





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (8): 3992-4006.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.08.037
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Wenjian1,2( ), XU Lei3(
), XU Lei3( ), ZHANG Ze1, YANG Rui1,4, XIN Lingxiang3, WANG Nan3, CHEN Xiang5,*(
), ZHANG Ze1, YANG Rui1,4, XIN Lingxiang3, WANG Nan3, CHEN Xiang5,*( ), XIN Ting1,*(
), XIN Ting1,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-03
Online:2025-08-23
Published:2025-08-28
Contact:
CHEN Xiang, XIN Ting
E-mail:dz120230047@stu.yzu.edu.cn;609697832@qq.com;chenxiang@yzu.edu.cn;xinting@caas.cn
CLC Number:
SHI Wenjian, XU Lei, ZHANG Ze, YANG Rui, XIN Lingxiang, WANG Nan, CHEN Xiang, XIN Ting. Screening and Identification of Biofilm-related Genes Based on the Random Mutant Library of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Variant bovis C68001[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3992-4006.
Table 1
Primers used in this work"
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′→ 3′) Sequence | 用途 Function |
| KanF | GATGGATTGCACGCAGGTTC | 转座子插入鉴定 |
| KanR | ATATCACGGGTAGCCAACGC | |
| H1F | CGGGGACTTATCAGCCAACCTG | 转座子插入区域侧翼扩增 |
| H1R | TAGAGACCGGGGACTTATCAGCCAA | |
| LFP | TTTTTTTT$\underline{GGCCTAAATGGCC}$CCTGCAAGCGGGAGCGACC | 扩增Rv3671c基因左臂 |
| LRP | TTTTTTTT$\underline{GGCCTTTCTGGCC}$CAGCATTGAGCCCAGCGCA | |
| RFP | TTTTTTTT$\underline{CCATAGATTGG}$CAGGTGCTCGGTGTGGTGTTC | 扩增Rv3671c基因右臂 |
| RRP | TTTTTTTT$\underline{CCATCTTTTGG}$CGAGGCCGCTGGTCATACTG |
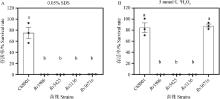
Fig. 2
Stress resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis variant bovis mutants Survival rate of C68001, Rv1906, Rv3425, and Rv3671c mutants in presence of 7H9-OADC medium supplemented 0.05%SDS (A), or 5 mmol·L-1 H2O2 (B), at 37℃ for 24 h. Data are presented as "mean±SEM". One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple comparison was used for statistical analysis, different letters indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.000 1)"
