





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 2486-2497.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.06.020
• Animal Biotechnology and Reproduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
Kaihui WU1( ), Liuguang ZHANG2, Chao WANG1,3, Shiyuan XU1,3, Songqi LIU1, Kaimin YUAN1,3, Dong WANG1,*(
), Liuguang ZHANG2, Chao WANG1,3, Shiyuan XU1,3, Songqi LIU1, Kaimin YUAN1,3, Dong WANG1,*( ), Yunwei PANG1,*(
), Yunwei PANG1,*( )
)
Received:2023-11-14
Online:2024-06-23
Published:2024-06-28
Contact:
Dong WANG, Yunwei PANG
E-mail:2840259661@qq.com;dwangcn2002@vip.sina.com;pangyunwei@caas.cn
CLC Number:
Kaihui WU, Liuguang ZHANG, Chao WANG, Shiyuan XU, Songqi LIU, Kaimin YUAN, Dong WANG, Yunwei PANG. Study on the Mechanism of Melatonin Relieving Testicular Damage in Mice Induced Busulfan[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2486-2497.
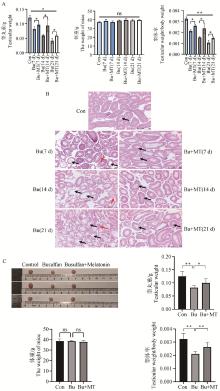
Fig. 1
Effect of melatonin treatment on mouse testis A. The effect of busulfan combined with melatonin treatment on testicular weight, body weight, and testicular body rate in mice (n=3); B. The HE staining results of experimental mouse testicular tissue: The black arrow indicating the lumen of the seminiferous tubules; The red arrow indicates inflammatory cell infiltration (n=3; 100×, scale=250 μm); C. The effects of busulfan combined with melatonin treatment on mouse volume (n=3), testicular weight, body weight, and testicular body rate for 7 days(n=8), * represents significant level of P < 0.05, ** represents extremely significant level of P < 0.01, the same as below"


Fig. 2
Effect of melatonin treatment on sperm count A.Effect of busulfan combined with melatonin treatment on sperm density(n=5);B. HE staining results of the epididymis tail of experimental mice: The black arrow represents the sperm, and the red arrow represents the cavity (n=3; 100×, scale=250 μm; 400×, scale=75 μm)"


Fig. 8
The effect of melatonin treatment on F-actin Green represents the positive signal of F-actin, blue represents the DAPI staining signal of the cell nucleus, white arrow indicating the positive signal of the basal layer and the white triangle indicating the positive signal of the lumen side (n=3; scale=20 μm)"

| 1 | 赵羚均. 白消安诱发小鼠睾丸炎损伤生精机能及褪黑素的缓解作用的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2023. |
| ZHAO L J. Study on the damage of spermatogenic function and the alleviative effect of melatonin induced by busulfan in mice with orchitis[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 2 |
PUR Y,LIUJ,ZHANGA P,et al.Modeling methods for busulfan-induced oligospermia and asthenozoospermia in mice: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].J Assist Reprod Genet,2023,40(1):19-32.
doi: 10.1007/s10815-022-02674-y |
| 3 | 李茹意. 白消安毒害小鼠睾丸的机理研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2021. |
| LI R Y. Study on the mechanism of busulfan poisoning mice testis[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 4 |
QINY S,LIUL,HEY N,et al.Testicular injection of busulfan for recipient preparation in transplantation of spermatogonial stem cells in mice[J].Reprod Fertil Dev,2016,28(12):1916-1925.
doi: 10.1071/RD14290 |
| 5 |
ALVESM G,RATOL,CARVALHOR A,et al.Hormonal control of Sertoli cell metabolism regulates spermatogenesis[J].Cell Mol Life Sci,2013,70(5):777-793.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1079-1 |
| 6 |
LIEP Y,CHENGC Y,MRUKD D.Signalling pathways regulating the blood-testis barrier[J].Int J Biochem Cell Biol,2013,45(3):621-625.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.12.009 |
| 7 |
LUY,LUOB,LIJ,et al.Perfluorooctanoic acid disrupts the blood-testis barrier and activates the TNFα/p38 MAPK signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro[J].Arch Toxicol,2016,90(4):971-983.
doi: 10.1007/s00204-015-1492-y |
| 8 |
BANTOUNOUM,PLASCEVICJ,GALLEYH F.Melatonin and related compounds: antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory actions[J].Antioxidants (Basel),2022,11(3):532.
