





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (9): 4657-4672.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.09.043
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Xinyue1( ), LI Danni1, ZONG Ying2,3,4, SHI Kun2,3,4, LI Jianming2,3,4, DIAO Naichao2,3,4, ZENG Fanli2,3,4,5,*(
), LI Danni1, ZONG Ying2,3,4, SHI Kun2,3,4, LI Jianming2,3,4, DIAO Naichao2,3,4, ZENG Fanli2,3,4,5,*( ), DU Rui2,3,4,5,*(
), DU Rui2,3,4,5,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-02
Online:2025-09-23
Published:2025-09-30
Contact:
ZENG Fanli, DU Rui
E-mail:2892144827@qq.com;zengfanli@jlau.edu.cn;durui@jlau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
LIU Xinyue, LI Danni, ZONG Ying, SHI Kun, LI Jianming, DIAO Naichao, ZENG Fanli, DU Rui. Transcriptome Analysis of RAW264.7 Macrophages Infected with Rv3435c Recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4657-4672.
Table 2
Primer sequences of qRT-PCR"
| 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′→3′) Sequence |
| CCL2 | F: ACCTGCTGCTACTCATTCACC R: TGAGCTTGGTGACAAAAACTAC |
| CCL3 | F: CCAGCCAGGTGTCATTTTCCTG R: ATTCAGTTCCAGGTCAGTGATG |
| CCL4 | F: CCAAGCCAGCTGTGGTATTCCT R: TTCAACTCCAAGTCACTCATGTACT |
| IL1RN | F: TCTCTCTCCTTCTCATCCTTCTGT R: GGCACCATGTCTATCTTTTCTTCT |
| PTGS2 | F: GCTCAGCCAGGCAGCAAATC R: CACCATAGAATCCAGTCCGGG |
| CCR2 | F: CCTCAGTTCATCCACGGCAT R: AGGGAGTAGAGTGGAGGCAG |
| SPP1 | F: TCCCTACAGTCGATGTCCCC R: TGTGGCATCAGGATACTGTTCAT |
| CXCL10 | F: GCCGTATTTTCTGCCTCAT R: TTTTTCATCGTGGCAATGATCTC |
| IGF1 | F: AGGCTATGGCTCCAGCATTC R: CGATAGGGACGGGGACTTCT |
| MTND2 | F: TTCGTCACACAAGCAACAGC R: GGGGCGAGGCCTAGTTTTAT |
| MTND1 | F: TCCGAGCATCTTATCCACGC R: GTATGGTGGTACTCCCGCTG |
Fig. 1
The mRNA expression levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 in cells infected with the recombinant strain at 6, 12, 24, and 48 hours post-infection mRNA expression levels of cytokines in Ms-pMV361, Ms-pMV361-Rv3435c infected RAW264.7 cells at 6, 12, 24, and 48 h(*. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001; ns. P>0.05). A. IL-1β; B. TNF-α; C. IL-6"
