





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (9): 3957-3967.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.09.020
• Animal Biotechnology and Reproduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yiming GONG( ), Yixuan JIA, Jiajun LI, Xiangyu WANG, Xiaoyun HE, Mingxing CHU*(
), Yixuan JIA, Jiajun LI, Xiangyu WANG, Xiaoyun HE, Mingxing CHU*( ), Ran DI*(
), Ran DI*( )
)
Received:2024-03-06
Online:2024-09-23
Published:2024-09-27
Contact:
Mingxing CHU, Ran DI
E-mail:82101215374@caas.cn;mxchu@263.net;dirangirl@163.com
CLC Number:
Yiming GONG, Yixuan JIA, Jiajun LI, Xiangyu WANG, Xiaoyun HE, Mingxing CHU, Ran DI. BMP/SMAD Pathway Activity and Protein Expression Profiles in Ovarian Follicles with Different Diameters in Diverse FecB Genotyped Ewes[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3957-3967.
Table 1
The category of different diameter follicles in Small Tail Han sheep with different FecB genotypes"
| 分组 Category | 基因型 Genotype | 卵巢个数 Amount of ovary | 卵泡直径(平均值±标准差) Diameter of ovarian follicle (Average ±Standard deviation) | 每只羊采样卵泡数量 Amount of ovarian follicle collected from each sheep |
| 大卵泡组 | FecB野生型 | 12 | 6.00±0.74a | 直径>5 mm的1个 |
| Large follicle group | FecB突变型 | 12 | 4.40±0.42b | 直径>4 mm的2个 |
| 小卵泡组 | FecB野生型 | 12 | 2.42±0.19 | 直径 < 3 mm的5个以上 |
| Small follicle group | FecB突变型 | 12 | 2.52±0.18 | 直径 < 3 mm的5个以上 |
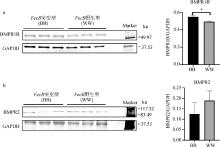
Fig. 1
Expression levels of BMP receptor proteins with FecB mutant and wild-type in the small follicle of Small Tail Han sheep a. Expression levels of BMPR1B protein with FecB mutant and wild-type in the small follicle of Small Tail Han sheep; b. Expression levels of BMPR2 protein with FecB mutant and wild-type in the small follicle of Small Tail Han sheep. *.P<0.05, the same as below"


Fig. 5
Expression levels of BMP receptor proteins with FecB mutant and wild-type in the large follicle of Small Tail Han sheep a. Expression levels of BMPR1B protein with FecB mutant and wild-type in the large follicle of Small Tail Han sheep; b. Expression levels of BMPR2 protein with FecB mutant and wild-type in the large follicle of Small Tail Han sheep"

| 1 |
XU Y F , LI E L , HAN Y D , et al. Differential expression of mRNAs encoding BMP/Smad pathway molecules in antral follicles of high- and low-fecundity Hu sheep[J]. Anim Reprod Sci, 2010, 120 (1-4): 47- 55.
doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2010.02.009 |
| 2 | 龚一鸣, 王翔宇, 贺小云, 等. 绵羊FecB突变对BMPR1B活性及BMP/SMAD通路的影响研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45 (4): 295- 305. |
| GONG Y M , WANG X Y , HE X Y , et al. Progress on the effect of FecB mutation on BMPR1B activity and BMP/SMAD pathway in sheep[J]. Hereditas, 2023, 45 (4): 295- 305. | |
| 3 |
MULSANT P , LECERF F , FABRE S , et al. Mutation in bone morphogenetic protein receptor-IB is associated with increased ovulation rate in Booroola Mérino ewes[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2001, 98 (9): 5104- 5109.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.091577598 |
| 4 | LI Q L . Inhibitory SMADs: potential regulators of ovarian function[J]. Biol Reprod, 2015, 92 (2): 50. |
| 5 |
YAO Y L , REHEMAN A , XU Y F , et al. miR-125b contributes to ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis through targeting BMPR1B, a major gene for sheep prolificacy[J]. Reprod Sci, 2019, 26 (2): 295- 305.
