





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (8): 4007-4017.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.08.038
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
GU Rifei1,2( ), ZHANG Siwei1,2(
), ZHANG Siwei1,2( ), ZHAO Zhijie1,2, SONG Weishuo1,2, ZHANG Junming1,2, MA Xiaoru1,2, GAO Yanjun1,2,*(
), ZHAO Zhijie1,2, SONG Weishuo1,2, ZHANG Junming1,2, MA Xiaoru1,2, GAO Yanjun1,2,*( ), BU Shijin1,2,*(
), BU Shijin1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-29
Online:2025-08-23
Published:2025-08-28
Contact:
GAO Yanjun, BU Shijin
E-mail:grfei926@163.com;1335322522@qq.com;820898490@qq.com;sjbo@yzu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
GU Rifei, ZHANG Siwei, ZHAO Zhijie, SONG Weishuo, ZHANG Junming, MA Xiaoru, GAO Yanjun, BU Shijin. Effectiveness Revaluation of Thiamphenicol Powder Oral Dosage Regimen in Chickens Based on PK/PD Model[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 4007-4017.
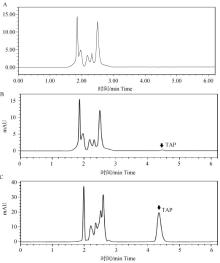
Fig. 1
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) detection of thiamphenicol in chicken plasma samples A. Chromatography of chicken blank plasma; B. Chromatogram of thiamphenicol standard added in chicken blank plasma at LOQ (0.05 μg·mL-1); C. Chromatogram of thiamphenicol in chicken No.2103 plasma sample at 30 minutes after administration; TAP. Chromatogram peak of thiamphenicol"
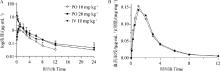
Fig. 2
Correlation curves of thiamphenicol and thiamphenicol powder after single dose administration in chickens A. Thiamphenicol and thiamphenicol powder plasma concentration-time curve after single dose administration in chicken; B. Thiamphenicol plasma concentration-dose ratio-time curve in chicken. The data is represented as "$\bar x \pm s$" (n=10)"
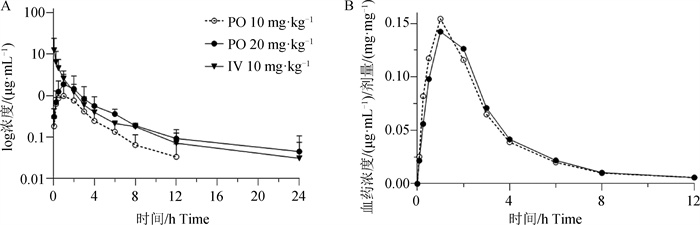
Table 1
PK parameters of thiamphenicol and thiamphenicol powder after single dose administration in chicken ($\bar x \pm s$)"
| 参数 Parameter | 静脉注射Ⅳ | 口服PO | ||
| 10 mg·kg-1 | 10 mg·kg-1 | 20 mg·kg-1 | ||
| Cmax / (μg·mL-1) | / | 1.70±0.27 | 3.36±0.98 | |
| Tmax /h | / | 1.30±0.48 | 1.50±0.53 | |
| AUClast / (μg·h·mL-1) | 13.98±5.57 | 4.73±0.76 | 12.04±3.14 | |
| AUCinf / (μg·h·mL-1) | 14.21±5.69 | 5.01±0.80 | 12.38±3.21 | |
| MRT /h | 1.31±0.55 | 2.45±0.49 | 3.15±1.09 | |
| VC / (mL·kg-1) | 403.63±93.74 | / | / | |
| CL / mL·(kg·h) -1 | 803.11±297.78 | / | / | |
| T1/2Z /h | 1.85±1.20 | 2.25±1.03 | 2.31±1.00 | |
| F /% | / | 33.84±5.43 | 43.08±11.23 | |
| 1 | 国家统计局. 中华人民共和国2023年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[EB/OL]. (2024-02-29)[2024-08-21]. https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202402/t20240228_1947915.html. |
| National Bureau Statistics. Statistical bulletin of the People's Republic of China on 2023 national economic and social development[EB/OL]. (2024-02-29)[2024-08-21]. https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202402/t20240228_1947915.html. (in Chinese) | |
| 2 |
YEHIAN,SALEMH M,MAHMMODY,et al.Common viral and bacterial avian respiratory infections: an updated review[J]. Poult Sci,2023,102(5):102553.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102553 |
| 3 |
XIAOJ,LIY,HUZ,et al.Characterization of Pasteurella multocida isolated from ducks in China from 2017 to 2019[J].Microb Pathog,2021,160,105196.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105196 |
| 4 | 熊诗玉,彭靖挥,蒋红霞,等.禽霍乱诊断与防控[J].养禽与禽病防治,2023(10):2-9. |
| XIONGS Y,PENGJ H,JIANGH X,et al.Diagnosis and control of cholera in poultry[J].Poultry Husbandry and Disease Control,2023(10):2-9. | |
| 5 |
ISLAMM S,RAHMANM T.A comprehensive review on bacterial vaccines combating antimicrobial resistance in poultry[J].Vaccines (Basel),2023,11(3):616.
