





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 3408-3422.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.07.033
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
GENG Xiaoling1,3( ), LI Ruifang1, XU Weibing2, DU Jingying1, ZHANG Manyu1, SUN Qing1, JIANG Wei1, MI Rongsheng1, CHEN Zhaoguo1, WANG Quan1,*(
), LI Ruifang1, XU Weibing2, DU Jingying1, ZHANG Manyu1, SUN Qing1, JIANG Wei1, MI Rongsheng1, CHEN Zhaoguo1, WANG Quan1,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-09
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
WANG Quan
E-mail:1757911780@qq.com;wangquan@shvri.ac.cn
CLC Number:
GENG Xiaoling, LI Ruifang, XU Weibing, DU Jingying, ZHANG Manyu, SUN Qing, JIANG Wei, MI Rongsheng, CHEN Zhaoguo, WANG Quan. Construction and Biological Function Research of TR and ROP5 Double Gene Deletion Strains of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3408-3422.
Table 1
The primers used to construct pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5 plasmid"
| 序号 No. | 名称 Name | 引物的序列(5′→3′) Sequence | 质粒名称 Plasmid | 目的 Purpose |
| 1 | gRNA1-F | gcttctcatgcccgctgcgtGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC | pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5-1 | PCR扩增片段1 |
| gRNA2-F | tgggggatgtatccgtgttgGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC | pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5-2 | ||
| CAS-1R | AAAAGGCAACGGATGTAAAAG | pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5 | ||
| 2 | CAS-2F | CTTTTACATCCGTTGCCTTTTCC | pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5 | PCR扩增片段2 |
| CAS-2R | GCCGTTTGTCTCGATCAGAGG | pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5 | ||
| 3 | CAS-3F | CCTCTGATCGAGACAAACGGC | pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5 | PCR扩增片段3 |
| 3gRNA1-R | acgcagcgggcatgagaagcAACTTGACATCCCCATTTACCAG | pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5-1 | ||
| 3gRNA2-R | caacacggatacatcccccaAACTTGACATCCCCATTTACCAG | pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5-2 | ||
| 4 | DgRNA-F | GCTTCCTCCCTGTGCGCT | 鉴定gRNA1是否插入质粒 | |