doi: 10.1177/1933719118770544 |
| 6 |
SHIMIZU T , KAYAMORI T , MURAYAMA C , et al. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-4 and BMP-7 suppress granulosa cell apoptosis via different pathways: BMP-4 via PI3K/PDK-1/Akt and BMP-7 via PI3K/PDK-1/PKC[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2012, 417 (2): 869- 873.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.12.064 |
| 7 |
WRANA J L . TGF-β receptors and signalling mechanisms[J]. Miner Electrolyte Metab, 1998, 24 (2-3): 120- 130.
doi: 10.1159/000057359 |
| 8 |
HUSE M , CHEN Y G , MASSAGUÉ J , et al. Crystal structure of the cytoplasmic domain of the type Ⅰ TGF β receptor in complex with FKBP12[J]. Cell, 1999, 96 (3): 425- 436.
doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80555-3 |
| 9 |
GALAT A . Functional diversity and pharmacological profiles of the FKBPs and their complexes with small natural ligands[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2013, 70 (18): 3243- 3275.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1206-z |
| 10 |
MASSAGUÉ J , BLAIN S W , LO R S . TGFβ signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders[J]. Cell, 2000, 103 (2): 295- 309.
doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00121-5 |
| 11 |
ATTISANO L , WRANA J L . Signal transduction by members of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 1996, 7 (4): 327- 339.
doi: 10.1016/S1359-6101(96)00042-1 |
| 12 |
FABRE S , PIERRE A , PISSELET C , et al. The Booroola mutation in sheep is associated with an alteration of the bone morphogenetic protein receptor-IB functionality[J]. J Endocrinol, 2003, 177 (3): 435- 444.
doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1770435 |
| 13 | 王伟. BMP/Smad信号通路对猪卵泡颗粒细胞的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010. |
| WANG W. Effect of BMP/SMAD signaling on porcine follicular granulosa cells[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2010. (in Chinese) | |
| 14 |
WANG X Y , GUO X F , HE X Y , et al. Effects of FecB mutation on estrus, ovulation, and endocrine characteristics in small tail han sheep[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2021, 8, 709737.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.709737 |
| 15 |
HIRSCHHORN T , LEVI-HOFMAN M , DANZIGER O , et al. Differential molecular regulation of processing and membrane expression of Type-Ⅰ BMP receptors: implications for signaling[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2017, 74 (14): 2645- 2662.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2488-y |
| 16 |
SCHNEIDER C A , RASBAND W S , ELICEIRI K W . NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis[J]. Nat Methods, 2012, 9 (7): 671- 675.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2089 |
| 17 |
ZHENG X L , ZHENG Y Q , QIN D X , et al. Regulatory role and potential importance of GDF-8 in ovarian reproductive activity[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2022, 13, 878069.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.878069 |
| 18 |
ERICKSON G F , SHIMASAKI S . The spatiotemporal expression pattern of the bone morphogenetic protein family in rat ovary cell types during the estrous cycle[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2003, 1, 9.
doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-1-9 |
| 19 |
SOUZA C J H , MACDOUGALL C , CAMPBELL B K , et al. The Booroola (FecB) phenotype is associated with a mutation in the bone morphogenetic receptor type 1 B (BMPR1B) gene[J]. J Endocrinol, 2001, 169 (2): R1- R6.
doi: 10.1677/joe.0.169r001 |
| 20 |
WILSON T , WU X Y , JUENGEL J L , et al. Highly prolific Booroola sheep have a mutation in the intracellular kinase domain of bone morphogenetic protein IB receptor (ALK-6) that is expressed in both oocytes and granulosa cells[J]. Biol Reprod, 2001, 64 (4): 1225- 1235.
doi: 10.1095/biolreprod64.4.1225 |
| 21 | CHU Y L , XU Y R , YANG W X , et al. The role of FSH and TGF-β superfamily in follicle atresia[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2018, 10 (3): 305- 321. |
| 22 |
OTSUKA F , MOORE R K , SHIMASAKI S . Biological function and cellular mechanism of bone morphogenetic protein-6 in the ovary[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276 (35): 32889- 32895.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103212200 |
| 23 |
JIAO Y , JIANG T T , LIN Q Y , et al. Molecular characterization of the follicular development of BMP15-edited pigs[J]. Reproduction, 2023, 166 (4): 247- 261.
