





畜牧兽医学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (12): 6034-6045.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.12.009
收稿日期:2024-11-11
出版日期:2025-12-23
发布日期:2025-12-24
通讯作者:
王祚
E-mail:3522916106@qq.com;zuowang@hunau.edu.cn
作者简介:马天一(2000-),男,山东济宁人,硕士生,主要从事动物营养与饲料科学研究,E-mail:3522916106@qq.com
基金资助:
MA Tianyi1,2( ), GUO Tongjun1, WAN Fachun2, WANG Zuo2,*(
), GUO Tongjun1, WAN Fachun2, WANG Zuo2,*( )
)
Received:2024-11-11
Online:2025-12-23
Published:2025-12-24
Contact:
WANG Zuo
E-mail:3522916106@qq.com;zuowang@hunau.edu.cn
摘要:
瘤胃是反刍动物特有的消化器官,其中栖息的大量各类微生物共同组成了一个复杂且高效的微生态系统。瘤胃微生物发酵的正常进行是保障反刍动物机体健康和生产性能的重要前提。反刍动物饲草料中的霉菌毒素污染较为普遍,其被反刍动物采食后会导致瘤胃微生态紊乱、影响瘤胃发酵,进而危害反刍动物的消化机能与生理健康。本文综述了各类霉菌毒素对反刍动物瘤胃微生物发酵所产生的影响,并探讨了霉菌毒素影响瘤胃微生物发酵的可能机制,以期为防控霉菌毒素危害反刍动物提供新思路。
中图分类号:
马天一, 郭同军, 万发春, 王祚. 霉菌毒素对反刍动物瘤胃微生物发酵的影响及其可能机制[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(12): 6034-6045.
MA Tianyi, GUO Tongjun, WAN Fachun, WANG Zuo. Impacts and Potential Mechanisms of Mycotoxins on Ruminal Microbial Fermentation in Ruminants[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(12): 6034-6045.
表 1
反刍动物饲料原料中常见的霉菌毒素种类"
| 饲料种类 Types of feed | 常见霉菌毒素污染情况 Common mycotoxin contamination scenarios | 参考文献 Reference |
| 玉米及其副产物(玉米酒糟、玉米胚芽饼粕、玉米蛋白粉等) Corn and its by-products (such as corn distiller′s grains, corn germ cake, corn gluten meal, etc.) | 黄曲霉毒素B1 (Aflatoxins B1,AFB1)、玉米赤霉烯酮(Zearalenone,ZEN)、脱氧雪腐镰刀菌烯醇(Deoxynivalenol,DON)、伏马菌素(Fumonisin,FUM)、白僵菌毒素(Beauvericin,BEA) | [ |
| 小麦Wheat | DON和ZEN | [ |
| 饼粕类饲料(豆粕、花生粕、菜籽粕、棉籽粕等) Cakes and meals feed (such as soybean meal, peanut meal, canola meal, cottonseed meal, etc.) | AFB1、DON、FUM和ZEN | [ |
| 牧草(苜蓿干草、羊草、象草等) Forages (such as alfalfa hay, sheepgrass, elephant grass, etc.) | DON、ZEN、AFB1、黄曲霉毒素B2(Aflatoxin B2,AFB2)、FUM、A类单端孢霉烯族毒素(Trichothecene,T-2)、赭曲霉毒素A (Ochratoxin A,OTA)、麦角生物碱(Ergot Alkaloid,EA) | [ |
| 水果及其副产物(苹果渣、柑橘渣和葡萄渣等) Fruits and their by-products (such as apple pomace, citrus pomace, and grape pomace, etc.) | 黄曲霉毒素(Aflatoxin,AF)、DON、T-2、OTA、ZEN | [ |
表 2
不同霉菌毒素及浓度对瘤胃发酵的影响"
