





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 2409-2420.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.06.013
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mingliang HE1( ), Xiaoyang LÜ2,3, Yongqing JIANG4, Zhenghai SONG5, Yeqing WANG6, Huiguo YANG7, Shanhe WANG1,2,3,*(
), Xiaoyang LÜ2,3, Yongqing JIANG4, Zhenghai SONG5, Yeqing WANG6, Huiguo YANG7, Shanhe WANG1,2,3,*( ), Wei SUN1,2,3,*(
), Wei SUN1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-25
Online:2024-06-23
Published:2024-06-28
Contact:
Shanhe WANG, Wei SUN
E-mail:13013706620@163.com;shanhe12315@163.com;dkxmsunwei@163.com
CLC Number:
Mingliang HE, Xiaoyang LÜ, Yongqing JIANG, Zhenghai SONG, Yeqing WANG, Huiguo YANG, Shanhe WANG, Wei SUN. Function Analysis of SOX18 in Hu Sheep Hair Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells Based on Transcriptome Sequencing[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2409-2420.
Table 1
Specific primers of related genes for qRT-PCR"
| 基因 Gene | 登录号 Accession number | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequence | 产物大小/bp Product size | 退火温度/℃ Annealing temperature |
| AHR | XM_060414533.1 | F: CGAATCCTTCAAAGAGGCATAG | 403 | 60 |
| R: GCTCGGTCTTCGGTATGG | ||||
| ANKRD1 | NM_001252178.1 | F: TACAGGGAAGAAGAACGG | 338 | 60 |
| R: TAGGCACATCCACAGGTT | ||||
| BMP4 | XM_060418703.1 | F: CCGTGAGGAGCTTCCACCA | 191 | 60 |
| R: GTTTATACGATGAAAGCCCTGCTCC | ||||
| CFB | XM_004018929.6 | F: TGTCCTTCTGGCTTCTACCC | 466 | 60 |
| R: AAGGCTCTGTTCCACTCCAA | ||||
| GANC | XM_060419122.1 | F: AGTCTACCTATCGGGCATTA | 269 | 60 |
| R: ATCTCCTTTCCCACTTGC | ||||
| HUNK | XM_004003742.6 | F: TTGCCAGGAAGAAATACGG | 189 | 60 |
| R: GCAGGAAGTTCACGGCTC | ||||
| PTGFR | NM_001009789.2 | F: TTTAGAAGTCAGCAGCAC | 354 | 60 |
| R: ATCAGAAATAGCAGCAAC | ||||
| PTGS2 | NM_001009432.1 | F: CCCGAACAGGATTCTATG | 481 | 60 |
| R: GCTGGTCCTCGTTCAATA | ||||
| SOX9 | XM_027974011.3 | F: TCAAGGGCTACGACTGGACG | 366 | 60 |
| R: TGGCGTTGGGCGAGATGTGC | ||||
| SOX18 | XM_027976914.2 | F: TGTGGGCGAAGGACGAGC | 253 | 60 |
| R: GCCAAGCCTGGGAGGAGGAG | ||||
| GAPDH | NM_001190390.1 | F: TCTCAAGGGCATTCTAGGCTAC | 151 | 60 |
| R: GCCGAATTCATTGTCGTACCAG |

Fig. 2
Identification of SOX18 gene in dermal papilla cells and construction of overexpression vector A. SOX18 is expressed in Hu sheep DPCs(100×); B. Gel electrophoresis of double enzyme digestion of SOX18 overexpression vector; C. Plasmid transfection status observed by microscopic(40×); D, E. The mRNA and protein expression levels of SOX18 after overexpression of SOX18 in Hu sheep DPCs. Data are expressed as "means±SEM (standard error of the mean)" (n=3). The unpaired Student′s t-test was used for statistical analysis. ns. P > 0.05; ***. P < 0.001"


Fig. 3