doi: 10.3390/vaccines11030616 |
| 6 | 林庆华.抗生素在兽医临床应用上的进展[J].福建畜牧兽医,2000(3):39-44. |
| LINQ H.Advances in clinical application of antibiotics in veterinary medicine[J].Fujian Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2000(3):39-44. | |
| 7 | 中国兽药典委员会.中华人民共和国兽药典[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2020. |
| Commission of Chinese Veterinanry Pharmacopoeia.Veterinary pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China[M].Beijing:China Agricultural Press,2020. | |
| 8 | 中国兽药典委员会.兽药质量标准[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2017. |
| Commission of Chinese Veterinanry Pharmacopoeia.Quality standard for veterinary drugs[M].Beijing:China Agricultural Press,2017. | |
| 9 | 吴福林.兽药地方标准升国家标准工作说明[J].农村养殖技术(新兽医),2006(4):43-46. |
| WUF L.Explanation of upgrading local standards to national standards for veterinary drugs[J].Rural Breeding Technology (New Veterinary),2006(4):43-46. | |
| 10 | EUROPEAN MEDICINES AGENCY. Committee for veterinary medicinal products thiamphenicol summery report(2)[R]. The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, 1997. [2024-08-21]. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/mrl-report/thiamphenicol-summary-report-2-committee-veterinary-medicinal-products_en.pdf. |
| 11 |
PALMERM E,ANDREWSL J,ABBEYT C,et al.The importance of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in antimicrobial drug development and their influence on the success of agents developed to combat resistant gram negative pathogens: A review[J]. Front Pharmacol,2022,13,888079.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.888079 |
| 12 | TOUTAINP,PELLIGANDL,LEESP,et al.The pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic paradigm for antimicrobial drugs in veterinary medicine: Recent advances and critical appraisal[J].J Vet Pharmacol Ther,2020,44(2):172-200. |
| 13 |
CHUAH C,TAMV H.Optimizing clinical outcomes through rational dosing strategies: roles of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling tools[J].Open Forum Infect Dis,2022,9(12):ofac626.
doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac626 |
| 14 |
FREIC R,WIEDERHOLDN P,BURGESSD S.Antimicrobial breakpoints for gram-negative aerobic bacteria based on pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models with Monte Carlo simulation[J].J Antimicrob Chemother,2008,61(3):621-628.
doi: 10.1093/jac/dkm536 |
| 15 |
LEWISK.The science of antibiotic discovery[J].Cell,2020,181(1):29-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.056 |
| 16 |
COOKM A,WRIGHTG D.The past, present, and future of antibiotics[J]. Sci Transl Med,2022,14(657):eabo7793.
doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abo7793 |
| 17 | WEIC F,SHIENJ H,CHANGS K,et al.Florfenicol as a modulator enhancing antimicrobial activity: example using combination with thiamphenicol against Pasteurella multocida[J].Front Microbiol,2016,7,389. |
| 18 |
RATTANAPANADDAP,KUOH C,VICKROYT W,et al.In vitro and in vivo synergistic effects of florfenicol and thiamphenicol in combination against swine Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae and Pasteurella multocida[J].Front Microbiol,2019,10,2430.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02430 |
| 19 |
KATSUDAK,HOSHINOOK,UENOY,et al.Virulence genes and antimicrobial susceptibility in Pasteurella multocida isolates from calves[J].Vet Microbiol,2013,167(3-4):737-741.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.09.029 |
| 20 |
IVANCHIKN V,SUKHORUKOVAМ V,CHAGARYANА N,et al.In vitro activity of thiamphenicol against Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes clinical isolates[J].Clin Microbiol Antimicrob Chemother,2021,23(1):92-99.
doi: 10.36488/cmac.2021.1.92-99 |
| 21 |
INAMOTOT,KIKUCHIK,IIJIMAH,et al.Antibacterial activity of tilmicosin against Pasteurella multocida and Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae isolated from pneumonic lesions in Swine[J].J Vet Med Sci,1994,56(5):917-921.
