





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (9): 3864-3875.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.09.012
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuhang JIA1,2( ), Liangfu GUO3, Runan ZHANG1, Ayong ZHAO2, Yufang LIU1,*(
), Liangfu GUO3, Runan ZHANG1, Ayong ZHAO2, Yufang LIU1,*( ), Mingxing CHU1,*(
), Mingxing CHU1,*( )
)
Received:2024-03-04
Online:2024-09-23
Published:2024-09-27
Contact:
Yufang LIU, Mingxing CHU
E-mail:15645551808@163.com;aigaiy@126.com;mxchu@263.net
CLC Number:
Yuhang JIA, Liangfu GUO, Runan ZHANG, Ayong ZHAO, Yufang LIU, Mingxing CHU. miR-127 Regulated the Proliferation and Differentiation of Sheep Skeletal Myoblasts and Its Transcription Factor PAX3 Screening[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3864-3875.
Table 2
Sequences of RT-qPCR primers"
| 基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID GenBank ID | 序列(5′→3′) Sequence | 产物大小/bp Product size |
| PCNA | XM_004014340.5 | F: TGCAGATGTACCCCTTGTGTGT R: CATCCTCGATCTTGGGAGCC | 83 |
| CDK4 | XM_012158548.4 | F: CAGTGTACAAGGCCCGTGAT R: GACGTCCATGAGCCTGACAA | 176 |
| BAX | XM_027978592.3 | F: GCCCTTTTGCTTCAGGGTTTC R: TCGGAAAACATTTCAGCCGC | 236 |
| Caspase3 | XM_060406953.1 | F: CCAGGAGTGGAATCCAGCAG R: CGACAGGCCATGCCAGTATT | 250 |
| MYOD1 | NM_001009390.1 | F: TGCACGTCTAGCAACCCAAA R: GCTGTAGTCCATCATGCCGT | 240 |
| MYHC | XM_004010325.3 | F: TCGTCAAGGCCACAATTTG R: CTGCTGCAACACCTGGTCCT | 101 |
| β-actin | XM_060405599.1 | F: CTTCCAGCCTTCCTTCCTGG R: GGGGCGCGATGATCTTGA | 215 |
| miR-127 | - | F: CCGATCGGATCGTCTGAGCTTGGCT R: 通用引物 | |
| U6 | - | F: CAAGGATGACACGCAAATTCG R: 通用引物 |
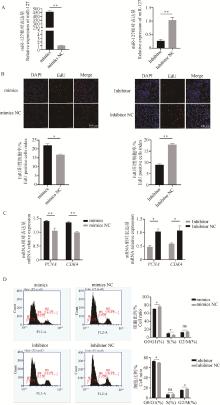
Fig. 2
miR-127 promoted myoblast proliferation A. miR-127 overexpression and inhibitor plasmids transfection efficiency assays; B. Proliferation rate of sheep myoblasts by EdU detection after miR-127 overexpression or inhibition, scale bar=100 μm (20×); C. Detection of the expression levels of proliferation marker genes in sheep myoblasts after miR-127 overexpression or inhibition; D. Analysis of sheep myoblast cycle after miR-127 overexpression or inhibition. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, the same as below"


Fig. 4
Effect of miR-127 on myoblast differentiation A. Detection of myotubular generation number and area, scale bar=200 μm (20×); B. Immunofluorescence detection of MYHC expression in myoblast, scale bar=100 μm (20×); C. MYHC relative fluorescence intensity; D. Detection of the expression levels of myoblast differentiation marker genes MYOD1 and MYHC"
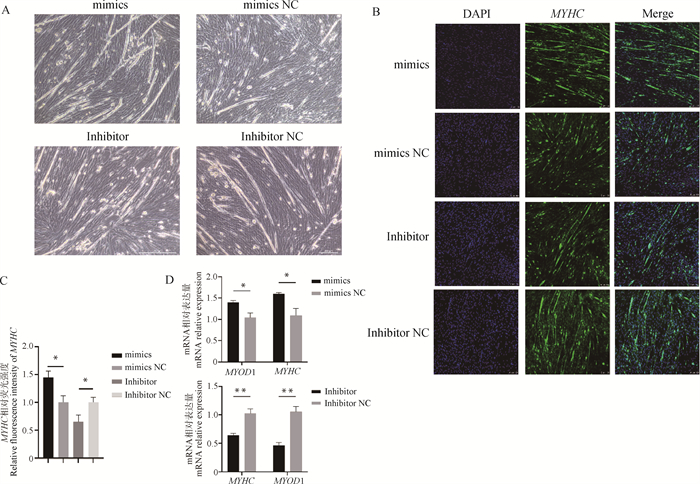

Fig. 5
Identification of the core promoter region of sheep miR-127 and prediction of transcription factor binding sites A. Relative luciferase activity of the truncated vectors of sheep miR-127 promoter region; B. Sequence of the core promoter region of sheep miR-127 (underlined sequences represent the binding sites of PAX3)"

| 1 | 康国磊, 王净, 王红娜, 等. 肌肽的生理作用及其在畜禽生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2022, 58 (9): 58- 62. |
| KANG G L , WANG J , WANG H N , et al. Research progress on physiological role of carnosine and its application in livestock and poultry production[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2022, 58 (9): 58- 62. | |
| 2 |
CHEN P R , LEE K . Invited review: inhibitors of myostatin as methods of enhancing muscle growth and development[J]. J Anim Sci, 2016, 94 (8): 3125- 3134.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2016-0532 |
| 3 |
HERNÁNDEZ-HERNÁNDEZ J M , GARCÍA-GONZÁLEZ E G , BRUN C E , et al. The myogenic regulatory factors, determinants of muscle development, cell identity and regeneration[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2017, 72, 10- 18.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.11.010 |