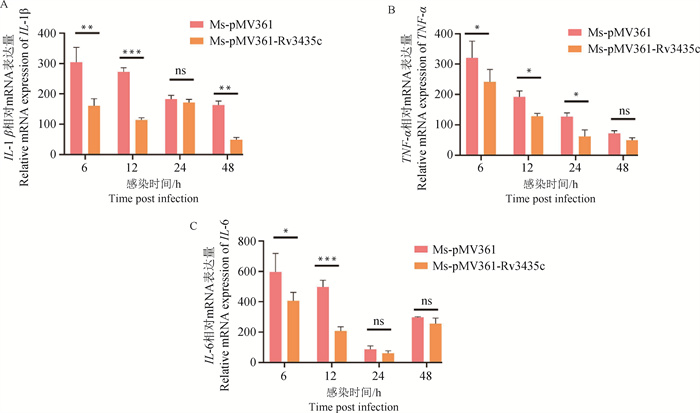
Table 3
Transcriptome sequencing data under recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis infection"
| 样品名称 Sample | 原始度数 Raw reads No. | 原始碱基/bp Raw bases | 过滤读取编号 Clean reads number | 过滤数据/bp Clean data | 过滤度数/% Clean reads | Q30大小/bp Q30 | GC含量/% GC(%) | Q20含量/% Q20 | Q30含量/% Q30 |
| Ms-pMV361_1 | 45 267 206 | 6 835 348 106 | 44 170 312 | 6 653 345 332 | 97.58 | 6 424 197 947 | 48.31 | 97.79 | 93.98 |
| Ms-pMV361_2 | 46 295 026 | 6 990 548 926 | 45 367 066 | 6 831 943 984 | 98.00 | 6 590 259 271 | 48.31 | 97.92 | 94.27 |
| Ms-pMV361_3 | 40 132 684 | 6 060 035 284 | 39 248 806 | 5 905 695 590 | 97.80 | 5 677 418 957 | 48.28 | 97.69 | 93.69 |
| Ms-pMV361- Rv3 435c_1 | 47 080 516 | 7 109 157 916 | 46 071 820 | 6 941 076 740 | 97.86 | 6 663 366 706 | 48.44 | 97.72 | 93.73 |
| Ms-pMV361- Rv3 435c_2 | 46 194 334 | 6 975 344 434 | 45 053 236 | 6 783 376 551 | 97.53 | 6 500 746 215 | 48.41 | 97.50 | 93.20 |
| Ms-pMV361- Rv3 435c_3 | 41 735 852 | 6 302 113 652 | 40 638 676 | 6 121 139 659 | 97.37 | 5 875 725 971 | 48.64 | 97.50 | 93.23 |
Fig. 4
Statistical results of differential expression A. Volcano diagram of expression differences[The horizontal axis is log2 (Fold change), and the vertical axis is-log10 (P-value). The two vertical dashed lines in the figure represent the threshold for expressing the difference factor; The horizontal dashed line represents the significance level threshold. The color represents genes that are red up (upregulated), blue down (downregulated), or gray none (non significantly differentially expressed), indicating the top 10 genes that are upregulated or downregulated (ranked by significance); B. Differential gene Venn diagram"
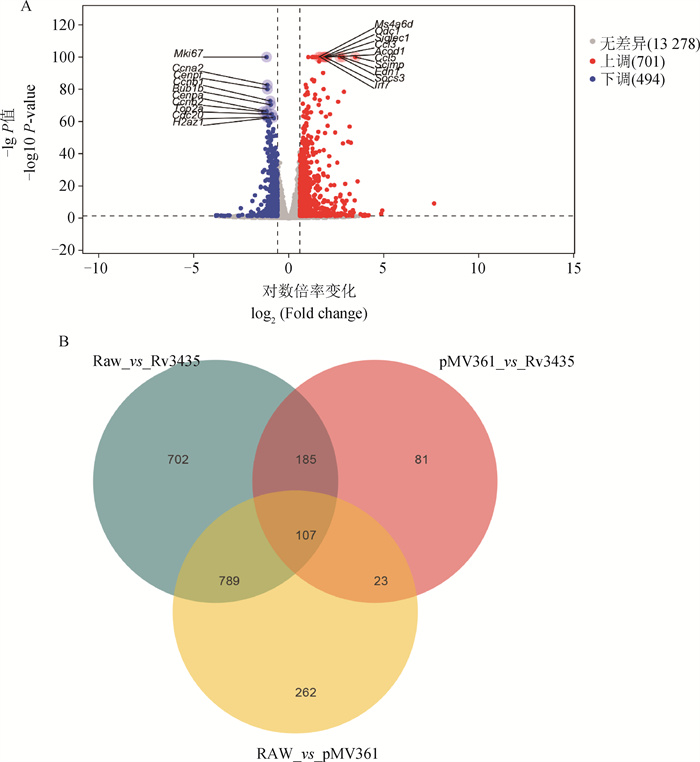
Table 5
The results of the top 10 GO enrichment analyses in the differentially igeneally speaking"
