





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (10): 5137-5147.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.10.033
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
MENG Chuang1,2,3( ), JIN Xuanchen1,3, PENG Tongtong1,3, ZHAI Xianyue1,2,3, KANG Xilong1,2,3, JIAO Xinan1,2,3, PAN Zhiming1,2,3,*(
), JIN Xuanchen1,3, PENG Tongtong1,3, ZHAI Xianyue1,2,3, KANG Xilong1,2,3, JIAO Xinan1,2,3, PAN Zhiming1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-03
Online:2025-10-23
Published:2025-11-01
Contact:
PAN Zhiming
E-mail:mengchuang@yzu.edu.cn;zmpan@yzu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
MENG Chuang, JIN Xuanchen, PENG Tongtong, ZHAI Xianyue, KANG Xilong, JIAO Xinan, PAN Zhiming. Investigation of Salmonella Contamination in Pork Production Process and Reduction Control of Key Points[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 5137-5147.
Table 1
Salmonella isolation rate of samples from different stages of the pork production chain"
| 采样环节 Sampling stages | 样品数量Number of samples (阳性率/% Positive rate) | ||||||||||
| Visit 1 | Visit 2 | Visit 3 | Visit 4 | Visit 5 | Visit 6 | Visit 7 | Visit 8 | Visit 9 | Visit 10 | 合计Total | |
| 养殖场Farm | |||||||||||
| 粪便Feces | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 (30.0%) | 20 (30.0%) | 20 (35.0%) | 20 (20.0%) | 80 (28.8%) |
| 屠宰场 Slaughterhouse | |||||||||||
| 待宰圈 Holding pens | 10 (50.0) | 10 (70.0) | 10 (60.0) | 10 (30.0) | 10 (40.0) | 10 (60.0) | 10 (40.0) | 10 (50.0) | 10 (40.0) | 10 (30.0) | 100 (47.0) |
| 劈半后Splitting | 10 (30.0) | 10 (60.0) | 10 (30.0) | 10 (70.0) | 10 (40.0) | 10 (50.0) | 10 (70.0) | 10 (50.0) | 10 (50.0) | 10 (60.0) | 100 (51.0) |
| 修饰后Dressing | 10 (40.0) | 10 (40.0) | 10 (50.0) | 10 (30.0) | 10 (60.0) | 10 (30.0) | 10 (30.0) | 10 (20.0) | 10 (10.0) | 10 (20.0) | 100 (33.0) |
| 冷却后Chilling | 10 (30.0) | 10 (0.0) | 10 (20.0) | 10 (30.0) | 10 (30.0) | 10 (30.0) | 10 (20.0) | 10 (30.0) | 10 (30.0) | 10 (10.0) | 100 (23.0) |
| 环境设备 Equipments | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 (40.0) | 15 (26.7) | 10 (0) | 10 (0) | 10 (10.0) | 10 (20.0) | 70 (18.6) |
| 超市Supermarkets | |||||||||||
| 肉样Pork | 40 (65.0) | 40 (80.0) | 40 (52.5) | 40 (60.0) | 40 (50.0) | 40 (57.5) | 40 (62.5) | 40 (55.0) | 40 (45.0) | 40 (40.0) | 400 (56.8) |
| 合计Total | 80 (51.3) | 80 (61.3) | 80 (46.3) | 80 (50.0) | 95 (45.3) | 95 (46.3) | 110 (40.9) | 110 (39.1) | 110 (35.5) | 110 (34.5) | 950 (43.9) |
Table 2
Serotypes distribution of Salmonella isolations in different sampling times"
| 序号 Number | 血清型 Serotypes | 菌株数Number of strains | 合计 Total | 阳性率/% Rate | |||||||||