| DgRNA-R | GGAACAAAAGCTGGAGCTCAAAAAAG | |||
| 5 | U6-F | $\underline{{\rm{CGAATTG}}}$GGTACCCAAGTAAGCAGAAGCACGCTG(Kpn Ⅰ) | pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5 | 扩增ROP5含Kpn Ⅰ和Xho Ⅰ酶切位点的gRNA2片段 |
| U6-R | $\underline{{\rm{TCGAC}}}$CTCGAGAATTAACCCTCACTAAAGG(Xho Ⅰ) | |||
| 6 | DgRNA-2F | AAAACGACGGCCAGTGAG | 鉴定gRNA2是否插入质粒 | |
| DgRNA-2R | GAAAAGGCAACGGATGTAA |
Table 2
Primers for the construction of pROP5::CAT-D plasmid"
| 序号 No. | 名称 Name | 引物的序列(5′→3′) Sequence | 目的 Purpose |
| 1 | ROP5 5′KO-F | ACATCGAGGTGGACGTGGAAATATA | 扩增ROP5 5′UTR |
| ROP5 5′KO-R | CTGGGAGATGTTGTGAGGTCTTGGT | ||
| 2 | ROP5 3′KO-F | GAAAACGGCTCTGCCAACGGGGCGT | 扩增ROP5 3′UTR |
| ROP5 3′KO-R | GCTGCCTCTGTGGATCTCTCTAAAC | ||
| 3 | CAT-F | accaagacctcacaacatctcccagACATGTCGGGCCCCCCCT | 扩增CAT抗性片段 |
| CAT-R | acgccccgttggcagagccgttttcTCTAGAACTAGTGGATCCCCC | ||
| 4 | pROP5:CAT-F | gtttagagagatccacagaggcagcGTCGTACAGTTGACGTCGA | 扩增质粒骨架 |
| pROP5:CAT-R | tatatttccacgtccacctcgatgtGACAACTTTTCTATACAAAGTTGATAG | ||
| 5 | ROP5-PCR-1-F | ACATCGAGGTGGACGTGGAAATATA | 判断5′UTR与CAT连接处是否连上 |
| ROP5-PCR-1-R | acgccccgttggcagagccgttttcTCTAGAACTAGTGGATCCCCC | ||
| 6 | ROP5-PCR-2-F | ACATCGAGGTGGACGTGGAAATATA | 判断3′UTR与CAT连接处是否连上 |
| ROP5-PCR-2-R | acgccccgttggcagagccgttttcTCTAGAACTAGTGGATCCCCC |
Table 3
Primers for identification of TR-ROP5-KO strain"
| 序号 No. | 名称 Name | 引物的序列(5′→3′) Sequence | 作用 Role | 目的 Purpose |
| 1 | TR-F | CGAGTTCTGTATCAGAGGCTGTCCG | 扩增TR基因的820 bp | 判断TR基因是否缺失 |
| TR-R | TGTCGAGTCAGCTCAAACGAGAGC | |||
| 2 | ROP5-F | CGGTGACCGATCTGTCGTATTTTTA | 扩增ROP5基因的901 bp | 判断ROP5基因是否缺失 |
| ROP5-R | AGGTTGTCCTGTTGATAGGCTGCTC | |||
| 3 | CAT-F | ACATGTCGGGCCCCCCCT | 扩增CAT抗性片段的1 546 bp | 判断虫体是否具有CAT抗性 |
| CAT-R | TCTAGAACTAGTGGATCCCCC | |||
| 4 | DHFR-F | AAGCTTCGCCAGGCTGTA | 扩增DHFR抗性片段的3 163 bp | 判断虫体是否具有DHFR抗性 |
| DHFR-R | GGAATTCATCCTGCAAGTGC |
Table 4
Primers of RT-PCR used to detect the mRNA transcription levels of cells infected by different strains of T. gondii"
| 引物名称 Name | 核苷酸序列(5′→3′) Nucleotide sequence | PCR产物长度/bp PCR product length |
| β-Actin-F | AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC | 138 |