Analysis of transcriptome data A. The correlation analysis used Pearson′s correlation analysis; B. The violin plot shows gene abundance expression at any location of all genes in each sample. The white dot represents the median, the black rectangle is the range from the lower quartile(Q1) to the upper quartile(Q3), the black line running up and down the violin chart represents the confidence interval; and the outer shape of the black rectangle represents a kernel density estimation; the length of the vertical axis of the figure represents the degree of data dispersion, and the length of the horizontal axis represents the gene expression distribution at a certain vertical coordinate position"


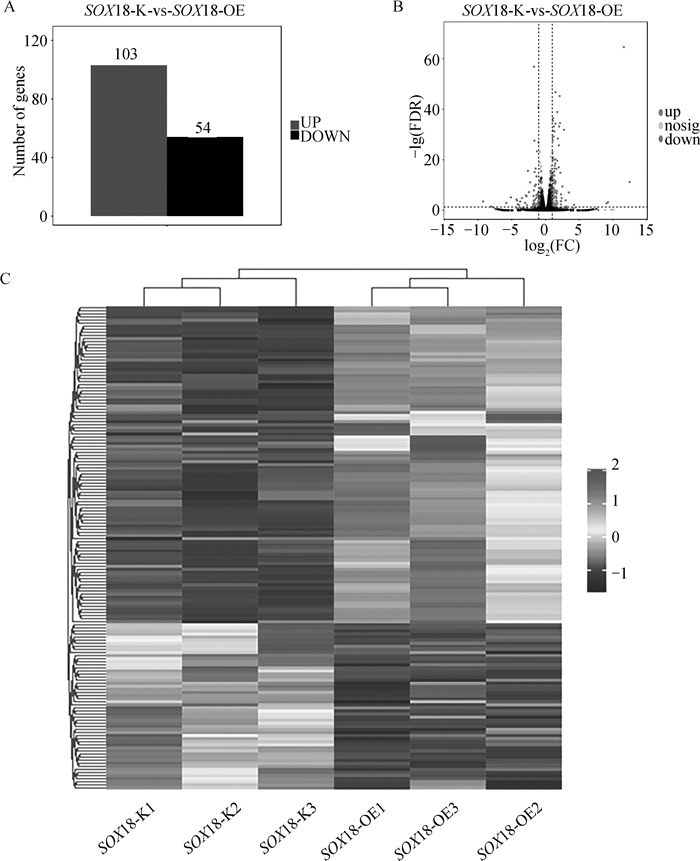
Fig. 4
Identification of differentially expressed genes A. A bar chart displayed the quantity of differentially expressed genes in SOX18-K vs. SOX18-OE groups; B. A volcano plot was used to determine the differentially expressed genes in SOX18-K vs. SOX18-OE groups; C. A heat map showing expression patterns of differentially expressed genes for SOX18-K vs. SOX18-OE groups"
| 1 |
TSAI S Y , SENNETT R , REZZA A , et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in dermal condensates is required for hair follicle formation[J]. Dev Biol, 2014, 385 (2): 179- 188.
doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.11.023 |
| 2 |
STENN K S , PAUS R . Controls of hair follicle cycling[J]. Physiol Rev, 2001, 81 (1): 449- 494.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.1.449 |
| 3 |
ZHOU L J , WANG H , JING J , et al. Regulation of hair follicle development by exosomes derived from dermal papilla cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 500 (2): 325- 332.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.067 |
| 4 |
KWACK M H , SEO C H , GANGADARAN P , et al. Exosomes derived from human dermal papilla cells promote hair growth in cultured human hair follicles and augment the hair-inductive capacity of cultured dermal papilla spheres[J]. Exp Dermatol, 2019, 28 (7): 854- 857.
doi: 10.1111/exd.13927 |
| 5 |
STENN K S , COTSARELIS G . Bioengineering the hair follicle: fringe benefits of stem cell technology[J]. Curr Opin Biotechnol, 2005, 16 (5): 493- 497.
doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2005.08.002 |
| 6 | 陈思琦, 金家民, 菅志远. SOX基因家族在结直肠癌中的研究进展[J]. 华夏医学, 2022, 35 (6): 143- 148. |
| CHEN S Q , JIN J M , JIAN Z Y . Research progress of SOX gene family in colorectal cancer[J]. Acta Medicinae Sinica, 2022, 35 (6): 143- 148. | |
| 7 |
PENNISI D , GARDNER J , CHAMBERS D , et al. Mutations in Sox18 underlie cardiovascular and hair follicle defects in ragged mice[J]. Nat Genet, 2000, 24 (4): 434- 437.
doi: 10.1038/74301 |
| 8 |
CARTER T C , PHILLIPS J S . RAGGED, a semidominant coat texture mutant: in the house mouse[J]. J Hered, 1954, 45 (4): 151- 154.
