





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (9): 3978-3987.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.09.022
• Animal Biotechnology and Reproduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yi WANG( ), Jianfei GONG, Nuo HENG, Yingfan HU, Rui WANG, Huan WANG, Ni ZHU, Wei HE, Zhihui HU, Haisheng HAO, Huabin ZHU, Shanjiang ZHAO*(
), Jianfei GONG, Nuo HENG, Yingfan HU, Rui WANG, Huan WANG, Ni ZHU, Wei HE, Zhihui HU, Haisheng HAO, Huabin ZHU, Shanjiang ZHAO*( )
)
Received:2024-03-05
Online:2024-09-23
Published:2024-09-27
Contact:
Shanjiang ZHAO
E-mail:yiwang86@hotmail.com;zhaoshanjiang@caas.cn
CLC Number:
Yi WANG, Jianfei GONG, Nuo HENG, Yingfan HU, Rui WANG, Huan WANG, Ni ZHU, Wei HE, Zhihui HU, Haisheng HAO, Huabin ZHU, Shanjiang ZHAO. Melatonin Alleviates Palmitic Acid-induced Damage in Bovine Endometrial Epithelial Cells by Improving Mitochondrial Dynamics[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3978-3987.
Table 1
Primers in formation sequence of qRT-PCR"
| 引物名称 Primer name | GenBank accession No. | 引物序列(5′→3′) Sequence | 产物长度/bp PCR size |
| β-Actin-Forward | NM_173979.3 | GCCCTGAGGCTCTCTTCCA | 101 |
| β-Actin-Reverse | GCGGATGTCGACGTCACA | ||
| MFN1-Forward | NM_001206508.1 | GAAAGCTGGGTGTCTTGTGC | 93 |
| MFN1-Reverse | TCTGTGCCCGGACTGTCTA | ||
| DRP1-Forward | NM_001046494.2 | GGCTGGGGTCTTGTGTGTTA | 141 |
| DRP1-Reverse | TCTTTCCACTGCTCTGCGTT | ||
| PGC1-α-Forward | NM_177945.3 | GACCACAAATGATGACCCTC | 90 |
| PGC1-α-Reverse | TGGTTTGGCTTGTAGATGTT |
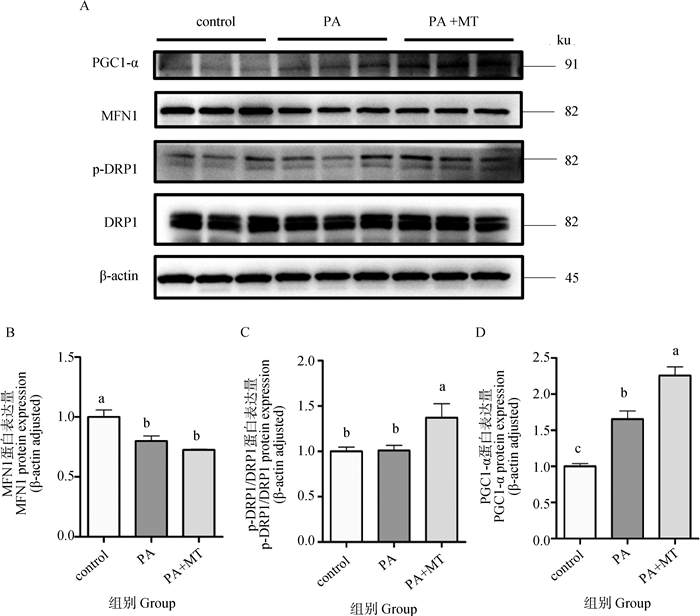
Fig. 6
The effect of melatonin on PA-induced mitochondrial dynamics-related proteins expression in BEECs A. The protein band plots of MFN1, p-DRP1/DRP1, PGC1-α, and β-actin in control, PA, and melatonin groups; B-D. The results of the analysis of protein expression of MFN1, p-DRP1/DRP1, and PGC1-α"
| 1 |
CASANOVA N , BEAULIEU K , FINLAYSON G , et al. Metabolic adaptations during negative energy balance and their potential impact on appetite and food intake[J]. Proc Nutr Soc, 2019, 78 (3): 279- 289.
doi: 10.1017/S0029665118002811 |
| 2 |
KRNJAIĆ S , CINCOVIĆ M , DJOKOVIĆ R , et al. The influence of energy balance, lipolysis and ketogenesis on metabolic adaptation in cows milked twice and three times daily[J]. Metabolites, 2022, 12 (11): 1090.
