





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 3071-3079.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.07.003
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZONG Yunhe1( ), YANG Yuze2(
), YANG Yuze2( ), SUN Yanyan1, CHEN Jilan1, LI Yunlei1,*(
), SUN Yanyan1, CHEN Jilan1, LI Yunlei1,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-09
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
LI Yunlei
E-mail:zongyunhe2022@163.com;yyz84929056@126.com;liyunlei@caas.cn
CLC Number:
ZONG Yunhe, YANG Yuze, SUN Yanyan, CHEN Jilan, LI Yunlei. Research Advances in the Investigation of the Protective Role of Lysine Acetylation in Chicken Semen Cryopreservation and Its Mechanism[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3071-3079.
Fig. 1
Comparison of fertility and fertility sustainability of fresh and post-thawed sperms Eggs were collected continuously for 20 days after artificial insemination, and the fertility was calculated every day. Sustained fertility was assessed using model of y=A/(1+eβ(τ-x))[9]. Abscissa indicate days after insemination(d); Ordinate indicate fertilization rate(%)"
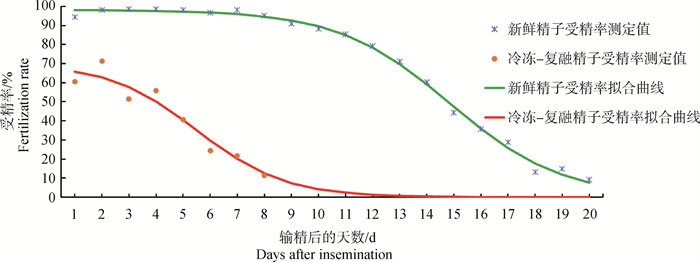
Table 1
Acetylases and their inhibitors in testis, sperm and seminal plasma of Beijing-You chicken"
| 家族 Family | 酶(别名) Enzyme (alias) | 特异性抑制剂 Specific inhibitor | 睾丸 Testis | 精子 Sperm | 精浆 Seminal plasma |
| GNAT | HAT1 (KAT1) | CPTH6 | - | √ | - |
| GCN5 (KAT2A) | CPTH2 (C14H14ClN3S) | √ | - | - | |
| MYST | Tip60 (KAT5) | TH1834 (C33H40N6O3) | - | √ | - |
| MORF (KAT6B) | - | - | √ | √ | |
| 其他Other | TAF1(KAT4) | CeMMEC13(C19H16N2O4) | √ | - | - |
Table 2
Deacetylases and their inhibitors in testis, sperm and seminal plasma of Beijing-You chicken"
| 家族 Family | 酶 Enzyme | 通用抑制剂 Universal inhibitor | 特异性抑制剂 Specific inhibitor | 睾丸 Testis | 精子 Sperm | 精浆 Seminal plasma |
| HDAC Zn2+依赖型 Zn2+-dependent | HDAC1 | TSA (C17H22N2O3) | HDAC1-IN-4 (C21H24BrClN6O2) | √ | - | - |
| HDAC2 | HDAC2-IN-1 (C22H23ClN4OS) | √ | - | - | ||
| HDAC8 | HDAC8-IN-3 (C18H12N4O3S2) | - | √ | - | ||
| HDAC7 | - | √ | - | - | ||
| HDAC10 | HDAC10-IN-2 (C19H22N2O2) | - | √ | - | ||
| HDAC11 | FT895 (C16H15F3N4O2) | √ | - | - | ||
| SIRT NAD+依赖型 NAD+-dependent | SIRT2 | NAM(C6H6N2O) | SirReal2 (C22H20N4OS2) | √ | √ | - |
| SIRT3 | 3-TYP (C7H6N4) | √ | √ | - | ||
| SIRT5 | NRD167 (C34H46N6O6S) | √ | √ | - |
| 1 | SUN Y , LI Y , ZONG Y , et al. Poultry genetic heritage cryopreservation and reconstruction: Advancement and future challenges[J]. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2023, 14 (1): 15- 32. |
| 2 | 聂瑞雪, 李俊英, 苗欢欢, 等. 鸡精液冷冻保存技术研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2021, 57 (7): 81- 86. |
| NIE R X , LI J Y , MIAO H H , et al. Progress in cryopreservation technology of chicken semen[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2021, 57 (7): 81- 86. | |
| 3 | ZONG Y , LI Y , SUN Y , et al. Chicken sperm cryopreservation: Review of techniques, freezing damage, and freezability mechanisms[J]. Agriculture (Basel), 2023, 13 (2): 445. |
| 4 | LI P F , YANG Q Z , LI S S , et al. Candidates for reproductive biomarkers: Protein phosphorylation and acetylation positively related to selected parameters of boar spermatozoa quality[J]. Anim Reprod Sci,, 2018, 197, 67- 80. |
| 5 | 贾春云, 许晓玲, 白佳桦, 等. 哺乳动物成熟精子的转录及翻译活性研究进展[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2022, 54 (3): 140- 144. |