| Visit 1 | Visit 2 | Visit 3 | Visit 4 | Visit 5 | Visit 6 | Visit 7 | Visit 8 | Visit 9 | Visit 10 | ||||
| 1 | 德尔卑沙门菌S. Derby | 18 | 17 | 15 | 22 | 16 | 19 | 24 | 14 | 13 | 7 | 165 | 39.6 |
| 2 | 鼠伤寒沙门菌S. Typhimurium | 12 | 22 | 18 | 15 | 11 | 13 | 9 | 20 | 18 | 21 | 159 | 38.1 |
| 3 | 伦敦沙门菌S. London | 4 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 13 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 43 | 10.3 | |
| 4 | 罗森沙门菌S. Rissen | 6 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 35 | 8.4 | ||
| 5 | 里定沙门菌S. Reading | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 1.4 | |||||||
| 6 | 病牛沙门菌S. Bovismorficans | 3 | 3 | 0.7 | |||||||||
| 7 | 汤普逊沙门菌S. Thompson | 3 | 3 | 0.7 | |||||||||
| 8 | 肠炎沙门菌S. Enteritidis | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 | ||||||||
| 9 | 阿贡纳沙门菌S. Agona | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | |||||||||
| 合计Total | 41 | 49 | 37 | 40 | 43 | 44 | 47 | 43 | 39 | 34 | 417 | 100.0 | |
Table 3
Serotypes distribution of Salmonella isolations in different sampling stages"
| 序号 Number | 血清型 Serotypes | 菌株数量Number of strains | 合计Total | ||
| 养殖场 Farm | 屠宰场 Slaughterhouse | 市场 Market | |||
| 1 | 德尔卑沙门菌S. Derby | 4 | 54 | 107 | 165 |
| 2 | 鼠伤寒沙门菌S. Typhimurium | 2 | 53 | 104 | 159 |
| 3 | 伦敦沙门菌S. London | 2 | 31 | 10 | 43 |
| 4 | 罗森沙门菌S. Rissen | 2 | 27 | 6 | 35 |
| 5 | 里定沙门菌S. Reading | 5 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| 6 | 病牛沙门菌S. Bovismorficans | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 7 | 汤普逊沙门菌S. Thompson | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 8 | 肠炎沙门菌S. Enteritidis | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 9 | 阿贡纳沙门菌S. Agona | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 合计Total | 23 | 167 | 227 | 417 | |
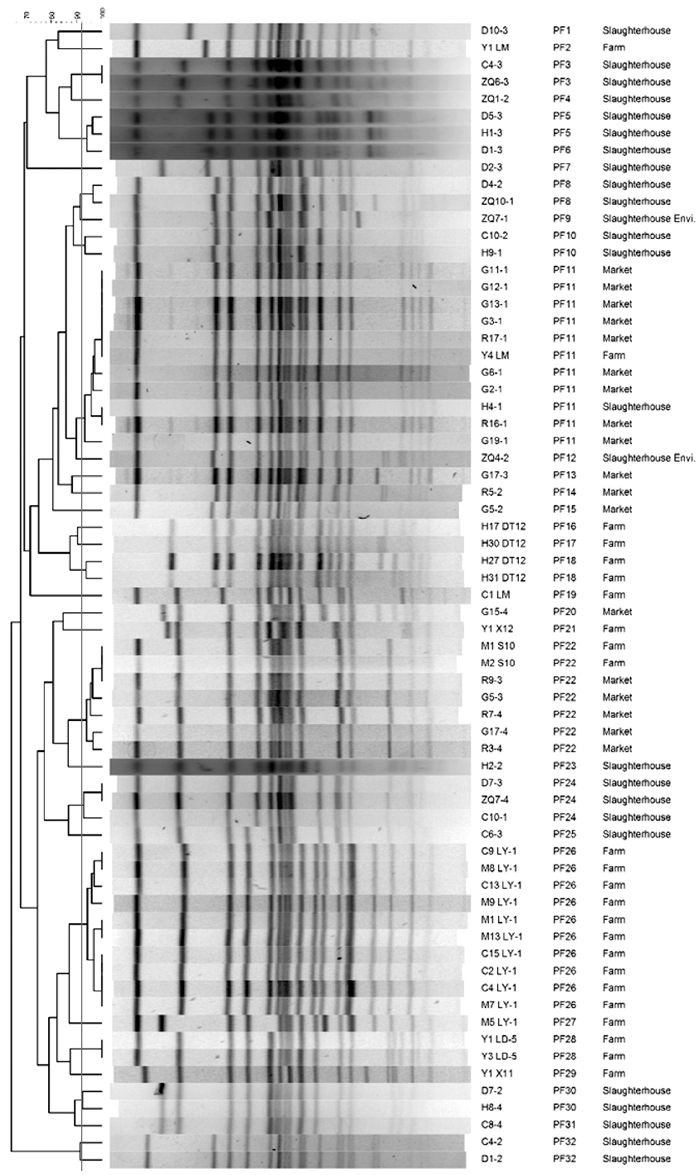
Fig. 1
PFGE typing of 67 Salmonella Derby strains A red line is drawn at the 85% similarity threshold, strains above this line were considered homologous and identified of 32 PFGE pulsotypes (PF1-PF32). LM, DT12, DH12, S10, LY1, LD5, X11, and X12 represent different farms and sampling batches, with the preceding letters and numbers indicating the sample numbers from different barns. C, D, H, and ZQ denotes samples taken after slaughter processing, cooling, splitting, and holding pen in slaughter house, as well as C, M, Y, and H denotes samples from farrowing house, sow house, finishing house, and gilt house in farm, respectively, with the following numbers indicating the sample serial numbers and the numbers after the hyphen representing the sampling batch. R and G denotes market pork and market bone-in pork, respectively, with the following numbers indicating the sample serial numbers and the numbers after the hyphen representing the sampling batch"