| β-Actin-R | CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT | |
| IL-12-F | GGAAGCACGGCAGCAGAATA | 180 |
| IL-12-R | AACTTGAGGGAGAAGTAGGAATGG | |
| IFN-γ-F | TCAAGTGGCATAGATGTGGAAGAA | 92 |
| IFN-γ-R | TGGCTCTGCAGGATTTTCATG | |
| NF-κB-F | TGGCTACTATGAGGCTGACC | 787 |
| NF-κB-R | GTTGATGGTGCTGAGGGAT |
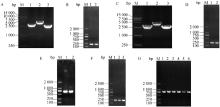
Fig. 1
Construction and identification of pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5 plasmid A, C. Amplification of pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5-1 plasmid and pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5-2 plasmid fragments by PCR [M. DL 15000 marker; 1. Fragment 1 of plasmid (3 000 bp); 2. Fragment 2 of plasmid (4 021 bp); 3. Fragment 3 of plasmid (2675 bp)]; B, D. Identification of pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5-1 plasmid and Identification of pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5-2 plasmid by PCR (M. DL 2000 marker; 1-2. Identify 220 bp of gRNA1/gRNA2); E. Amplification of gRNA2 (including Kpn Ⅰ and Xho Ⅰ restriction sites) fragment of ROP5 by PCR (M. DL 2000 marker; 1-2. 676 bp of gRNA2 fragment); F. Identification of pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5 plasmid by PCR (M. DL 2000 marker; 1-3. Identify 220 bp of gRNA1); G. Identification of pSAG1::CAS9-U6::sgROP5 plasmid by PCR (M. DL 2000 marker; 1-6. Identify 778 bp of gRNA2)"
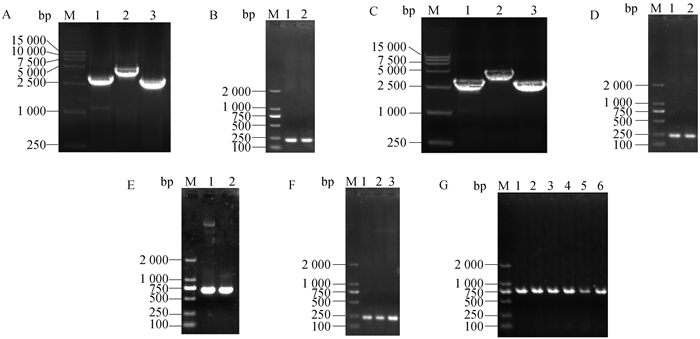
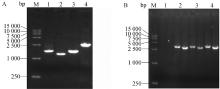
Fig. 2
Construction and identification of pROP5::CAT-D plasmid A. Amplification of pROP5::CAT-D plasmid fragments by PCR (M. DL 15000 marker; 1. Fragment 1 of plasmid; 2. Fragment 2 of plasmid; 3. Fragment 3 of plasmid; 4. Fragment 4 of plasmid); B. Identification of pROP5::CAT-D plasmid by PCR (M. DL 15000 marker; 1. Blank control; 2-4. Positive plasmid, the two fragments are 3 146 bp at the junction of 5′UTR and CAT and 2 875 bp at the junction of CAT and 3′UTR)"
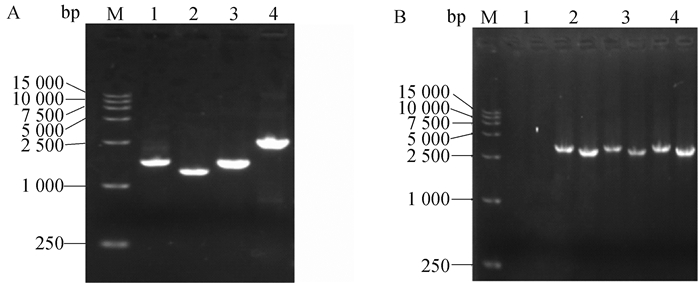
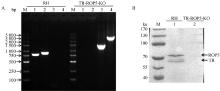
Fig. 3