| 霉菌毒素 Mycotoxin | 动物 Animal | 试验方法 Experimental Method | 剂量(作用时间) Dosage(action time) | 参数变化 Parameter Change | 参考文献 Reference |
| AFB1 | 迈赫拉班羊 | 体外发酵 | 10 μg·mL-1(96 h) | TVFA↓、pH↑、NH3-N↑、乙酸/丙酸↑ | [ |
| 荷斯坦奶牛 | 体内试验 | 40 μg·kg-1(7 d) | 乙酸↓、丙酸↓、丁酸↓、戊酸↓、异戊酸↓、异丁酸↓、NH3-N↑ | [ | |
| 奶牛 | 体外发酵 | 0.75 μg·L-1(24 h) | TVFA↓、NH3-N↑ | [ | |
| DON | 荷斯坦奶牛 | 体内试验 | 10 mg·kg-1(56 d) | 丙酸↓、异丁酸↓、戊酸↓、TVFA↓、MCP↓、NH3-N↑ | [ |
| 荷斯坦奶牛 | 体外发酵 | 40 mg·kg-1(6 h) | 产气量↓、NH3-N↓、乙酸↓、丙酸↓ | [ | |
| EA | 荷斯坦奶牛 | 体外发酵 | 20 mg·kg-1(14 d) | 乙酸/丙酸↓ | [ |
| PAT | 奶牛 | 体外发酵 | 20 mg·L-1(7 d) | pH↑、NH3-N↑、TVFA↓ | [ |
| ZEN | 荷斯坦奶牛 | 体内试验 | 5 mg·d-1(2 d) | pH↓、TVFA↓、异丁酸↑ | [ |
| AFB1+、AFB2+、DON+、ZEN | 乐至黑山羊 | 体外发酵 | 74.49 μg·kg-1、2.08 μg·kg-1、59.71 μg·kg-1、36.51 μg·kg-1(28 d) | 产气量↓、NH3-N↓ | [ |
| DON+EA | 安格斯杂交牛 | 体内试验 | 5.0 mg·kg-1、2.1 mg·kg-1(112 d) | TVFA↓、pH↑ | [ |
表 3
不同霉菌毒素及浓度对瘤胃微生物的影响"
| 霉菌毒素 Mycotoxin | 动物 Animal | 试验方法 Experimental Method | 剂量(作用时间) Dosage(action time) | 微生物变化 Microbial Change | 参考文献 Reference |
| AFB1 | 公牦牛 | 体内试验 | 60 μg·kg-1(7 d) | 拟杆菌门↓、厚壁菌门↓、普雷沃氏菌属↓ | [ |
| 多赛特公羊 | 体内试验 | 1.0 mg·kg-1(单次摄入) | 厚壁菌门↓、拟杆菌门↑、螺旋体门↑、变形菌门↓、普雷沃氏菌属↓、琥珀酸菌属↓、瘤胃球菌属↓、假丁酸弧菌属↓ | [ | |
| 荷斯坦奶牛 | 体外发酵 | 50 μg·kg-1(10 d) | 普雷沃氏菌属↓、拟杆菌门↓、厚壁菌门↓、变形菌门↑、侧口纲原虫↓、壶菌属真菌↓、枝梗鞭菌属↑ | [ | |
| DON | 荷斯坦奶牛 | 体内试验 | 10 mg·kg-1(56 d) | 瘤胃球菌、AC2044组↓、脱硫弧菌属↓、硒单胞菌属↓ | [ |
| FUM | 荷斯坦奶牛 | 体内试验 | 20 mg·d-1(2 d) | 毛螺菌科↓、普雷沃氏菌科↓ | [ |
| ZEN | 荷斯坦奶牛 | 体内试验 | 5 mg·d-1(2 d) | 毛螺菌科↓、普雷沃氏菌科↓ | [ |
| 湘东黑山羊 | 体内试验 | 500 μg·kg-1(28 d) | 丁酸弧菌属↓、毛螺旋菌属↓、厚壁菌门↓、毛螺菌属↓、普雷沃氏菌属↓ | [ |
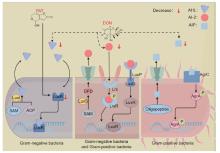
图 1
霉菌毒素对瘤胃微生物群体感应影响机制(本图由Figdraw绘制) PAT. 棒曲霉毒素;DON. 脱氧雪腐镰刀菌烯醇;SAM. S-腺苷甲硫氨酸;ACP. 酰基载体蛋白;AHL. 酰基高丝氨酸内酯;LuxI. AHLs合成酶;LuxS. LuxS蛋白;Lrs. Lrs蛋白;LuxR. LuxR蛋白;LuxP. LuxP蛋白;LuxQ. LuxQ蛋白;AI-2. 自体诱导物2;DPD. 4,5-二羟基-2,3-戊二酮;P. 磷酸基团;Oligopeptide. 寡肽;AIP. 自诱导肽;AgrC. 自诱导肽受体;AgrA. AgrA调控蛋白;Decrease. 降低。图中虚线表示通过Tax4Fun2功能预测发现的潜在结果"
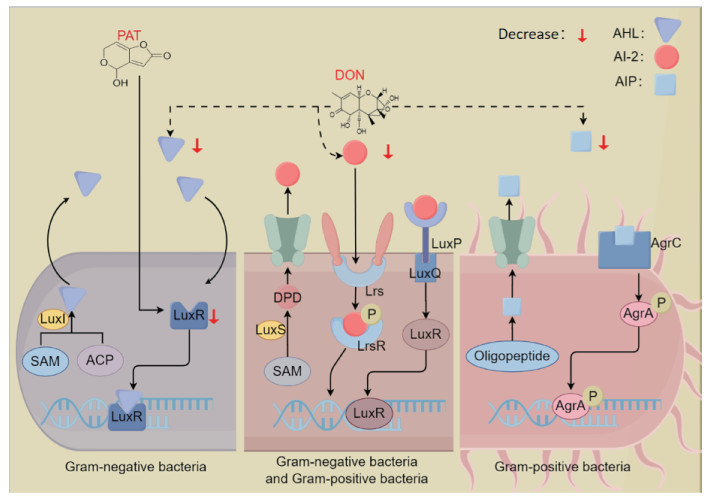
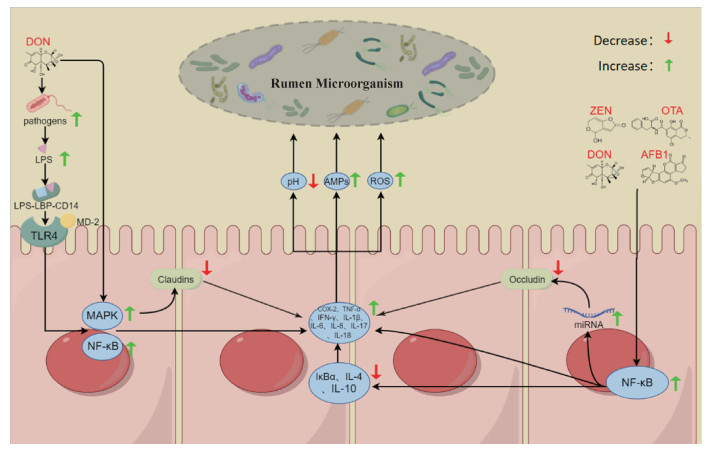
图 3