| 1 |
BESSER J M . Salmonella epidemiology: A whirlwind of change[J]. Food Microbiol, 2018, 71, 55- 59.
doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2017.08.018 |
| 2 |
SHI C L , SINGH P , RANIERI M , et al. Molecular methods for serovar determination of Salmonella[J]. Crit Rev Microbiol, 2015, 41 (3): 309- 325.
doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2013.837862 |
| 3 |
KNODLER L A , ELFENBEIN J R . Salmonella enterica[J]. Trends Microbiol, 2019, 27 (11): 964- 965.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2019.05.002 |
| 4 |
PRADHAN D , DEVI N V . Stress-induced adaptations in Salmonella : A ground for shaping its pathogenesis[J]. Microbiol Res, 2019, 229, 126311.
doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2019.126311 |
| 5 |
KURTZ J R , GOGGINS J A , MCLACHLAN J B . Salmonella infection: Interplay between the bacteria and host immune system[J]. Immunol Lett, 2017, 190, 42- 50.
doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.07.006 |
| 6 | 罗郑, 彭忠, 杨迪, 等. 2018年湖北省猪源沙门菌的分离鉴定及耐药性分析[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2020, 40 (6): 1147- 1152. |
| LUO Z , PENG Z , YANG D , et al. Isolation and antimicrobial resistance of porcine Salmonella isolates from Hubei Province in 2018[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2020, 40 (6): 1147- 1152. | |
| 7 |
BONARDI S . Salmonella in the pork production chain and its impact on human health in the European Union[J]. Epidemiol Infect, 2017, 145 (8): 1513- 1526.
doi: 10.1017/S095026881700036X |
| 8 |
BUTAYE P , HALLIDAY-SIMMONDS I , VAN SAUERS A . Salmonella in pig farms and on pig meat in Suriname[J]. Antibiotics (Basel), 2021, 10 (12): 1495.
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10121495 |
| 9 |
PIRES S M , VIGRE H , MAKELA P , et al. Using outbreak data for source attribution of human salmonellosis and campylobacteriosis in Europe[J]. Foodborne Pathog Dis, 2010, 7 (11): 1351- 1361.
doi: 10.1089/fpd.2010.0564 |
| 10 |
SHER A A , MUSTAFA B E , GRADY S C , et al. Outbreaks of foodborne Salmonella enteritidis in the United States between 1990 and 2015:An analysis of epidemiological and spatial-temporal trends[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2021, 105, 54- 61.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.022 |
| 11 |
SNYDER T R , BOKTOR S W , M'IKANATHA N M . Salmonellosis outbreaks by food vehicle, serotype, season, and geographical location, United States, 1998 to 2015[J]. J Food Prot, 2019, 82 (7): 1191- 1199.
doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-18-494 |
| 12 | FERRARI R G , ROSARIO D K A , CUNHA-NETO A , et al. Worldwide epidemiology of Salmonella serovars in animal-based foods: a Meta-analysis[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2019, 85 (14): e00591- 19. |
| 13 |
SMID J H , VAN HOEK A H , AARTS H J , et al. Quantifying the sources of Salmonella on dressed carcasses of pigs based on serovar distribution[J]. Meat Sci, 2014, 96 (4): 1425- 1431.
doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2013.12.002 |
| 14 |
PESCIAROLI M , CUCCO L , DE LUCA S , et al. Association between pigs with high caecal Salmonella loads and carcass contamination[J]. Int J Food Microbiol, 2017, 242, 82- 86.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.11.021 |
| 15 |
ARGUELLO H , ALVAREZ-ORDOÑEZ A , CARVAJAL A , et al. Role of slaughtering in Salmonella spreading and control in pork production[J]. J Food Prot, 2013, 76 (5): 899- 911.
doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-12-404 |
| 16 |
ZHOU Z H , JIN X C , ZHENG H J , et al. The prevalence and load of Salmonella, and key risk points of Salmonella contamination in a swine slaughterhouse in Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Food Control, 2018, 87, 153- 160.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.12.026 |
| 17 |
ISSENHUTH-JEANJEAN S , ROGGENTIN P , MIKOLEIT M , et al. Supplement 2008-2010 (No. 48) to the White-Kauffmann-Le Minor scheme[J]. Res Microbiol, 2014, 165 (7): 526- 530.
doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2014.07.004 |
| 18 |
ZHOU Z H , LI J W , ZHENG H J , et al. Diversity of Salmonella isolates and their distribution in a pig slaughterhouse in Huaian, China[J]. Food Control, 2017, 78, 238- 246.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.02.064 |
| 19 |
TIAN Y Q , GU D , WANG F , et al. Prevalence and characteristics of Salmonella spp. from a pig farm in Shanghai, China[J]. Foodborne Pathog Dis, 2021, 18 (7): 477- 488.
doi: 10.1089/fpd.2021.0018 |
| 20 |
CHIOU C S , TORPDAHL M , LIAO Y S , et al. Usefulness of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profiles for the determination of Salmonella serovars[J]. Int J Food Microbiol, 2015, 214, 1- 3.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.07.016 |
| 21 |
FERRARI R G , PANZENHAGEN P H N , CONTE-JUNIOR C A . Phenotypic and genotypic eligible methods for Salmonella Typhimurium source tracking[J]. Front Microbiol, 2017, 8, 2587.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02587 |
| 22 |
高远, 王兰茜, 张丽娜, 等. 广州市农贸市场猪肉源伦敦沙门菌的流行情况及耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2021, 52 (2): 488- 497.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.02.021 |
|
GAO Y , WANG L Q , ZHANG L N , et al. Characterization of prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica serovar London from markets in Guangzhou[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52 (2): 488- 497.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.02.021 |
|
| 23 | 蒋增海, 姚璐璐, 张超君, 等. 河南省猪产业链中耐头孢菌素沙门菌对β-内酰胺类和喹诺酮类药物的耐药机制分析[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2023, 43 (11): 2274- 2280. |
| JIANG Z H , YAO L L , ZHANG C J , et al. Analysis of mechanisms of resistance to β-lactams and quinolones for cephalosporin-resistant Salmonella isolates from pig-borne food chain of Henan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2023, 43 (11): 2274- 2280. | |
| 24 |
XU Z , CHEN X Y , TAN W , et al. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella and Staphylococcus aureus in fattening pigs in Hubei Province, China[J]. Microb Drug Resist, 2021, 27 (11): 1594- 1602.
doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0585 |
| 25 |
BJORK K E , FIELDS V , GARBER L P , et al. Factors associated with Salmonella prevalence in U.S. swine grower-finisher operations, 2012[J]. Foodborne Pathog Dis, 2018, 15 (8): 489- 497.