Identification of TR-ROP5-KO strain by PCR and Western blot A. Identification of TR-ROP5-KO strain by PCR (M. DL 5000 marker; 1. Amplification of 820 bp fragment in TR gene; 2. Amplification of 901 bp fragment in ROP5 gene; 3. Amplify 1546 bp of CAT resistant fragment; 4. Amplify 3 163 bp of DHFR resistant fragment); B. Identification of TR-ROP5-KO strain by Western blot (M. Protein marker; 1. RH strain of T. gondii; 2. TR-ROP5-KO strain of T. gondii)"
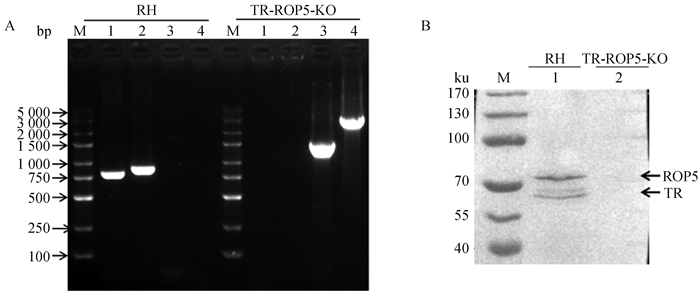
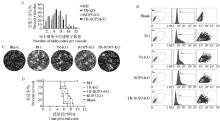
Fig. 4
Study on biological activity of TR and ROP5 double-gene deletion strains of T. gondii A. Proliferation assay of TR-ROP5-KO strain in Vero cells; B. Invasion assay of TR-ROP5-KO strain in Vero cells; C. Plaque assay of TR-ROP5-KO strain in Vero cells; D. Virulence assay of TR-ROP5-KO strain in mice"
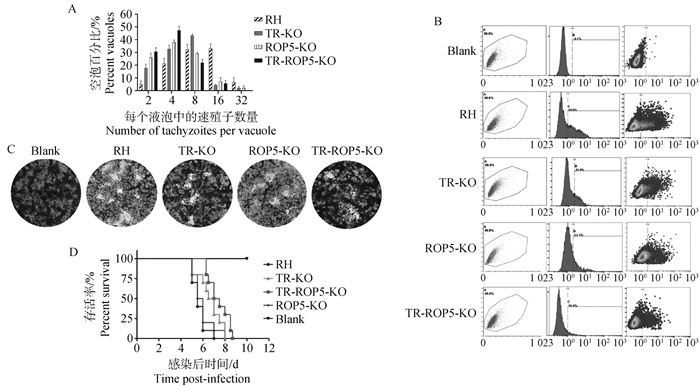
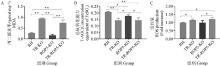
Fig. 5
Oxidative stress levels in TR and ROP5 gene deletion strains of T. gondii A. MDA levels in TR and ROP5 gene deletion strains of T. gondii; B. T-AOC levels in TR and ROP5 gene deletion strains of T. gondii; C.ROS levels in TR and ROP5 gene deletion strains of T. gondii. *. P < 0.05, **. P < 0.01"
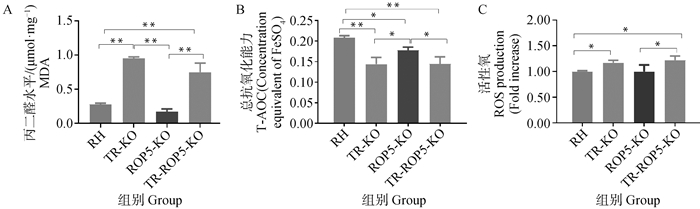
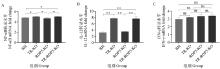
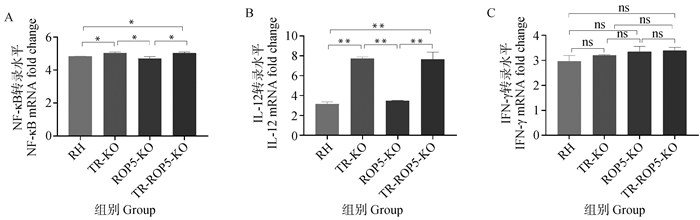
Fig. 7
Effects of TR and ROP5 gene deletion strains of T. gondii on the expression of NF-κB, IL-12, IFN-γ mRNA in RAW264.7 cells A. Effects of TR and ROP5 gene deletion strains of T. gondii on the expression of NF-κB mRNA in RAW264.7 cells; B. Effects of TR and ROP5 gene deletion strains of T. gondii on the expression of IL-12 mRNA in RAW264.7 cells; C. Effects of TR and ROP5 gene deletion strains of T. gondii on the expression of IFN-γ mRNA in RAW264.7 cells. *. P < 0.05, **. P < 0.01, ns. P > 0.05"
| 1 | KOCHANOWSKY J A , KOSHY A A . $ Toxoplasma \;gondii$[J]. Curr Biol, 2018, 28 (14): R770- R771. |
| 2 |
JACOBSON F S , MORGAN R W , CHRISTMAN M F , et al. An alkyl hydroperoxide reductase from Salmonella typhimurium involved in the defense of DNA against oxidative damage[J]. J Biol Chem, 1989, 264 (3): 1488- 1496.