| JIA C Y , XU X L , BAI J H , et al. Research progress on transcription and translation activity of mammalian mature sperm[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 54 (3): 140- 144. | |
| 6 | CHEN G , REN L , CHANG Z , et al. Lysine acetylation participates in boar spermatozoa motility and acrosome status regulation under different glucose conditions[J]. Theriogenology, 2021, 159, 140- 146. |
| 7 | TIAN Y , WANG H , PAN T , et al. Global proteomic analyses of lysine acetylation, malonylation, succinylation, and crotonylation in human sperm reveal their involvement in male fertility[J]. J Proteomics, 2024, 303, 105213. |
| 8 | ZONG Y , SUN Y , LI Y , et al. Regulation of winter wheat-originated antifreeze glycoprotein on rooster spermatozoa freezability[J]. Poult Sci, 2024, 103 (9): 104053. |
| 9 | KIRBY J D , FROMAN D P . Analysis of poultry fertility data[J]. Poult Sci, 1990, 69 (10): 1764- 1768. |
| 10 |
HAI E , LI B , ZHANG J , et al. Sperm freezing damage: The role of regulated cell death[J]. Cell Death Discovery, 2024, 10 (1): 239.
doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02013-3 |
| 11 | BOZKURT Y , YA VA . Comparison of different freezing techniques, extenders, and cryoprotectants on quality and fertility of cryopreserved Salmo trutta f. fario sperm[J]. Acta Scientiarum Technol, 2024, 45 (1): e64924. |
| 12 | 韩修远, 赵亮, 王闯, 等. 烟酸通过降低氧化应激水平提高绵羊精子低温保存效果[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (5): 1979- 1989. |
| HAN X Y , ZHAO L , WANG C , et al. Nicotinic acid enhances low temperature preservation of sheep sperm by reducing oxidative stress levels[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (5): 1979- 1989. | |
| 13 | WOELDERS H , DE WIT A A C , ENGEL B , et al. Freezing chicken semen: Influence of base medium osmolality, cryoprotectants, cryoprotectant concentration, and cooling rate on post-thaw sperm survival[J]. Cryobiology, 2022, 108, 67- 77. |
| 14 | ZONG Y , LI Y , SUN Y , et al. Mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase (GOT2) protein as a potential cryodamage biomarker in rooster spermatozoa cryopreservation[J]. Poult Sci, 2025, 104 (2): 104690. |
| 15 | LIN H H , MERMILLOD P , GRASSEAU I , et al. Exploring how sucrose-colloid selection improves the fertilizing ability of chicken sperm after cryo-preservation with glycerol[J]. Poult Sci, 2024, 103 (3): 103448. |
| 16 | LI X , WANG L , LIU H , et al. C (60) Fullerenes suppress reactive oxygen species toxicity damage in boar sperm[J]. Nanomicro Lett, 2019, 11 (1): 104. |
| 17 | MEHDIPOUR M , DAGHIGH-KIA H , NAJAFI A , et al. Type Ⅲ antifreeze protein (AFP) improves the post-thaw quality and in vivo fertility of rooster spermatozoa[J]. Poult Sci, 2021, 100 (8): 101291. |
| 18 | GVNGR B H , TVRK G , YVCE S D C C . Reduction of cryopreservation-induced structural, functional and molecular damages in ram sperm by hydrated C (60) fullerene[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2024, 59 (1): e14511- e14513. |
| 19 | ZONG Y , SUN Y , LI Y , et al. Effect of glycerol concentration, glycerol removal method, and straw type on the quality and fertility of frozen chicken semen[J]. Poult Sci, 2022, 101 (6): 101840. |
| 20 | LIN H H , BLESBOIS E , VITORINO CARVALHO A . Chicken semen cryopreservation: importance of cryoprotectants[J]. World 's Poultry Science Journal, 2022, 78 (1): 139- 160. |
