





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 3265-3277.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.07.020
• Animal Biotechnology and Reproduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
TANG Yu( ), ZHANG Ying, YANG Yifeng, XUE Hailong, LIU Lixiang, XU Baozeng*(
), ZHANG Ying, YANG Yifeng, XUE Hailong, LIU Lixiang, XU Baozeng*( )
)
Received:2024-10-18
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
XU Baozeng
E-mail:tangyu6182@163.com;xubaozeng@caas.cn
CLC Number:
TANG Yu, ZHANG Ying, YANG Yifeng, XUE Hailong, LIU Lixiang, XU Baozeng. Mechanisms of Glycine Improving Vitrification Cryopreservation Efficiency of Mink Oocytes[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3265-3277.
Table 1
Primers for qRT-PCR"
| 基因 Gene | 参考序列 Reference sequence | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primers sequence | 产物大小/bp Amplicon size |
| GAPDH | XM_044227464 | GGTTGTCTCCTGCGACTTCA; ATTCCTTGGAGGCCATGTGG | 168 |
| BAX | XM_059151377 | CCGAGCTGATCAGGACCATC; ATAGTAGGAGAGGAGGCCGT | 106 |
| CASP3 | XM_044225635 | ATTATTCAGGCCTGCCGAGG; GGCATACAGGAAGTCCGCTT | 114 |
| BCL-2 | XM_044242855 | TTGAGTTCGGTGGGGTCATG; CTGGATCCAGGTGTGCAAGT | 118 |
| DNMT1 | XM_044254246 | CAGAGTGGGAATGGCAGAG; GTCTGCCTGGTAGTTTGCCT | 138 |
Fig. 1
Effects of glycine supplementation on survival, maturation and development of mink oocytes during vitrification, thawing and IVM A. Representative images of oocytes were collected 24 h after IVM. The arrow indicates dead cells, but not all dead cells. Scale: 100 μm. B. Impact of varying glycine concentrations (0, 1, 5, 10 mmol·L-1) on post-thaw oocyte survival rate. C. Statistical charts of the survival rate of oocytes collected in 3 groups. D. Characteristic representative images of the nuclei of oocytes at different stages of development. Scale bar: 20 μm. E. Statistical analysis of 4 major stages of oocyte nuclear development in 3 groups"
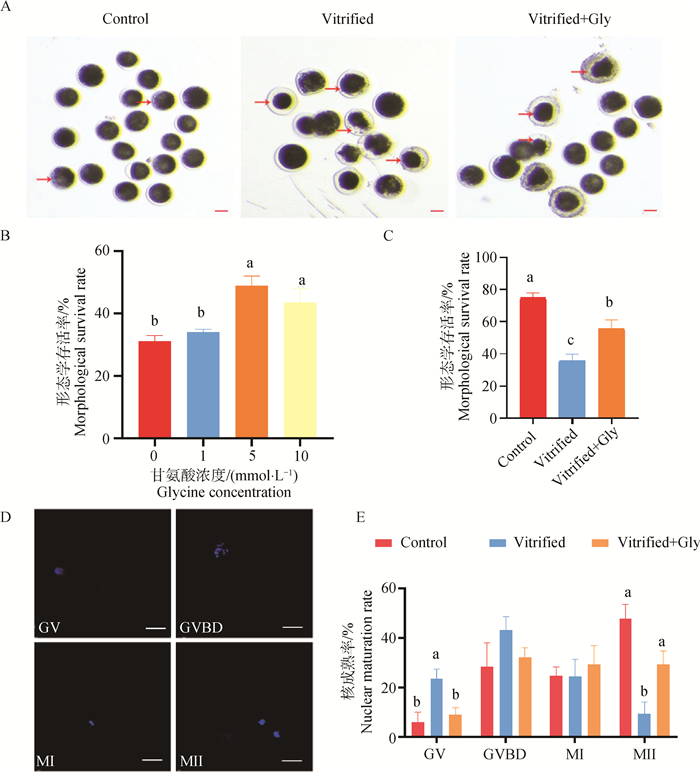
Fig. 2
Effects of glycine supplementation during vitrification, thawing and IVM on mitochondrial distribution and activity of mink oocytes at GV stage A. Oocyte functional mitochondrial immunofluorescence staining (red), DAPI (blue). Merge. Red and blue overlap. Scale bar: 20 μm. B. Percentage of oocytes with normal mitochondrial distribution. C. Oocyte mitochondrial activity in different experimental treatments"
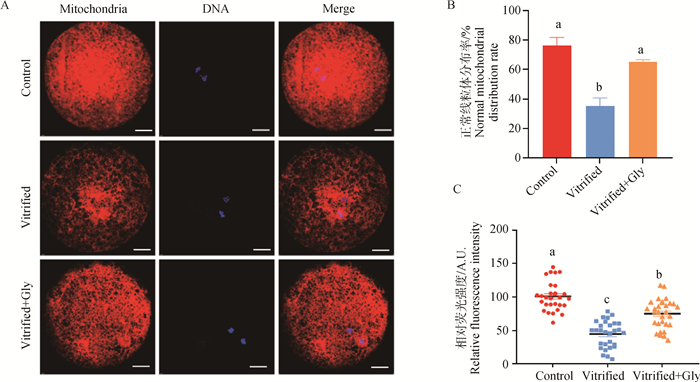

Fig. 3
Effects of glycine supplementation during vitrification, thawing and IVM on ROS levels in mature oocytes at GV stage of mink A. ROS staining representative images of oocytes in the experimental group (green). Scale bar: 100 μm. B. Statistical plots of relative fluorescence intensity of ROS staining of oocytes under different treatments"
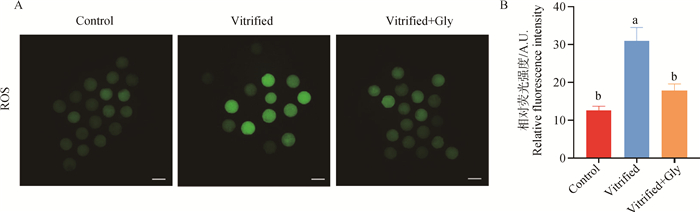
Fig. 4