doi: 10.1016/S0005-2728(89)80408-6 |
| 3 | WHITE M W , RADKE J R , RADKE J B . Toxoplasma development-turn the switch on or off?[J]. Cell Microbiol, 2014, 16 (4): 466- 472. |
| 4 | SANCHEZ S G , BESTEIRO S . The pathogenicity and virulence of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Virulence, 2021, 12 (1): 3095- 3114. |
| 5 | SMITH N C , GOULART C , HAYWARD J A , et al. Control of human toxoplasmosis[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2021, 51 (2-3): 95- 121. |
| 6 | HAMPTON M M . Congenital toxoplasmosis: a review[J]. Neonatal Netw, 2015, 34 (5): 274- 278. |
| 7 | BEN-HARARI R R , CONNOLLY M P . High burden and low awareness of toxoplasmosis in the United States[J]. Postgrad Med, 2019, 131 (2): 103- 108. |
| 8 | HUNTER C A , SIBLEY L D . Modulation of innate immunity by Toxoplasma gondii virulence effectors[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2012, 10 (11): 766- 778. |
| 9 | 蒲元华, 张德林, 等. 弓形虫入侵宿主机制及免疫学研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2012, 30 (6): 480-485, 490. |
| PU Y H , ZHANG D L . Research progress on invasion mechanism and immunology of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases, 2012, 30 (6): 480-485, 490. | |
| 10 | 陆金苗, 韦娜娜, 周金林, 等. 硫氧还蛋白还原酶结构与功能研究进展[J]. 动物医学进展, 2019, 40 (9): 79- 83. |
| LU J M , WEI N N , ZHOU J L , et al. Progress on structures and functions of thioredoxin reductase[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 40 (9): 79- 83. | |
| 11 | XUE J X , JIANG W , CHEN Y J , et al. Thioredoxin reductase from Toxoplasma gondii: an essential virulence effector with antioxidant function[J]. FASEB J, 2017, 31 (10): 4447- 4457. |
| 12 | 郑斌, 陆绍红. 刚地弓形虫免疫逃避相关分子的研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2012, 30 (5): 396- 400. |
| ZHENG B , LU S H . Immune evasion molecules of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases, 2012, 30 (5): 396- 400. | |
| 13 | REESE M L , SHAH N , BOOTHROYD J C . The Toxoplasma pseudokinase ROP5 is an allosteric inhibitor of the immunity-related GTPases[J]. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289 (40): 27849- 27858. |
| 14 | NIEDELMAN W , GOLD D A , ROSOWSKI E E , et al. The rhoptry proteins ROP18 and ROP5 mediate Toxoplasma gondii evasion of the murine, but not the human, interferon-gamma response[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2012, 8 (6): e1002784. |
| 15 | ETHERIDGE R D , ALAGANAN A , TANG K L , et al. The Toxoplasma pseudokinase ROP5 forms complexes with ROP18 and ROP17 kinases that synergize to control acute virulence in mice[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2014, 15 (5): 537- 550. |
| 16 | ISHINO Y , SHINAGAWA H , MAKINO K , et al. Nucleotide sequence of the iap gene, responsible for alkaline phosphatase isozyme conversion in Escherichia coli, and identification of the gene product[J]. J Bacteriol, 1987, 169 (12): 5429- 5433. |
| 17 | HRYHOROWICZ M , LIPIŃSKI D , ZEYLAND J , et al. CRISPR/Cas9 immune system as a tool for genome engineering[J]. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz), 2016, 65 (3): 233- 240. |
| 18 | GASIUNAS G , BARRANGOU R , HORVATH P , et al. Cas9-crRNA ribonucleoprotein complex mediates specific DNA cleavage for adaptive immunity in bacteria[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2012, 109 (39): E2579- E2586. |
| 19 | JINEK M , CHYLINSKI K , FONFARA I , et al. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity[J]. Science, 2012, 337 (6096): 816- 821. |
| 20 | XU R F , QIN R Y , XIE H J , et al. Genome editing with type Ⅱ-C CRISPR-Cas9 systems from Neisseria meningitidis in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnol J, 2022, 20 (2): 350- 359. |