doi: 10.3390/antiox11030532 |
| 9 |
ASHRAFIZADEHM,NAJAFIM,KAVYIANIN,et al.Anti-inflammatory activity of melatonin: a focus on the role of NLRP3 inflammasome[J].Inflammation,2021,44(4):1207-1222.
doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01428-9 |
| 10 |
YANGD H,WEIY D,LUQ Z,et al.Melatonin alleviates LPS-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in spermatogonial stem cells[J].J Cell Physiol,2021,236(5):3536-3551.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.30088 |
| 11 |
FENGR,ADENIRANSO,HUANGF S,et al.The ameliorative effect of melatonin on LPS-induced Sertoli cells inflammatory and tight junctions damage via suppression of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in newborn calf[J].Theriogenology,2022,179,103-116.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2021.11.020 |
| 12 |
ZHANGX Y,XIAQ,WEIR,et al.Melatonin protects spermatogonia from the stress of chemotherapy and oxidation via eliminating reactive oxidative species[J].Free Radic Biol Med,2019,137,74-86.
doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.04.009 |
| 13 | MOGHADAMM T,DADFARR,KHORSANDIL.The effects of ozone and melatonin on busulfan-induced testicular damage in mice[J].JBRA Assist Reprod,2021,25(2):176-184. |
| 14 |
DEHDARI EBRAHIMIN,SADEGHIA,SHOJAEI-ZARGHANIS,et al.Protective effects of exogenous melatonin therapy against oxidative stress to male reproductive tissue caused by anti-cancer chemical and radiation therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies[J].Front Endocrinol (Lausanne),2023,14,1184745.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1184745 |
| 15 |
LIB,HEX,ZHUANGM R,et al.Melatonin ameliorates busulfan-induced spermatogonial stem cell oxidative apoptosis in mouse testes[J].Antioxid Redox Signal,2018,28(5):385-400.
doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6792 |
| 16 |
HAYDENM S,GHOSHS.NF-κB in immunobiology[J].Cell Res,2011,21(2):223-244.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.13 |
| 17 |
ZHANGX Y,WANGT,DENGT T,et al.Damaged spermatogenic cells induce inflammatory gene expression in mouse Sertoli cells through the activation of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4[J].Mol Cell Endocrinol,2013,365(2):162-173.
doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.10.016 |
| 18 |
ABARIKWUS O,NJOKUR C C,JOHNI G,et al.Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory protective effects of rutin and kolaviron against busulfan-induced testicular injuries in rats[J].Syst Biol Reprod Med,2022,68(2):151-161.
doi: 10.1080/19396368.2021.1989727 |
| 19 |
QUN,KURAMASUM,HIRAYANAGIY,et al.Gosha-jinki-gan recovers spermatogenesis in Mice with busulfan-induced aspermatogenesis[J].Int J Mol Sci,2018,19(9):2606.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19092606 |
| 20 |
QUN,KURAMASUM,NAGAHORIK,et al.Co-administration of the traditional medicines hachimi-jio-gan and hochu-ekki-to can reverse busulfan-induced aspermatogenesis[J].Int J Mol Sci,2020,21(5):1716.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21051716 |
| 21 |
DENGS L,ZHANGB L,REITERR J,et al.Melatonin ameliorates inflammation and oxidative stress by suppressing the p38MAPK signaling pathway in LPS-induced sheep orchitis[J].Antioxidants,2020,9(12):1277.
doi: 10.3390/antiox9121277 |
| 22 |
ZHANGY J,LIUT,YANGH L,et al.Melatonin: a novel candidate for the treatment of osteoarthritis[J].Ageing Res Rev,2022,78,101635.
doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101635 |
| 23 | HEIDARIZADIS,RASHIDIZ,JALILIC,et al.Overview of biological effects of melatonin on testis: a review[J].Andrologia,2022,54(11):e14597. |
| 24 |
MRUKD D,CHENGC Y.The mammalian blood-testis barrier: its biology and regulation[J].Endocr Rev,2015,36(5):564-591.