Effect of glycine supplementation during vitrification, thawing, and IVM on the migration of cortical granules (CGs) in mink oocytes A. Representative images of CGs distribution in oocytes collected after maturation in each experimental group. Green indicate cortical granules (CGs); Blue indicate chromatin; Merge indicate green and blue overlap. Scale bar: 20 μm. B. Percentage of oocytes with normal CGs distribution in each experimental group"
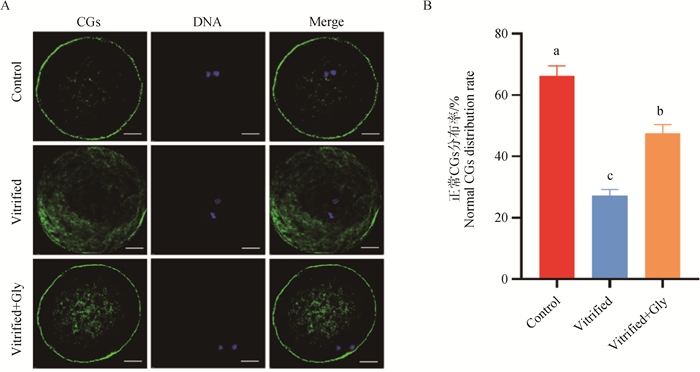
Fig. 5
Effect of glycine supplementation during vitrification, thawing and IVM on oocyte apoptosis of mink A. Representative images of early apoptosis labeled with Annexin-V in each experimental group. Green indicate Annexin-V dyed. Scale: 100 μm. B. Relative fluorescence intensity of Annexin-V staining of oocytes in each experimental group. C. The relative transcription levels of genes involved in oocyte apoptosis in each experimental group, with GAPDH as the house-keeping gene"
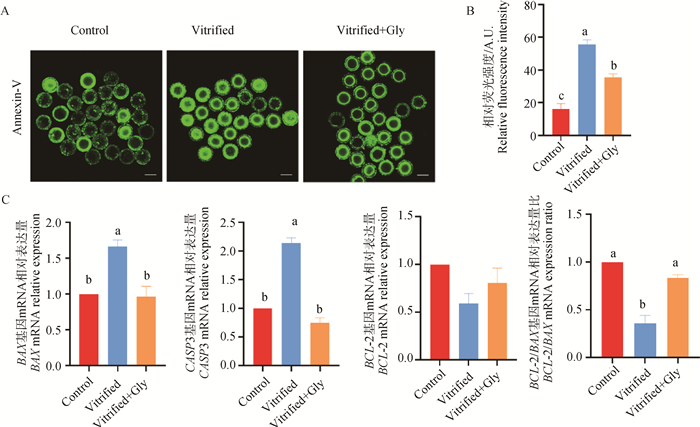
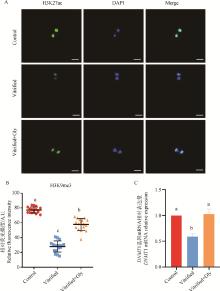
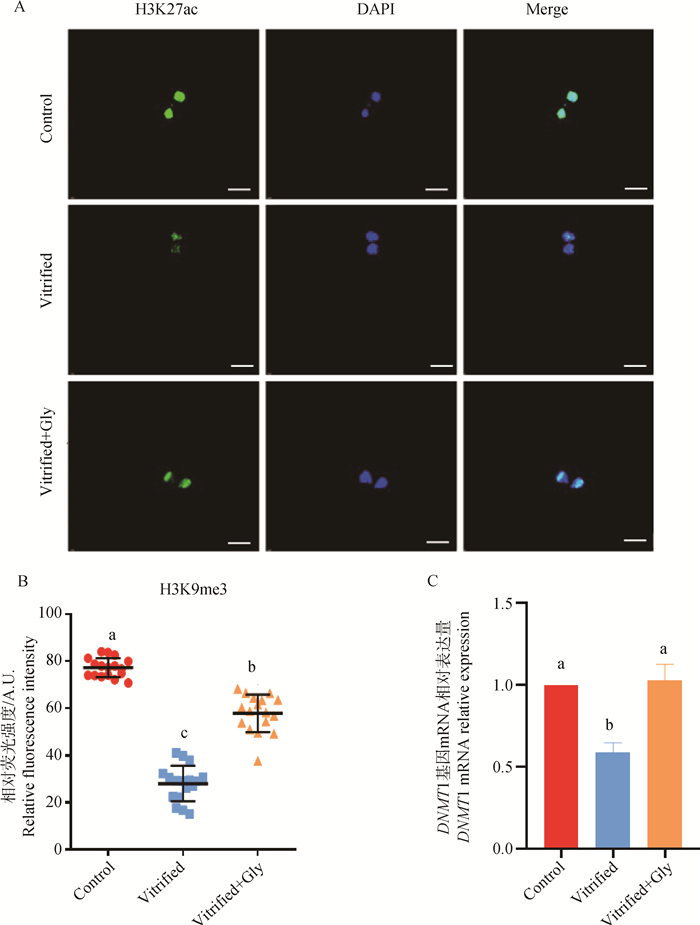
Fig. 6
Effects of glycine supplementation during vitrification, thawing and IVM on epigenetic modification of mink oocytes A. Representative images of the distribution of H3K9me3 in oocytes collected after maturity in each experimental group. Green indicate H3K9me3; Blue indicate chromatin; Merge indicate green and blue overlap. Scale bar: 20 μm. B. The relative fluorescence intensity of H3K9me3 in each experimental group. C. Relative transcription levels of DNA methyltransferase 1(DNMT1) in oocytes of each experimental group, with GAPDH acting as the house-keeping gene"
| 1 | 李虎, 石宏宇, 杨童奥, 等. 水貂育种技术研究进展[J]. 特产研究, 2023, 1- 8. |
| LI H , SHI H Y , YANG T A , et al. Research progress of mink breeding technology[J]. Special Wild Economic Animal and Plant Research, 2023, 1- 8. | |
| 2 | ZHANG T , LI H , LARSEN P F , et al. The genetic diversity of mink (Neovison vison) populations in China[J]. Animals (Basel), 2023, 13 (9): 264- 274. |
| 3 | FENELON J C , MURPHY B D . Culture of mink preimplantation embryos[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2019, 2006, 269- 277. |
| 4 | 韩玉萍, 赵向远, 范冰峰, 等. 基于高通量测序的水貂胚胎滞育期和激活期卵巢转录组分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2021, 48 (11): 4035- 4046. |
| HAN Y P , ZHAO X Y , FAN B F , et al. Transcriptomic analysis of mink ovaries at embryonic diapause and activation stages based on high-throughput sequencing technology[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 48 (11): 4035- 4046. | |
| 5 | DENG D , XIE J , TIAN Y , et al. Effects of meiotic stage-specific oocyte vitrification on mouse oocyte quality and developmental competence[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14, 1200051. |
| 6 | CHANG C C , SHAPIRO D B , NAGY Z P . The effects of vitrification on oocyte quality[J]. Biol Reprod, 2022, 106 (2): 316- 327. |