doi: 10.3390/metabo12111090 |
| 3 | 宋玉锡. 能量负平衡对奶牛泌乳早期繁殖性能和卵泡发育的影响[D]. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2020. |
| SONG Y X. Effects of negative energy balance on reproductive performance and follicular development during early lactation in dairy cows[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 4 |
CHANKEAW W , GUO Y Z , BÅGE R , et al. Elevated non-esterified fatty acids impair survival and promote lipid accumulation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in bovine endometrial epithelial cells[J]. Reprod Fertil Dev, 2018, 30 (12): 1770- 1784.
doi: 10.1071/RD17537 |
| 5 |
FERST J G , GLANZNER W G , GUTIERREZ K , et al. Supplementation of oleic acid, stearic acid, palmitic acid and β-hydroxybutyrate increase H3K9me3 in endometrial epithelial cells of cattle cultured in vitro[J]. Anim Reprod Sci, 2021, 233, 106851.
doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2021.106851 |
| 6 |
MEKURIAW Y . Negative energy balance and its implication on productive and reproductive performance of early lactating dairy cows: review paper[J]. J Appl Anim Res, 2023, 51 (1): 220- 228.
doi: 10.1080/09712119.2023.2176859 |
| 7 |
TIWARY S , NANDWANI A , KHAN R , et al. GRP75 mediates endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria coupling during palmitate-induced pancreatic β-cell apoptosis[J]. J Biol Chem, 2021, 297 (6): 101368.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101368 |
| 8 |
WANG X H , ZHU M Y , LOOR J J , et al. Propionate alleviates fatty acid-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and apoptosis by upregulating PPARG coactivator 1 alpha in hepatocytes[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2022, 105 (5): 4581- 4592.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-21198 |
| 9 |
LI Y , DING H Y , LIU L H , et al. Non-esterified fatty acid induce dairy cow hepatocytes apoptosis via the mitochondria-mediated ROS-JNK/ERK signaling pathway[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8, 245.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00245 |
| 10 |
VEZZA T , DÍAZ-POZO P , CANET F , et al. The role of mitochondrial dynamic dysfunction in age-associated type 2 diabetes[J]. World J Men's Health, 2022, 40 (3): 399- 411.
doi: 10.5534/wjmh.210146 |
| 11 |
CHIU Y H , LIN S C A , KUO C H , et al. Molecular machinery and pathophysiology of mitochondrial dynamics[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9, 743892.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.743892 |
| 12 |
GIACOMELLO M , PYAKUREL A , GLYTSOU C , et al. The cell biology of mitochondrial membrane dynamics[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21 (4): 204- 224.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0210-7 |
| 13 |
WANG J X , WU J N , LI W J , et al. Linking mitochondrial function to insulin resistance: focusing on comparing the old and the young[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9, 892719.
doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.892719 |
| 14 |
CHEN D , LI X , ZHANG L T , et al. A high-fat diet impairs mitochondrial biogenesis, mitochondrial dynamics, and the respiratory chain complex in rat myocardial tissues[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018, 119 (11): 9602.
doi: 10.1002/jcb.27068 |
| 15 |
HUANG A , SANCHES D . Abstract 4853:evaluating the role of melatonin in thyroid cancer cell (MDA-T41) apoptosis and metabolism modulation[J]. Cancer Res, 2023, 83 (7_Supplement): 4853.
doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2023-4853 |
| 16 |
KOPUSTINSKIENE D M , BERNATONIENE J . Molecular mechanisms of melatonin-mediated cell protection and signaling in health and disease[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13 (2): 129.
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020129 |
| 17 |
ZHU Q , DING D , YANG H , et al. Melatonin protects mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative damage against the decline of human oocytes development caused by prolonged cryopreservation[J]. Cells, 2022, 11 (24): 4018.
doi: 10.3390/cells11244018 |
| 18 |
NASONI M G , CARLONI S , CANONICO B , et al. Melatonin reshapes the mitochondrial network and promotes intercellular mitochondrial transfer via tunneling nanotubes after ischemic-like injury in hippocampal HT22 cells[J]. J Pineal Res, 2021, 71 (1): e12747.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12747 |
| 19 |
AGIL A , CHAYAH M , VISIEDO L , et al. Melatonin improves mitochondrial dynamics and function in the kidney of zücker diabetic fatty rats[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9 (9): 2916.