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a106464 |
| 9 |
PENNISI D , BOWLES J , NAGY A , et al. Mice null for Sox18 are viable and display a mild coat defect[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2000, 20 (24): 9331- 9336.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.24.9331-9336.2000 |
| 10 |
SLEE J . The morphology and development of ragged-a mutant affecting the skin and hair of the house mouse Ⅱ. Genetics, embryology and gross juvenile morphology[J]. J Genet, 1957, 55 (3): 570- 584.
doi: 10.1007/BF02984073 |
| 11 |
WANG S H , WU T Y , SUN J Y , et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals the molecular anatomy of sheep hair follicle heterogeneity and wool curvature[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9, 800157.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.800157 |
| 12 |
LIVAK K J , SCHMITTGEN T D . Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method[J]. Methods, 2001, 25 (4): 402- 408.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 |
| 13 | DRISKELL R R , CLAVEL C , RENDL M , et al. Hair follicle dermal papilla cells at a glance[J]. J Cell Sci, 2011, 124 (Pt 8): 1179- 1182. |
| 14 |
SCHMIDT-ULLRICH R , PAUS R . Molecular principles of hair follicle induction and morphogenesis[J]. Bioessays, 2005, 27 (3): 247- 261.
doi: 10.1002/bies.20184 |
| 15 |
SCHNEIDER M R , SCHMIDT-ULLRICH R , PAUS R . The hair follicle as a dynamic miniorgan[J]. Curr Biol, 2009, 19 (3): R132- R142.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.12.005 |
| 16 |
WU C L , LI J Y , XU X M , et al. Effect of the FA2H gene on cashmere fineness of Jiangnan cashmere goats based on transcriptome sequencing[J]. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23 (1): 527.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08763-7 |
| 17 |
雷志惠, 张利平, 赵洪昌, 等. 全基因组选择信号揭示绵羊毛囊发育及脱毛性状相关的候选基因[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (2): 381- 390.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.02.006 |
|
LEI Z H , ZHANG L P , ZHAO H C , et al. Genome-wide selection signals reveal candidate genes associated with the sheep of hair follicle development and depilation traits[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (2): 381- 390.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.02.006 |
|
| 18 |
HUI B Q , JI H , XU Y T , et al. RREB1-induced upregulation of the lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 regulates the proliferation and migration of pancreatic cancer partly through suppressing ANKRD1 and ANGPTL4[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10 (3): 207.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1384-9 |
| 19 |
王翠月, 李明睿, 高玉时, 等. 肉鸡骨骼发育的调控机制[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (7): 2057- 2065.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.07.003 |
|
WANG C Y , LI M R , GAO Y S , et al. Regulation mechanism of bone development in broilers[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (7): 2057- 2065.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.07.003 |
|
| 20 |
徐超, 李凤, 郝海生, 等. 性别相关基因在牛早期性别发育中的表达规律研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2017, 48 (10): 1892- 1901.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2017.10.012 |
|
XU C , LI F , HAO H S , et al. Sex-related genes expression during development of the early bovine fetuses[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2017, 48 (10): 1892- 1901.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2017.10.012 |
|
| 21 |
WANG X L , DAI Y Q , ZHANG X X , et al. CXCL6 regulates cell permeability, proliferation, and apoptosis after ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating Sirt3 expression via AKT/FOXO3a activation[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, 22 (1): 30- 39.
doi: 10.1080/15384047.2020.1842705 |
| 22 |
WU L , CHEN X , ZHAO J J , et al. A novel IL-17 signaling pathway controlling keratinocyte proliferation and tumorigenesis via the TRAF4-ERK5 axis[J]. J Exp Med, 2015, 212 (10): 1571- 1587.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20150204 |
| 23 |
LIU W T , WANG H H , JIAN C Z , et al. The RNF26/CBX7 axis modulates the TNF pathway to promote cell proliferation and regulate sensitivity to TKIs in ccRCC[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18 (5): 2132- 2145.