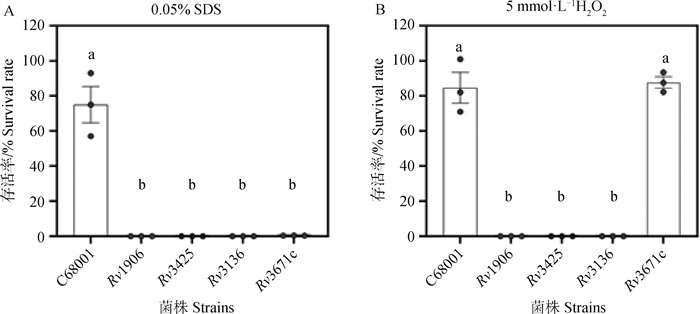
Fig. 5
The biofilm properties of Rv3671c The biofilm of C68001, pMV-Rv3671c, Comp-Rv3671c and KO-Rv3671c cultured in 7H9-OADC medium (A), and Sauton's medium (B-C). The growth curve of C68001, pMV-Rv3671c, Comp-Rv3671c, KO-Rv3671c cultured in 7H9-OADC-tylooxapol medium (D). SEM observation images (F). Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple comparison was used for statistical analysis, *. P < 0.05, **. P < 0.01, ***. P < 0.001, the same as below"
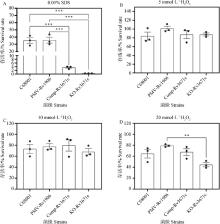
Fig. 6
Effect of Rv3671c gene on anti-SDS and anti-oxidation of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis variant bovis The resistant to 0.05% SDS and H2O2 of C68001, pMV-Rv3671c, Comp-Rv3671c and KO-Rv3671c in 7H9-OADC-tylooxapol medium supplemented with 0.05% SDS (A), 5 mmol·L-1 H2O2 (B), 10 mmol·L-1 H2O2 (C), or 20 mmol·L-1 H2O2 (D)"
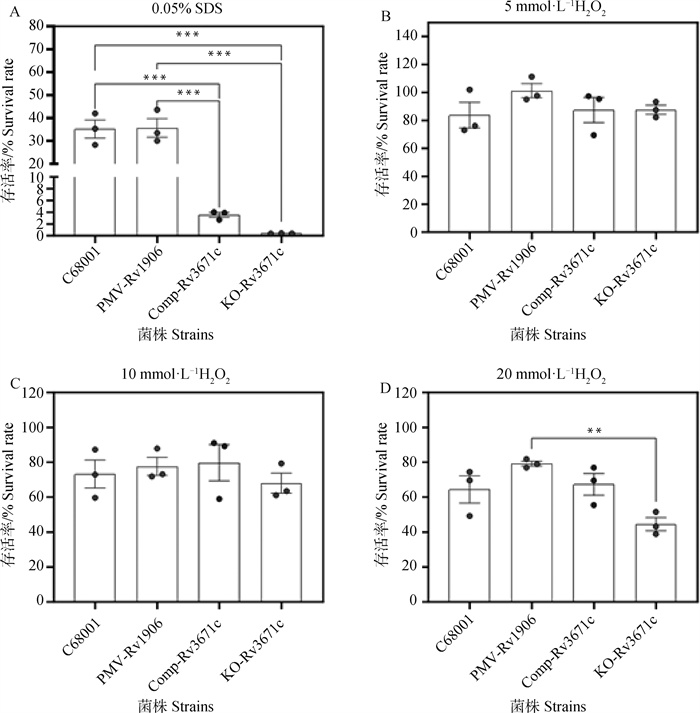
Fig. 7
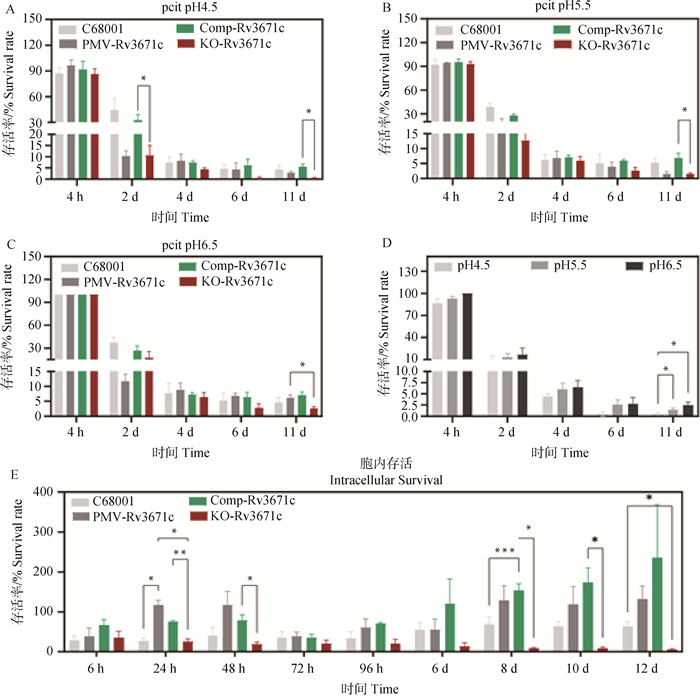
Effect of Rv3671c gene on acid-fast and intracellular survival ability of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis variant bovis The resistant to acid of C68001, pMV-Rv3671c, Comp-Rv3671c and KO-Rv3671c in Citrate-Phosphate Buffer at pH 4.5 (A), pH5.5 (B), and pH6.5 (C). The survival rate of KO-Rv3671c in Citrate-Phosphate Buffer at different pH (D). The intracellular survival ability of C68001, pMV-Rv3671c, Comp-Rv3671c and KO-Rv3671c in J774A.1 cell line"
| 1 |
MEIRINGC,VAN HELDENP D,GOOSENW J.Tb control in humans and animals in south africa: A perspective on problems and successes[J].Front Vet Sci,2018,5,298.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00298 |
| 2 |
COUSINSD V.Mycobacterium bovis infection and control in domestic livestock[J].Rev Sci Tech,2001,20(1):71-85.