| 4 |
UMANSKY K B , GRUENBAUM-COHEN Y , TSOORY M , et al. Runx1 transcription factor is required for myoblasts proliferation during muscle regeneration[J]. PLoS Genet, 2015, 11 (8): e1005457.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005457 |
| 5 |
LI Y Y , CHEN X N , SUN H , et al. Long non-coding RNAs in the regulation of skeletal myogenesis and muscle diseases[J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 417, 58- 64.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.12.015 |
| 6 |
HERKENHOFF M E , OLIVEIRA A C , NACHTIGALL P G , et al. Fishing into the microRNA transcriptome[J]. Front Genet, 2018, 9, 88.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00088 |
| 7 |
SORIANO-ARROQUIA A , MCCORMICK R , MOLLOY AP , et al. Age-related changes in miR-143-3p: Igfbp5 interactions affect muscle regeneration[J]. Aging Cell, 2016, 15 (2): 361- 369.
doi: 10.1111/acel.12442 |
| 8 |
ZHANG D H , RAN J S , LI J J , et al. miR-21-5p regulates the proliferation and differentiation of skeletal muscle satellite cells by targeting KLF3 in chicken[J]. Genes (Basel), 2021, 12 (6): 814.
doi: 10.3390/genes12060814 |
| 9 |
NGUYEN M T , LEE W . MiR-320-3p regulates the proliferation and differentiation of myogenic progenitor cells by modulating actin remodeling[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (2): 801.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23020801 |
| 10 |
ZHU Y , LI P , DAN X G , et al. miR-377 inhibits proliferation and differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by targeting FHL2[J]. Genes (Basel), 2022, 13 (6): 947.
doi: 10.3390/genes13060947 |
| 11 |
ZHANG W , WANG S Y , DENG S Y , et al. MiR-27b promotes sheep skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation by targeting myostatin gene[J]. J Genet, 2018, 97 (5): 1107- 1117.
doi: 10.1007/s12041-018-0998-5 |
| 12 |
GONNOT F , LANGER D , BOURILLOT P Y , et al. Regulation of cyclin E by transcription factors of the naïve pluripotency network in mouse embryonic stem cells[J]. Cell Cycle, 2019, 18 (20): 2697- 2712.
doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1656475 |
| 13 |
HOLSTEIN I , SINGH A K , POHL F , et al. Post-transcriptional regulation of MRTF-A by miRNAs during myogenic differentiation of myoblasts[J]. Nucl Acids Res, 2020, 48 (16): 8927- 8942.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa596 |
| 14 | KOUTALIANOS D , KOUTSOULIDOU A , MASTROYIANNOPOULOS N P , et al. MyoD transcription factor induces myogenesis by inhibiting Twist-1 through miR-206[J]. J Cell Sci, 2015, 128 (19): 3631- 3645. |
| 15 | MOK G F , LOZANO-VELASCO E , MANIOU E , et al. miR-133-mediated regulation of the Hedgehog pathway orchestrates embryo myogenesis[J]. Development, 2018, 145 (12): dev159657. |
| 16 |
ZHU M H , CHEN G , YANG Y , et al. miR-217-5p regulates myogenesis in skeletal muscle stem cells by targeting FGFR2[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 22 (2): 850- 858.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11133 |
| 17 |
PODKALICKA P , MUCHA O , BRONISZ-BUDZYŃSKA I , et al. Lack of miR-378 attenuates muscular dystrophy in mdx mice[J]. JCI Insight, 2020, 5 (11): e135576.
doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.135576 |
| 18 |
WANG K M , LIUFU S , YU Z G , et al. miR-100-5p regulates skeletal muscle myogenesis through the Trib2/mTOR/S6K signaling pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (10): 8906.
doi: 10.3390/ijms24108906 |
| 19 |
ZHAI L L , WU R M , HAN W H , et al. miR-127 enhances myogenic cell differentiation by targeting S1PR3[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8 (3): e2707.