doi: 10.1530/REP-23-0034 |
| 24 |
CHAIKUAD A , BULLOCK A N . Structural basis of intracellular TGF-β signaling: receptors and smads[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2016, 8 (11): a022111.
doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022111 |
| 25 |
BAHIRE S V , RAJPUT P K , KUMAR V , et al. Quantitative expression of mRNA encoding BMP/SMAD signalling genes in the ovaries of Booroola carrier and non-carrier GMM sheep[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2019, 54 (10): 1375- 1383.
doi: 10.1111/rda.13535 |
| 26 |
FABRE S , PIERRE A , MULSANT P , et al. Regulation of ovulation rate in mammals: contribution of sheep genetic models[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2006, 4, 20.
doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-4-20 |
| 27 | 种玉晴. 绵羊产羔数性状的分子遗传机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2021. |
| ZHONG Y Q. Study on molecular genetic mechanism of litter size in sheep[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 28 |
MONTGOMERY G W , GALLOWAY S M , DAVIS G H , et al. Genes controlling ovulation rate in sheep[J]. Reproduction, 2001, 121 (6): 843- 852.
doi: 10.1530/rep.0.1210843 |
| 29 |
MONTGOMERY G W , MCNATTY K P , DAVIS G H . Physiology and molecular genetics of mutations that increase ovulation rate in sheep[J]. Endocr Rev, 1992, 13 (2): 309- 328.
doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-2-309 |
| 30 |
SHACKELL G H , HUDSON N L , HEATH D A , et al. Plasma gonadotropin concentrations and ovarian characteristics in Inverdale ewes that are heterozygous for a major gene (FecX1) on the X chromosome that influences ovulation rate[J]. Biol Reprod, 1993, 48 (5): 1150- 1156.
doi: 10.1095/biolreprod48.5.1150 |
| 31 |
MCNATTY K P , HEATH D A , CLARK Z , et al. Ovarian characteristics in sheep with multiple fecundity genes[J]. Reproduction, 2017, 153 (2): 233- 240.
doi: 10.1530/REP-16-0587 |
| 32 |
JUENGEL J L , FRENCH M C , QUIRKE L D , et al. Differential expression of CART in ewes with differing ovulation rates[J]. Reproduction, 2017, 153 (4): 471- 479.
doi: 10.1530/REP-16-0657 |
| 33 |
MCNATTY K P , HEATH D A , HUDSON N L , et al. Gonadotrophin-responsiveness of granulosa cells from bone morphogenetic protein 15 heterozygous mutant sheep[J]. Reproduction, 2009, 138 (3): 545- 551.
doi: 10.1530/REP-09-0154 |
| 34 |
ONGARO L , SCHANG G , HO C C , et al. TGF-β superfamily regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone synthesis by gonadotrope cells: is there a role for bone morphogenetic proteins?[J]. Endocrinology, 2019, 160 (3): 675- 683.
doi: 10.1210/en.2018-01038 |
| 35 |
WEI C C , CHEN X Y , PENG J Z , et al. BMP4/SMAD8 signaling pathway regulated granular cell proliferation to promote follicle development in Wanxi white goose[J]. Poult Sci, 2023, 102 (1): 102282.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102282 |
| 36 | 徐梦思, 黄涛, 刘丽娟, 等. TGFβ-SMAD信号通路基因在梅山猪与杜洛克猪不同级别卵泡中的表达分析[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2016, 37 (2): 12- 18. |
| XU M S , HUANG T , LIU L J , et al. Expression patterns of genes of TGFβ-SMAD signaling pathway in meishan and duroc follicle of different size[J]. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2016, 37 (2): 12- 18. | |
| 37 |
DU X , ZHANG L F , LI X Y , et al. TGF-β signaling controls FSHR signaling-reduced ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis through the SMAD4/miR-143 axis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2016, 7 (11): e2476.