doi: 10.1089/fpd.2017.2364 |
| 26 | HOMANN C , ECKEY I , CHUPPAVA B , et al. Rye and rye bran as components of diets in piglet production-effects on Salmonella prevalence[J]. Animals (Basel), 2023, 13 (14): 2262. |
| 27 |
ZENG H , RASSCHAERT G , DE ZUTTER L , et al. Identification of the source for Salmonella contamination of carcasses in a large pig slaughterhouse[J]. Pathogens, 2021, 10 (1): 77.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens10010077 |
| 28 |
VAN HOEK A H , DE JONGE R , VAN OVERBEEK W M , et al. A quantitative approach towards a better understanding of the dynamics of Salmonella spp. in a pork slaughter-line[J]. Int J Food Microbiol, 2012, 153 (1-2): 45- 52.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.10.013 |
| 29 |
SHEN W , CHEN H , GENG J , et al. Prevalence, serovar distribution, and antibiotic resistance of Salmonella spp.isolated from pork in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int J Food Microbiol, 2022, 361, 109473.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109473 |
| 30 |
KUUS K , KRAMARENKO T , SÕGEL J , et al. Prevalence and serotype diversity of Salmonella enterica in the Estonian meat production chain in 2016-2020[J]. Pathogens, 2021, 10 (12): 1622.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens10121622 |
| 31 |
BROADWAY P R , BROOKS J C , MOLLENKOPF D F , et al. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella serovars isolated from U.S. retail ground pork[J]. Foodborne Pathog Dis, 2021, 18 (3): 219- 227.
doi: 10.1089/fpd.2020.2853 |
| 32 |
SOLIANI L , RUGNA G , PROSPERI A , et al. Salmonella infection in pigs: Disease, prevalence, and a link between swine and human health[J]. Pathogens, 2023, 12 (10): 1267.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens12101267 |
| 33 |
HARRISON O L , LI K , GEBHARDT J T , et al. Investigation of the environmental presence of Salmonella spp. in finishing pigs at commercial swine farms in Kansas (USA)[J]. Lett Appl Microbiol, 2023, 76 (6): ovad065.
doi: 10.1093/lambio/ovad065 |
| 34 | PLUMB I D , BROWN A C , STOKES E K , et al. Increased multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica I serotype 4, [5], 12: i: - infections associated with pork, United States, 2009-2018[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2023, 29 (2): 314- 322. |
| 35 |
WANG Z , GU D , HONG Y , et al. Microevolution of Salmonella 4,[J]. Cell Rep, 2023, 42 (10): 113227.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113227 |
| 36 |
TRAGLIA G M , BETANCOR L , YIM L , et al. Genotypic and phenotypic analysis of Salmonella enterica serovar Derby, looking for clues explaining the impairment of egg isolates to cause human disease[J]. Front Microbiol, 2024, 15, 1357881.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1357881 |
| 37 | European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) , European Centre For Disease Prevention And Control (ECDC) . The European Union one health 2022 zoonoses report[J]. EFSA J, 2023, 21 (12): e8442. |
| 38 |
BONARDI S , BOLZONI L , BRINDANI F , et al. Salmonella detection and counting on pig carcasses and cutting lines in Italian slaughterhouses[J]. Foodborne Pathog Dis, 2018, 15 (6): 339- 345.