doi: 10.1292/jvms.56.917 |
| 22 | 徐海军,周科伟.某养鸡场禽霍乱分离菌对常用抗菌药物的敏感性研究[J].家畜生态学报,2006(3):86-89. |
| XUH J,ZHOUK W.Medicinal sensitivity test of Pasteurella multocida strain isolated from dead chicken in a hennery[J]. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology,2006(3):86-89. | |
| 23 |
YOSHIMURAH,ISHIMARUM,ENDOHY S,et al.Antimicrobial susceptibility of Pasteurella multocida isolated from cattle and pigs[J].J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health,2001,48(7):555-560.
doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.2001.00468.x |
| 24 | NOED A.Parameter estimation and reporting in noncompartmental analysis of clinical pharmacokinetic data[J].Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev,2020,9(S1):S1-S35. |
| 25 | 陈晓兰,卜仕金.甲砜霉素在鸡体内的药动学[J].中国兽医学报,2008(7):824-827. |
| CHENX L,BUS J.Pharmacokinetics of thiamphenicol in chickens[J].Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science,2008(7):824-827. | |
| 26 | 薛伟芳. 甲砜霉素在健康及多杀性巴氏杆菌感染鸡的药动学[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2008: 37-40. |
| XUE W F. Pharmacokinetics of thiamphenicol in healthy and experimentally infected chickens with Pasteurella multocida[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2008: 37-40. (in Chinese) | |
| 27 | 辛怡霖. 甲砜霉素纳米粒的研制及其在鸡体内的药动学评价[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022, 37-38. |
| XIN Y L. Development and pharmacokinetic evaluation in hens of thiamphenicol nanoparticles[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2022, 37-38. (in Chinese) | |
| 28 | 张丽萍. 甲砜霉素颗粒在鸡体内残留消除规律研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2022, 30-37. |
| ZHANG L P. Study on the elimination of thiamphenicol granules in chickens[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2022, 30-37. (in Chinese) | |
| 29 |
陈超群,陈佳莉,周萱仪,等.β-内酰胺类药物对副猪嗜血杆菌流行病学临界值的建立及耐药性的测定[J].畜牧兽医学报,2021,52(11):3234-3245.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.011.025 |
|
CHENC Q,CHENJ L,ZHOUX Y,et al.Establishment of epidemiological cut-off values and determination of drug resistance of Haemophilus parasuis with β-lactam drugs[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2021,52(11):3234-3245.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.011.025 |
|
| 30 |
ANDERSSOND I,HUGHESD.Microbiological effects of sublethal levels of Antibiotics[J].Nat Rev Microbiol,2014,12(7):465-478.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3270 |
| 31 | European Medicines Agency. Guideline on the use of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in the development of antimicrobial medicinal Products[Z](2016)[2024-08-21]. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-use-pharm-acokinetics-andpharmacodynamics-development-anti-microbial-medicinal-products_en.pdf. |
| 32 | 国家食品药品监督管理局. 抗菌药物药代动力学/药效学研究技术指导原则[EB/OL]. (2017-08-21)[2024-08-21]. wzx https://www.nmpa.gov.cn/xxgk/ggtg/ypggtg/ypqtggtg/20170821170301371.html. |
| National Medical Products Administration. Technical guidelines for pharmacokinetics pharmacodynamic studies of antimicrobials[EB/OL]. (2017-08-21)[2024-08-21]. https://www.nmpa.gov.cn/xxgk/ggtg/ypggtg/ypqtggtg/20170821170301371.html(in Chinese) | |
| 33 |
ANDESD,CRAIGW A.Animal model pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: A critical Review[J].Int J Antimicrob Agents,2002,19(4):261-268.