霉菌毒素通过导致瘤胃上皮炎症以及提高瘤胃上皮通透性影响瘤胃微生物的可能机制(本图由Figdraw绘制) TLR4. Toll受体4;NF-κB. 核因子κB;COX-2. 环氧合酶-2;TNF-α. 肿瘤坏死因子-α;IFN-γ. 干扰素-γ;IL-1β. 白细胞介素-1β;IL-6. 白细胞介素-6;IL-8. 白细胞介素-8;IL-17. 白细胞介素-17;IL-18. 白细胞介素-18;IL-4. 白细胞介素-4;IL-10. 白细胞介素-10;IκBα. NF-κB抑制蛋白α;AMPs. 抗菌肽;LPS. 脂多糖;LPS-LBP-CD14. LPS-LBP-CD14复合物;MD-2. 髓样分化蛋白-2;MAPK. 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶;miRNA. 微小核糖核酸;Claudins. 紧密连接蛋白;Occludin. 闭合蛋白"
| 1 |
GELDERBLOM W C , KRIEK N , MARASAS W , et al. Toxicity and carcinogenicity of the Fusanum monilzforine metabolite, fumonisin B1, in rats[J]. Carcinogenesis, 1991, 12 (7): 1247- 1251.
doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.7.1247 |
| 2 |
ZAIN M E . Impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals[J]. J Saudi Chem Soc, 2011, 15 (2): 129- 144.
doi: 10.1016/j.jscs.2010.06.006 |
| 3 |
HOLANDA D M , KIM S W . Investigation of the efficacy of mycotoxin-detoxifying additive on health and growth of newly-weaned pigs under deoxynivalenol challenges[J]. Anim Biosci, 2021, 34 (3): 405.
doi: 10.5713/ajas.20.0567 |
| 4 |
MAGNOLI A P , POLONI V L , CAVAGLIERI L . Impact of mycotoxin contamination in the animal feed industry[J]. Curr Opin Food Sci., 2019, 29, 99- 108.
doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2019.08.009 |
| 5 |
LOH Z H , OUWERKERK D , KLIEVE A V , et al. Toxin Degradation by Rumen Microorganisms: A Review[J]. Toxins, 2020, 12 (10): 664.
doi: 10.3390/toxins12100664 |
| 6 | 刘康, 张佩华. 奶牛饲料中霉菌毒素的危害及对策[J]. 湖南饲料, 2018 (2): 27- 29. |
| LIU K , ZHANG P H . The harm of mycotoxins in dairy cattle feed and countermeasures[J]. Hunan Feed, 2018 (02): 27- 29. | |
| 7 | 李子谦, 文勇立, 齐沛森, 等. AFB1与吸附剂对牦牛瘤胃发酵性能的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2018, 49 (04): 59- 66. |
| LI Z Q , WEN L Y , QI P S , et al. Effect of aflatoxin B1 and adsorbents on rumen fermentation performance of yaks[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2018, 49 (4): 59- 66. | |
| 8 |
GALLO A , GIUBERTI G , FRISVAD J C , et al. Review on mycotoxin issues in ruminants: Occurrence in forages, effects of mycotoxin ingestion on health status and animal performance and practical strategies to counteract their negative effects[J]. Toxins, 2015, 7 (8): 3057- 3111.