doi: 10.20506/rst.20.1.1263 |
| 3 |
RAMANUJAMH,PALANIYANDIK.Bovine tuberculosis in India: The need for one health approach and the way forward[J].One Health,2023,16,100495.
doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2023.100495 |
| 4 |
THOMASA,HALLIDAYA,CLAPPG,et al.High Mycobacterium bovis exposure but low igra positivity in UK farm workers[J].Zoonoses Public Health,2025,72(4):369-378.
doi: 10.1111/zph.13214 |
| 5 |
AGULLŗ-ROSI,VAZ-RODRIGUESR,DOMíNGUEZM,et al.Immunological mechanisms involved in the protection against development of pulmonary tuberculosis in naturally infected goats[J].Veterinary Microbiology,2025,300,110320.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2024.110320 |
| 6 |
刘悦阳,李梦媛,聂雪伊,等.钙结合蛋白S100A4对BCG感染THP-1细胞自噬的调控作用[J].畜牧兽医学报,2024,55(1):311-322.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.01.029 |
|
LIUY Y,LIM Y,NIEX Y,et al.The regulation of calcium- binding protein S100A4 on autophagy in THP- 1 cells infected with Bacillus Calmette- Guérin[J].Acta Veterinaeria et Zootechnica Sinica,2024,55(1):311-322.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.01.029 |
|
| 7 | 张喜悦,路广计,曹瑞,等.我国北方某地区的牛结核病流行病学调查[J].中国预防兽医学报,2018,40(4):350-352. |
| ZHANGX Y,LUG J,CAOR,et al.Epidemiological investigation of bovine tuberculosis in one north region of China[J].Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine,2018,40(4):350-352. | |
| 8 |
ZHUX,YANY,WANGZ,et al.An abattoir-based study on the prevalence of bovine tuberculosis from culled adult dairy cows in Wuhan, China[J].Prev Vet Med,2021,196,105477.
doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2021.105477 |
| 9 |
DEANG S,RHODESS G,COADM,et al.Minimum infective dose of Mycobacterium bovis in cattle[J].Infect Immun,2005,73(10):6467-71.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.6467-6471.2005 |
| 10 | 中国疾病预防控制中心传染病预防控制所,中国防痨协会人兽共患结核病专业分会.分枝杆菌菌种中文译名专家共识[J].中国人兽共患病学报,2023,39(3):205-220. |
| National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention,Chinese Centre for Disease Control and Prevention Zoonotic Tuberculosis Sub-association of Chinese Antituberculosis Association.Expert consensus on the Chinese translation of Mycobacterium nomenclature[J].Chinese Journal of Zoonoses,2023,39(3):205-220. | |
| 11 |
于有利,王建东,郭亚男,等.鸟苷酸结合蛋白2b在牛分枝杆菌诱导巨噬细胞极化过程中的作用[J].畜牧兽医学报,2024,55(6):2641-2651.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.06.035 |
|
YUY L,WANGJ D,GUOY N,et al.Role of guanylate binding protein 2b during macrophage polarization induced by Mycobacterium bovis[J].Acta Veterinaeria et Zootechnica Sinica,2024,55(6):2641-2651.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.06.035 |
|
| 12 | PESCIAROLIM,ALVAREZJ,BONIOTTIM B,et al.Tuberculosis in domestic animal species[J].Res Vet Sci,2014,97(Suppl):S78-85. |
| 13 |
LAMATTINAD,MARTINEZM F,COUTOE M,et al.Detection of Mycobacterium bovis in free-ranging Sapajus nigritus, Argentina[J].Zoonoses Public Health,2025,72(1):95-99.