| 21 | FOX B A , RISTUCCIA J G , GIGLEY J P , et al. Efficient gene replacements in Toxoplasma gondii strains deficient for nonhomologous end joining[J]. Eukaryotic Cell, 2009, 8 (4): 520- 529. |
| 22 | SHEN B , BROWN K , LONG S J , et al. Development of CRISPR/Cas9 for efficient genome editing in Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2017, 1498, 79- 103. |
| 23 | LONG S J , BROWN K M , DREWRY L L , et al. Calmodulin-like proteins localized to the conoid regulate motility and cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2017, 13 (5): e1006379. |
| 24 | REESE M L , ZEINER G M , SAEIJ J P J , et al. Polymorphic family of injected pseudokinases is paramount in Toxoplasma virulence[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011, 108 (23): 9625- 9630. |
| 25 | STEINFELDT T , KÖNEN-WAISMAN S , TONG L , et al. Phosphorylation of mouse immunity-related GTPase (IRG) resistance proteins is an evasion strategy for virulent Toxoplasma gondii[J]. PLoS Biol, 2010, 8 (12): e1000576. |
| 26 | 陈芸, 刘旗, 张曼玉, 等. 弓形虫ROP5与ROP18的双基因缺失株构建及表型鉴定[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2023, 31 (3): 1- 11. |
| CHEN Y , LIU Q , ZHANG M Y , et al. Construction and phenotype identification of ROP5 and ROP18 double gene deletion strain of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2023, 31 (3): 1- 11. | |
| 27 | RANI V , DEEP G , SINGH R K , et al. Oxidative stress and metabolic disorders: pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies[J]. Life Sci, 2016, 148, 183- 193. |
| 28 | DOMAŃSKI L , PIETRZAK-NOWACKA M , SZMATŁOCH E , et al. [Malonyldialdehyde, uric acid and white cell count as markers of oxidative stress in acute myocardial infarction and acute coronary insufficiency][J]. Pol Merkur Lekarski, 2001, 11 (62): 121- 124. |
| 29 | TSIKAS D . Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: analytical and biological challenges[J]. Anal Biochem, 2017, 524, 13- 30. |
| 30 | YAROVINSKY F , ZHANG D K , ANDERSEN J F , et al. TLR11 activation of dendritic cells by a protozoan profilin-like protein[J]. Science, 2005, 308 (5728): 1626- 1629. |
| 31 | DEBIERRE-GROCKIEGO F , CAMPOS M A , AZZOUZ N , et al. Activation of TLR2 and TLR4 by glycosylphosphatidylinositols derived from Toxoplasma gondii[J]. J Immunol, 2007, 179 (2): 1129- 1137. |
| 32 | SCANGA C A , ALIBERTI J , JANKOVIC D , et al. Cutting edge: MyD88 is required for resistance to Toxoplasma gondii infection and regulates parasite-induced IL-12 production by dendritic cells[J]. J Immunol, 2002, 168 (12): 5997- 6001. |
| 33 | SUZUKI Y , ORELLANA M A , SCHREIBER R D , et al. Interferon-γ: the major mediator of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Science, 1988, 240 (4851): 516- 518. |
| 34 | YAP G S , SHER A . Effector cells of both nonhemopoietic and hemopoietic origin are required for interferon (IFN)-γ- and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-dependent host resistance to the intracellular pathogen, Toxoplasma gondii[J]. J Exp Med, 1999, 189 (7): 1083- 1092. |
| [1] | ZHANG Fan, ZENG Wei, ZHOU Ao. Advances in Gene Editing for Disease Resistance Breeding in Livestock and Poultry [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3047-3056. |
| [2] | ZHANG Yanjun, ZHANG Jianmin, YANG Jian, ZHOU Shuze, WU Weiwei, YU Liang, GONG Daoqing, MIAO Hong. Progress in the Detection of Body Composition in Livestock Based on Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3057-3070. |
| [3] | LI Qingyun, CAO Fengfeng, XING Zhou, LI Zhuoying, TAO Jinzhong. Progress in the Study of the Formation and Lysis of Corpus Luteum in Dairy Cows and Its Role in the Maintenance of Pregnancy [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3088-3095. |
