





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2026, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (1): 305-316.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2026.01.026
• ANIMAL NUTRITION AND FEEDS • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Fuxi1,2( ), MA Cui2, HUANG Kang1,2, LI Ruitong2, ZHAO Qingyu2, ZHANG Junmin2, YAN Yibo1(
), MA Cui2, HUANG Kang1,2, LI Ruitong2, ZHAO Qingyu2, ZHANG Junmin2, YAN Yibo1( ), SI Wei2(
), SI Wei2( )
)
Received:2025-01-14
Online:2026-01-23
Published:2026-01-26
Contact:
YAN Yibo, SI Wei
E-mail:wangfuxi0514@163.com;yibo10679@163.com;siwei01@caas.cn
CLC Number:
WANG Fuxi, MA Cui, HUANG Kang, LI Ruitong, ZHAO Qingyu, ZHANG Junmin, YAN Yibo, SI Wei. 18β-glycyrrhetinic Acid can Alleviate Oxidative Stress Induced Lung Injury in Weaned Piglets Induced by D-galactose[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2026, 57(1): 305-316.
Table 1
Composition and nutritional components of basic diets (Dry matter basis)"
| 项目 Item | 含量 Content |
|---|---|
| 原料组成 Raw material composition | |
| 玉米 Corn | 42.83 |
| 膨化玉米 Puffed corn | 12.00 |
| 46%豆粕46% Soybean meal | 11.00 |
| 膨化大豆 Extruded full-fat soybean | 8.80 |
| 大豆浓缩蛋白 Soybean protein concentrate | 4.50 |
| 乳清粉 Whey powder | 10.00 |
| 鱼粉 Fish meal | 3.10 |
| 豆油 Soybean oil | 0.60 |
| 石粉 Limestone | 0.65 |
| 磷酸氢钙 Calcium monophosphate | 1.20 |
| 氯化钠 Sodium chloride | 0.30 |
| 葡萄糖 Glucose | 3.00 |
| 98.5%赖氨酸98.5% Lysine | 0.54 |
| 98.5%蛋氨酸98.5% Methionine | 0.22 |
| 苏氨酸 Threonine | 0.21 |
| 色氨酸 Tryptophan | 0.05 |
| 预混料① Premix | 1.00 |
| 合计 Total | 100.00 |
| 营养成分② Nutrient level | |
| 净能/(MJ·kg-1 ) Net energy | 10.58 |
| 粗蛋白质 Crude protein | 18.92 |
| 钙 Calcium | 1.21 |
| 赖氨酸 Lysine | 1.41 |
| 蛋氨酸 Methionine | 0.54 |
| 苏氨酸 Threonine | 0.85 |
| 色氨酸 Tryptophan | 0.25 |
| 蛋氨酸+半胱氨酸 Methionine+Cysteine | 0.85 |
Table 2
Gene primer sequence"
基因 Gene | 引物序列(5'→3') Primer sequences(5'→3') | 产物长度/bp Product length | 退火温度/℃ Annealing temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 | AAGGGGTTGCGAAGGGAGT | 821 | 60 |
| TTGGGAATGTGGGCTACCTG | |||
| CAT | CCTGCAACGTTCTGTAAGGC | 72 | 60 |
| GCTTCATCTGGTCACTGGCT | |||
| SOD1 | GCGAGTCATGGCGACGAA | 298 | 60 |
| CACAGTGGCCACACCATCTT | |||
| PI3K | GTGGTGAGAAGCATTGGGGA | 85 | 60 |
| GCTAGGATCCAAGATCTGTTACAT | |||
| AKT | TCGCCCCTCAACAACTTCTC | 266 | 60 |
| AGGGACACCTCCATCTCCTC | |||
| TP53 | TCCTCGCCAGTGCAAAAGAA | 68 | 60 |
| CTCGGAACATCTCGAAGCGT |
Table 4
The effect of 18β-GA on antioxidant levels in the lungs"
| 项目 Item | CK组 CK group | D-gal组 D-gal group | GA+gal组 GA+gal group | P值 P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAT/(μmol·(min·mg)-1) | 588.08±60.28ab | 747.22±63.91a | 428.93±40.06b | 0.010 |
| SOD/(U·mg-1) | 0.15±0.01b | 0.21±0.02a | 0.13±0.01b | 0.015 |
| MDA/(nmol·g-1) | 1.45±0.08ab | 1.66±0.14a | 1.04±0.16b | 0.004 |
| 8-OHdG/(ng·g-1) | 55.32±5.98ab | 84.17±12.88a | 34.90±7.54b | 0.014 |
Table 6
The effect of 18β-GA on the content of inflammatory cytokines in the lungs"
项目 Item | CK组 CK group | D-gal组 D-gal group | GA+gal组 GA+gal group | P值 P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-8/(g·ng-1) | 55.54±5.50b | 91.07±10.21a | 43.85±14.16b | 0.019 |
| IL-18/(ng·g-1) | 23.29±2.36a | 24.94±1.47a | 16.23±1.76b | 0.016 |
| TGF-β/(pg·mg-1) | 43.37±2.22b | 55.80±2.77a | 38.21±5.31b | 0.016 |
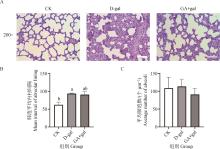
Fig.1
The effect of 18β-GA on the histopathology of weaned piglets’ lungs (Scale bar=50 μm)A. Pathological section image of lung tissue; B. Mean alveolar lining interval; C. Mean number of alveoli. The same lowercase letters above bar charts B and C indicate no significant difference (P>0.05), while different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05). The same as the figure below"

| [1] | BALAM-MAY A J,RAMIREZ-ESTUDILLO C,LAZO-VÁZQUEZ G,VEGA-LÓPEZ M A.Postnatal development of lung T lymphocytes in a porcine model[J].Lung,2014,192:793-802. |