| 21 | TANG M , CAO J , YU Z , et al. New semen freezing method for chicken and drake using dimethylacetamide as the cryoprotectant[J]. Poult Sci, 2021, 100 (8): 101091. |
| 22 | MURUGESAN S , MAHAPATRA R . Cryopreservation of Ghagus chicken semen: effect of cryoprotectants, diluents and thawing temperature[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2020, 55 (8): 951- 957. |
| 23 | DAS S , NANDI P R , SARKAR P , et al. Effect of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione reductase supplementation on cryopreservation of Black Bengal buck semen[J]. Trop Anim Health Prod, 2021, 53 (6): 552. |
| 24 | SUSHADI P S , KUWABARA M , ⅡMURA H , et al. Factors affecting cryopreservation-associated damages in sperm motility of cockerels (Gallus gallus domesticus)[J]. Br Poult Sci, 2023, 64 (1): 129- 136. |
| 25 | OLEXIKOVA L , MIRANDA M , KULIKOVA B , et al. Cryodamage of plasma membrane and acrosome region in chicken sperm[J]. Anatomia Histologia Embryologia, 2019, 48 (1): 33- 39. |
| 26 | XU X , WANG Z , LV L , et al. Molecular regulation of DNA damage and repair in female infertility: a systematic review[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2024, 22 (1): 103. |
| 27 | LIU S , LI F . Cryopreservation of single-sperm: where are we today?[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2020, 18 (1): 41. |
| 28 | PARTYKA A , NIŻAŃSKI W . Supplementation of avian semen extenders with antioxidants to improve semen quality—Is it an effective strategy?[J]. Antioxidants, 2021, 10 (12): 1927. |
| 29 | LEÃO A P A , SOUZA A V D , MESQUITA N F , et al. Antioxidant enrichment of rooster semen extenders-A systematic review[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2021, 136, 111- 118. |
| 30 | 姜丽君, 宗云鹤, 李云雷, 等. 抗氧化剂在家禽精液储存中的应用研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (3): 913- 923. |
| JIANG L J , ZONG Y H , LI Y L , et al. Research progress of antioxidant application in poultry semen storage[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (3): 913- 923. | |
| 31 | KHAN I M , CAO Z , LIU H , et al. Impact of Cryopreservation on spermatozoa freeze-thawed traits and relevance OMICS to assess sperm cryo-tolerance in farm animals[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2021, 8, 609180. |
| 32 | LAMMERS M . Post-translational lysine ac(et)ylation in bacteria: a biochemical, structural, and synthetic biological perspective[J]. Front Microbiol, , 2021, 12, 757179. |
| 33 | LI H , LIU H , PEI X , et al. Comparative genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of histone acetyltransferases and histone deacetylases involved in the response to drought in wheat[J]. J Plant Growth Regul, 2022, 41, 1065- 1078. |
| 34 | PENG Z , YANG Q , YEERKEN R , et al. Multi-omics analyses reveal the mechanisms of Arsenic-induced male reproductive toxicity in mice[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2022, 424, 127548. |
| 35 | SILVA R F E , BASSI G , CÂMARA N O S , et al. Sirtuins: key pieces in the host response to pathogens ' puzzle[J]. Mol Immunol,, 2023, 160, 150- 160. |
| 36 | ZHANG Y , WEN P , LUO J , et al. Sirtuin 3 regulates mitochondrial protein acetylation and metabolism in tubular epithelial cells during renal fibrosis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12 (9): 847. |
| 37 | ZHOU T , XIA X , LIU J , et al. Beyond single modification: Reanalysis of the acetylproteome of human sperm reveals widespread multiple modifications[J]. J Proteomics, 2015, 126, 296- 302. |