doi: 10.1111/zph.13189 |
| 14 |
CONTEDDUK,ENGLISHH M,BYRNEA W,et al.A scoping review on bovine tuberculosis highlights the need for novel data streams and analytical approaches to curb zoonotic diseases[J].Vet Res,2024,55(1):64.
doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01314-w |
| 15 |
BOUCHEZ-ZACRIAM,RUETTES,RICHOMMEC,et al.Analysis of a multi-type resurgence of Mycobacterium bovis in cattle and badgers in southwest france, 2007-2019[J].Vet Res,2023,54(1):41.
doi: 10.1186/s13567-023-01168-8 |
| 16 |
NAVARROJ A,SANCHEZJ,BUENDIAA J.Value of anatomopathological examination in goats with a positive comparative intradermal tuberculin test as part of a tuberculosis control programme[J].Vet Rec,2025,196(5):e4963.
doi: 10.1002/vetr.4963 |
| 17 |
MASONP S,RISALDEM A,GORTÁZARC,et al.Early antibody responses to lipid antigens in red deer infected with Mycobacterium bovis[J].Veterinary Microbiology,2024,298,110269.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2024.110269 |
| 18 | KOUENGOUAA P K,TSISSAY L,NOUDEKEN D,et al.Prevalence and zoonotic risk factors of Mycobacterium bovis tuberculosis in cattle at the cattle-wildlife-human interface in South and East Cameroon[J].Vet World,2024,17(1):8-16. |
| 19 |
EVANSJ T,SMITHE G,BANERJEEA,et al.Cluster of human tuberculosis caused by Mycobacterium bovis: Evidence for person-to-person transmission in the UK[J].Lancet,2007,369(9569):1270-1276.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60598-4 |
| 20 |
BUSSB F,KEYSER-METOBOA,ROTHERJ,et al.Possible airborne person-to-person transmission of Mycobacterium bovis-nebraska 2014-2015[J].MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep,2016,65(8):197-201.
doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6508a1 |
| 21 |
GALLIVANM,SHAHN,FLOODJ.Epidemiology of human Mycobacterium bovis disease, California, USA, 2003-2011[J].Emerg Infect Dis,2015,21(3):435-443.
doi: 10.3201/eid2103.141539 |
| 22 |
BLANCOF C,MARINIM R,KLEPPL I,et al.Long-term evaluation in balbc mice of a triple mutant of Mycobacterium bovis and the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin as potential vaccines against bovine tuberculosis[J].Veterinary Microbiology,2025,302,110371.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2025.110371 |
| 23 |
GUBELMANNC,WASZAKS M,ISAKOVAA,et al.A yeast one-hybrid and microfluidics-based pipeline to map mammalian gene regulatory networks[J].Mol Syst Biol,2013,9,682.
doi: 10.1038/msb.2013.38 |
| 24 |
NICHOLSR J,SENS,CHOOY J,et al.Phenotypic landscape of a bacterial cell[J].Cell,2011,144(1):143-156.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.11.052 |
| 25 |
SAUNDERSS H,AHMEDA M.Orbit for E. Coli: Kilobase-scale oligonucleotide recombineering at high throughput and high efficiency[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2024,52(8):e43.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae227 |
| 26 |
HAMERL,DEZWAANT M,MONTENEGRO-CHAMORROM V,et al.Recent advances in large-scale transposon mutagenesis[J].Curr Opin Chem Biol,2001,5(1):67-73.
doi: 10.1016/S1367-5931(00)00162-9 |
| 27 |
BAOH Y,LIH J,ZHANGY Y,et al.Transposon-based identification of genes involved in the rimocidin biosynthesis in Streptomyces rimosus m527[J].World J Microbiol Biotechnol,2023,39(12):359.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03814-x |
| 28 |
WINKLERK R,MIZRAHIV,WARNERD F,et al.High-throughput functional genomics: A (myco)bacterial perspective[J].Mol Microbiol,2023,120(2):141-158.