| 项目 Item | 中文名称 Chinese name | 调整后P值 Adjusted P-value |
| Immune system process | 免疫系统过程 | < 0.001 |
| Response to virus | 对病毒的响应 | < 0.001 |
| Defense response | 防御响应 | < 0.001 |
| Response to external stimulus | 对外部刺激的反应 | < 0.001 |
| Immune response | 免疫应答 | < 0.001 |
| Innate immune response | 先天免疫反应 | < 0.001 |
| Response to external biotic stimulus | 对外部生物刺激的反应 | < 0.001 |
| Response to biotic stimulus | 对生物刺激的反应 | < 0.001 |
| Response to other organism | 对其他微生物的反应 | < 0.001 |
| Defense response to other organism | 对其他生物体的防御反应 | < 0.001 |
Table 6
KEGG pathway categories of differentially expressed genes"
| 大类 Major categories | 中文名称 Chinese name | 调整后P值 Adjusted P-value |
| 环境信息处理 Environmental information processing | TNF信号通路 | < 0.001 |
| 细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用 | < 0.001 | |
| 病毒蛋白与细胞因子和细胞因子受体的相互作用 | < 0.001 | |
| 细胞过程 Cellular processes | 细胞周期 | < 0.001 |
| p53信号通路 | < 0.001 | |
| 人类疾病 Human diseases | 类风湿性关节 | < 0.001 |
| 炎脂质和动脉粥样硬化 | < 0.001 | |
| 有机体系统 Organic system | IL-17信号通路 | < 0.001 |
| Toll样受体信号通路 | < 0.001 |
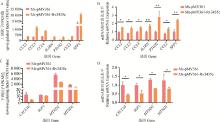
Fig. 8
Verification of transcriptome results by RT-qPCR A. FPKM value of the up-regulation factors; B. Relative expression of up-regulated factors; C. FPKM value of the down-regulation factors; D. Relative expression of down-regulated factors. *.P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001; ns. P>0.05"
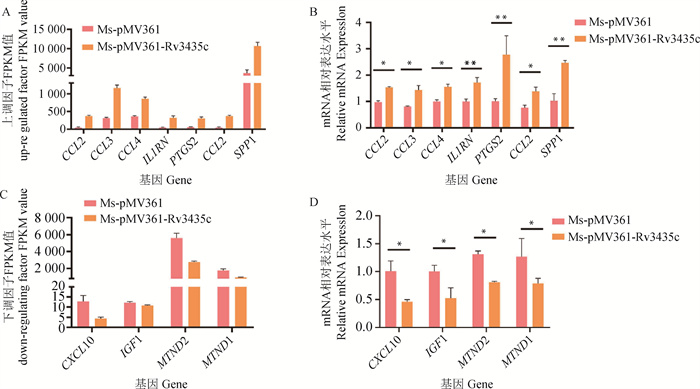
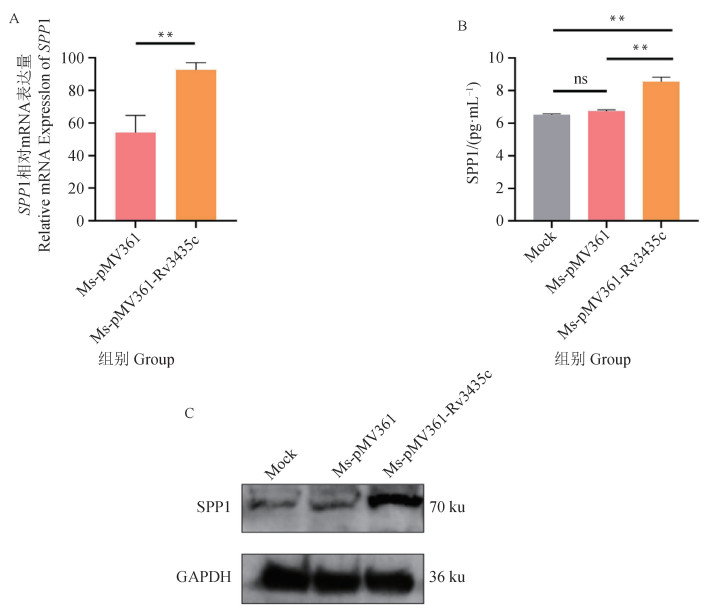
Fig. 9
SPP1 as a potential target for the function of Rv3435c A. Spp1 mRNA expression of recombinant strain 12 hours after infection; B. SPP1 secretion of recombinant strain 12 hours after infection; C. SPP1 protein level 12 h after infection by the recombinant strain.*.P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001; ns. P>0.05"
| 1 |
ANESE,PIRESD,MANDALM,et al.ESAT-6 a Major virulence factor of mycobacterium tuberculosis[J].Biomolecules,2023,13(6):968.