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.128 |
| 20 |
DE SOUSA M C , GJORGJIEVA M , DOLICKA D , et al. Deciphering miRNAs' action through miRNA editing[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20 (24): 6249.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20246249 |
| 21 |
SU J L , CHEN P S , JOHANSSON G , et al. Function and regulation of let-7 family microRNAs[J]. MicroRNA, 2012, 1 (1): 34- 39.
doi: 10.2174/2211536611201010034 |
| 22 |
FABIAN M R , SONENBERG N , FILIPOWICZ W . Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs[J]. Annu Rev Biochem, 2010, 79, 351- 379.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060308-103103 |
| 23 |
ZAMMIT P S . Function of the myogenic regulatory factors Myf5, MyoD, Myogenin and MRF4 in skeletal muscle, satellite cells and regenerative myogenesis[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2017, 72, 19- 32.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.11.011 |
| 24 |
LIANG H Y , WARD W F . PGC-1α: a key regulator of energy metabolism[J]. Adv Physiol Educ, 2006, 30 (4): 145- 151.
doi: 10.1152/advan.00052.2006 |
| 25 |
JIANG Y , QIAN H Y . Transcription factors: key regulatory targets of vascular smooth muscle cell in atherosclerosis[J]. Mol Med, 2023, 29 (1): 2.
doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00586-2 |
| 26 |
TAYLOR D F , BISHOP D J . Transcription factor movement and exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis in human skeletal muscle: current knowledge and future perspectives[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (3): 1517.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23031517 |
| 27 |
ARORA S , RANA R , CHHABRA A , et al. miRNA-transcription factor interactions: a combinatorial regulation of gene expression[J]. Mol Genet Genomics, 2013, 288 (3-4): 77- 87.
doi: 10.1007/s00438-013-0734-z |
| 28 |
ASHRAFIZADEH M , ZARRABI A , OROUEI S M , et al. Interplay between SOX9 transcription factor and microRNAs in cancer[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 183, 681- 694.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.185 |
| 29 |
DODD R D , SACHDEVA M , MITO J K , et al. Myogenic transcription factors regulate pro-metastatic miR-182[J]. Oncogene, 2016, 35 (14): 1868- 1875.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.252 |
| 30 |
DU Y , ZHAO Y , WANG Y , et al. MiR-25-3p regulates the differentiation of intramuscular preadipocytes in goat via targeting KLF4[J]. Arch Anim Breed, 2021, 64 (1): 17- 25.
doi: 10.5194/aab-64-17-2021 |
| 31 |
SKRZYPEK K , NIESZPOREK A , BADYRA B , et al. Enhancement of myogenic differentiation and inhibition of rhabdomyosarcoma progression by miR-28-3p and miR-193a-5p regulated by SNAIL[J]. Mol Ther Nucl Acids, 2021, 24, 888- 904.
doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.04.013 |
| 32 |
CHANDY M , ISHIDA M , SHIKATANI E A , et al. c-Myb regulates transcriptional activation of miR-143/145 in vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13 (8): e0202778.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202778 |
| 33 | GUY J L, MOR G G. Transcription factor-binding site identification and enrichment analysis[M]//ALVERO A B, MOR G G. Detection of Cell Death Mechanisms: Methods and Protocols. New York: Humana, 2021: 241-261. |
| 34 |
NAVET S , BURESI A , BARATTE S , et al. The Pax gene family: highlights from cephalopods[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12 (3): e0172719.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172719 |
| 35 |
LAGHA M , KORMISH J D , ROCANCOURT D , et al. Pax3 regulation of FGF signaling affects the progression of embryonic progenitor cells into the myogenic program[J]. Genes Dev, 2008, 22 (13): 1828- 1837.
doi: 10.1101/gad.477908 |
| 36 |
MAGLI A , SCHNETTLER E , RINALDI F , et al. Functional dissection of Pax3 in paraxial mesoderm development and myogenesis[J]. Stem Cells, 2013, 31 (1): 59- 70.
doi: 10.1002/stem.1254 |
| 37 |
MESSINA G , SIRABELLA D , MONTEVERDE S , et al. Skeletal muscle differentiation of embryonic mesoangioblasts requires Pax3 activity[J]. Stem Cells, 2009, 27 (1): 157- 164.
doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2008-0503 |
| 38 |
AZHAR M , WARDHANI B W K , RENESTEEN E . The regenerative potential of Pax3/Pax7 on skeletal muscle injury[J]. J Genet Eng Biotechnol, 2022, 20 (1): 143.