doi: 10.1111/mmi.15103 |
| 29 |
MARTINC,TIMMJ,RAUZIERJ,et al.Transposition of an antibiotic resistance element in mycobacteria[J].Nature,1990,345(6277):739-743.
doi: 10.1038/345739a0 |
| 30 |
GUILHOTC,OTALI,VAN ROMPAEYI,et al.Efficient transposition in mycobacteria: Construction of Mycobacterium smegmatis insertional mutant libraries[J].J Bacteriol,1994,176(2):535-539.
doi: 10.1128/jb.176.2.535-539.1994 |
| 31 |
RATHNAIAHG,BANNANTINEJ P,BAYLESD O,et al.Analysis of Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis mutant libraries reveals loci-dependent transposition biases and strategies for novel mutant discovery[J].Microbiology (Reading),2016,162(4):633-641.
doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000258 |
| 32 |
JANISCHN,LEVENDOSKYK,BUDELLW C,et al.Genetic underpinnings of carotenogenesis and light-induced transcriptome remodeling in the opportunistic pathogen Mycobacterium kansasii[J].Pathogens,2023,12(1):86.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens12010086 |
| 33 |
JOSHIH,KANDARID,MAITRAS S,et al.Identification of genes associated with persistence in Mycobacterium smegmatis[J].Front Microbiol,2024,15,1302883.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1302883 |
| 34 |
PATELR R,ARUNP P,SINGHS K,et al.Mycobacterial biofilms: Understanding the genetic factors playing significant role in pathogenesis, resistance and diagnosis[J].Life Sci,2024,351,122778.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122778 |
| 35 | LIB,ZHANGY,GUOQ,et al.Antibacterial peptide rp557 increases the antibiotic sensitivity of Mycobacterium abscessus by inhibiting biofilm formation[J].Sci Total Environ,2022,807(Pt 3):151855. |
| 36 |
DAVIESD.Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents[J].Nature reviews Drug discovery,2003,2(2):114-122.
doi: 10.1038/nrd1008 |
| 37 |
FUXC A,COSTERTONJ W,STEWARTP S,et al.Survival strategies of infectious biofilms[J].Trends in microbiology,2005,13(1):34-40.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.11.010 |
| 38 | ABUDUKADIERA,ZHANGQ A,LIP B,et al.Regulation of Mycobacterium biofilm development and novel measures against antibiotics resistance[J].Yi Chuan,2024,46(1):34-45. |
| 39 |
LIUX,HUJ,WANGW,et al.Mycobacterial biofilm: Mechanisms, clinical problems, and treatments[J].Int J Mol Sci,2024,25(14):7771.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25147771 |
| 40 |
NASROLLAHIANS,POURMOSHTAGHH,SABOURS,et al.Biofilm formation in mycobacterial genus; mechanism of biofilm formation and anti-mycobacterial biofilm agents[J].Curr Pharm Biotechnol,2025,26(7):982-991.
doi: 10.2174/0113892010277107240227054933 |
| 41 |
KARTHIKEYANA,TABASSUMN,JEONGG J,et al.Alleviation of mycobacterial infection by impairing motility and biofilm formation via natural and synthetic molecules[J].World J Microbiol Biotechnol,2025,41(4):113.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04322-w |
| 42 | YADAVP,GOELM,GUPTAR D.Anti-biofilm potential of human senescence marker protein 30 against Mycobacterium smegmatis[J].World J Microbiol Biotechnol,2023,40(2):45. |
| 43 | 林伟东,隋修锟,王召阳,等.牛分枝杆菌MarP蛋白的表达纯化及其单克隆抗体制备[J].中国畜牧兽医,2019,46(6):1774-1782. |
| LINW D,SUIX K,WANGZ Y,et al.Expression and purification of MarP protein of Mycobacterium bovis and preparation of its monoclonal antibody[J].China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2019,46(6):1774-1782. | |
| 44 |
LAMPED J,CHURCHILLM E,ROBERTSONH M.A purified mariner transposase is sufficient to mediate transposition in vitro[J].Embo j,1996,15(19):5470-5479.
doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb00930.x |
| 45 |
LAMPED J,GRANTT E,ROBERTSONH M.Factors affecting transposition of the himar1 mariner transposon in vitro[J].Genetics,1998,149(1):179-187.
doi: 10.1093/genetics/149.1.179 |
| 46 |
VANDEWALLEK,FESTJENSN,PLETSE,et al.Characterization of genome-wide ordered sequence-tagged Mycobacterium mutant libraries by cartesian pooling-coordinate sequencing[J].Nature Communications,2015,6(1):7106.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms8106 |
| 47 | 谢宇晴,沈也驰,李昕,等.结核分枝杆菌转座突变库的建立及应用[J].扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2022,43(3):34-39. |
| XIEY Q,SHENY C,LIX,et al.Establishment and application of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis transposon mutation library[J].Journal of Yangzhou University(Agricultural and Life Science Edition),2022,43(3):34-39. | |
| 48 | 任宁宁. 结核分枝杆菌RD区诊断标识抗原的筛选及卡介苗突变体库的构建[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018. |
| REN N N, Screening of diagnostic antigen markers in RD region of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and construction of mutant library of BCG[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese) | |
| 49 | LEVENDOSKYK,JANISCHN,QUADRIL E N.Comprehensive essentiality analysis of the Mycobacterium kansasii genome by saturation transposon mutagenesis and deep sequencing[J].mBio,2023,14(4) |
| 50 | 时文健,徐磊,张泽,等.结核分枝杆菌牛变种c68001转座子突变体库的构建[J].微生物学通报,2025,52(2):703-712. |
| SHIW J,XUL,ZHANGZ,et al.Construction of an insertional mutant library of Mycobacterium tuberculosis variant bovis[J].Microbiology China,2025,52(2):703-712. | |
| 51 |
DOMINGUEJ C,DREWESJ L,MERLOC A,et al.Host responses to mucosal biofilms in the lung and gut[J].Mucosal Immunol,2020,13(3):413-422.
doi: 10.1038/s41385-020-0270-1 |
| 52 |
CIOFUO,ROJO-MOLINEROE,MACIÀM D,et al.Antibiotic treatment of biofilm infections[J].Apmis,2017,125(4):304-319.
doi: 10.1111/apm.12673 |
| 53 |
LEBEAUXD,GHIGOJ M,BELOINC.Biofilm-related infections: Bridging the gap between clinical management and fundamental aspects of recalcitrance toward antibiotics[J].Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,2014,78(3):510-543.
doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00013-14 |
| 54 | LÖWENSTEINE.Vorlesungen über bakteriologie, immunität, spezifische diagnostik und therapie der tuberkulose[M].Fischer.1920. |
| 55 | CALMETTEA,BOQUETA,NÈGREL.L'infection bacillaire et la tuberculose chez l'homme et chez les animaux: Processus d'infection et de défense, étude biologique et expérimentale, vaccination préventive[M].Masson.1928. |
| 56 |
HALL-STOODLEYL,STOODLEYP.Biofilm formation and dispersal and the transmission of human pathogens[J].Trends in microbiology,2005,13(1):7-10.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.11.004 |
| 57 |
COSTERTONJ W,STEWARTP S,GREENBERGE P.Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections[J].Science,1999,284(5418):1318-1322.
doi: 10.1126/science.284.5418.1318 |
| 58 |
BALABANN Q,MERRINJ,CHAITR,et al.Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch[J].Science,2004,305(5690):1622-1625.