doi: 10.1210/er.2014-1101 |
| 25 |
LUACESJ P,TORO-URREGON,OTERO-LOSADAM,et al.What do we know about blood-testis barrier?Current understanding of its structure and physiology[J].Front Cell Dev Biol,2023,11,1114769.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1114769 |
| 26 | WU S W, WANG L L, TANG E I, et al. An in vitro assay to monitor sertoli cell blood-testis barrier (BTB) integrity[M]//TURKSEN K. Permeability Barrier: New York: Humana, 2021: 207-213. |
| 27 |
ZHUX,CAOL,LIUY F,et al.Genotoxicity of bisphenol AF in rats: detrimental to male reproductive system and probable stronger micronucleus induction potency than BPA[J].J Appl Toxicol,2024,44(3):428-444.
doi: 10.1002/jat.4552 |
| 28 |
VENDITTIM,BEN RHOUMAM,ROMANOM Z,et al.Evidence of melatonin ameliorative effects on the blood-testis barrier and sperm quality alterations induced by cadmium in the rat testis[J].Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,2021,226,112878.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112878 |
| 29 |
GHAFOURI-FARDS,SHOOREIH,MOHAQIQM,et al.The role of different compounds on the integrity of blood-testis barrier: a concise review based on in vitro and in vivo studies[J].Gene,2021,780,145531.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.145531 |
| 30 |
LIUJ H,RENL H,WEIJ L,et al.Fine particle matter disrupts the blood-testis barrier by activating TGF-β3/p38 MAPK pathway and decreasing testosterone secretion in rat[J].Environ Toxicol,2018,33(7):711-719.
doi: 10.1002/tox.22556 |
| 31 | LUIW Y,CHENGC Y.Regulation of cell junction dynamics by cytokines in the testis-a molecular and biochemical perspective[J].Cytokine Growth Factor Rev,2007,18(3/4):299-311. |
| 32 |
ZHUC L,WANGL,ZHAOX Q,et al.Antimicrobial peptide MPX attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory response and blood-testis barrier dysfunction in sertoli cells[J].Theriogenology,2022,189,301-312.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.07.001 |
| 33 | VOGLA W,VAIDK S,GUTTMANJ A.The sertoli cell cytoskeleton[J].Adv Exp Med Biol,2008,186-211. |
| 34 |
HONGX Y,SHAON M,YINL,et al.Exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles affects testicular structure, reproductive development and spermatogenesis in parental and offspring male rats[J].Ann Transl Med,2022,10(13):751.
doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3047 |
| 35 |
CHENN,WANX Y,WANGM,et al.Cross-talk between Vimentin and autophagy regulates blood-testis barrier disruption induced by cadmium[J].Environ Pollut,2024,346,123625.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123625 |
| 36 |
LIUL Q,ZHANGY B,CHANGX L,et al.Fluorochloridone perturbs blood-testis barrier/Sertoli cell barrier function through Arp3-mediated F-actin disruption[J].Toxicol Lett,2018,295,277-287.
doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.07.001 |
| 37 |
TANGE I,CHENGC Y.Mark2 and mark4 regulate sertoli cell BTB dynamics through microtubule and actin cytoskeletons[J].Endocrinology,2022,163(11):bqac130.
doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqac130 |
| 38 |
WUS W,LVL X,LIL X,et al.KIF15 supports spermatogenesis via its effects on sertoli cell microtubule, actin, vimentin, and septin cytoskeletons[J].Endocrinology,2021,162(4):bqab010.
doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab010 |
| 39 |
BUONCERVELLOM,MACCARIS,ASCIONEB,et al.Inflammatory cytokines associated with cancer growth induce mitochondria and cytoskeleton alterations in cardiomyocytes[J].J Cell Physiol,2019,234(11):20453-20468.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.28647 |
| 40 |
BENITEZ-KINGG,RAMIREZ-RODRIGUEZG,ORTIZL,et al.The neuronal cytoskeleton as a potential therapeutical target in neurodegenerative diseases and schizophrenia[J].Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord,2004,3(6):515-533.
