





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 2438-2450.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.05.040
• Clinical Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
LUO Shishi1,2( ), CHEN Beilei1,2, ZHANG Lei1, FENG Qixian1,2, WU Ruisen1,2, CHEN Jiaqi1,2, WANG Yuan1,2, JIAN Zixin1, XU Lihui1,2, CHEN Qiuyong3, MA Yufang1,2, WANG Quanxi1,2,*(
), CHEN Beilei1,2, ZHANG Lei1, FENG Qixian1,2, WU Ruisen1,2, CHEN Jiaqi1,2, WANG Yuan1,2, JIAN Zixin1, XU Lihui1,2, CHEN Qiuyong3, MA Yufang1,2, WANG Quanxi1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-03
Online:2025-05-23
Published:2025-05-27
Contact:
WANG Quanxi
E-mail:2272892708@qq.com;wqx608@126.com
CLC Number:
LUO Shishi, CHEN Beilei, ZHANG Lei, FENG Qixian, WU Ruisen, CHEN Jiaqi, WANG Yuan, JIAN Zixin, XU Lihui, CHEN Qiuyong, MA Yufang, WANG Quanxi. Radix Pseudostellariae Polysaccharide Regulates Let-7d-3p to Alleviates Inflammatory-induced by Pseudorabies Virus Infection in Mice[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2438-2450.
Table 1
Primer sequences of target gene fragments"
| 基因 Genes | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequences | 基因库登录号 GenBank accession No. |
| IL-6-pig | F: CAGTCCAGTCGCCTTCT | NM_214399.1 |
| R: CACCTTTGGCATCTTCTT | ||
| TNF-α-pig | F: TTCCAGCTGGCCCCTTGAGC | JF831365.1 |
| R: GAGGGCATTGGCATACCCAC | ||
| IL-17-pig | F: CTGTCACTGCTGCTTCTGCTGAG | KF646141.1 |
| R: TGGAGTAATCTGAGGGCCGTCTG | ||
| β-Actin-pig | F: CAGGTCATCACCATCGGCAACG | NC_010445.4 |
| R: GACAGCACCGTGTTGGCGTAGAGGT | ||
| Let-7d-3p | F: AACGCTATACGACCTGCTGC | NR_128407 |
| R: AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | ||
| 茎环:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGT CCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACAGAAAG | ||
| U6 | F: GACCCGCAATAGTGAGAGAAGC | EU520423.1 |
| R: CATGGGAAATTGGCCCTCTGC | ||
| PRV-gB | F: GCGGTCACCTTGTGGTTGTT | MN718167.1 |
| R: AACGTCATCGTCACGACCGT | ||
| IL-6-mouse | F: CACAGAAGGAGTGGCTAA | XM_032905335.1 |
| R: GCATAACGCACTAGGTTT | ||
| TNF-α-mouse | F: CTGTCTTAACTAACCTCCTTCT | M20155.1 |
| R: ATGTCTAACTGCCCTTCC | ||
| I L-17-mouse | F: GGTCCAGCTTTCCCTCC | XM_021176489.1 |
| R: AGACTACCTCAACCGTTCCA | ||
| β-Actin-mouse | F: TACGAGTTGCCTGATGGTC | KC215183.1 |
| R: ATGATGGAGTTGAAGGTGGT |
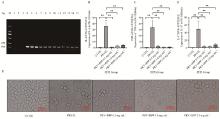
Fig. 2