doi: 10.3390/toxins7083057 |
| 9 |
MARTÍN I , GÁLVEZ L , GUASCH L , et al. Fungal pathogens and seed storage in the dry state[J]. Plants, 2022, 11 (22): 3167.
doi: 10.3390/plants11223167 |
| 10 |
CONTE G , FONTANELLI M , GALLI F , et al. Mycotoxins in feed and food and the role of ozone in their detoxification and degradation: An update[J]. Toxins, 2020, 12 (8): 486.
doi: 10.3390/toxins12080486 |
| 11 | 尹清强, 常娟, 王平, 等. 饲料中多种霉菌毒素的危害与生物防控[J]. 饲料工业, 2021, 42 (21): 9- 14. |
| YIN Q Q , CHANG J , WANG P , et al. Hazard and biological control of multi-mycotoxins in feed[J]. Feed Industry, 2021, 42 (21): 9- 14. | |
| 12 | 张勇, 杨玉林, 齐莎日娜, 等. 2021年国内饲料和饲料原料中霉菌毒素污染状况调查[J]. 饲料工业, 2022, 43 (15): 55- 58. |
| ZHANG Y , YANG Y L , QISHA R N , et al. A survey on the mycotoxin contamination of domestic feed and raw materials in 2021[J]. Feed Industry, 2022, 43 (15): 55- 58. | |
| 13 |
XING F , LIU X , WANG L , et al. Distribution and variation of fungi and major mycotoxins in pre- and post-nature drying maize in North China Plain[J]. Food Control, 2017, 80, 244- 251.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.03.055 |
| 14 |
HAN X , XU W , ZHANG J , et al. Natural occurrence of beauvericin and enniatins in corn-and wheat-based samples harvested in 2017 collected from Shandong Province, China[J]. Toxins, 2018, 11 (1): 9.
doi: 10.3390/toxins11010009 |
| 15 |
WEI H , SHU G , ANPING L , et al. Mycotoxin occurrence in feeds and raw materials in China: A five-year investigation[J]. Toxins, 2023, 15 (1): 63.
doi: 10.3390/toxins15010063 |
| 16 | 李思齐, 吕素芳, 李峰, 等. 鲁北地区全株玉米青贮饲料霉菌毒素检测分析[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2018, 38 (5): 27- 29. |
| LI S Q , LV S F , LI F , et al. Detection and analysis on mycotoxins in whole corn silage in North Shandong[J]. China Herbivore Science, 2018, 38 (5): 27- 29. | |
| 17 | 李卫娟, 洪琼花, 高新, 等. 云南省反刍动物用饲草料霉菌毒素污染情况初报[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2017, 37 (2): 20- 23. |
| LI W J , HONG Q H , GAO X , et al. Investigation on mycotoxins contamination of ruminant forage grass and feed in Yunnan[J]. China Herbivore Science, 2017, 37 (2): 20- 23. | |
| 18 | 郑会超, 黄新, 吴建良, 等. 浙江省主要青粗饲料霉菌毒素残留检测分析[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2014, 35 (11): 73- 76. |
| ZHENG H C , HUANG X , WU J L , et al. Detection of mycotoxins residues in major forages in Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2014, 35 (11): 73- 76. | |
| 19 | 张欣昕, 张福金, 张尧, 等. 中国青贮玉米中霉菌毒素的污染情况分析与动物健康风险评估[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2021, 48 (12): 4451- 4459. |
| ZHANG X X , ZHANG F J , ZHANG Y , et al. Analysis of mycotoxin contamination and animal health risk assessment in silage corn of China[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 48 (12): 4451- 4459. | |
| 20 | 席俊程, 殷术鑫, 王璐, 等. 2018年不同地区全株玉米青贮品质分析[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2019, 31 (5): 55- 59. |
| XI J C , YIN S X , WANG L , et al. Quality analysis of whole plant corn silage in different regions in 2018[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2019, 31 (05): 55- 59. | |
| 21 |
LU-XI L , QIN-QIN C , CHAO-DONG Z , et al. Aflatoxin B1 causes oxidative stress and apoptosis in sheep testes associated with disrupting rumen microbiota[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 232, 113225.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113225 |
| 22 |
AMIN A B , MAO S . Influence of yeast on rumen fermentation, growth performance and quality of products in ruminants: A review[J]. Anim Nutr, 2021, 7 (1): 31- 41.
doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.10.005 |
| 23 |
HAN L , XUE W , CAO H , et al. Comparison of rumen fermentation parameters and microbiota of yaks from different altitude regions in Tibet, China[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 12, 807512.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.807512 |
| 24 |
WANG H , LI H , WU F , et al. Effects of dietary energy on growth performance, rumen fermentation and bacterial community, and meat quality of Holstein-Friesians bulls slaughtered at different ages[J]. Animals, 2019, 9 (12): 1123.