| 38 | MOSTEK-MAJEWSKA A , MAJEWSKA A , JANTA A , et al. New insights into posttranslational modifications of proteins during bull sperm capacitation[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21 (1): 72. |
| 39 | MARTIN-HIDALGO D , GONZÁLEZ-FERNÁNDEZ L , BRAGADO M J , et al. The sirtuin 1 activator YK 3-237 stimulates capacitation-related events in human spermatozoa[J]. Reprod BioMed Online, 2023, 46 (1): 165- 178. |
| 40 | HOQUE M , LI F Q , WEBER W D , et al. The Cby3/ciBAR1 complex positions the annulus along the sperm flagellum during spermiogenesis[J]. J C B,, 2024, 223 (3): 23. |
| 41 | 祝天喻, 李妍, 刘小飞, 等. 精子发生过程中翻译后修饰的蛋白质组学研究进展[J]. 生理学报, 2020, 72 (1): 75- 83. |
| ZHU T Y , LI Y , LI X F , et al. Advances in proteomic studies of post-translational modifications during spermatogenesis[J]. Acta Physiologica Sinica, 2020, 72 (1): 75- 83. | |
| 42 | ESHUN-WILSON L , ZHANG R , PORTRAN D , et al. Effects of α-tubulin acetylation on microtubule structure and stability[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2019, 116 (21): 10366- 10371. |
| 43 | ZHAO W , LI Z , PING P , et al. Outer dense fibers stabilize the axoneme to maintain sperm motility[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22 (3): 1755- 1768. |
| 44 | CHAWAN V , YEVATE S , GAJBHIYE R , et al. Acetylation/deacetylation and microtubule associated proteins influence flagellar axonemal stability and sperm motility[J]. Biosci Rep, 2020, 40 (12): BSR20202442. |
| 45 | MARTIN-HIDALGO D , GONZALEZ-FERNANDEZ L , BRAGADO M J , et al. The sirtuin 1 activator YK 3-237 stimulates capacitation-related events in human spermatozoa[J]. Reprod Biomed Online, 2023, 46 (1): 165- 178. |
| 46 | BOWKER Z , GOLDSTEIN S , BREITBART H . Protein acetylation protects sperm from spontaneous acrosome reaction[J]. Theriogenology, 2022, 191, 231- 238. |
| 47 | SUN Y , LI Y , SHI L , et al. Differential proteomics highlights specific testicular proteins associated with chicken sperm motility and fertility potential[J]. Ann Agric Sci, 2023, 68, 36- 47. |
| 48 | LI Y , SUN Y , NI A , et al. Seminal plasma proteome as an indicator of sperm dysfunction and low sperm motility[J]. Mol Cell Proteomics,, 2020, 19 (6): 1035- 1046. |
| 49 | SKULACHEV V , VYSSOKIKH M , CHERNYAK B V , et al. Mitochondrion-targeted antioxidant SkQ1 prevents rapid animal death caused by highly diverse shocks[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13 (1): 4326. |
| 50 | MORAES C R , MORAES L E , BLAWUT B , et al. Effect of glucose concentration and cryopreservation on mitochondrial functions of bull spermatozoa and relationship with sire conception rate[J]. Anim Reprod Sci, 2021, 230, 106779. |
| 51 | LEE H , YOON H . Mitochondrial sirtuins: Energy dynamics and cancer metabolism[J]. Mol Cells, 2024, 47 (2): 100029. |
| 52 | M. P R , CHAPA-DUBOCQ X R , SABZALI J . Acetylation of mitochondrial proteins in the heart: The role of sirt3[J]. Front Physiol, 2018, 9, 1094. |
| 53 | MORITZ L , SCHON S B , RABBANI M. , et al. Sperm chromatin structure and reproductive fitness are altered by substitution of a single amino acid in mouse protamine[J]. Nat Struct Mol Biol,, 2023, 30, 1077- 1091. |
| 54 | MARIN-HERNANDEZ A , RODRIGUEZ-ZAVALA J S , JASSO-CHAVEZ R , et al. Protein acetylation effects on enzyme activity and metabolic pathway fluxes[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2022, 123 (4): 701- 718. |