mRNA expression of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-17 genes in PK-15 cell and the change of the PK-15 cell morphological A. PCR amplification result using PRV-gB primer (M. DL2000 DNA marker; 1-3. PCR amplification result of control group; 4-6. PCR amplification result of PRV group; 7-9. PCR amplification result of 0.5 mg·mL-1 RPP group; 10-12. PCR amplification of result of 1.0 mg·mL-1 RPP group; 13-15. PCR amplification result of 2.0 mg·mL-1 RPP group); B-D. qPCR detection of inflammatory factor mRNA transcription levels; E. The change of the PK-15 cell morphological"
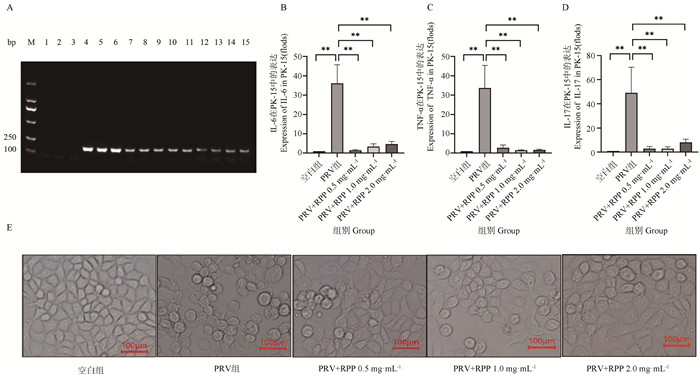
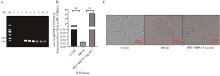
Fig. 3
Expression of Let-7d-3p and the change of the PK-15 cell morphological A. PCR amplification result using PRV-gB primer (M. DL2000 DNA marker; 1-3. PCR amplification result of control group; 4-6. PCR amplification result of PRV group; 7-9. PCR amplification result of 0.5 mg·mL-1 RPP group); B. qPCR detected expression of Let-7d-3p; C. The change of the PK-15 cell morphological"
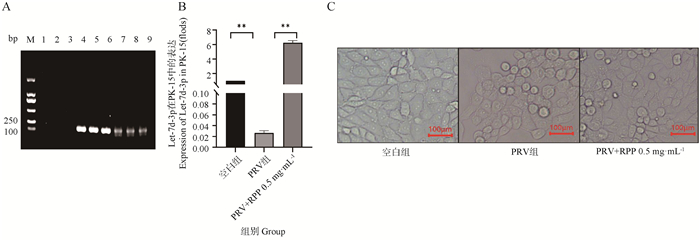
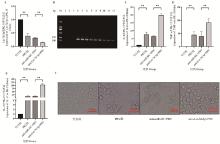
Fig. 4
Interference of Let-7d-3p on the expression levels of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-17 mRNA and the change of the PK-15 cell morphological A. qPCR detected expression of Let-7d-3p; B. PCR amplification result using PRV-gB primer (M. DL2000 DNA marker; 1-3. PCR amplification result of control group; 4-6. PCR amplification result of PRV group; 7-9. PCR amplification result of anti-Let-7d-3p+PRV group group; 10-12. PCR amplification of result of anti-Let-7d-3p+PRV group); C-E. qPCR detection of inflammatory factor mRNA transcription levels; F. The change of the PK-15 cell morphological"
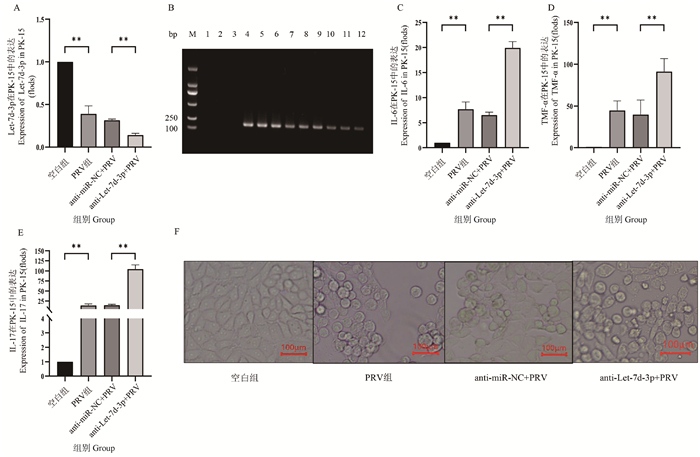
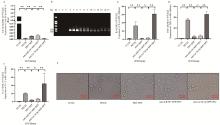
Fig. 5
The effect of RPP on the expression levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-17 mRNA after the interference of Let-7d-3p and the change of the PK-15 cell morphological A. qPCR detected expression of Let-7d-3p; B. PCR amplification result using PRV-gB primer (M. DL2000 DNA marker; 1-3. PCR amplification result of control group; 4-6. PCR amplification result of PRV group; 7-9. PCR amplification result of RPP+PRV group group; 10-12. PCR amplification of result of anti-miR-NC+RPP+PRV group; 13-15. PCR amplification result of anti-let-7d-3p+RPP+PRV group); C-E. qPCR detection of inflammatory factor mRNA transcription levels; F. The change of the PK-15 cell morphological"