| 7 | MOGAS T , GARCIA-MARTINEZ T , MARTINEZ-RODERO I . Methodological approaches in vitrification: Enhancing viability of bovine oocytes and in vitro-produced embryos[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2024, 59 (Suppl 3): e14623. |
| 8 | SOMFAI T . Vitrification of immature oocytes in pigs[J]. Anim Sci J, 2024, 95 (1): e13943. |
| 9 | ZHU Y , LIU H , ZHENG L , et al. Vitrification of mammalian oocytes: Recent studies on mitochondrial dysfunction[J]. Biopreserv Biobank, 2024, 22 (5): 428- 440. |
| 10 | CALLE A , RAMIREZ M A . Cryobanking European mink (Mustela lutreola) mesenchymal stem cells and oocytes[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (16): 544- 556. |
| 11 | LU L , XING Y B , XUE Q W , et al. Improving vitrification efficiency of human in vitro matured oocytes by the addition of LEA proteins[J]. Hum Reprod, 2024 (6): 6. |
| 12 | KAMOSHITA M , SUGITA H , KAGEYAMA A , et al. Recent advances of oocyte/embryo vitrification in mammals from rodents and large animals[J]. Anim Sci J, 2024, 95 (1): e13931. |
| 13 | STEEVES C L , HAMMER M A , WALKER G B , et al. The glycine neurotransmitter transporter GLYT1 is an organic osmolyte transporter regulating cell volume in cleavage-stage embryos[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2003, 100 (24): 13982- 13987. |
| 14 | TARTIA A P , RUDRARAJU N , RICHARDS T , et al. Cell volume regulation is initiated in mouse oocytes after ovulation[J]. Development, 2009, 136 (13): 2247- 2254. |
| 15 | STEEVES C L , BALTZ J M . Regulation of intracellular glycine as an organic osmolyte in early preimplantation mouse embryos[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2005, 204 (1): 273- 279. |
| 16 | CAO X Y , ROSE J , WANG S Y , et al. Glycine increases preimplantation development of mouse oocytes following vitrification at the germinal vesicle stage[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6, 37262. |
| 17 | TANG Y , ZHANG Y , LIU L , et al. Glycine and melatonin improve preimplantation development of porcine oocytes vitrified at the germinal vesicle stage[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10, 856486. |
| 18 | SOMFAI T , YOSHIOKA K , TANIHARA F , et al. Generation of live piglets from cryopreserved oocytes for the first time using a defined system for in vitro embryo production[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9 (5): e97731. |
| 19 | XU J , SUN L , WU C , et al. Involvement of PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in mitochondrial functional disruption under oxidative stress in vitrified porcine oocytes[J]. Theriogenology, 2021, 174, 160- 168. |
| 20 | MOMOZAWA K , MATSUZAWA A , TOKUNAGA Y , et al. Efficient vitrification of mouse embryos using the Kitasato Vitrification System as a novel vitrification device[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2017, 15 (1): 29. |