| 55 | ÇAKıR D A , YIRÜN A , ERDEMLI-KÖSE S B. , et al. The combined effects of hsv-1 glycoprotein d and aluminum hydroxide on human neuroblastoma cells: insights into oxidative DNA damage, apoptosis, and epigenetic modifications[J]. Neurotoxicology, , 2025, 18, S0161- 813X(25)00033-6. |
| 56 | ANKE G , HUANYIN T , JIN H , et al. The deacetylase SIRT6 promotes the repair of UV-induced DNA damage by targeting DDB2[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020, 48 (16): 9181- 9194. |
| 57 | NASIRI A , VAISI-RAYGANI A , RAHIMI Z , et al. Evaluation of the relationship among the levels of sirt1 and sirt3 with oxidative stress and dna fragmentation in asthenoteratozoospermic men[J]. Int J Fertil Steril, 2021, 15 (2): 135- 140. |
| 58 | ZHU C H , WEI Y , CHEN F , et al. Investigation on the mechanisms of human sperm DNA damage based on the proteomics analysis by SWATH-MS[J]. Clin Proteomics, 2023, 20 (1): 2. |
| 59 | 汤加勇, 李瑞婷, 赵华, 等. 热应激对雄性哺乳动物精液品质的影响机制及热应激公猪的营养调控[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2021, 57 (2): 7. |
| TANG J Y , LI R T , ZHAO H , et al. Effect of heat stress on semen quality of male mammal and its regulation mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2021, 57 (2): 7. | |
| 60 | 秦娜, 黄林, 董瑞, 等. 虎杖苷减轻大鼠创伤性颅脑损伤后的肠损伤: 基于激活Sirt1介导的SOD2和HMGB1去乙酰化抑制氧化应激和炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42 (1): 93- 100. |
| QI N , HUANG L , DONG R , et al. Polydatin improves intestinal barrier injury after traumatic brain injury in rats by reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory response via activating SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of SOD2 and HMGB1[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42 (1): 93- 100. | |
| 61 | GUO J , NIE J , CHEN Z , et al. Cold exposure-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress regulates autophagy through the SIRT2/FoxO1 signaling pathway[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237 (10): 3960- 3970. |
| 62 | PEIFEI L , QIANGZHEN Y , SISI L , et al. Candidates for reproductive biomarkers: Protein phosphorylation and acetylation positively related to selected parameters of boar spermatozoa quality[J]. Anim Reprod Sci, 2018, 197, S1845112071. |
| 63 | SALEHI M , MAHDAVI A H , SHARAFZ M , et al. Cryopreservation of rooster semen: Evidence for the epigenetic modifications of thawed sperm[J]. Theriogenology, 2019, 142, 15- 25. |
| [1] | MIAO Junjie, ZHANG Riquan, WU Houyi, YOU Xinming, HUANG Yiwen, HUANG Xiaoying, GUO Zhenyang, LIU Jianlin, XIAO Weihua, GUO Tianhua, CHEN Hao, KANG Dongliu. Genome-Wide SNP Analysis Revealed the Characteristics of Germplasm Resources and Genetic Diversity of Jinggang Black-Palm Geese [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3199-3209. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xulin, TANG Yu, LIU Lixiang, FAN Bingfeng, ZHANG Yushi, ZHANG Ying, SHAO Jing, SUN Huimin, CHU Xiaoyu, PENG Feiyu, XU Baozeng. Effect of TLR7/8 Agonist R848 on the Efficiency of Y Sperm Sorting in Sika Deer [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3278-3289. |
| [3] | DONG Jiaojiao, DING Hong, ZHANG Yinliang, ZHANG Ran, LIU Huage, ZANG Sumin, ZHANG Zhenhong, ZHOU Rongyan, LI Lanhui. Differences and Functional Analysis of Cecal Flora in Taihang Chickens Infected with Salmonella Pullorum [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2741-2751. |