doi: 10.1016/S0924-8579(02)00022-5 |
| 34 |
DOREYL,PELLIGANDL,CHENGZ,et al.Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic integration and modelling of florfenicol for the pig pneumonia pathogens Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae and Pasteurella Multocida[J].PLoS One,2017,12(5):e0177568.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177568 |
| 35 |
XIAOX,LANW,ZHAOY,et al.In vivo pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) modeling and establishment of the PK/PD cutoff of florfenicol against Pasteurella multocida in ducks[J]. Front Microbiol,2021,11,616685.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.616685 |
| 36 | 胡功政,苑丽,刘智明,等.氟苯尼考及其与多西环素联合的体外抗菌作用[J].中国兽医学报,2004(4):379-383. |
| HUG Z,YUANL,LIUZ M,et al.Antibacterial activity of florfenicol and it's combinations with doxycycline in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science,2004(4):379-383. | |
| 37 | ASHRAF M. The pharmacokinetics and the mechanism of renal excretion of thiamphenicol in cattle[D]. University of Minnesota, 1989. |
| 38 | 谢恺舟,张小杰,陈学森,等.甲砜霉素在鸡肌肉中的残留消除规律[J].畜牧兽医学报,2012,43(7):1150-1155. |
| XIEG Z,ZHANGX J,CHENX S,et al.Thiamphenicol residue depletion in chicken muscle[J].Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2012,43(7):1150-1155. | |
| 39 | 卢运战. 鸡组织中甲砜霉素和氟苯尼考残留的检测方法及消除规律[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2007, 22-23. |
| LU Y Z. The determination method of thiamphenicol and florfenicol residues and their elimination in chicken tissues. [D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2007, 22-23. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | MA Caiping, ZHU Yao, LIU Hongdao, ZHOU Guangbin, XU Qiu, LIN Longhua, CHAI Jiyun, HOU Jie, SUN Hongfei, DU Susu, FAN Cuilong, XIA Lining, ZHANG Wanjiang. Typing and Antimicrobial Resistance Analysis of Thirty-four Pasteurella multocida Strains from Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 4074-4085. |
| [2] | WANG Jinxiang, SU Jinbo, FU Huanru, SUN Shikun, GAO Chengfang, CHEN Dongjin, SANG Lei, XIE Xiping. Pathogenicity and Genomic Features of Rabbit Sourced Serogroup A Pasteurella multocida Isolates Pm3 and Pm6 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2340-2352. |
| [3] | Bohua LIU, Hanyu FU, Yuheng WANG, Suolangsizhu, Jiaqiang NIU, Yuhua BAO, Jiakui LI, Yefen XU. Isolation, Identification and Genome Analysis of Type B Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Yak in Tibetan Nakchu City [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3105-3118. |
| [4] | YANG Rongrong, ZHANG Ting, TANG Pingping, HE Shuangfang, ZHAO Miaomiao, LEI Liancheng, ZHANG Fuxian. Analysis of Drug Resistance and Pathogenicity of Metallo-β-Lactamase-producing Porcine ST201 Pasteurella multocida [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5692-5705. |
| [5] | Xiangxiang SHEN, Lijun GUAN, Junfeng ZHANG, Yun XUE, Lifang SI, Zhanqin ZHAO. Research Progress on Iron Uptake Mechanism of Pasteurella multocida [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 4852-4862. |
| [6] | GAO Yanjun, WANG Meihong, NIE Ya, WANG Zhen, BU Shijin. Reevaluation of the Efficacy of Enrofloxacin Soluble Powder Mixed Drink Administration Regimen in Chicken by Modelling of Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Data [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 3199-3207. |
| [7] | XU Wenbo, WU Limei, LIU Xin, LI Sheng, HUANG Fushen, LI Runcheng. Analysis on Complete Genome Sequence and Pathogenic Genes of a Pasteurella multocida Strain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(6): 1858-1869. |
| [8] | WANG Fei, YANG Jie, Lü Qingjie, WANG Mixue, LIU Peng, ZHANG Ruoyu, SHI Congcong, WANG Xueying, LIN Lin, HUA Lin, SONG Wenbo, LIANG Wan, CHEN Huanchun, WU Bin, PENG Zhong. Isolation and Genomic Characterization of a Meningitis Causing Pasteurella multocida [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(12): 4346-4355. |
| [9] | YANG Yang, XIE Liqing, HU Pei, GAO Lixu, YUAN Xiang, LI Pan, PENG Yuanyi, LI Nengzhang. Construction of Bovine Pasteurella multocida Type A hyaD Mutant and Its Cross-protection Analysis in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(10): 3582-3597. |
| [10] | LI Tian, YANG Yang, XIE Liqing, WANG Yuanlan, LI Pan, PENG Yuanyi, LI Nengzhang. Study on the Immunoprotection of Inactivated Vaccine of Bovine Mannheimia haemolytica and Bovine Pasteurella multocida Capsular Serotype A in Mouse Model [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(9): 2579-2588. |
| [11] | ZHANG Yanan, LI Yafei, CHEN Rujia, YU Bo, PENG Shan, LI Ting, PU Ling, XU Jinge. Resistance and Virulence Analysis of Type A: L1 ST128 Pasteurella multocida from Ducks [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(10): 2852-2863. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||