| 21 | GENDELMAN M , ROTH Z . Incorporation of coenzyme Q10 into bovine oocytes improves mitochondrial features and alleviates the effects of summer thermal stress on developmental competence[J]. Biol Reprod, 2012, 87 (5): 118. |
| 22 | RUIZ-CONCA M , GARDELA J , MOGAS T , et al. Apoptosis and glucocorticoid-related genes mRNA expression is modulated by coenzyme Q10 supplementation during in vitro maturation and vitrification of bovine oocytes and cumulus cells[J]. Theriogenology, 2022, 192, 62- 72. |
| 23 | RAJAEI F , ABEDPOUR N , SALEHNIA M , et al. The effect of vitrification on mouse oocyte apoptosis by cryotop method[J]. Iran Biomed J, 2013, 17 (4): 200- 205. |
| 24 | SPINACI M , VALLORANI C , BUCCI D , et al. Vitrification of pig oocytes induces changes in histone H4 acetylation and histone H3 lysine 9 methylation (H3K9)[J]. Vet Res Commun, 2012, 36 (3): 165- 171. |
| 25 | FRAGOULI E , WELLS D . Mitochondrial DNA assessment to determine oocyte and embryo viability[J]. Semin Reprod Med, 2015, 33 (6): 401- 409. |
| 26 | BARBERET J , BARRY F , CHOUX C . What impact does oocyte vitrification have on epigenetics and gene expression?[J]. Clin Epigenetics, 2020, 12 (1): 121. |
| 27 | ARNANZ A , DE MUNCK N , BAYRAM A , et al. Blastocyst mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is not affected by oocyte vitrification: a sibling oocyte study[J]. J Assist Reprod Genet, 2020, 37 (6): 1387- 1397. |
| 28 | CHATTERJEE A , SAHA D , NIEMANN H , et al. Effects of cryopreservation on the epigenetic profile of cells[J]. Cryobiology, 2017, 74, 1- 7. |
| 29 | SCIORIO R , PLUCHINO N , FULLER B J . Review of human oocyte cryopreservation in ART programs: Current challenges and opportunities[J]. Cryobiology, 2023, 113, 104590. |
| 30 | YODRUG T , PARNPAI R , HIRAO Y , et al. Effect of vitrification at different meiotic stages on epigenetic characteristics of bovine oocytes and subsequently developing embryos[J]. Anim Sci J, 2021, 92 (1): e13596. |
| 31 | LIANG Y , FU X W , LI J J , et al. DNA methylation pattern in mouse oocytes and their in vitro fertilized early embryos: effect of oocyte vitrification[J]. Zygote, 2014, 22 (2): 138- 145. |
| 32 | SOMFAI T , HIEP N T , KIKUCHI K , et al. The effect of vitrification at the immature stage on DNA methylation in porcine oocytes and its relevance to subsequent embryo development[J]. Reprod Fertil Dev, 2021, 23 (4): 391- 394. |
| 33 | BALTZ J M , TARTIA A P . Cell volume regulation in oocytes and early embryos: connecting physiology to successful culture media[J]. Hum Reprod Update, 2010, 16 (2): 166- 176. |
| 34 | JAHN M , RAUH O , FAUTH T , et al. Cell volume regulation in the epidermis[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2021, 55 (S1): 57- 70. |