| [4] | ZHANG Jian, HAI Erhan, ZHANG Jianjun, LI Boyuan, ZHANG Jiaxin. Glutamine Enhances Frozen-Thawed Semen Quality in Sheep via Activation of the HSF1/HSP70 Signaling Pathway [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2219-2229. |
| [5] | ZHANG Hongyan, WANG Shanpeng, CAO Hailiang, MIN Lingjiang, ZHOU Kaifeng, ZHU Zhendong. Study on Freeze Resistance and Fatty Acid Composition of Boar Sperm [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1755-1767. |
| [6] | QIU Qian, SANG Rui, WANG Wei, LIU Xinman, YU Minghong, LIU Xiaotong, YU Tian, ZHANG Xuemei. Study on the Activity of Huning Powder against Chicken Lung-derived E. coli and the in vitro Effects of Anti-inflammation and Anti-oxidation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1969-1980. |
| [7] | LI Xiaotong, WANG Pengyu, FANG Yingyan, YU Hongxi, ZHANG Yi, WANG Yachun, ZHANG Yuanpei, LI Yanqin, JIANG Li. Mining and Functional Verification of Gene Polymorphisms Loci Related to Bull Sperm Freezability [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1981-1988. |
| [8] | LI Yuanfang, ZHANG Hongyuan, LI Hongtai, LI Zhi, WEI Qianran, WANG Yadong, LI Guoxi, WANG Dandan, LIU Qiaoming. The Effect of Riboflavin Supplementation in Embryonic Eggs on the Development of Skeletal Muscle of Chickens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1159-1169. |
| [9] | WANG Haoyu, MA Keyan, LI Taotao, LI Dengpan, ZHAO Qing, MA Youji. Population Genetic Diversity and Population Structure Analysis of Small-boned Goat Based on Specific-Locus Amplified Fragment Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1170-1179. |
| [10] | YAN Yan, LIU Yanchen, WANG Zhongfa, LI Minjuan, HE Yunan, GUAN Weijun, JIANG Yunliang. Isolation, Culture and Differentiation Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Yolk Sacs from Rhode Island Red Chicken [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1252-1263. |
| [11] | YANG Miaomiao, XIE Li, JIAN Baoyi, LUO Chaowei, XIE Zhuojun, ZHU Piao, ZHOU Tianri, LI Hua, XIANG Hai. Construction and Optimization of Prediction Models for Abdominal Fat Deposition in Adult Hens based on Early Body Size Traits using Machine Learning [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 548-558. |
| [12] | WANG Tao, WANG Qi, DONG Jiaojiao, WANG Dehe, LI Lanhui. Bidirectional Promoter Regulate Transcriptional Expression of PRLR and SPEF2 in Chicken Embryonic Gonads [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 666-678. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xiwen, YIN Yue, LI Xiang, WANG Min, WANG Yongfang, JIN Shuning, FENG Xinhui, ZHAO Yurong. Effects of Ursolic Acid on Breast Meat Quality and Wooden Breast of Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 711-721. |
| [14] | LI Yuanfang, WU Ran, LI Shuaihao, WEI Qianran, WANG Yadong, WANG Dandan, LI Zhi, LI Guoxi, LIU Qiaoming. The Role of G3BP1 in the Proliferation and Differentiation of Chicken Intramuscular Preadipocytes and Identification of Its Molecular Markers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 159-167. |
| [15] | YIN Qiong, GAO Mingchao, YAO Xiumei, LIU Kunyu, LIU Wei, JIE Hongwei, LI Hua, YE Fei. Correlation Analysis between Melanin Content in Breast Muscle and PMEL17 Gene of Muchuan Black-bone Chickens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 168-177. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||