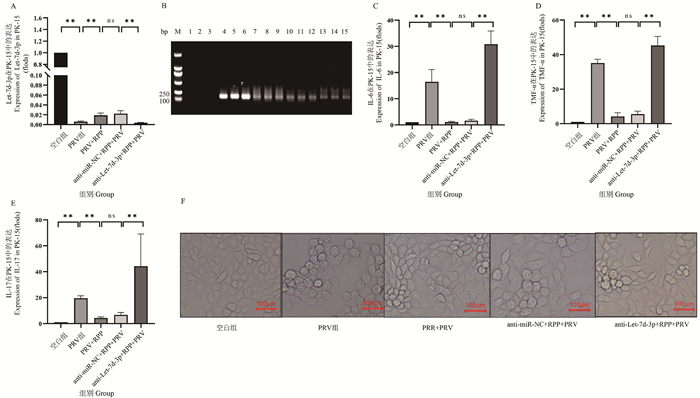
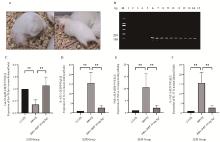
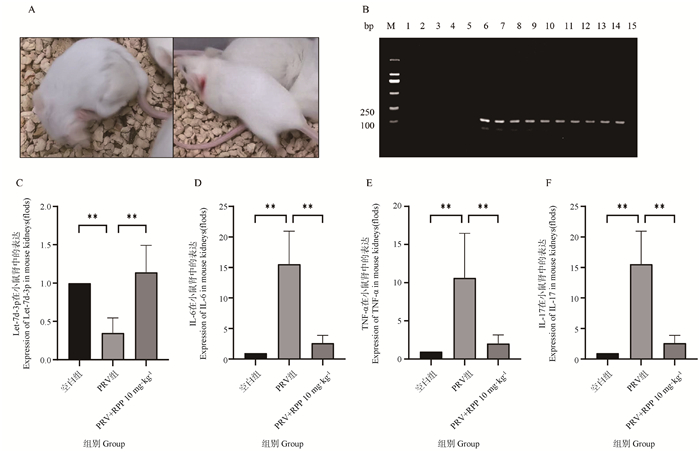
Fig. 6
RPP regulates the expression of Let-7d-3p, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-17 mRNA in mouse kidneys infected with PRV A. Scratching bleeding in PRV group mouse; B.PCR amplification result using PRV-gB primer (M. DL2000 DNA marker; 1-5. PCR amplification result of control group; 6-10. PCR amplification result of PRV group; 11-15. PCR amplification result of RPP group); C. qPCR detected expression of Let-7d-3p; D-F. qPCR detection of inflammatory factor mRNA transcription levels"
| 1 | 丁春花, 林培玲, 曾建伟, 等. 太子参块根和参须中多糖及总皂苷含量的测定[J]. 福建中医药大学学报, 2012, 22 (3): 40- 43. |
| DING C H , LIN P L , ZENG J W , et al. Determination of polysaccharides and total saponins in root tuber and fibrous root of Pseudostellaria Heterophylla[J]. Rehabilitation Medicine, 2012, 22 (03): 40- 43. | |
| 2 | 曾丽, 陈赛红, 赵佳梅, 等. 太子参参须多糖对RAW264.7细胞免疫调节作用的研究[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2023, 45 (1): 79- 87. |
| ZENG L , CHEN S H , ZHAO J M , et al. Immuomodulatory effects of Radix Pseudostellariae fibrous root polysaccharides on RAW264.7 cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 45 (1): 79- 87. | |
| 3 | 闵思明, 赵晓瑶, 陈赛红, 等. 太子参参须多糖对免疫抑制小鼠的免疫调节作用研究[J]. 动物医学进展, 2020, 41 (8): 23- 28. |
| MIN S M , ZHAO X Y , CHEN S H , et al. Immunomodulatory effects of Radix Pseudostellariae fibrous root polysaccharideson cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 41 (8): 23- 28. | |
| 4 |
华利忠, 刘剑锋, 冯志新, 等. 猪伪狂犬病病毒新流行变异毒株的研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2017, 33 (2): 476- 480.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2017.02.037 |
|
HUA L Z , LIU J F , FENG Z X , et al. Progress in novel pseudorabies virus variants prevalent in China[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 33 (2): 476- 480.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2017.02.037 |
|
| 5 |
ZHOU Q , ZHANG L , LIN Q , et al. Pseudorabies virus infection activates the TLR-NF-κB axis and AIM2 inflammasome to enhance inflammatory responses in mice[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97 (3): e0000323.