doi: 10.1089/fpd.2017.2375 |
| 39 |
NTAKIYISUMBA E , LEE S , WON G . Identification of risk profiles for Salmonella prevalence in pig supply chains in South Korea using meta-analysis and a quantitative microbial risk assessment model[J]. Food Res Inter, 2023, 170, 112999.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112999 |
| [1] | MA Caiping, ZHU Yao, LIU Hongdao, ZHOU Guangbin, XU Qiu, LIN Longhua, CHAI Jiyun, HOU Jie, SUN Hongfei, DU Susu, FAN Cuilong, XIA Lining, ZHANG Wanjiang. Typing and Antimicrobial Resistance Analysis of Thirty-four Pasteurella multocida Strains from Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 4074-4085. |
| [2] | ZHAO Qiuyun, SHEN Huanjun, SONG Houhui, JIANG Hongxia, XU Chenggang. Isolation and Characterization of Salmonella Phage P1-CTX Carrying blaCTX-M-27 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3519-3527. |
| [3] | GE Lei, QIU Rulong, FAN Zhiyu, HU Bo, WEI Houjun, CHEN Mengmeng, SONG Yanhua, LI Yiming, XU Weizhong, WANG Fang. Construction and Biological Characterization of ompW Gene Deletion and Complemented Strain of Salmonella Typhimurium [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1865-1875. |
| [4] | Wei LIU, Jiayi MA, Haoyu GENG, Tian XIE, Sunan MIAO, Zongjie LIAO, Shizhong GENG. Isolation, Identification and Characterization of a Broad Spectrum Salmonella Phage [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4061-4068. |
| [5] | WANG Dong, LIU Kexin, HE Yanjun, DENG Shouxiang, LIU Yun, MA Weiming. Effects of Dietary Sodium Humate Supplementation on Liver Tissue Inflammation and Antioxidant Capacity of Salmonella Typhimurium-Infected Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 629-639. |
| [6] | LI Zhaolong, KONG Xiangrui, LIN Fengqiang, WANG Xiuping, ZHAO Ran, PENG Xiaoli, CHEN Changsong. Preliminary Study of the Mechanism of Inhibition of Salmonella Typhimurium by Ec-12 Supernatant [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 739-750. |
| [7] | Menglei CAI, Dongxu ZHAO, Zhenggang ZHANG, Donghai LIU, Tingting JIANG, Shixuan SU, Xuemin YAN, Xiaoyang XUE, Guolin CUI. The Effect of GreA Protein on the Biological Characteristics and Pathogenicity of Salmonella Enteritidis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5173-5182. |
| [8] | Nana PENG, Huimin NING, Yuhao CHEN, Xinying LI, Fuqiang ZHU, Guobin YU, Wei DONG. Competitive Blocking Effect of Salmonella Enteritis Fimbriae Recombinant Protein on Its Cell Adhesion [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5183-5190. |
| [9] | ZHANG Ping, ZHUANG Linlin, ZHANG Di, DONG Yongyi, SHENG Zhongwei, WANG Chengming, XU Bu, DOU Xinhong, GONG Jiansen. Research Progress on Molecular Detection Methods of Salmonella [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3217-3229. |
| [10] | ZHANG Qianwen, LIU Yumei, SHI Lihui, LIANG Wenjun, LI Mengyun, WANG Yuqin, ZHANG Ziqiang. Pathological Observation and Drug Sensitivity Analysis of Salmonella Infection in Female Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3510-3518. |
| [11] | CHEN Songbiao, SHANG Ke, DU Fuxi, YU Zuhua, LI Jing, JIA Yanyan, LIAO Chengshui, ZHANG Chunjie, DING Ke, CHENG Xiangchao. Research Process of Assembly, Structural Features, and Secretion Regulatory Networks of Type VI Secretion System in Salmonella [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2252-2263. |
| [12] | SUN Yufan, YU Panyuan, CHEN Hongyu, TAN Yiqing, CHEN Xiabing, ZHANG Tengfei, GAO Ting, ZHOU Rui, LI Lu. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Potassium Diformate in the Prevention of Salmonella Infection and the Effect on Intestinal Flora [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 2101-2113. |
| [13] | QIN Lei, WU Huimin, XU Qiqi, CHEN Wanzhao, WANG Dong, LI Hongbo, XIA Panpan, LIU Zepeng, XIA Lining. Effect of Exogenous Drug-Resistant Salmonella Typhimurium on Intestinal Flora in Healthy Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 2158-2169. |
| [14] | TIAN Yanhong, YU Jiangxu, JIAO Yuzhou, GAO Dongyang, CAI Xuwang. Research Progress on Structural Modification and Its Effects of Salmonella Lipopolysaccharides [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(4): 1392-1402. |
| [15] | YAO Min, SHI Bomei, HUANG Tinghua. A Preliminary Research of the Regulation of MAPK-CDK6-RB Pathway by Salmonella SptP in Macrophages [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 1187-1198. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||