| 35 | WANG M , YANG Y , HAN L , et al. Cell mechanical microenvironment for cell volume regulation[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235 (5): 4070- 4081. |
| 36 | ISHIHARA S , ICHIJO H , WATANABE K . A novel lens for cell volume regulation: Liquid-liquid phase separation[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2021, 55 (S1): 135- 160. |
| 37 | ORTMAN C S , BALTZ J M . The cell volume-regulatory glycine transporter GLYT1 is activated following metallopeptidase-mediated detachment of the oocyte from the zona pellucida[J]. Mol Reprod Dev, 2023, 90 (12): 824- 834. |
| 38 | TSCHERNER A K , MACAULAY A D , ORTMAN C S , et al. Initiation of cell volume regulation and unique cell volume regulatory mechanisms in mammalian oocytes and embryos[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236 (10): 7117- 7133. |
| 39 | TSCHERNER A K , MCCLATCHIE T , KABOBA G , et al. Oocyte-specific deletion of Slc6a9 encoding the GLYT1 glycine transporter eliminates glycine transport in mouse preimplantation embryos and their ability to counter hypertonic stress[J]. Cells, 2023, 12 (20): 503- 512. |
| 40 | YAQOUT K A , BARD M R , EL-WISHY A , et al. Influences of glycine supplementation during vitrification on the developmental potential of vitrified/warmed immature dromedary camel oocytes[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2023, 58 (5): 614- 621. |
| 41 | DAWSON K M , COLLINS J L , BALTZ J M . Osmolarity-dependent glycine accumulation indicates a role for glycine as an organic osmolyte in early preimplantation mouse embryos[J]. Biol Reprod, 1998, 59 (2): 225- 232. |
| [1] | SUN Yawen, CHEN Siying, LI Kang, LENG Xuan, WANG Dong, PANG Yunwei. Strategies for Alleviating Cryoinjury of Porcine Vitrified-Oocytes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 36-44. |
| [2] | YANG Baigao, XU Jiehuan, ZHANG Liang, LONG Xi, DAI Jianjun, ZHAO Xueming, PAN Hongmei. Exploring the Effect of Vitrification on Genome Methylation Level of Porcine Parthenogenetic Activation Blastocysts by scWGBS [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 222-231. |
| [3] | Baigao YANG, Xi LONG, Liang ZHANG, Jiehuan XU, Jianjun DAI, Xueming ZHAO, Hongmei PAN. Exploring the Effect of Vitrification on Gene Expression in Porcine Parthenogenetic Blastocysts by Smart-seq2 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3936-3946. |
| [4] | LI Wanjun, XU Jiehuan, HE Mengxian, KONG Yuting, ZHANG Defu, DAI Jianjun. Cytochalasin B Alleviates the Migration Disorder of Cortical Particle Caused by Vitrification in Porcine Oocytes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1999-2010. |
| [5] | Jianhua DONG, Xiaoyi FENG, Baigao YANG, Chongyang LI, Hongmei PAN, Lihua LÜ, Xueming ZHAO. Advances in Cryopreservation of Porcine Embryo [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 4796-4807. |