| [4] | XIANG Lingxian, JI Qianyu, SHAN Xinxin, LI Lin. Advances in the Study of Drug Resistance and Pathogenicity of Bacterial Two-component Systems [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3116-3128. |
| [5] | ZHANG Jialiang, HUANG Chang, YANG Yonglin, YANG Hua, BAI Wenlin, MA Yuehui, ZHAO Qianjun. Genetic Structure and Wool Trait Selection Signatures Analysis of Chinese Sheep Populations Based on 50K Liquid SNP Chip [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3164-3176. |
| [6] | LAN Mingxi, QIN Qing, ZHANG Chongyan, LIU Zhichen, ZHANG Jingwen, ZHAO Dan, WU Danni, QIN Tian, WANG Zhixin, LIU Zhihong. Determination and Analysis of Slaughtering Performance and Meat Quality of Different Parts of Ujumqin Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3177-3187. |
| [7] | TANG Yu, ZHANG Ying, YANG Yifeng, XUE Hailong, LIU Lixiang, XU Baozeng. Mechanisms of Glycine Improving Vitrification Cryopreservation Efficiency of Mink Oocytes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3265-3277. |
| [8] | XIONG Pingwen, XU Chuanhui, AI Gaoxiang, JI Huayuan, HU Yan, CHEN Jiang, SONG Qiongli, SONG Wenjing, CHEN Xiaolian, CHEN Xiaolian, ZOU Zhiheng, CHEN Hehong. Effects of Golden Buckwheat Stem and Leaf Meal on Nutrient Apparent Digestibility, Serum Biochemical Indices, Fecal Microflora Composition of Gannan Tibetan Sows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3290-3304. |
| [9] | SUN Shujia, ZHENG Jiaqi, LU Shuwan, LIU Jinsong, YAO Chunlei, YANG Caimei, XU Yinglei, ZHANG Ruiqiang. Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria on Growth Performance, Digestive Function and Nutrient Utilization of Yellow-feathered Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3335-3343. |
| [10] | HE Yindi, SHI Zhengwang, SHI Xintai, CHEN Jie, LIAO Huancheng, ZHANG Fan, LUO Juncong, ZHU Yuqian, XI Tao, LI Shuaipeng, WANG Chuan, TIAN Hong, ZHENG Haixue. Development and Preliminary Application of Colloidal Gold Immunochromatographic Test Strips for Antibodies against Capripoxvirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3368-3377. |
| [11] | LIU Yuze, YU Zhuoya, GONG Zhiguo, REN Peipei, ZHAO Jiamin, MAO Wei, ZHANG Shuangyi,FENG Shuang. The Impact of Lipoprotein on the Secretion of Inflammatory Mediators and the Synthesis of Prostaglandin E2 in Bovine Bone Marrow-derived Macrophages Infected with Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3474-3483. |
| [12] | XU Huihao, LI Qijuan, DENG Hang, DU Xinyue, PENG Yunying, YANG Heng, ZHANG Dezhi, CAO Lijing, GAN Ling, ZHENG Xiaobo, YI Huashan. Clinical Study of Novel Acellular Bioengineering Cornea Eccentric Deep Lamellar Keratoplasty for the Treatment of Feline Corneal Injury [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3528-3539. |
| [13] | LU Le, LUO Xianzu, HUANG Xinyu, ZOU Hui, GU Jianhong, LIU Xuezhong, BIAN Jianchun, LIU Zongping, YUAN Yan. Cadmium Can Induce Oxidative Stress in the Cerebral Cortices by Affecting the Intestinal Flora of Rats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3540-3547. |
| [14] | RUI Xue, ZHANG Yunhang, LI Yang, TAN Chen, CAI Yifei, LIU Yuanyuan, CAO Zongxi, ZHANG Yan, SUN Ruiping, LIU Guangliang. Establishment of a Triple PCR Method for the Detection of Porcine Endogenous Retroviruses and Its Preliminary Application to the Detection of Wuzhishan Pig Tissue Samples [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3548-3554. |
| [15] | ZHAO Shunran, FU Guixin, PANG Zhaoqi, XIA Wei, LI Junjie, TAO Chenyu. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Porcine Granulosa Cells in Follicular Atresia [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2537-2545. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||