doi: 10.3390/biom13060968 |
| 2 |
KOCHA,MIZRAHIV.Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J].Trends Microbiol,2018,26(6):555-556.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.02.012 |
| 3 |
KANABALANR D,LEEL J,LEET Y,et al.Human tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex: A review on genetic diversity, pathogenesis and omics approaches in host biomarkers discovery[J].Microbiol Res,2021,246,126674.
doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2020.126674 |
| 4 |
EHRTS,SCHNAPPINGERD,RHEEK Y.Metabolic principles of persistence and pathogenicity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J].Nat Rev Microbiol,2018,16(8):496-507.
doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0013-4 |
| 5 | World Organisation for Animal Health. Report of the meeting of the ad hoc group on alternative strategies for the control and elimination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex infection (MTBC) in livestock[C/OL]. Paris, France, 2024. [2025-07-02]https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2024/02/en-20240222-ahg-mtb-report.pdf. |
| 6 | 世界动物卫生组织.哺乳动物、禽、蜜蜂A和B类疾病诊断试验和疫苗标准手册[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2002:337-349. |
| World Organisation for Animal Health.Manual of diagnostic tests and vaccines for terrestrial animals (mammals, birds and bees): List A and B diseases[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2002:337-349. | |
| 7 |
ZHAOD,SONGY H,LID,et al.Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv3435c regulates inflammatory cytokines and promotes the intracellular survival of recombinant Mycobacteria[J].Acta tropica,2023,246,106974.
doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2023.106974 |
| 8 |
SINGHA K,CARETTEX,POTLURIL P,et al.Investigating essential gene function in Mycobacterium tuberculosis using an efficient CRISPR interference system[J].Nucl Acids Res,2016,44(18):e143.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw625 |
| 9 |
LUQ,ZHANGW,FANGJ,et al.Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv1096, facilitates mycobacterial survival by modulating the NF-κB/MAPK pathway as peptidoglycan N-deacetylase[J].Mol Immunol,2020,127,47-55.
doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.08.005 |
| 10 |
XIAA,LIX,QUANJ,et al.Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv0927c inhibits NF-κB pathway by downregulating the phosphorylation level of IκBα and enhances Mycobacterial survival[J].Front Immunol,2021,12,721370.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.721370 |
| 11 | 韩梅,韩璞,邹静波.结核分枝杆菌感染与细胞因子的关系[J].检验医学与临床,2021,18(2):270-272. |
| HANM,HANP,ZOUJ B,et al.Relationship between Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and cytokines[J].Laboratory Medicine and Clinical,2021,18(2):270-272. | |
| 12 | 付加芳,张佩佩,古苑欣,等.结核分枝杆菌Rv1057基因对巨噬细胞感染早期细胞因子表达的影响分析[J].生命科学研究,2017,21(6):494-500. |
| FUJ F,ZHANGP P,GUY X,et al.Effect of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv1057 gene on the cytokine expression in the early stage of macrophage infection[J].Life Science Research,2017,21(6):494-500. | |
| 13 | 张泽霖. Viperin通过IRAK1-TRAF6-TAK1负调节炎症细胞因子和NO促进结核分枝杆菌感染[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2020. |
| ZHANG Z L. Viperin impairs innate immune response through IRAK1-TRAF6-TAK1 axis to promote Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 14 | 邓傲竹, 张少言, 冯雅, 等. 结核分枝杆菌与巨噬细胞: 从感染机制到免疫逃逸策略的研究进展[C]//第35届中国防痨协会全国学术大会暨第四届中国防痨科技颁奖大会. 湖州, 2024. |
| DENG A Z, ZHANG S Y, FENG Y, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis and macrophages: Research progress from infection mechanisms to immune escape strategies[C]//Proceedings of the 35th National Academic Conference of China Anti-Tuberculosis Association and the 4th China Anti-Tuberculosis Science and Technology Award Conference. Huzhou, Zhejiang, China, 2024. (in Chinese) | |
| 15 | 李娜,宋银娟,储岳峰.结核分枝杆菌免疫逃逸机制研究进展[J].科学通报,2024,69(Z1):531-41. |
| LIN,SONGY J,CHUY F.Research advances in immune evasion mechanisms of Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2024,69(Z1):531-541. | |
| 16 | 李玉洁,余海燕,杨雨婷,等.结核分枝杆菌分泌蛋白早期分泌性抗原6(ESAT-6)的免疫学性质及其在新型疫苗中作用的研究进展[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2024,40(1):89-94. |
| LIY J,YUH Y,YANGY T,et al.Immunological properties of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-secreted early secretory antigenic target 6 (ESAT-6) and its role in novel vaccines[J].Cellular & Molecular Immunology,2024,40(1):89-94. | |
| 17 |
AKASHIS,SUZUKAWAM,TAKEDAK,et al.IL-1RA in the supernatant of QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube and QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus is useful for discriminating active tuberculosis from latent infection[J].J Infect Chemother,2021,27(4):617-624.
doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2020.11.023 |
| 18 | 马子淳,尚媛媛,逄宇,等.趋化因子用于结核病诊断的研究进展[J].中国防痨杂志,2023,45(3):305-310. |
| MAZ C,SHANGY Y,PANGY,et al.Research progress on the application of chemokines in the diagnosis of tuberculosis[J].Chinese Journal of Antituberculosis,2023,45(3):305-310. | |
| 19 | WANGT,QUIJADAD,AHMENDAT,et al.Targeting CCRL2 enhances therapeutic outcomes in a tuberculosis mouse model[J].bioRxiv,2024,2024.09.23.614576. |
| 20 |
KUMARN P,MOIDEENK,NANCYA,et al.Plasma chemokines are baseline predictors of unfavorable treatment outcomes in pulmonary tuberculosis[J].Clin Infect Dis,2021,73(9):e3419-e3427.
doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1104 |
| 21 |
HUANGH.Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a cancer biomarker and MMP-9 biosensors: recent advances[J].Sensors (Basel),2018,18(10):3249.
doi: 10.3390/s18103249 |
| 22 |
SEITZ-HOLLANDJ,ALEMN-GÓMEZY,CHOK I K,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) activity, hippocampal extracellular free water, and cognitive deficits are associated with each other in early phase psychosis[J].Neuropsychopharmacology,2024,49(7):1140-1150.
doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01814-5 |
| 23 | 李军霞,赵青,何红彦,等.基质金属蛋白酶-9与血脑屏障和结核性脑膜炎[J].中国感染与化疗杂志,2017,17(4):463-467. |
| LIJ X,ZHAOQ,HEH Y,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and its role in the blood-brain barrier and tuberculous meningitis[J].Chinese Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy,2017,17(4):463-467. | |
| 24 | 杨泽伟,冯飞,杨颖,等.脑脊液ESAT-6、ADA、INF-γ、MMP-9检测在结核性脑膜炎诊断及转归中的应用价值[J].山东医药,2018,58(18):56-58. |
| YANGZ W,FENGF,YANGY,et al.Diagnostic and prognostic value of ESAT-6, ADA, INF-γ, and MMP-9 in cerebrospinal fluid for tuberculous meningitis[J].Shandong Medical Journal,2018,58(18):56-58. | |
| 25 | 王霞,黄健,牛文一,等.IFN-γ、MMP-9水平在肺结核中的表达及与其病情活动性的相关性[J].分子诊断与治疗杂志,2024,16(7):1372-1376. |
| WANGX,HUANGJ,NIUW Y,et al.Expression of IFN-γ and MMP-9 in pulmonary tuberculosis and their correlation with disease activity[J].Journal of Molecular Diagnostics and Therapy,2024,16(7):1372-1376. | |
| 26 | 韦爽. 血清MMP-9、MMP-2、TIMP-1及TIMP-2在婴幼儿肺炎中的表达水平及临床意义[D]. 遵义: 遵义医科大学, 2023. |
| WEI S. Expression and clinical significance of serum MMP-9, MMP-2, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 in infantile pneumonia[D]. Zunyi: Zunyi Medical University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 27 | LIC,DENGT,CAOJ,et al.Identifying ITGB2 as a potential prognostic biomarker in ovarian cancer[J].Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland),2023,13(6):1169. |
| 28 | 贾红彦,董静,张宗德,等.结核分枝杆菌感染的免疫学检测技术研究进展及临床应用现状[J].中国防痨杂志,2022,44(07):720-6. |
| JIAH Y,DONGJ,ZHANGZ D,et al.Advances in immunological detection techniques and clinical applications of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection[J].Chinese Journal of Antituberculosis,2022,44(7):720-726. | |
| 29 | 潘琳,蔡睿志,陶金,等.IL-6经NF-κB信号通路上调人胎盘MSC SPP1表达促进M2型巨噬细胞极化的作用机制研究[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2024,40(11):961-967. |
| PANL,CAIR Z,TAOJ,et al.IL-6 promotes M2 macrophage polarization via NF-κB signaling pathway by upregulating SPP1 expression in human placental MSCs[J].Cellular & Molecular Immunology,2024,40(11):961-967. | |
| 30 |
WANGC,LIY,WANGL,et al.SPP1 represents a therapeutic target that promotes the progression of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma by driving M2 macrophage infiltration[J].Br J Cancer,2024,130(11):1770-1782.
doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02683-x |
| 31 |
KOGUCHIY,KAWAKAMIK,UEZUK,et al.High plasma osteopontin level and its relationship with interleukin-12-mediated type 1 T helper cell response in tuberculosis[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2003,167(10):1355-1359.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.200209-1113OC |
| 32 |
NAUG J,LIAWL,CHUPPG L,et al.Attenuated host resistance against Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection in mice lacking osteopontin[J].Infect Immun,1999,67(8):4223-4230.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.8.4223-4230.1999 |
| 33 | 申福国,杨钰,孔维丽,等.肺结核病合并骨结核患者血清中KL-6和OPN表达及临床意义[J].中国防痨杂志,2024,46(S1):91-93. |
| SHENF G,YANGY,KONGW L,et al.Expression and clinical significance of serum KL-6 and OPN in pulmonary tuberculosis patients with bone tuberculosis[J].Chinese Journal of Antituberculosis,2024,46(S1):91-93. | |
| 34 | 吴轶.胸腔积液癌胚抗原与血清癌胚抗原比值和胸腔积液分泌性磷蛋白1在鉴别结核性胸腔积液和肺癌所致胸腔积液中的应用价值[J].广西医学,2020,42(12):1503-1506. |
| WUY.Value of pleural fluid CEA/serum CEA ratio and pleural fluid SPP1 in differentiating tuberculous pleural effusion from lung cancer-related effusion[J].Guangxi Medical Journal,2020,42(12):1503-1506. | |
| 35 |
HATTORIT,IWASAKI-HOZUMIH,BAIG,et al.Both full-length and protease-cleaved products of osteopontin are elevated in infectious diseases[J].Biomedicines,2021,9(8):1006.
doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9081006 |
| 36 |
MAHMUDF J,DUY,GREIFE,et al.Osteopontin/secreted phosphoprotein-1 behaves as a molecular brake regulating the neuroinflammatory response to chronic viral infection[J].J Neuroinflammation,2020,17(1):273.
doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01949-4 |
| 37 |
ARGANDONA LOPEZC,BROWNA M.Microglial- neuronal crosstalk in chronic viral infection through mTOR, SPP1/OPN and inflammasome pathway signaling[J].Front Immunol,2024,15,1368465.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1368465 |
| 38 | 孙冰生,张真发.骨桥蛋白及其受体CD44v对肿瘤侵袭调控的研究进展[J].中国肺癌杂志,2015,18(11):714-717. |
| SUNB S,ZHANGZ F.Advances in research of osteopontion and its receptor CD44v in tumor invasion and metastasis[J].Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer,2015,18(11):714-717. | |
| 39 | 梁文婷,霍开明,古裕鸟,等.肺炎支原体肺炎患儿血清MICA、OPN水平及其与反复呼吸道感染的相关性研究[J].检验医学与临床,2024,21(13):1870-1874. |
| LIANGW T,HUOK M,GUY N,et al.Correlation between serum MICA, OPN levels and recurrent respiratory infections in children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia[J].Laboratory Medicine and Clinical,2024,21(13):1870-1874. | |
| 40 |
ICERM A,GEZMEN-KARADAGM.The multiple functions and mechanisms of osteopontin[J].Clin Biochem,2018,59,17-24.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.07.003 |
| [1] | LI Jiapeng, LIU Qing, SUN Jiayu, MA Zefang, CUI Kai. Screening of Key Genes for Coat Color Formation in Silver Fox Based on Transcriptome and Proteome Analyses [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4379-4392. |
| [2] | FAN Jing, LI Wei, ZHU Yan, Wudubala , SHI Jiahui, Husile , WU Jianghong. Study on Rumen Morphological Changes and Gene Expression Differences in Hu Sheep at Different Developmental Stages [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3773-3786. |
| [3] | SHI Wenjian, XU Lei, ZHANG Ze, YANG Rui, XIN Lingxiang, WANG Nan, CHEN Xiang, XIN Ting. Screening and Identification of Biofilm-related Genes Based on the Random Mutant Library of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Variant bovis C68001 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3992-4006. |