doi: 10.3390/ani9121123 |
| 25 |
WANG R , HE S , HUANG D , et al. The response of rumen pH, fermentation parameters and rumen bacteria to feeds of different concentrate to roughage ratios in buffalos[J]. Front. Microbiomes, 2023, 1, 1053794.
doi: 10.3389/frmbi.2022.1053794 |
| 26 |
FINK-GREMMELS J . The role of mycotoxins in the health and performance of dairy cows[J]. Vet J, 2008, 176 (1): 84- 92.
doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.12.034 |
| 27 | YOSHIZAWA T , COTE L , SWANSON S P , et al. Confirmation of DOM-1, a de-epoxidation metabolite of deoxynivalenol, in biological fluids of lactating cows[J]. Agric Biol Chem, 1986, 50 (1): 227- 229. |
| 28 |
MOBASHAR M , HUMMEL J , BLANK R , et al. Ochratoxin A in ruminants-A review on its degradation by gut microbes and effects on animals[J]. Toxins, 2010, 2 (4): 809- 839.
doi: 10.3390/toxins204809 |
| 29 |
FINK-GREMMELS J . Mycotoxins in cattle feeds and carry-over to dairy milk: A review[J]. Food Addit. Contam., 2008, 25 (2): 172- 180.
doi: 10.1080/02652030701823142 |
| 30 | KHODABANDEHLOO M , MALECKY M , ALIARABI H , et al. In vitro evaluation of aflatoxin B1 effect on gas production and ruminal fermentation parameters[J]. Iran J Vet Res, 2019, 20 (4): 263. |
| 31 |
WANG Q , ZHANG Y , ZHENG N , et al. Biological system responses of dairy cows to aflatoxin B1 exposure revealed with metabolomic changes in multiple biofluids[J]. Toxins, 2019, 11 (2): 77.
doi: 10.3390/toxins11020077 |
| 32 |
JIANG Y , OGUNADE I M , ARRIOLA K G , et al. Effects of a physiologically relevant concentration of aflatoxin B1 with or without sequestering agents on in vitro rumen fermentation of a dairy cow diet[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2020, 103 (2): 1559- 1565.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-17318 |
| 33 |
DONG J , ZHAO Z , WANG Z , et al. Impact of deoxynivalenol on rumen function, production, and health of dairy cows: Insights from metabolomics and microbiota analysis[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2024, 465, 133376.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.133376 |
| 34 |
JEONG J S , LEE J H , SIMIZU Y , et al. Effects of the Fusarium mycotoxin deoxynivalenol on in vitro rumen fermentation[J]. Anim Feed Sci Technol, 2010, 162 (3-4): 144- 148.
doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2010.09.009 |
| 35 |
SARICH J M , STANFORD K , SCHWARTZKOPF-GENSWEIN K S , et al. Effect of ergot alkaloids and a mycotoxin deactivating product on in vitro ruminal fermentation using the Rumen simulation technique (RUSITEC)[J]. J Anim Sci, 2022, 100 (9): c226.
doi: 10.1093/jas/skac226 |
| 36 |
RICCIO M B , TAPIA M O , MARTÍNEZ G , et al. Effect of the combination of crude extracts of Penicillium griseofulvum and Fusarium graminearum containing patulin and zearalenone on rumen microbial fermentation and on their metabolism in continuous culture fermenters[J]. Arch Anim Nutr, 2014, 68 (4): 309- 319.
doi: 10.1080/1745039X.2014.927709 |
| 37 |
HARTINGER T , GRABHER L , PACÍFICO C , et al. Short-term exposure to the mycotoxins zearalenone or fumonisins affects rumen fermentation and microbiota, and health variables in cattle[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2022, 162, 112900.
doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.112900 |
| 38 | XUE B , CHUNHUA G , ZHENGFAN Z , et al. Effect of mycotoxins contaminated corn on growth nutrient digestibility and in vitro rumen fermentation in goats[J]. Indian J Anim Sci, 2016, 86 (2): 226- 231. |
| 39 | BIERWORTH R M. Deoxynivalenol and ergot alkaloid levels in wheat grain and their effects on growth performance, rumen parameters, and health status of feedlot cattle. [D]. Saskatoon: University of Saskatchewan, 2023. |
| 40 | 安雅静, 文勇立, 赵佳琦, 等. 宏基因组学揭示AFB1对牦牛瘤胃微生物多样性及CAZy谱影响[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2019, 40 (2): 13- 20. |
| AN Y J , WEN Y L , ZHAO J Q , et al. Metagenomics reveals the effect of AFB1 on rumen microbial diversity and CAZy of yak[J]. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2019, 40 (2): 13- 20. | |
| 41 |
LIN L , CAO Q , ZHANG C , et al. Aflatoxin B1 causes oxidative stress and apoptosis in sheep testes associated with disrupting rumen microbiota[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2022, 232, 113225.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113225 |
| 42 | 张洋. 河南地区玉米青贮黄曲霉毒素B1污染调查及其对瘤胃内环境的影响[D]. 湖南: 湖南农业大学, 2022. |
| ZHANG Y. Contamination investigation of maize silage AFT-B1 and its effect on rumen environment in Henan Province[D]. Hunan: Hunan Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 43 |
颜琼娴, 陈文勋, 惠浩阳, 等. 玉米赤霉烯酮对山羊生长性能、胃肠道发酵模式和菌群结构的影响研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (3): 1109- 1123.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.03.023 |
|
YAN Q X , CHEN W X , HUI H Y , et al. Effects of zearalenone on growth performance, gastrointestinal fermentation and microbiota community structure of goats[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (3): 1109- 1123.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.03.023 |
|
| 44 |
GHEDIRA-CHEKIR L , MAAROUFI K , ZAKHAMA A , et al. Induction of a SOS repair system in lysogenic bacteria by zearalenone and its prevention by vitamin E[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 1998, 113 (1): 15- 25.