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.69325 |
| 24 |
张文建, 马广伟, 张潇飞, 等. 羊毛品质性状相关基因CCNY的验证和分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2017, 48 (8): 1389- 1400.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2017.08.003 |
|
ZHANG W J , MA G W , ZHANG X F , et al. Verification and analysis of wool quality traits-associated CCNY gene[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2017, 48 (8): 1389- 1400.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2017.08.003 |
|
| 25 |
许甜甜, 张彤彤, 王蒙, 等. 转录因子Foxq1通过WNT/β-catenin信号通路影响绒山羊毛囊干细胞增殖的研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (6): 2653- 2661.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.06.041 |
|
XU T T , ZHANG T T , WANG M , et al. Transcription factor Foxq1 affects the proliferation of hair follicle stem cells in cashmere goats via WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (6): 2653- 2661.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.06.041 |
|
| 26 |
李晓波, 刘占发, 刘悦, 等. 基于WGCNA与GSEA方法挖掘调控中卫山羊羊毛弯曲相关基因[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (9): 2930- 2943.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.09.011 |
|
LI X B , LIU Z F , LIU Y , et al. Mining genes related to wool bending of Zhongwei goat based on WGCNA and GSEA[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (9): 2930- 2943.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.09.011 |
| [1] | WANG Xin, NIE Tong, LI Aqun, MA Jun. Hesperidin Alleviates High-fat-diet Induced Hepatic Oxidative Stress in Mice via Oxidative Phosphorylation Pathway [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1302-1313. |
| [2] | KANG Jia, DUAN Xiangru, YIN Xuejiao, YANG Ruochen, LI Taichun, SHAN Xinyu, CHEN Meijing, ZHANG Yingjie, LIU Yueqin. Effects of Cysteine and Methionine on Secondary Hair Follicle Growth and Hair Dermal Papilla Cell Proliferation in vitro in Cashmere Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 515-527. |
| [3] | LIU Linli, PENG Xuelan, LI Bo, CHENG Lefan, CIREN Lamu, ZHANG Enping. Effect of Overexpression of UCP3 Gene on the Differentiation of Sahu Sheep Preadipocytes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3275-3285. |
| [4] | HU Ting, ZHANG Yonghong, HOU Xiaolin, YAO Hua, CUI Defeng, PAN Zaozao, ZHANG Lingyu, ZHANG Jiaxi, WU Qiong. The Effects of Bisphenol A on Inflammation and Amino Acid Metabolism Pathways in Porcine Testis Sertoli Cells Based on Transcriptome Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 2858-2871. |
| [5] | XIONG Chengkun, ZHANG Daoliang, YANG Yue, DING Hongyan, ZHAO Jie, LI Yu, WANG Xichun, FENG Shibin, ZHAO Chang, TANG Jishun, WU Jinjie. Effect of Rutin on Rumen Fermentation, Rumen Flora Structure and Antioxidant Properties in Perinatal Hu Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 2898-2909. |
| [6] | YE Qianwen, CHEN Zhuo, LI Xin, SUN Yawei, JIN Xiaoye, LI Ziqian, WUMAIERJIANG·Yahefu, ZHONG Qi, MA Xuelian, YAO Gang. Dynamic Changes of Gut Microbiota Composition and Its Predicted Metabolism Function in One-month-old Sucking Lambs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 1095-1108. |
| [7] | LIU Yuanyi, LI Xinyu, Bayinnamula, CUI Fang, MANG Lai, DU Ming. Single-Cell Transcriptome Sequencing Technology and its Application in Animal Reproduction [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(2): 421-433. |
| [8] | WANG Yahan, ZHENG Yujing, ZHONG Pei, LI Xiaodan, WANG Feng. Expression Patterns and Functional Analysis of YAP1 in Endometrium of Hu Sheep with Different Fertility during Estrus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(1): 189-200. |
| [9] | LI Xiaobo, LIU Zhanfa, LIU Yue, CHEN Qian, MA Yuehui, ZHAO Qianjun, YE Shaohui. Mining Genes Related to Wool Bending of Zhongwei Goat Based on WGCNA and GSEA [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 2930-2943. |
| [10] | WEI Xiao, ZHANG Jiantong, LONG Tanghui, LI Kairong, LI Yanjiao, OUYANG Kehui, QIU Qinghua. Effects of Dietary Energy Level on Rumen Fermentation Characteristics and Microbial Composition of Hu Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 3042-3051. |
| [11] | MAO Yanni, CHANG Jiawei, LI Na, WANG Xin, KANG Xinyun, MA Qiang, MA Liang, WANG Guiqin. Transcriptome Differential Expression Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus in Biofilm State and Planktonic State [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(8): 2697-2707. |
| [12] | LI Yu, DUAN Chunhui, SONG Zhipan, YUE Sicong, WANG Yuan, ZHANG Yingjie, LIU Yueqin. Effects of PGF2α on Reproductive Hormones and Related Cytokines during Luteal Phase in Ewes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(6): 1807-1818. |
| [13] | LUO Jinhong, CHEN Xiang, SHANG Yishun, AO Ye, LI Pengcheng. Transcriptome Sequencing Screening the Genes Related to Goat Embryo Attachment in Early Pregnancy [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 1465-1474. |
| [14] | WANG Luyao, HAO Xuepiao, LEI Baishi, ZHAO Kuan, ZHANG Wuchao, YUAN Wanzhe. Differential Expression of Transcriptome in Liver, Thymus and Ileum of Ducks Infected with Novel Goose Parvovirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(2): 654-657. |
| [15] | LI Jie, ZHAO Ruipeng, CHEN Chuwen, YANG Chaowu, WU Jinbo, LI Zhixiong. Screening of the Differentially Expressed mRNA and lncRNA and the Construction of Their Competitive Regulatory Network in Embryonic Leg Muscles of Different Chicken Breeds [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(12): 4207-4220. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||