| [4] | LIU Sha, SU Meng, GAO Qianmei, SONG Danli, ZHAO Guiping, LI Jianhui, LI Qinghe. Transcriptome Analysis of Chicken Macrophages after SIRT1 Activated [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2661-2671. |
| [5] | LIU Zilong, LI Qiao, WU Yi, WANG Huihui, LI Taotao, MA Youji. Transcriptomics Reveals the Effects of Chinese Herbal Feed Additives on Bile Acids Metabolism and Immune Function in Hu Sheep Liver Tissue [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 3014-3026. |
| [6] | SU Meng, LIU Sha, SONG Danli, GAO Qianmei, ZHENG Maiqing, WEN Jie, ZHAO Guiping, LI Qinghe. Identification of Candidate Genes Associated with Ascites Syndrome in Broilers Based on Transcriptome Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 559-570. |
| [7] | HU Hanwen, BAO Tugeqin, REN Xiujuan, DING Wenqi, GONG Wendian, JIA Zijie, SHI Lin, MA Muren, Baorigele , DUGARJAVIIN Manglai, BAI Dongyi. Comparative Study on Muscle Fiber Development Phenotype and Gene Expression Profile of Two Mongolian Horse Populations [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 643-656. |
| [8] | WU Shuang, YIN Na, YU Mohan, PING Yuyu, BAI Hao, CHEN Shihao, CHANG Guobin. The Effect of TRIM39.2 Overexpression on the Transcriptional Expression of Chicken Macrophages [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 178-188. |
| [9] | LU Xiu, ZHANG Ming'ai, KONG Min, ZHANG Jing, WANG Binghan, HOU Zhongyi, TENG Xingyi, JIANG Yajing, FAN Wenlei, WANG Baowei. Screening for Candidate Genes Related to Egg Production in Wulong Geese Based on Transcriptome and Proteome Analyses [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 232-245. |
| [10] | Xiaoxu ZHANG, Hao LI, Pingjie FENG, Hao YANG, Xinyue LI, Ran LÜ, Zhangyuan PAN, Mingxing CHU. Application of Single-Cell Transcriptome Sequencing Technology in Domesticated Animals [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3276-3287. |
| [11] | Jing CHEN, Xuebei WU, Dongzhi MIAO, Chi ZHANG, Zhenyu GUO, Ying WANG. Comparative Analysis of Transcriptome of Pigeon Follicles at Early Stage of Laying Interval Reveals Genes Related to Follicular Development [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3503-3515. |
| [12] | Wanqing LI, Yaqi ZENG, Xinkui YAO, Jianwen WANG, Xinxin YUAN, Chen MENG, Yuanfang SUN, Xuan PENG, Jun MENG. Comparative Analysis of Blood Transcriptome in Yili Horses Bred for Meat Performance [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2951-2962. |
| [13] | Mingliang HE, Xiaoyang LÜ, Yongqing JIANG, Zhenghai SONG, Yeqing WANG, Huiguo YANG, Shanhe WANG, Wei SUN. Function Analysis of SOX18 in Hu Sheep Hair Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells Based on Transcriptome Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2409-2420. |
| [14] | CHEN Zhe, QU Xiaolu, GUO Binbin, SUN Xuefeng, YAN Leyan. Study on Candidate Genes for Green Light Affecting Early Development of Goose Embryo Heart Based on Transcriptome Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1978-1988. |
| [15] | XU Junjie, ZHANG Lutong, WANG Jinjie, CHEN Xiaochen, HE Weixian, CAI Chuanjiang, CHU Guiyan, YANG Gongshe. Exploring the Effect of Epimedium on Estrus of Gilts Based on Multiomics and Network Pharmacology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1615-1628. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||