| [2] | RUGGERI J,SALOGNI C,GIOVANNINI S,et al.Association between infectious agents and lesions in post-weaned piglets and fattening heavy pigs with porcine respiratory disease complex (PRDC)[J].Front Vet Sci,2020,7:636 |
| [3] | KUBERKA Z,MEE J F,WALASZEK-KAYAOGLU A,et al.Relationships between pig farm management and facilities and lung lesions’ scores and between lung lesions scores and carcass characteristics[J].BMC Vet Res,2024,20(1):124. |
| [4] | 黄凯勇,王其龙,杨景森,等 .甘草主要活性成分及其在动物生产中的应用研究进展[J].中国畜牧杂志,2022,58(6):48-52. |
| HUANG K Y,WANG Q Y,YANG J S,et al.Research progress on application of main active components of liquorice in animal production[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Science,2022,58(6):48-52.(in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 郭柳彤,宿树兰,季 浩,等.甘草次酸制备工艺及其抗氧化、酪氨酸酶抑制活性研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2022,24(10):46-50. |
| GUO L T,SU S L,JI H,et al.Preparation technology of glycyrrhetinic acid and its antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibitory activities[J].Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022,24(10):46-50.(in Chinese) | |
| [6] | GUO P,JIN L,ZHOU H,et al.Glycyrrhetinic acid protects against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii-induced lung epithelial cells injury by regulating inflammation and oxidative stress[J].BMC Pharmacol Toxicol,2023,24(1):5. |
| [7] | QING C,ZIYUN L,XUEFEI Y,et al.Protective effects of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid on neonatal rats with hyperoxia exposure[J].Inflammation,2022,45(3):1224-1238. |
| [8] | AHMAD S,KHAN A,ALI W,et al.Fisetin rescues the mice brains against D-galactose-induced oxidative stress,neuroinflammation and memory impairment[J].Front Pharmacol,2021,12:612078 |
| [9] | EL-FAR A H,ELGHAITY M M,MOHAMED S A,et al.Diosgenin alleviates D-galactose-induced oxidative stress in rats’ brain and liver targeting aging and apoptotic marker genes[J].Front Mol Biosci,2024,11:1303379. |
| [10] | PINTANA H,SAENGMEARNUPARP T,APAIJAI N,et al.Chronic exposure with 5-alpha reductase inhibitor ameliorates anxiety and depression-like behaviors by reducing systemic oxidative stress in D-galactose-induced aging male rats[J].Alzheimer’s & Dementia,2023,19(S13):074018. |
| [11] | 郭 欣,胡代菊,梅晓冬.烟雾暴露小鼠肺部氧化应激与炎症的变化及戒烟的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报,2015,50(6):757-60. |
| GUO X,HU D J,MEI X D.Oxidative stress and inflammatory changes in the lung caused by cigarette smoking exposure in mice and the effect of smoking cessation[J].Acta Universitatis Medicinalis Anhui,2015,50(6):757-760.(in Chinese) | |
| [12] | ZHANG X Y,ZHANG C,SUN Q Y,et al.Infliximab protects against pulmonary emphysema in smoking rats[J].Chin Med J (Engl),2011,124(16):2502-2506. |
| [13] | WANG G,XIONG D,WU M,et al.Induction of time- and dose-dependent oxidative stress of triazophos to brain and liver in zebrafish (Danio rerio)[J].Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol,2019,228:108640. |
| [14] | 车丽涛,张春勇,韩佃刚,等.甘草次酸对青年母猪生长性能、抗氧化能力及生殖激素浓度的影响[J].动物营养学报,2020,32(4):1586-1594. |
| CHE L T,ZHANG C Y,HAN D G,et al.Effects of glycyrrhetinic acid on growth performance,antioxidant capacity and reproductive hormone concentrations of prepubertal gilts[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2020,32(4):1586-1594.(in Chinese) | |
| [15] | CHEN C-M,HWANG J,CHOU H-C.Immunization with anti-Tn immunogen in maternal rats protects against hyperoxia-induced kidney injury in newborn offspring[J].Pediatr Res,2021,89(3):476-482. |
| [16] | KHUMSRI W,PAYUHAKRIT W,KONGKAEW A,et al.Box a of HMGB1 maintains the DNA gap and prevents DDR-induced kidney injury in D-galactose induction rats[J].In Vivo,2024,38(3):1170. |
| [17] | MA Q.Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity[J].Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,2013,53(1):401-426. |