doi: 10.1016/S0009-2797(98)00013-1 |
| 45 |
SENGUPTA K , HIVARKAR S S , PALEVICH N , et al. Genomic architecture of three newly isolated unclassified Butyrivibrio species elucidate their potential role in the rumen ecosystem[J]. Genomics, 2022, 114 (2): 110281.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110281 |
| 46 |
WEMHEUER F , TAYLOR J A , DANIEL R , et al. Tax4Fun2: prediction of habitat-specific functional profiles and functional redundancy based on 16S rRNA gene sequences[J]. Environ. Microbiome, 2020, 15, 1- 12.
doi: 10.1186/s40793-019-0349-z |
| 47 |
DAVIES J S , CURRIE M J , WRIGHT J D , et al. Selective nutrient transport in bacteria: multicomponent transporter systems reign supreme[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2021, 8, 699222.
doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.699222 |
| 48 | 陈福暖, 黄瑜, 蔡佳, 等. ABC转运蛋白结构及其在细菌致病性中的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38 (6): 43- 52. |
| CHEN F N , HUANG Y , CAI J , et al. Structure of ABC transporter and research progress of it in bacterial pathogenicity[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2022, 38 (6): 43- 52. | |
| 49 |
MUKHERJEE S , BASSLER B L . Bacterial quorum sensing in complex and dynamically changing environments[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2019, 17 (6): 371- 382.
doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0186-5 |
| 50 |
RASMUSSEN T B , SKINDERSOE M E , BJARNSHOLT T , et al. Identity and effects of quorum-sensing inhibitors produced by Penicillium species[J]. Microbiology, 2005, 151 (5): 1325- 1340.
doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27715-0 |
| 51 | QUADRIYA H , ADEEB MUJTABA ALI S , PARAMESHWAR J , et al. Microbes living together: Exploiting the art for making biosurfactants and biofilms[J]. Implication of Quorum Sensing System in Biofilm Formation and Virulence, 2018, 161- 177. |
| 52 |
GALIÉ S , GARCÍA-GUTIÉRREZ C , MIGUÉLEZ E M , et al. Biofilms in the food industry: health aspects and control methods[J]. Front Microbiol, 2018, 9, 898.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00898 |
| 53 |
DEL MAZO-MONSALVO I , SANTIAGO-MARTÍNEZ M G . Microbes produce biofilms to support their communities in nutrient-limited environments[J]. Nat Microbiol, 2024, 9 (7): 1636- 1637.
doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01743-5 |
| 54 |
XIROS C , SHAHAB R L , STUDER M H . A cellulolytic fungal biofilm enhances the consolidated bioconversion of cellulose to short chain fatty acids by the rumen microbiome[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2019, 103, 3355- 3365.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09706-1 |
| 55 |
WANG H , CHU W , YE C , et al. Chlorogenic acid attenuates virulence factors and pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by regulating quorum sensing[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2019, 103, 903- 915.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9482-7 |
| 56 |
GARCÍA-PÉREZ E , RYU D , LEE C , et al. Ochratoxin A induces oxidative stress in HepG2 Cells by impairing the gene expression of antioxidant enzymes[J]. Toxins, 2021, 13 (4): 271.
doi: 10.3390/toxins13040271 |
| 57 |
CHEN J , HUANG Z , CAO X , et al. Plant-derived polyphenols as Nrf2 activators to counteract oxidative stress and intestinal toxicity induced by deoxynivalenol in swine: An emerging research direction[J]. Antioxidants, 2022, 11 (12): 2379.
doi: 10.3390/antiox11122379 |
| 58 |
MA J , LIU Y , GUO Y , et al. Transcriptional profiling of aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response in macrophages[J]. Toxins, 2021, 13 (6): 401.