doi: 10.2174/1568007043336761 |
| 41 |
BENITEZ-KINGG.Melatonin as a cytoskeletal modulator: implications for cell physiology and disease[J].J Pineal Res,2006,40(1):1-9.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2005.00282.x |
| 42 |
YOONY M,GOG,YUNC W,et al.Melatonin suppresses renal cortical fibrosis by inhibiting cytoskeleton reorganization and mitochondrial dysfunction through regulation of miR-4516[J].Int J Mol Sci,2020,21(15):5323.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21155323 |
| 43 |
MISSAWIO,JEDDOUI B,VENDITTIM,et al.Environmental microplastic accumulation exacerbates liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat: protective effects of melatonin[J].Sci Total Environ,2023,860,160155.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160155 |
| [1] | Hang ZHANG, Peipei ZHANG, Baigao YANG, Xiaoyi FENG, Yifan NIU, Zhou YU, Jianhua CAO, Pengcheng WAN, Xueming ZHAO. Combination of IGF1, CoQ10 and MT Alleviated the Effects of Heat Stress on Bovine IVF Blastocysts [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2474-2485. |
| [2] | Meiyan LI, Xiaoying XING, Na LI, Yeli ZHANG, Hongping QIAO, Xiaoying WU. Regulation of Glycyrrhizol Polysaccharide Alleviate LPS-induced Orchitis in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2741-2750. |
| [3] | GAO Yawei, PENG Di, SUN Zhaoyang, YAN Ziyue, CUI Kai, MA Zefang. Mining the Molecular Mechanism of Exogenous Melatonin Affecting the Development of Mink Ovary Based on Transcriptome Data [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 607-618. |
| [4] | HE Mingyang, MA Yujing, WANG Yong, YANG Ruochen, LIU Yueqin, ZHANG Yingjie, DUAN Chunhui. Effects of Melatonin on Proliferation, Apoptosis of Ovarian Granulosa Cells, and Its Secretion of Steroid Hormones of Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3313-3324. |
| [5] | LI Chunyan, ZHANG Yan, Lü Chunrong, DENG Weidong, QUAN Guobo. Research Progress on Antioxidant Mechanisms of Melatonin and Its Application in Cryopreservation of Mammalian Spermatozoa [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4468-4476. |
| [6] | SHAO Jing, ZHANG Ying, TANG Yu, XU Baozeng. Research Progress of ERM Proteins in Mammalian Oocyte Maturation and Fertilization [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4477-4487. |
| [7] | CHENG Huaqin, YUAN Yujie, LUO Wen, GAO Shaoshuai, YE Linxia, LI Jian, YIN Shi. Research on the Effect of Melatonin on the Growth and Function of Yak Luteal Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(2): 459-469. |
| [8] | HUANG Chengyu, XU Dequan, FENG Zhe, ZHOU Ling, LIU Min. The Addition of Melatonin Reduces the Oxidative Damage of Pig Spermatogonial Stem Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(7): 1880-1890. |
| [9] | LI Ruyi, ZHAO Junjin, ZHAO Lingjun, DUAN Chenying, LI Xin, WANG Dong. Study on the Damage Mechanism of Busulfan on Mouse Testis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(7): 1903-1911. |
| [10] | ZHANG Wenhua, WEN Shuangquan, WANG Li, XU Mingchang, MA Yonggang, ZOU Hui, GU Jianhong, LIU Xuezhong, BIAN Jianchun, LIU Zongping, YUAN Yan. Protective Effect of Melatonin on Toxic Damage Caused by Cadmium in Cerebral Cortex of Duck [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(10): 2953-2959. |
| [11] | ZHANG Haiyang, LU Xiangyu, ZHANG Jiahua, LIU Xin, HAN Zhengxuan, CUI An, ZHAO Yuan, SONG Manyu, LIU Tao, FAN Honggang. Protective Effects of Melatonin on LPS-induced Hippocampal Inflammatory Lesion in Rats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(1): 226-234. |
| [12] | LI Ruyi, MENGAL Kifayatullah, CHEN Xiaoli, WANG Dong. Study on the Toxic Effect and Mechanism of Busulfan on Testis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(3): 426-432. |
| [13] | YANG Yue, GUO Zeming, HAN Haoshu, LI Weitian, GAO Ting, WANG Xintong, CHEN Yaoxing. Effect of Acute Sleep Deprivation on Melatonin Level of Plasma and Clock Gene Expression of Hypothalamus in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(10): 2609-2612. |
| [14] | ZHENG Jiaming, HE Shuangjiang, ZHAO Hongyan, SONG Ruilong, LIU Zongping. Effect of RhoU Silencing on Osteoclast Differentiation [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2019, 50(9): 1904-1911. |
| [15] | WANG Jianmeng, FU Shaoyin, LI Chun, BAI Xue, LIU Bin, JI Xiaoyang, LIU Yongbin, ZHANG Wenguang. Effects of Melatonin on let-7 Family and Its Target Genes in Skin of Inner Mongolian Cashmere Goats [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2019, 50(7): 1367-1379. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||