| [18] | WANG J,WANG S,GUO H,et al.Rosmarinic acid protects rats against post-stroke depression after transient focal cerebral ischemic injury through enhancing antioxidant response[J].Brain Res,2021,1757:147336. |
| [19] | SUN Y,YANG J,WANG L,et al.Crocin attenuates cisplatin-induced liver injury in the mice[J].Hum Exp Toxicol,2014,33(8):855-862. |
| [20] | HUO H,WANG S,BAI Y,et al.Copper exposure induces mitochondrial dynamic disorder and oxidative stress via mitochondrial unfolded protein response in pig fundic gland[J].Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,2021,223:112587. |
| [21] | ZHANG Y,YU D,ZHANG J,et al.The role of necroptosis and apoptosis through the oxidative stress pathway in the liver of selenium-deficient swine[J].Metallomics,2020,12(4):607-616. |
| [22] | ZHU L,WEI M,YANG N,et al.Glycyrrhizic acid alleviates the meconium-induced acute lung injury in neonatal rats by inhibiting oxidative stress through mediating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway[J].Bioengineered,2021,12(1):2616-2626. |
| [23] | MALLIDIS C,AGBAJE I,ROGERS D,et al.Distribution of the receptor for advanced glycation end products in the human male reproductive tract:prevalence in men with diabetes mellitus[J].Hum Reprod,2007,22(8):2169-2177. |
| [24] | JI M,SU X,LIU J,et al.Comparison of naturally aging and D‑galactose induced aging model in beagle dogs[J].Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine,2017,14(6):5881-5888. |
| [25] | BONCOEUR E,CRIQ V S,BONVIN E,et al.Oxidative stress induces extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase in cystic fibrosis lung epithelial cells:Potential mechanism for excessive IL-8 expression[J].The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology,2008,40(3):432-446. |
| [26] | AN X,SUN X,YANG X,et al.Oxidative stress promotes ventilator-induced lung injury through activating NLRP3 inflammasome and TRPM2 channel[J].Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol,2019,47(1):3448-3455. |
| [27] | OMMATI M M,SABOURI S,NIKNAHAD H,et al.Pulmonary inflammation,oxidative stress,and fibrosis in a mouse model of cholestasis:the potential protective properties of the dipeptide carnosine[J].Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol,2023,396(6):1129-1142. |
| [28] | YOSHIDA T,ABE K,IKEDA T,et al.Inhibitory effect of glycyrrhizin on lipopolysaccharide and D-galactosamine-induced mouse liver injury[J].European Journal of Pharmacology,2007,576(1):136-142. |
| [29] | CHEN J,WANG C,PAN X,et al.Glycyrrhetinic acid mitigates radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting the secretion of TGF-β1 by treg cells[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2024,118(1):218-230. |
| [30] | SHANG Y,ZHOU Q,WANG T,et al.Airborne nitro-PAHs induce Nrf2/ARE defense system against oxidative stress and promote inflammatory process by activating PI3K/Akt pathway in A549 cells[J].Toxicology in Vitro,2017,44:66-73. |
| [31] | SHETTY S K,TIWARI N,MARUDAMUTHU A S,et al.p53 and miR-34a feedback promotes lung epithelial injury and pulmonary fibrosis[J].Am J Pathol,2017,187(5):1016-1034. |
| [32] | LUO D,TANG X,WANG Y,et al.Selenium deficiency exacerbated Bisphenol A-induced intestinal toxicity in chickens:Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest mediated by ROS/P53[J].Sci Total Environ,2024,913:169730. |
| [33] | SHEN L,FAN L,LUO H,et al.Cow placenta extract ameliorates d-galactose-induced liver damage by regulating BAX/CASP3 and p53/p21/p16 pathways[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2024,323:117685. |
| [34] | ZHENWEN L,YU C,RIFANG G,et al.Asiaticoside prevents oxidative stress and apoptosis in endothelial cells by activating ROS-dependent p53/Bcl-2/Caspase-3 signaling pathway[J].Curr Mol Med,2023,23(10):1116-1129. |
| [35] | GUO X L.Glycyrrhizic acid attenuates CCl4-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in ratsviaa p53-mediated pathway[J].World J Gastroenterol,2013,19(24):3781-3791. |