doi: 10.3390/toxins13060401 |
| 59 |
CHEN X , ABDALLAH M F , GROOTAERT C , et al. Bioenergetic status of the intestinal and hepatic cells after short term exposure to fumonisin B1 and aflatoxin B1[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (13): 6945.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23136945 |
| 60 |
CHENG Q , JIANG S , HUANG L , et al. Zearalenone induced oxidative stress in the jejunum in postweaning gilts through modulation of the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway and relevant genes[J]. J Anim Sci, 2019, 97 (4): 1722- 1733.
doi: 10.1093/jas/skz051 |
| 61 |
LI J , WANG Y , DENG Y , et al. Toxic mechanisms of the trichothecenes T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol on protein synthesis[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2022, 164, 113044.
doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.113044 |
| 62 |
KIM J J , LEE S B , PARK J K , et al. TNF-α-induced ROS production triggering apoptosis is directly linked to Romo1 and Bcl-XL[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2010, 17 (9): 1420- 1434.
doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.19 |
| 63 |
MA Q . Transcriptional responses to oxidative stress: pathological and toxicological implications[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2010, 125 (3): 376- 393.
doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.11.004 |
| 64 |
SUGIHARA K , KAMADA N . Metabolic network of the gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Inflamm Regen, 2024, 44 (1): 11.
doi: 10.1186/s41232-024-00321-w |
| 65 |
NGUYEN T , NIOI P , PICKETT C B . The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress[J]. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284 (20): 13291- 13295.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.R900010200 |
| 66 |
SUN Y , YANG T , K LEAK R , et al. Preventive and protective roles of dietary Nrf2 activators against central nervous system diseases[J]. Drug Targets, 2017, 16 (3): 326- 338.
doi: 10.2174/1871527316666170102120211 |
| 67 |
JIN S , YANG H , JIAO Y , et al. Dietary curcumin alleviated acute ileum damage of ducks (Anas platyrhynchos) induced by AFB1 through regulating Nrf2-ARE and NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Foods, 2021, 10 (6): 1370.
doi: 10.3390/foods10061370 |
| 68 |
GAO Y , WANG Z , YANG X , et al. Aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A induce a competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network of intestinal immunosuppression by whole-transcriptome analysis[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2023, 854, 158777.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158777 |
| 69 |
BEISL J , PAHLKE G , ABELN H , et al. Combinatory effects of cereulide and deoxynivalenol on in vitro cell viability and inflammation of human Caco-2 cells[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2020, 94 (3): 833- 844.
doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02658-w |
| 70 |
WOJTACHA P , TRYBOWSKI W , PODLASZ P , et al. Effects of a low dose of T-2 toxin on the percentage of T and B lymphocytes and cytokine secretion in the porcine ileal wall[J]. Toxins, 2021, 13 (4): 277.
doi: 10.3390/toxins13040277 |
| 71 |
ZHANG H , WANG Y , ZHOU X , et al. Zearalenone induces immuno-compromised status via TOR/NF/κB pathway and aggravates the spread of Aeromonas hydrophila to grass carp gut (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2021, 225, 112786.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112786 |
| 72 |
SHAITO A , THUAN D T B , PHU H T , et al. Herbal medicine for cardiovascular diseases: efficacy, mechanisms, and safety[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11, 422.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00422 |
| 73 |
POLINÁRIO G , PRIMO L M D G , ROSA M A B C , et al. Antimicrobial peptides as drugs with double response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis coinfections in lung cancer[J]. Front Microbiol, 2023, 14, 1183247.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1183247 |
| 74 | WANG J , CHEN W , WANG Y . The relationship between gut microbiota and inflammatory diseases: the role of macrophages[J]. Front Microbiol, 2020, 11, 535016. |
| 75 |
HURLEY J C . Endotoxemia: methods of detection and clinical correlates[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 1995, 8 (2): 268- 292.
doi: 10.1128/CMR.8.2.268 |
| 76 |
GIOANNINI T L , WEISS J P . Regulation of interactions of Gram-negative bacterial endotoxins with mammalian cells[J]. Immunol Res, 2007, 39, 249- 260.
doi: 10.1007/s12026-007-0069-0 |
| 77 | MIYAKE K. Innate immune sensing of pathogens and danger signals by cell surface Toll-like receptors: Seminars in immunology[C]. Elsevier, 2007. |
| 78 |
TSUKAMOTO H , TAKEUCHI S , KUBOTA K , et al. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein stimulates CD14-dependent Toll-like receptor 4 internalization and LPS-induced TBK1-IKK$\epsilon$-IRF3 axis activation[J]. J Biol Chem, 2018, 293 (26): 10186- 10201.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.796631 |
| 79 |
PINTON P , BRAICU C , NOUGAYREDE J , et al. Deoxynivalenol impairs porcine intestinal barrier function and decreases the protein expression of claudin-4 through a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanism[J]. J Nutr, 2010, 140 (11): 1956- 1962.