doi: 10.3390/jcm9092916 |
| 20 | 王盼. 褪黑素对Aβ1-42介导AD模型保护作用的研究[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2020. |
| WANG P. Protective effect of melatonin in Aβ1-42 induced AD model[D]. Shenyang: China Medical University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 21 | 郭攀. 褪黑素保护镉暴露所致肝毒性效应的机制探讨[D]. 重庆: 第三军医大学, 2015. |
| GUO P. The mechanism study of protection effect of melatonin in cadmium induced hepatotoxicity[D]. Chongqing: Third Military Medical University of Chinese, 2015. (in Chinese) | |
| 22 | SUN B J , CHEN M H , ZHANG W H , et al. Palmitic acid induces GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis in periodontal ligament cells via the NF-κB pathway[J]. Oral Dis, 2023, 30 (4): 2546- 2557. |
| 23 |
KONAR S , HEDGES C P , CALLON K E , et al. Palmitic acid reduces viability and increases production of reactive oxygen species and respiration in rat tendon-derived cells[J]. bioRxiv, 2023,
doi: 10.1101/2023.02.08.527761 |
| 24 |
CHU S G , VILLALBA J A , LIANG X L , et al. Palmitic acid-rich high-fat diet exacerbates experimental pulmonary fibrosis by modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2019, 61 (6): 737- 746.
doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0324OC |
| 25 |
CHOROSZY M , S'RODA-POMIANEK K , WAWRZYN'SKA M , et al. The role of palmitic acid in the co-toxicity of bacterial metabolites to endothelial cells[J]. Vasc Health Risk Manag, 2023, 19, 399- 409.
doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S408897 |
| 26 |
BRONIAREK I , KOZIEL A , JARMUSZKIEWICZ W . The effect of chronic exposure to high palmitic acid concentrations on the aerobic metabolism of human endothelial EA.hy926 cells[J]. Pflügers Arch-Eur J Physiol, 2016, 468 (9): 1541- 1554.
doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1856-z |
| 27 | MERHAN O. Biochemistry and antioxidant effects of melatonin[M]//GELEN V, ŞENGÜL E, KÜKÜRT A. Melatonin-Recent Updates. Rijeka: IntechOpen. 2022: Ch. 3. |
| 28 |
JOSEPH T J , SCHUCH V , HOSSACK D J , et al. Melatonin: the placental antioxidant and anti-inflammatory[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15, 1339304.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1339304 |
| 29 |
RUBIO-GONZÁLEZ A , REITER R J , DE LUXÁN-DELGADO B , et al. Pleiotropic role of melatonin in brain mitochondria of obese mice[J]. Melatonin Res, 2020, 3 (4): 538- 557.
doi: 10.32794/mr11250078 |
| 30 |
AGIL A , NAVARRO-ALARCON M , ALI F A Z , et al. Melatonin enhances the mitochondrial functionality of brown adipose tissue in obese—diabetic rats[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2021, 10 (9): 1482.
doi: 10.3390/antiox10091482 |
| 31 |
CHENG C T , KUO C Y , OUYANG C N , et al. Metabolic stress-induced phosphorylation of KAP1 Ser473 blocks mitochondrial fusion in breast cancer cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2016, 76 (17): 5006- 5018.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2921 |
| 32 |
KNOTT A B , PERKINS G , SCHWARZENBACHER R , et al. Mitochondrial fragmentation in neurodegeneration[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2008, 9 (7): 505- 518.
doi: 10.1038/nrn2417 |
| 33 |
DING M G , FENG N , TANG D S , et al. Melatonin prevents Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission in diabetic hearts through SIRT1-PGC1α pathway[J]. J Pineal Res, 2018, 65 (2): e12491.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12491 |
| 34 |
CHEN W R , ZHOU Y J , SHA Y , et al. Melatonin attenuates vascular calcification by inhibiting mitochondria fission via an AMPK/Drp1 signalling pathway[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24 (11): 6043- 6054.
doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15157 |
| 35 | CHANG J Y A , YU F , SHI L H , et al. Melatonin affects mitochondrial fission/fusion dynamics in the diabetic retina[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2019, 2019, 8463125. |
| 36 | HU B , CHEN Z J , LIANG L L , et al. Melatonin promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial degradation in hepatocytes during sepsis[J]. Altern Ther Health Med, 2023, 29 (7): 284- 289. |
| [1] | 古丽米热·阿布都热依木, Xinru ZHANG, Yangsheng WU, Ying CHEN, Liqin WANG, Xinming XU, Juncheng HUANG, Jiapeng LIN. Effects of FKBP5 on Function of Sheep Follicular Granulosa Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3947-3956. |
| [2] | Zenghua LU, Yan CUI, Sijiu YU, Xuefeng BAI, Hongqin LU, Junfeng HE, Kai LU, Guoliang ZHAI, Zhengman QI. Effect of Erythropoietin on the Expression of Apoptotic Factor in Yak Renal Interstitial Fibroblasts [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3460-3471. |
| [3] | Zuhua YU, Mengru GAO, Lei HE, Ying WEI, Jian CHEN, Songbiao CHEN, Ke DING. Effects of mdv1-miR-M4-5p Encoded by MDV on Proliferation and Apoptosis of MDCC-MSB1 Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3678-3687. |
| [4] | Milan MA, Qi WANG, Qiu YAN, Tianan LI, Xingxu ZHAO, Yong ZHANG. Expression of HIG1 Hypoxia Inducible Domain Family Member 1C in Cryptorchidism of Yak and Its Regulatory Mechanism [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2983-2994. |
| [5] | Jinting LUO, Fafang XU, Lei WANG, Xuan LUO, Yuhong MA, Jianbo ZHANG, Weihua HUANG, Yuejun SHANG, Guofang WU. The Effect of RSP on Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis of Porcine Leydig Cells with Hypoxia [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2441-2450. |
| [6] | Hang ZHANG, Peipei ZHANG, Baigao YANG, Xiaoyi FENG, Yifan NIU, Zhou YU, Jianhua CAO, Pengcheng WAN, Xueming ZHAO. Combination of IGF1, CoQ10 and MT Alleviated the Effects of Heat Stress on Bovine IVF Blastocysts [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2474-2485. |
| [7] | Kaihui WU, Liuguang ZHANG, Chao WANG, Shiyuan XU, Songqi LIU, Kaimin YUAN, Dong WANG, Yunwei PANG. Study on the Mechanism of Melatonin Relieving Testicular Damage in Mice Induced Busulfan [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2486-2497. |
| [8] | DONG Shucan, MAO Shuaixiang, WU Cuiying, LI Yaokun, SUN Baoli, GUO Yongqing, DENG Ming, LIU Dewu, LIU Guangbin. The Effect of the Androgen Receptor Inhibitor Enzalutamide on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Goat Ovarian Granulosa Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2022-2031. |
| [9] | WANG Jiying, YIN Ruiru, XIE Xing, WANG Haiyan, LIU Hudong, HU Hui, XIONG Qiyan, FENG Zhixin, SHAO Guoqing, YU Yanfei. Effects of LDH in Mesomycoplasma (Mycoplasma) hyopneumoniae on Apoptosis of Porcine Bronchial Epithelial Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2195-2205. |
| [10] | LI Qiuyun, TIAN Xinyuan, LIAO Wensheng, ZHANG Huanrong, REN Yupeng, YANG Falong, ZHU Jiangjiang, XIANG Hua. Effects of SOCS2 on Proliferation, Cycle and Apoptosis of Turbinate Bone Cells in Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2226-2240. |
| [11] | LAN Xinrui, ZHAO Baobao, ZHANG Bihan, LIN Xiaoyu, MA Huiming, WANG Yongsheng. Effects of β-sitosterol on Porcine Oocyte Maturation and Embryonic Development in Vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1629-1637. |
| [12] | HU Qiaoyan, ZHAI Xiangqin, LI Yidan, HAN Jiale, LEI Chuzhao, DANG Ruihua. Effects of bta-miR-101 on Proliferation, Apoptosis and Secretion of Bovine Testicular Sertoli Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1040-1051. |
| [13] | HUO Yuannan, QIU Meijia, ZHANG Jiaojiao, YANG Weirong, WANG Xianzhong. Arginine and Its Metabolites Attenuate Heat Stress-induced Apoptosis of Immature Boar Sertoli Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 587-597. |
| [14] | GAO Yawei, PENG Di, SUN Zhaoyang, YAN Ziyue, CUI Kai, MA Zefang. Mining the Molecular Mechanism of Exogenous Melatonin Affecting the Development of Mink Ovary Based on Transcriptome Data [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 607-618. |
| [15] | QIU Wenyue, SU Yiman, YE Jiali, ZHANG Xinting, PANG Xiaoyue, WANG Rongmei, XIE Zimao, ZHANG Hui, TANG Zhaoxin, SU Rongsheng. Study on Asiatic Acid Alleviates LPS-induced Acute Kidney Injury by Regulating Apoptosis and Autophagy of Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 809-821. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||