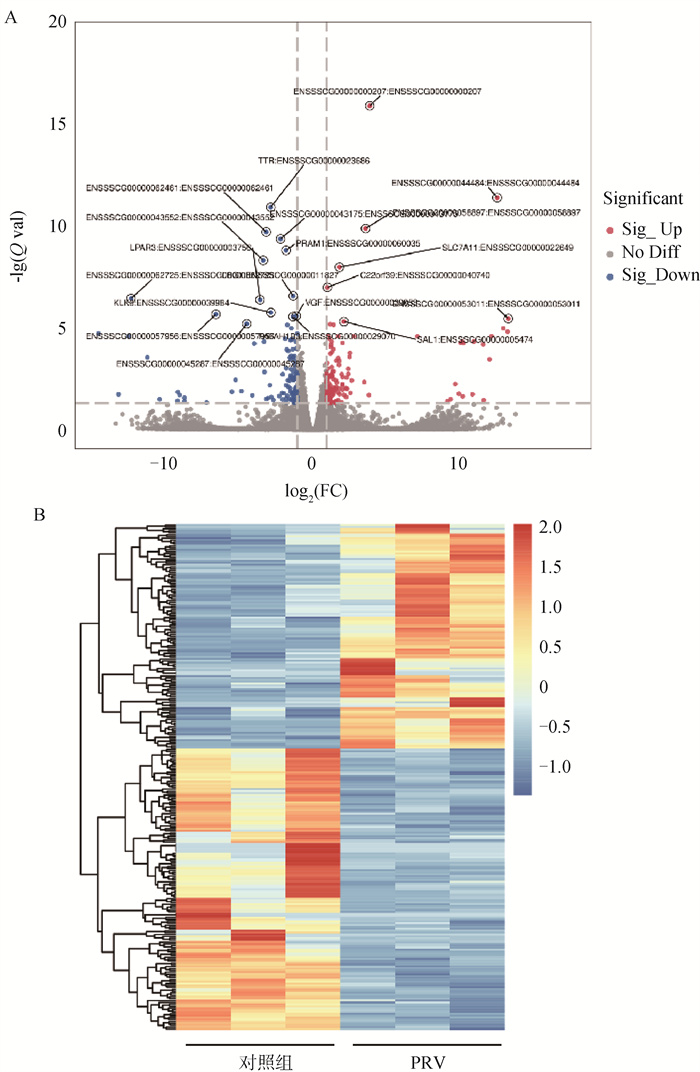
Table 2
Transcriptomics gene regulation situation"
| 通路名称 Pathway Name | 基因名称 Gene Name | Fc | log2(Fc) | 调节 Regulation |
| 神经活性配体-受体相互作用 Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | LPAR3 | -3.57 | 0.08 | down |
| GZMA | -5.25 | 0.03 | down | |
| P2RY2 | -1.36 | 0.39 | down | |
| NMB | -1.70 | 0.31 | down | |
| CNR1 | 1.14 | 2.21 | up | |
| CALCR | 1.33 | 2.51 | up | |
| NTSR1 | 1.61 | 3.05 | up | |
| 铁死亡 Ferroptosis | SLC7A11 | 3.74 | 1.90 | up |
| TF | 0.46 | -1.12 | down | |
| SLC40A1 | 2.13 | 1.09 | up | |
| IL-17信号通路 IL-17 signaling pathway | FOS | 0.31 | -1.69 | down |
| FOSB | 0.36 | -1.48 | down | |
| MAPK15 | 0.44 | -1.18 | down |
| 1 |
SU B Q , YANG G Y , WANG B B . Pseudorabies virus inhibits progesterone-induced inactivation of TRPML1 to facilitate viral entry[J]. Plos Pathog, 2024, 20 (1): e1011956.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011956 |
| 2 |
SEHL J , TEIFKE J P . Comparative pathology of pseudorabies in different naturally and experimentally infected species-a review[J]. Pathogens, 2020, 9 (8): 633.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens9080633 |
| 3 |
袁生, 李安琪, 吕文珂, 等. 一株猪伪狂犬病病毒的主要毒力相关基因的变异分析及其对家兔的致病性[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (5): 2195- 2199.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.05.039 |
|
YUAN S , LI A Q , LV W K , et al. Analysis of variationin major virulence-related genes of a strain of pseudorabiesvirus and its pathogenicity to rabbits[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (5): 2195- 2199.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.05.039 |
|
| 4 |
YANG H , HAN H , WANG H , et al. A case of human viral encephalitis caused by pseudorabies virus infection in China[J]. Front Neurology, 2019, 10, 534.
doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00534 |
| 5 |
CHEN Y , GAO J , HUA R , et al. Pseudorabies virus as a zoonosis: scientific and public health implications[J]. Virus Genes, 2025, 61, 9- 25.
doi: 10.1007/s11262-024-02122-2 |
| 6 |
SHANGGUAN A , LI J , SUN Y , et al. Host-virus interactions in PK-15 cells infected with pseudorabies virus Becker strain based on RNA-seq[J]. Virus Res, 2022, 318, 198829.