doi: 10.1128/jvi.00003-23 |
| 6 | 杨志刚, 汤德元, 曾智勇, 等. 伪狂犬病病毒(PRV)感染小鼠三叉神经节对NF-κB信号通路的影响及其调控炎症因子分泌[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2023, 43 (1): 115- 122. |
| YANG Z G , TANG D Y , ZENG Z Y , et al. Effects of PRV-infected mouse trigeminal ganglion on NF-κB signaling pathway and its regulation of inflammatory factor secretion[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 43 (1): 115- 122. | |
| 7 |
WU Y Q , CHEN D J , HE H B , et al. Pseudorabies virus infected porcine epithelial cell line generates a diverse set of host microRNAs and a special cluster of viral microRNAs[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7 (1): e30988.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030988 |
| 8 |
LIU H , YANG L , SHI Z , et al. Functional analysis of prv-miR-LLT11a encoded by pseudorabies virus[J]. Vet Sci, 2019, 20 (6): e68.
doi: 10.4142/jvs.2019.20.e68 |
| 9 |
QIU G , FAN J , ZHENG G , et al. Diagnostic potential of plasma extracellular vesicle miR-483-3p and Let-7d-3p for sepsis[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2022, 9, 814240.
doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.814240 |
| 10 |
DIDIANO D , HOBERT O . Molecular architecture of a miRNA-regulated 3'UTR[J]. RNA, 2008, 14 (7): 1297- 317.
doi: 10.1261/rna.1082708 |
| 11 |
ITOKAZU M , ONODERA Y , MORI T , et al. Adipose-derived exosomes block muscular stem cell proliferation in aged mouse by delivering miRNA Let-7d-3p that targets transcription factor HMGA2[J]. Biol Chem, 2022, 298 (7): 102098.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102098 |
| 12 |
KHOKHAR M , TOMO S , PUROHIT P . MicroRNAs based regulation of cytokine regulating immune expressed genes and their transcription factors in COVID-19[J]. Meta Gene, 2022, 31, 100990.
doi: 10.1016/j.mgene.2021.100990 |
| 13 | 陈思. PCV2和PRV在吉林省流行变异分析及其引起细胞凋亡的机制研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023. |
| CHEN S. Analysis of the epidemic variation of PCV2 and PRV in Jilin Province and the mechanisms underlying their induction of cell apoptosis[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 14 |
SUN W , LIU S , HUANG X , et al. Cytokine storms and pyroptosis are primarily responsible for the rapid death of mice infected with pseudorabies virus[J]. R Soc Open Sci, 2021, 8 (8): 210296.
doi: 10.1098/rsos.210296 |
| 15 | WANG Z , CAI X , REN Z , et al. Piceatannol as an antiviral inhibitor of PRV infection in vitro and in vivo[J]. Animals (Basel), 2023, 13 (14): 2376. |
| 16 | 张王芝, 舒相华, 张莹, 等. 黄芩多糖对PRV感染猪睾丸细胞的作用及其差异基因表达分析[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2023, 59 (10): 129- 137. |
| ZHANG W Z , SHU X H , ZHANG Y , et al. Effects of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi polysaccharide on PRV-infected ST cells and analysis of differential gene expression[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 59 (10): 129- 137. | |
| 17 | 谢美林, 徐海清, 李景明, 等. 太子参多糖的纯化、组成及对LPS损伤Raw264.7巨噬细胞的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技, 2022, 43 (14): 392- 400. |
| XIE M L , XU H Q , LI J M , et al. Purification and composition of polysaccharides from Pseudostellaria heterophylla and protective effect on Raw 264.7 cells induced by LPS[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43 (14): 392- 400. | |
| 18 | 乔石, 闵思明, 李若南, 等. 太子参参须多糖促进小鼠脾淋巴细胞体外增殖及细胞因子分泌的研究[J]. 动物医学进展, 2022, 43 (3): 73- 77. |
| QIAO S , MIN S M , LI R N , et al. Study on Radix Pseudostellaria fibrous root polysaccharide promoting proliferation and cytokine secretion of mouse spleen lymphocytes in vitro[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 43 (3): 73- 77. | |
| 19 | 唐琦, 吴鹏, 李国辉. 人巨细胞病毒编码miRNA功能及其作用机制[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2018, 34 (7): 706- 712. |
| TANG Q , WU P , LI G H . The biological function and mechanism of human cytomegalovirus encoded miRNAs[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2018, 34 (7): 706- 712. | |
| 20 |
HENNIG T , PRUSTY A , KAUFER B , et al. Selective inhibition of miRNA processing by a herpesvirus-encoded miRNA[J]. Nature, 2022, 605 (7910): 539- 544.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04667-4 |
| 21 | KOLENDA T , PRZYBYŁA W , TERESIAK A , et al. The mystery of let-7d-a small RNA with great power[J]. Contemp Oncol (Pozn), 2014, 18 (5): 293- 301. |
| 22 |
LETAFATI A , NAJAFI S , MOTTAHEDI M , et al. MicroRNA let-7 and viral infections: focus on mechanisms of action[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2022, 27 (1): 14.
doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00317-9 |
| 23 |
DE SANTIS C , GÖTTE M . The role of microRNA Let-7d in female malignancies and diseases of the female reproductive tract[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (14): 7359.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22147359 |
| 24 | 艾威, 周游. miRNA let-7家族在胶质瘤发生与发展中作用的进展[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志, 2021, 26 (7): 561- 563. |
| AI W , ZHOU Y . Advances in the role of miRNA let-7 family in glioma development and development[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Neurosurgery, 2021, 26 (7): 561- 563. | |
| 25 | 黄江标, 韦艳, 张志敏. Let-7 miRNA家族: 一种潜在的免疫治疗靶点[J]. 肿瘤学杂志, 2020, 26 (11): 929- 934. |
| HUANG J B , WEI Y , ZHANG Z M . Let-7 miRNA family: A potential target for immunotherapy[J]. Journal of Chinese Oncology, 2020, 26 (11): 929- 934. | |
| 26 | 谷兆琪, 尹训强, 王东梅, 等. 原因不明复发性自然流产患者外周血IL-6、let-7d-5p水平变化及其关系[J]. 山东医药, 2019, 59 (2): 23- 27. |
| GU Z Q , YIN X Q , WANG D M , et al. Changes in levels of IL-6 and let-7d-5p in peripheral blood of URSA patients and the relationships between them[J]. Shandong Medical Journal, 2019, 59 (2): 23- 27. | |
| 27 | WANG J , WANG X , WANG L , et al. MiR-let-7d-3p regulates IL-17 expression through targeting AKT1/mTOR signaling in CD4+T cells[J]. In vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim, 2020, 56 (1): 67- 74. |
| 28 | 王建博. NRG1与microRNA-193a-3p抑制剂共同作用于巨噬细胞发挥抗炎抗纤维化作用的研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2023. |
| WANG J B. NRG1 and microrNA-193A-3p inhibitors reduce the pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic ability of macrophages[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 29 | ROMERO C H , MEADE P N , SHULTZ J E , et al. Venereal transmission of pseudorabies viruses indigenous to feral swine[J]. J Wildl Dis, 2001, 37 (2): 289- 296. |
| 30 | MA J J , WU WY , LIAO J , et al. Preparation of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide by lactic acid bacterium fermentation and its protective mechanism against alcoholic liver damage in mice[J]. Agric Food Chem, 2024, 72 (31): 17633- 17648. |
| 31 | 韩玲, 赵伟. 枸杞多糖通过miR-29b/MAPK1通路发挥视网膜血管内皮细胞的抗凋亡作用[J]. 解剖学研究, 2023, 45 (6): 555-561, 572. |
| HAN L , ZHAO W . Lycium barbarum polysaccharide exerts anti-apoptotic effects on retinal vascular endothelial cells through the miR-29b/MAPK1 pathway[J]. Anatomy Research, 2023, 45 (6): 555-561, 572. |
| [1] | CHEN Zehan, ZHANG Ruoyi, LIN Huiying, ZENG Chunli, LIN Fu, LI Jian. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Chelidonium majus on IPEC-J2 Cells based on HPLC Fingerprint and Network Pharmacology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2466-2480. |
| [2] | ZHAO Ying, WANG Jinglei, WANG Meng, WANG Libin, ZHANG Qian, LI Zhijie, MA Xin, YU Sijiu, PAN Yangyang. Preparation and Characterization of Forsythiaside A and Kaempferol Encapsulated in Milk-derived Exosomes and Evaluation of Anti-inflammatory Effects in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2481-2495. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xiwen, YIN Yue, LI Xiang, WANG Min, WANG Yongfang, JIN Shuning, FENG Xinhui, ZHAO Yurong. Effects of Ursolic Acid on Breast Meat Quality and Wooden Breast of Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 711-721. |