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.379 |
| [1] | Yuhang JIA, Liangfu GUO, Runan ZHANG, Ayong ZHAO, Yufang LIU, Mingxing CHU. miR-127 Regulated the Proliferation and Differentiation of Sheep Skeletal Myoblasts and Its Transcription Factor PAX3 Screening [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3864-3875. |
| [2] | Xinyu CAO, Jiawei CAI, Zhiyuan BAO, Shuyu YAO, Yunpeng LI, Yang CHEN, Xinsheng WU, Bohao ZHAO. The Function Analysis of ATG14 Regulates the Autophagy Process in Rabbit Hair Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3472-3481. |
| [3] | Peng SHEN, Yi WANG, Weijie REN, Yongchun YANG, Houhui SONG, Zhiliang WANG. Meta Analysis of Immune Antibody Monitoring for Lumpy Skin Disease [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3649-3658. |
| [4] | Ting WANG, Yuanqing ZHANG, Yibo YAN, Mingjun SHANGGUAN, Hongyu GUO, Zhiwu WANG. The Genetic Structure Analysis and the Comparative Analysis of Selection Signals in 'Tezanghan' Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2913-2926. |
| [5] | Lirui ZHANG, Beiyu ZHANG, Yujuan LI, Yongxu LIU, Hong ZHAO, Fuchang LI, Lei LIU. Effects of Dietary Methionine Level on Wool Production Performance and Hair Follicle Development of Angora Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3024-3031. |
| [6] | Xiaosong WANG, Dong LI, Shu LI, Jiali CHEN, Yongxu LIU, Hong ZHAO, Fuchang LI, Lei LIU. Effects of Dietary Different Copper Levels on Production Performance and Hair Follicle Development in Angora Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3032-3039. |
| [7] | Haoran SONG, Xiaoyi FENG, Peipei ZHANG, Hang ZHANG, Yifan NIU, Zhou YU, Pengcheng WAN, Kai CUI, Xueming ZHAO. The Mechanism of Follicular Granulosa Cells in Follicular Development in Dairy Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2313-2324. |
| [8] | Mingliang HE, Xiaoyang LÜ, Yongqing JIANG, Zhenghai SONG, Yeqing WANG, Huiguo YANG, Shanhe WANG, Wei SUN. Function Analysis of SOX18 in Hu Sheep Hair Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells Based on Transcriptome Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2409-2420. |
| [9] | Chang LIU, Kexing HAO, Yan CHEN, Weibin ZENG, Hengbin YU, Lei CHEN, Jing WANG, Guangdong HU. Effects of Interference with PPARγ Gene on Proliferation, Apoptosis, Migration and Lipid Accumulation of Trophoblast Cells in Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2421-2430. |
| [10] | Ying CHEN, Dayong CHEN, Riga WU, Chunjuan QIU, Lihong FAN, Meirong BAO, Yuan YUE, Hongyan LIANG, Jiaxin ZHANG, Jianhui TIAN, Lei AN, Liqin WANG. Influence of Meat Sheep Varieties on the Scale Application of in vitro Embryo Production Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2451-2459. |
| [11] | Zhibin LUO, Huimin OU, Jianzhong LI, Zhiliang TAN, Jinzhen JIAO. Effects of Low Protein Diet Supplemented with Rumen-protected Amino Acids on Growth Performance, Nutrient Apparent Digestibility and Meat Quality of Hulun Buir Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2498-2509. |
| [12] | PENG Peiya, CHEN Yuhan, YANG Long, WANG Ming, ZHAO Ruiting, HE Jun, YIN Yulong, LIU Mei. Research Progress of Copy Number Variation in Livestock [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1356-1369. |
| [13] | ZHANG Shaohua, WANG Shuai, ZOU Yang, LIU Zhongli, CAI Xuepeng. Advances in Detection Approaches for Ovine Haemonchosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1499-1510. |
| [14] | YANG Yang, YU Qian, LIU Yucheng, YANG Hua, ZHAO Zhuo, WANG Limin, ZHOU Ping, YANG Qingyong, DAI Rong. Identification and Tissue Expression Analysis of the Sheep MYL Gene Family [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1551-1564. |
| [15] | CHANG Xindan, HU Fan, WU Zhiwu, YE Bingsen, LIU Tiehai, LIN Jie, HE Zhixiong, TAN Zhiliang. Effect of High Proportion Rumen Bypass Fat Diet on Feeding Behavior of Growing Mutton Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1077-1084. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||