doi: 10.3945/jn.110.123919 |
| 80 |
WANG S , ZHANG C , WANG X , et al. Deoxynivalenol inhibits porcine intestinal trefoil factors expression in weanling piglets and IPEC-J2 cells[J]. Toxins, 2019, 11 (11): 670.
doi: 10.3390/toxins11110670 |
| 81 |
LI Y , LIU J , PONGKORPSAKOL P , et al. Relief effects of icariin on inflammation-induced decrease of tight junctions in intestinal epithelial cells[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13, 903762.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.903762 |
| 82 |
NASCIMENTO D D S M , MOTA A C C C , CARVALHO M C D C , et al. Can diet alter the intestinal barrier permeability in healthy people? A aystematic review[J]. Nutrients, 2024, 16 (12): 1871.
doi: 10.3390/nu16121871 |
| 83 |
HU J , CHEN J , XU X , et al. Gut microbiota-derived 3-phenylpropionic acid promotes intestinal epithelial barrier function via AhR signaling[J]. Microbiome, 2023, 11 (1): 102.
doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01551-9 |
| [1] | 高博泉, 王秀敏, 韩冰, 陶慧, 王振龙, 王金全. 漆酶降解霉菌毒素研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(8): 3650-3657. |
| [2] | 宋琳, 赵小伟, 齐英杰, 张养东. 短链脂肪酸对奶牛瘤胃微生物菌群的影响研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(5): 2082-2092. |
| [3] | 张仕琦, 郑楠, 王加启, 赵圣国. 饲粮NFC/NDF比例对奶牛瘤胃中微生物尿素氮代谢流的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(3): 1302-1312. |
| [4] | 杨文慧, 王菲菲, 李晨雷, 孙宇, 秦俊杰, 朱浩, 郭延生. 基于奶牛瘤胃菌群分析四君子散健脾效应的作用机制[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(12): 6487-6501. |
| [5] | 李玮, 吴禧龙, 赵兴瑞, 许兰娇, 杨小斌, 宋小珍. 中药健脾四胃方剂对断奶湖羊生长性能、瘤胃发酵及菌群组成的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(1): 466-478. |
| [6] | 李陇平, 李托, 曹培文, 朱海鲸, 张小玲, 张宸, 肖普辉, 董书伟, 冯平, 屈雷, 毕台飞. 饲粮不同能量水平对陕北白绒山羊断奶公羔瘤胃发酵特性和微生物组成的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(7): 3011-3023. |
| [7] | 龙唐晖, 周江汇, 詹彦波, 张健, 赵向辉, 李艳娇, 欧阳克蕙, 邱清华. 反刍动物瘤胃微生物LuxS/AI-2群体感应研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(5): 1893-1903. |
| [8] | 熊程坤, 张道亮, 杨悦, 丁红研, 赵杰, 李玉, 王希春, 冯士彬, 赵畅, 汤继顺, 吴金节. 芦丁对围产期湖羊瘤胃发酵、瘤胃菌群结构及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(7): 2898-2909. |
| [9] | 赵威, Mahmoud M. Abdelsattar, 柴建民, 王昕, 刁其玉, 张乃锋. 瘤胃微生物移植及应用研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(5): 1792-1803. |
| [10] | 胡立萍, 沈子亮, 王全, 于紫桐, 张琦绮, 毛永江, 杨章平, 张慧敏. 泌乳早期奶牛瘤胃微生物与牛奶脂肪酸组成的变化[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(9): 3018-3028. |
| [11] | 韦肖, 张建童, 龙唐晖, 李开嵘, 李艳娇, 欧阳克蕙, 邱清华. 日粮能量水平对湖羊瘤胃发酵特性和微生物组成的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(9): 3042-3051. |
| [12] | 郭海康, 万发春, 沈维军, 王祚. 畜禽消化道细菌群体感应及相关调控技术研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(6): 1678-1688. |
| [13] | 车大璐, 程素彩, 张伟涛, 赵娟娟, 刘爱瑜, 李晓宇, 周英昊, 高玉红, 孙新胜, 李雪梅. 热应激条件下藿朴蒲苓散对育肥羔羊生长性能、消化性能和血清生化指标的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(6): 1829-1840. |
| [14] | 刘志豪, 贾鹏, 赖琦, 董利锋, 吴秋珏, 高彦华, 田忠红, 刁其玉. 泌乳牛不同胎次干奶期瘤胃发酵指标与甲烷产量的特征[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(12): 4296-4305. |
| [15] | 任曼, 刘欣, 唐玉林, 张瑞雪, 秦俊杰, 朱浩, 郭延生. 归芪益母复方制剂对产后奶牛瘤胃微生物和短链脂肪酸的调节[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(12): 4461-4469. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