| [4] | LI Fan, SUN Haifeng, SUN Meng, GAO Yanxiao, SUN Yangyang, ZHANG Lujie, BAI Juan, JIANG Ping. Preparation and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Porcine IL-1β Monoclonal Antibody [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 890-899. |
| [5] | Yiqian FU, Dongge LIANG, Mingyang WANG, Jiajia PAN, Yanbin YANG, Lei ZENG, Xiangtao KANG. Construction of Interferon Regulatory Factor Knockdown Cell Line and Its Effect on Pseudorabies Virus Proliferation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4100-4109. |
| [6] | Mengdi WANG, Yumin WANG, Zhen ZHANG, Xiuxiang LU, Heng WANG, Wenjie FAN, Chen YAO, Pengxiang LIU, Yanjie MA, Beibei CHU, Jiang WANG, Guoyu YANG. Effect of TSG101 Gene Knockdown on Proliferation of Pseudorabies Virus in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4110-4120. |
| [7] | Ling LIU, Wanyu SHI, Xiumei LI, Minghua WANG, Xianghe ZHAI, Weiwei ZHOU. Intervention of Essential Oils from Citrus reticulata Blanco on Lipopolysaccharide- induced Inflammation in RAW264.7 Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4153-4160. |
| [8] | Huihui GUO, Hao ZHAGN, Dan YANG, Yan KUANG, Yafei LI, Shaomeng LIU, Qingyun LIU, Xiangru WANG. Construction of Fluorescently Labelled Pseudorabies Viruses and Their Preliminary Application in Antiviral Drug Screening [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3600-3611. |
| [9] | Ya’nan LI, Tianwen MA, Yuhui MA, Chengwei WEI. Bilobalide Regulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis Mediated by AMPK-SIRT3 Positive Feedback Loop and Improves Inflammatory Damage of ATDC5 Chondrocytes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3714-3724. |
| [10] | Chengquan HAN, Jingtao LIU, Miao YU, Lizeng GUAN, Lu XU, Yueshang WANG. Study on the Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Effect of Rutin in BV2 Cells and Its Mechanism [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3119-3131. |
| [11] | SUN Wenli, WANG Haoqi, ZE Licuo, GAO Yufan, ZHANG Feifan, ZHANG Jian, DUAN Mengqi, SHANG Peng, QIANG Bayangzong. Polymorphism of Pro-Inflammatory Factors (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) in Tibetan Pigs and Its Association Analysis with Immune Traits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1958-1969. |
| [12] | YANG Xiaofeng, QIN Xiaowei, LÜ Lihua. Protective Effect of a Derivative of MNQ Against LPS-Induced Inflammatory Injury in Bovine Ovarian Follicular Granulosa Cells in Vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2032-2041. |
| [13] | ZHANG Ying, SONG Chunlian, ZHANG Ying, SHEN Hong, SHU Xianghua, YANG Honggui. Study on the Damage of Blood-brain Barrier by Tight Junction Protein Mediated by MMP-9 in Pseudorabies Virus-infected Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2186-2194. |
| [14] | LIU Sidi, MA Ben, ZHENG Yan, QIU Yunqiao, YAO Zelong, CAO Zhongzan, LUAN Xinhong. Research Progress in the Regulation of Intestinal Flora on Intestinal Mucosal Immunity and Inflammation in Animals [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1423-1431. |
| [15] | DAI Fan, LIU Zhanyou, ZHANG Xuyang, LI Wu. Aconitate Decarboxylase 1 Could Regulate the Inflammatory Response Caused by BCG [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1696-1706. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||