| [1] | GUO Zhennan, LÜ Shizheng, XIAO Zongxian, WU Qiji, BAO Yujia, LI Qing, LI Qifa, LI Qiqi, DU Xing. KLF5 Inhibits the Transcription of miR-370 and miR-219a in Sow Follicular Granulosa Cells under Oxidative Stress [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2026, 57(1): 234-245. |
| [2] | MENG Yunlong, DENG Yuankun, TAN Bi’e, WANG Jing. Research Progress on Tryptophan Metabolites in Alleviating Intestinal Oxidative Stress [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2026, 57(1): 46-57. |
| [3] | LI Jiapeng, LIU Qing, SUN Jiayu, MA Zefang, CUI Kai. Screening of Key Genes for Coat Color Formation in Silver Fox Based on Transcriptome and Proteome Analyses [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4379-4392. |
| [4] | QIN Yang, XIA Siting, HE Liuqin, WANG Tianli, LIU Yuyan, JIANG Xiaohan, LIU Zhihao, LIU Siwei, LI Tiejun, YIN Yulong. Effect of Chronic Oxidative Stress on Trace Elements in Organ Tissues of Weaned Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4452-4460. |
| [5] | LIU Xinyue, LI Danni, ZONG Ying, SHI Kun, LI Jianming, DIAO Naichao, ZENG Fanli, DU Rui. Transcriptome Analysis of RAW264.7 Macrophages Infected with Rv3435c Recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4657-4672. |
| [6] | WANG Chaohui, LIU Xiaoying, YANG Xiaojun, LIU Yanli. The Mechanism of Betaine in Alleviating Abnormal Lipid Metabolism and Oxidative Stress Induced by Oleic Acid in Chicken Embryo Liver Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4741-4749. |
| [7] | FAN Jing, LI Wei, ZHU Yan, Wudubala , SHI Jiahui, Husile , WU Jianghong. Study on Rumen Morphological Changes and Gene Expression Differences in Hu Sheep at Different Developmental Stages [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3773-3786. |
| [8] | MENG Yaxuan, LIU Yan, WANG Jing, CHEN Guoshun, FENG Tao. Effects of Glucosamine on Serum Anti-oxidation, Inflammatory Indexes and Intestinal Microbes in Weaned Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3908-3921. |
| [9] | LU Le, LUO Xianzu, HUANG Xinyu, ZOU Hui, GU Jianhong, LIU Xuezhong, BIAN Jianchun, LIU Zongping, YUAN Yan. Cadmium Can Induce Oxidative Stress in the Cerebral Cortices by Affecting the Intestinal Flora of Rats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3540-3547. |
| [10] | LIU Sha, SU Meng, GAO Qianmei, SONG Danli, ZHAO Guiping, LI Jianhui, LI Qinghe. Transcriptome Analysis of Chicken Macrophages after SIRT1 Activated [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2661-2671. |
| [11] | ZHU Aiwen, WANG Jian, ZHU Gehui, LIU Haixia, PINGCUO Bandan, WANG Jun, DEQING Zhuoga, YAN Wei, HAN Dayong. Zearalenone Induced Proliferation, Apoptosis, Oxidative Stress and NAC Protective Mechanism of Sertoli Cells in Pengbo Semi-fine Wool Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2752-2764. |
| [12] | LIU Zilong, LI Qiao, WU Yi, WANG Huihui, LI Taotao, MA Youji. Transcriptomics Reveals the Effects of Chinese Herbal Feed Additives on Bile Acids Metabolism and Immune Function in Hu Sheep Liver Tissue [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 3014-3026. |
| [13] | CHEN Yun, CHEN Liyuan, SONG Wenjing, ZHANG Xinke, XU Han, WU Jiayi, ZHAO Cuiyan, ZHANG Shouquan. Research Progress on the Mechanism of T-2 Toxin 's Impact on Male Animal Reproduction [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2038-2046. |
| [14] | ABABAIKERI Buweihailiqiemu, AIHEMAITIJIANG Aihemaitiniyazi, MOHAMMADTURSUN Nabijan, SHAN Wenjuan. Preliminary Study on the Function of PRDX1 Antioxidant Gene in Tarim Red Deer [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1216-1230. |
| [15] | ZHOU Wentao, WANG Chenyu, ZHOU Hui, LIU Hongbiao, FENG Shuhuan, FAN Gaosheng, LI Tiejun, HE Liuqin. Effects of Tannic Acid on Muscle Morphology, Flavor Amino Acids, and Expression of Muscle Fiber-related Genes in Immunostressed Weaned Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1290-1301. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||