doi: 10.1186/s43141-022-00429-x |
| [1] | GONG Yiming, JIA Yixuan, LI Jiajun, WANG Xiangyu, HE Xiaoyun, CHU Mingxing, DI Ran. BMP/SMAD Pathway Activity and Protein Expression Profiles in Ovarian Follicles with Different Diameters in Diverse FecB Genotyped Ewes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3957-3967. |
| [2] | Peng SHEN, Yi WANG, Weijie REN, Yongchun YANG, Houhui SONG, Zhiliang WANG. Meta Analysis of Immune Antibody Monitoring for Lumpy Skin Disease [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3649-3658. |
| [3] | Ting WANG, Yuanqing ZHANG, Yibo YAN, Mingjun SHANGGUAN, Hongyu GUO, Zhiwu WANG. The Genetic Structure Analysis and the Comparative Analysis of Selection Signals in 'Tezanghan' Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2913-2926. |
| [4] | Mingliang HE, Xiaoyang LÜ, Yongqing JIANG, Zhenghai SONG, Yeqing WANG, Huiguo YANG, Shanhe WANG, Wei SUN. Function Analysis of SOX18 in Hu Sheep Hair Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells Based on Transcriptome Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2409-2420. |
| [5] | Chang LIU, Kexing HAO, Yan CHEN, Weibin ZENG, Hengbin YU, Lei CHEN, Jing WANG, Guangdong HU. Effects of Interference with PPARγ Gene on Proliferation, Apoptosis, Migration and Lipid Accumulation of Trophoblast Cells in Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2421-2430. |
| [6] | Ying CHEN, Dayong CHEN, Riga WU, Chunjuan QIU, Lihong FAN, Meirong BAO, Yuan YUE, Hongyan LIANG, Jiaxin ZHANG, Jianhui TIAN, Lei AN, Liqin WANG. Influence of Meat Sheep Varieties on the Scale Application of in vitro Embryo Production Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2451-2459. |
| [7] | Zhibin LUO, Huimin OU, Jianzhong LI, Zhiliang TAN, Jinzhen JIAO. Effects of Low Protein Diet Supplemented with Rumen-protected Amino Acids on Growth Performance, Nutrient Apparent Digestibility and Meat Quality of Hulun Buir Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2498-2509. |
| [8] | PENG Peiya, CHEN Yuhan, YANG Long, WANG Ming, ZHAO Ruiting, HE Jun, YIN Yulong, LIU Mei. Research Progress of Copy Number Variation in Livestock [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1356-1369. |
| [9] | ZHANG Shaohua, WANG Shuai, ZOU Yang, LIU Zhongli, CAI Xuepeng. Advances in Detection Approaches for Ovine Haemonchosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1499-1510. |
| [10] | YANG Yang, YU Qian, LIU Yucheng, YANG Hua, ZHAO Zhuo, WANG Limin, ZHOU Ping, YANG Qingyong, DAI Rong. Identification and Tissue Expression Analysis of the Sheep MYL Gene Family [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1551-1564. |
| [11] | CHANG Xindan, HU Fan, WU Zhiwu, YE Bingsen, LIU Tiehai, LIN Jie, HE Zhixiong, TAN Zhiliang. Effect of High Proportion Rumen Bypass Fat Diet on Feeding Behavior of Growing Mutton Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1077-1084. |
| [12] | GAO Hui, FANG Min, JIANG Lingling, MA Yaoyu, LIU Qiang, ZHANG Gang, NIU Xiaoxia, WANG Pu, LI Yong, ZHANG Sinong. Meta-analysis of Bluetongue Virus Prevalence in Sheep Flocks in China from 2012—2022 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 706-717. |
| [13] | WANG Haibo, ZHAN Jinshun, GU Zhiyong, CHEN Xinfeng, PAN Yue, JIA Haobin, ZHONG Xiaojun, LI Kairong, ZHAO Shengguo, HUO Junhong. Comparative Study on Meat Quality Characteristics of Three-Way Hybrid Sheep Charolais×Duper×Hu and Charolais×Australian White×Hu and Hu Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 110-119. |
| [14] | DUAN Xiangru, KANG Jia, YANG Ruochen, SHAN Xinyu, LI Taichun, ZHAO Wen, ZHANG Yingjie, LIU Yueqin. Effect of L-cysteine on Proliferation, Apoptosis and the Secretion of Steroid Hormone in Ovine Ovarian Granulosa Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 179-191. |
| [15] | ZHANG Hanyue, ZHAO Dan, LIANG Yu, ZHAO Bishi, FAN Mengdan, QIAO Liying, LIU Jianhua, YANG Kaijie, PAN Yangyang, LIU Wenzhong. miR-150 Regulates Ovine Preadipocyte Differentiation by Targeting AOC3 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3262-3274. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||