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2022.198829 |
| 7 |
MA Z , JIANG C , LIU D , et al. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of a quadruple gene-deleted pseudorabies virus variant as a vaccine candidate[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2024, 288, 109931.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2023.109931 |
| 8 |
LI X , CHEN S , ZHANG L , et al. Coinfection of porcine circovirus 2 and pseudorabies virus enhances immunosuppression and inflammation through NF-κB, JAK/STAT, MAPK, and NLRP3 pathways[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (8): 4469.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23084469 |
| 9 |
CHEN X , XUE J , ZOU J , et al. Resveratrol alleviated neuroinflammation induced by pseudorabies virus infection through regulating microglial M1/M2 polarization[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 160, 114271.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114271 |
| 10 |
SUN W , LIU S , HUANG X , et al. Cytokine storms and pyroptosis are primarily responsible for the rapid death of mice infected with pseudorabies virus[J]. Roy Soc Open Sci, 2021, 8 (8): 210296.
doi: 10.1098/rsos.210296 |
| 11 |
XU L , TAO Q , XU T , et al. Pathogenicity characteristics of different subgenotype pseudorabies virus in newborn piglets[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2024, 11, 1438354.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1438354 |
| 12 |
LIU Q , WANG X , XIE C , et al. Erratum to: A novel human acute encephalitis caused by pseudorabies virus variant strain[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2022, 74 (4): 756.
doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab550 |
| 13 | 孙伟, 刘杉杉, 李华磊. 感染伪狂犬病病毒对小鼠脑细胞周期及相关因子的影响[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2023 (3): 73- 78. |
| SUN W , LIU S S , LI H L . The effect of pseudorabies virus on the cell cycle related factors in mice brain[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2023 (3): 73- 78. | |
| 14 |
SONG C , HUANG X , GAO Y , et al. Histopathology of brain functional areas in pigs infected by porcine pseudorabies virus[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2021, 141, 203- 211.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2021.10.011 |
| 15 |
XU L , ZHANG Y , TAO Q , et al. Transcriptome and metabolomeanalysis reveals PRV XJ delgE/gl/TK protects intracranially infectedmice from death by regulatingthe inflammation[J]. Front Microbiol, 2024, 15, 1374646.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1374646 |
| 16 |
LAUSS M , KRIEGNER A , VIERLINGER K , et al. Characterization of the drugged human genome[J]. Pharmacogenomics, 2007, 8 (8): 1063- 1073.
doi: 10.2217/14622416.8.8.1063 |
| 17 | ZHI J , YIN L , ZHANG Z , et al. Network pharmacology-based analysis of Jin-Si-Wei on the treatment of Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 319 (Pt 3): 117291. |
| 18 | HAN Z , ZHANG Y , WANG P , et al. Is acupuncture effective in the treatment of COVID-19 related symptoms? Based on bioinformatics/network topology strategy[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2021, 22 (5): 1- 11. |
| 19 | ZHENG Y , YAN F , HE S , et al. Targeting ferroptosis in autoimmune diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic prospects[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2024, 103640. |
| 20 | HUANG X , WANG Y , CUI X , et al. Insight into myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury from the perspective of ferroptosis[J]. Perfusion, 2024, 2676591241280371. |
| 21 |
XU X Q , XU T , JI W , et al. Herpes simplex virus 1-induced ferroptosis contributes to viral encephalitis[J]. mBio, 2023, 14 (1): e0237022.