| [6] | LU Jian, ZHANG Xin, JIANG Dongcai, MA Meng, WANG Qiang, WANG Xingguo, LI Yongfeng, GUO Jun, DOU Taocun, HU Yuping, LI Shangmin, SHAO Dan, QU Liang. Effects of Glycine Manganese on Laying Performance and Gut Microbiota in Aged Laying Hens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 218-231. |
| [7] | XU Xi, YANG Baigao, ZHANG Hang, FENG Xiaoyi, HAO Haisheng, DU Weihua, ZHU Huabin, ZHANG Peipei, ZHAO Xueming. Effects of NMN on Lipid Droplet Content and Cryopreservation Effect of Bovine Oocytes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3348-3357. |
| [8] | YANG Sha, YANG Yuze, XU Xi, HAO Haisheng, DU Weihua, PANG Yunwei, ZHAO Shanjiang, ZOU Huiying, ZHU Huabin, ZHAO Xueming. The Regulation of Methylation Level of IGF2R Gene in IVF Blastocysts Derived from Vitrified Bovine Oocytes by dCas9-SunTag-DNMT3A Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(6): 2015-2023. |
| [9] | ZHANG Peipei, WANG Jingjing, HAO Haisheng, DU Weihua, PANG Yunwei, QUAN Guobo, ZHAO Shanjiang, ZOU Huiying, HAO Tong, ZHU Huabin, ZHAO Xueming. Study on Whole Genome Methylation Pattern in Vitrified Bovine GV Oocytes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(5): 1030-1039. |
| [10] | YANG Yuanxiao, ZI Xiangdong. Effect of Vitrification on Developmental Competence of Immature Oocytes and COC Transcriptome of Yaks [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(2): 288-298. |
| [11] | ZHAO Yahan, HAO Haisheng, DU Weihua, PANG Yunwei, YAN Changliang, LIU Yan, ZHAO Shanjiang, ZHAO Xueming, ZHU Huabin. Study on Whole Genome Methylation Pattern of in vitro Fertilized Blastocysts from Fresh and Vitrified Bovine Oocytes [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2019, 50(6): 1179-1188. |
| [12] | PU Si-ying, ZHENG Jie, YANG Yuan-xiao, WANG Qin, YANG Rao-fen, ZI Xiang-dong. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis between Fresh and Vitrified-thawed Blastocysts of the Yak (Bos grunniens) [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(4): 709-717. |
| [13] | CHEN Ya-ning, WU Cai-feng, DAI Jian-jun, ZHANG Shu-shan, NIU Ying-fang, ZHANG De-fu. Effect of Vitrification on Cell Apoptotic Levels of Porcine Parthenogenetic Blastocysts [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2017, 48(2): 243-251. |
| [14] | ZHENG Jie, PU Si-ying, YANG Yuan-xiao, WANG Qin, YANG Rao-fen, ZI Xiang-dong. Exploring Mechanism for Vitrification Damage of the Cross-bred Blastocysts of the Yak via High-throughput Sequencing [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2017, 48(10): 1871-1881. |
| [15] | WU Cai-feng,DAI Jian-jun,ZHANG Shu-shan,LI Wei-jie,XU Li,ZHANG De-fu. Effects of Three Vitrification Methods on the Microfilament Distribution and Lipid Droplets Changes of Porcine MII-stage Oocytes [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2014, 45(7): 1097-1103. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||