doi: 10.1126/science.1099390 |
| 59 | ROBERTSM E,STEWARTP S.Modelling protection from antimicrobial agents in biofilms through the formation of persister cells[J].Microbiology (Reading),2005,151(Pt 1):75-80. |
| 60 |
LID N,LIUX Y,XUJ B,et al.Mycobacterium tuberculosis rv1048c affects the biological characteristics of recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis[J].Sci Rep,2024,14(1):29749.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81405-y |
| 61 |
YOUNGBLOMM A,SMITHT M,MURRAYH J,et al.Adaptation of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis transcriptome to biofilm growth[J].PLoS Pathog,2024,20(4):e1012124.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012124 |
| 62 | 周慧. 结核分枝杆菌Rv1096的表达及功能鉴定[D]. 大连: 大连医科大学, 2012. |
| ZHOU H. Expression and functional characterization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv1096[D]. Dalian: Dalian Medical University, 2012. (in Chinese) | |
| 63 |
LUQ,ZHANGW,FANGJ,et al.Mycobacterium tuberculosis rv1096, facilitates mycobacterial survival by modulating the NF-κB/MAPK pathway as peptidoglycan n-deacetylase[J].Molecular Immunology,2020,127,47-55.
doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.08.005 |
| 64 |
DENGG,JIN,SHIX,et al.Effects of Mycobacterium tuberculosis RV1096 on mycobacterial cell division and modulation on macrophages[J].Microbial Pathogenesis,2020,141,103991.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.103991 |
| 65 | 赵雅敏,朱胜玲,翁术锋,等.结核分枝杆菌蛋白rv3425对细菌表型及毒力影响的研究[J].微生物与感染,2020,15(4):241-250. |
| ZHAOY M,ZHUS L,WENGS F,et al.The effect of Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein Rv3425 in Mycobacterium smegmatis[J].Journal of Microbes and Infections,2020,15(4):241-250. | |
| 66 |
WANGJ L,QIEY Q,ZHUB D,et al.Evaluation of a recombinant bcg expressing antigen ag85b and ppe protein RV3425 from DNA segment rd11 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in C57bl/6 mice[J].Medical Microbiology and Immunology,2009,198(1):5-11.
doi: 10.1007/s00430-008-0098-x |
| 67 | 王瑞. 结核分枝杆菌PPE家族基因Rv3136影响胞壁重塑及其分子机理[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2016. |
| WANG R. The role of Mycobacterium tuberculosis PPE family gene Rv3136 effecting on cell wall remodeling and underlying molecular mechanisms[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2016. (in Chinese) | |
| 68 |
WANGQ,BOSHOFFH I M,HARRISONJ R,et al.Pe/ppe proteins mediate nutrient transport across the outer membrane of Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J].Science,2020,367(6482):1147-1151.
doi: 10.1126/science.aav5912 |
| 69 |
BABU SAITM R,KOLIWER-BRANDLH,STEWARTJ A,et al.Ppe51 mediates uptake of trehalose across the mycomembrane of Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J].Sci Rep,2022,12(1):2097.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06109-7 |
| 70 |
BISWAST,SMALLJ,VANDALO,et al.Structural insight into serine protease RV3671c that protects M. Tuberculosis from oxidative and acidic stress[J].Structure,2010,18(10):1353-63.
doi: 10.1016/j.str.2010.06.017 |
| 71 |
NIROULAN,LIMZ L,WALKERS,et al.Domestic pigs experimentally infected with Mycobacterium bovis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis exhibit different disease outcomes[J].Tuberculosis,2022,133,102167.
doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2022.102167 |
| 72 |
XIONGX,WANGR,DENGD,et al.Comparative genomics of a bovine Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolate and other strains reveals its potential mechanism of bovine adaptation[J].Front Microbiol,2017,8,2500.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02500 |
| [1] | LI Zhenya, LIU Jie, LI Yun, WANG Fei, KONG Yuanyuan, LI Yong, JIA Rongling. Biological Characteristics and Comparative Genomic Analysis of Virulent and Attenuated Strains of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 851-859. |
| [2] | ZHANG Lei, CHEN Liang, FENG Wanyu, LAN Shijie, MIAO Yan, TIAN Qiufeng, BAI Changsheng, ZHANG Bei, DONG Jiaqiang, JIANG Botao, WANG Hongbao, SHI Tongrui, HUANG Xuankai. The Role of Biofilms in the Pathogenesis of Animal Bacterial Infections [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 107-114. |
| [3] | Hengjie CUI, Jinlong QIN, Zhihao ZHU, Xue BAO, Shaowen LI, Xianrong MENG. Correlation Analysis of Benzalkonium Bromide Sensitivity and Biofilm Formation Ability in Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3669-3677. |
| [4] | LONG Tanghui, ZHOU Jianghui, ZHAN Yanbo, ZHANG Jian, ZHAO Xianghui, LI Yanjiao, OUYANG Kehui, QIU Qinghua. Research Progress on LuxS/AI-2 Quorum Sensing of Rumen Microbe in Ruminants [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1893-1903. |
| [5] | HAO Ruochen, TANG Minjia, LIU Guangliang, ZHANG Yan, MUHAMMAD Shoaib, SHANG Ruofeng, CAO Zongxi, PU Wanxia. Distribution and Genotyping of Major Enterobacteriaceae Bacteria in Milk Sources and Dairy Farm Environment of Hainan Province [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5184-5197. |
| [6] | LI Lili, CHEN Kaifeng, CHEN Bing, ZHOU Zhouping, WANG Nanwei, QU Xiaoyun, XU Chenggang, LIAO Ming, ZHANG Jianmin. Regulatory Role of STM1827 in the Biofilm Formation and Environmental Stress of Salmonella Typhimurium [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5207-5217. |
| [7] | WU Zhouhui, WANG Yu, DU Heng, WANG Zhiwen, XIAO Shuang, WU Jinliang, WANG Zhen. Analysis of the Antibacterial Sensitization Activity of Tirapazamine against Multi-Drug Resistant Salmonella [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4362-4371. |
| [8] | MAO Yanni, CHANG Jiawei, LI Na, WANG Xin, KANG Xinyun, MA Qiang, MA Liang, WANG Guiqin. Transcriptome Differential Expression Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus in Biofilm State and Planktonic State [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(8): 2697-2707. |
| [9] | LI Hui, XIONG Jing, MEI Cui, WANG Shiyuan, ZHOU Yang, LI Xiaofen, FU Guihua, ZHANG Yang, CHENG Peng, HE Yuzhang, CHEN Hongwei. The Safety and Stability of the Antimicrobial Peptide CRAMP and Its Role in Eradicating Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 1576-1586. |
| [10] | HE Lüqin, YAN Xuefeng, WEN Xintian, CAO Sanjie, HUANG Xiaobo, WU Rui, ZHAO Qin, WEN Yiping. Construction and Biological Characteristic of Glaesserella parasuis Strain with qseB, qseC Double Gene Deletion [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(2): 529-537. |
| [11] | JIANG Kai, ZHAO Pengyu, WANG Tianshuo, YU Siwen, BI Lan, XIAO Jiawei, HE Xianjing, GUO Donghua. Analysis of Biological Characteristics of Fusobacterium necrophorum 43K OMP Genes Mutant Strain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(11): 4019-4026. |
| [12] | HOU Bo,WANG Chenyan,ZHOU Lunjiang. The Roles and Regulatory Mechanisms of Toxin-antitoxin System in Bacterial Biofilm Formation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(10): 3326-3334. |
| [13] | ZHANG Hang, LI Xinpu, WU Xiaohu, DING Xuezhi, YAN Zuoting, WANG Shengyi, LI Hongsheng. Investigation of Biofilm Formation, Virulence Genes and agr Typing of Staphylococcus aureus from Bovine Mastitis Cases [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(11): 2903-2910. |
| [14] | SONG Jun, XU Ruoyang, JIN Yuqi, CHEN Li, WANG Yuhui, RUAN Hongri, ZHENG Jiasan, WU Rui. Isolation and Identification of Lytic Phages Infecting Proteus mirabilis from Canine-derived and Their Effects on Biofilm [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(11): 2785-2793. |
| [15] | XIAO Yating, FU Dandan, MUHAMMAD AKMAL RAHEEM, XUE Mei, GU Yi, TU Jian, SONG Xiangjun, SHAO Ying, QI Kezong. Study on the Regulation Mechanism of Type Ⅲ Secretion System 2 Transcription Factor YqeI on the Biofilm of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2019, 50(12): 2488-2497. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||