doi: 10.1128/mbio.02370-22 |
| [1] | LUO Shishi, CHEN Beilei, ZHANG Lei, FENG Qixian, WU Ruisen, CHEN Jiaqi, WANG Yuan, JIAN Zixin, XU Lihui, CHEN Qiuyong, MA Yufang, WANG Quanxi. Radix Pseudostellariae Polysaccharide Regulates Let-7d-3p to Alleviates Inflammatory-induced by Pseudorabies Virus Infection in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2438-2450. |
| [2] | LI Changying, LI Jun, LI Xifeng, BI Shicheng, CAO Liting. Effect of Dietary Yeast β-glucan Supplementation on Intestinal Immune Function in Chickens Immunized against Newcastle Disease Vaccine based on Transcriptomic [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1441-1452. |
| [3] | FENG Yuhuan, ZHANG Yiqian, LIU Xia, ZHOU Xuehui, LIU Yanyan, NIU Luting, NI Xingwei, ZHAO Zhiguo, WANG Yan, YANG Xiaowei, XU Tingting, ZHAO Guangwei. Research Progress on the Interaction Mechanisms between Akabane Virus and Host [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 4877-4888. |
| [4] | WANG Shengqi, JI Xinyu, HUANG Fuqing, HU Manli, WANG Rouqi, GENG Yuxin, SUN Yingxue, QI Zhili, ZHANG Xin. Effects of Salidroside-added Complete Nutrition Food on Blood Biochemical Indexes and Liver Transcriptomics in Dogs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 455-465. |
| [5] | Yiqian FU, Dongge LIANG, Mingyang WANG, Jiajia PAN, Yanbin YANG, Lei ZENG, Xiangtao KANG. Construction of Interferon Regulatory Factor Knockdown Cell Line and Its Effect on Pseudorabies Virus Proliferation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4100-4109. |
| [6] | Mengdi WANG, Yumin WANG, Zhen ZHANG, Xiuxiang LU, Heng WANG, Wenjie FAN, Chen YAO, Pengxiang LIU, Yanjie MA, Beibei CHU, Jiang WANG, Guoyu YANG. Effect of TSG101 Gene Knockdown on Proliferation of Pseudorabies Virus in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4110-4120. |
| [7] | Yue LI, Changchun ZHANG, Guangyu LIU, Mengyuan GAO, Chaojun FU, Jiabao XING, Sijia XU, Qiyuan KUANG, Jing LIU, Xiaopeng GAO, Heng WANG, Lang GONG, Guihong ZHANG, Yankuo SUN. Application and Analysis of Meta-transcriptomics Sequencing Technology in the Diagnosis of Viral Diarrhea Diseases in Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3579-3589. |
| [8] | Huihui GUO, Hao ZHAGN, Dan YANG, Yan KUANG, Yafei LI, Shaomeng LIU, Qingyun LIU, Xiangru WANG. Construction of Fluorescently Labelled Pseudorabies Viruses and Their Preliminary Application in Antiviral Drug Screening [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3600-3611. |
| [9] | ZHANG Ying, SONG Chunlian, ZHANG Ying, SHEN Hong, SHU Xianghua, YANG Honggui. Study on the Damage of Blood-brain Barrier by Tight Junction Protein Mediated by MMP-9 in Pseudorabies Virus-infected Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2186-2194. |
| [10] | LI Yixuan, NIU Jingyi, LI Gang, WAN Chao, FANG Rendong, YE Chao. Research Progress on the Biological Functions of Tegument Proteins Encoded by Pseudorabies Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 957-970. |
| [11] | XIAO Le, LIU Junyuan, ZENG Wenyu, WANG Qin, HAN Wenjue, LIU Yanling, FAN Yu, XU Yuting, YANG Beini, XIAO Xiong, WANG Zili. Microbiome and Transcriptome Analyses Revealed the Regulatory Mechanism of Xiangsha Liujunzi Decoction on Ileal Injury Induced by ETEC in Weaned Piglets with Diarrhea [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 797-808. |
| [12] | CHEN Hongjian, CAO Yan, FAN Jie, GAN Rongxuan, SONG Wenbo, YU Shengwei, YANG Ting, ZHAO Yanxia, WEI Chunyan, XIE Rui, HUA Lin, PENG Zhong, WU Bin. Prevalence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Pseudorabies Virus within Pig Slaughterhouses in Hubei Province of China during 2020-2022 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 2972-2981. |
| [13] | YUAN Sheng, LI Anqi, Lü Wenke, YANG Lulu, ZHOU Feng, HUANG Liangzong, BAI Aiquan, WEN Feng, HUANG Shujian, GUO Jinyue. Analysis of Variation in Major Virulence-related Genes of a Strain of Pseudorabies Virus and Its Pathogenicity to Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 2195-2199. |
| [14] | NI Zheng, YE Weicheng, CHEN Liu, YUN Tao, HUA Jionggang, ZHU Yinchu, ZHANG Cun. Genetic Variation and Pathogenicity of a Pseudorabies Virus Variant Strain in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(4): 1766-1770. |
| [15] | LIU Ling, WANG Dandan, CUI Kai, MA Yuehui, JIANG Lin. Advances of Disease-Resistant Breeding on Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(2): 434-442. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||