





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (2): 679-688.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.02.019
• Animal Biotechnology and Reproduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
HE Yu1( ), WANG Xiangyu2, DI Ran2, CHU Mingxing2,*(
), WANG Xiangyu2, DI Ran2, CHU Mingxing2,*( ), LIANG Chen1,*(
), LIANG Chen1,*( )
)
Received:2024-08-09
Online:2025-02-23
Published:2025-02-26
Contact:
CHU Mingxing, LIANG Chen
E-mail:heyu_22@163.com;chumingxing@caas.cn;cekiv@163.com
CLC Number:
HE Yu, WANG Xiangyu, DI Ran, CHU Mingxing, LIANG Chen. BMP4/SMAD4 Downregulates GJA1 Gene Expression to Affect the Gap Junctional Intercellular Communication Activity in Sheep Ovarian Granulosa Cells[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 679-688.
Table 1
Primer sequences of amplifying genes and gene interference sequences"
| 基因 Gene | GenBank登录号 GenBank ID | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequence | 产物长度/bp Products size |
| GJA1 | XM_004011159.5 | F:GGAAAGTACCAAACAGCAGCAGAC R:GCAAGCCAAGTGATTGAACTCCTC | 114 |
| SMAD4 | XM_060405186.1 | F:CTTCAGCACCACCCGCCTATG R:ACACCAATACTCAGGAGCAGGATG | 120 |
| si-NC | F:CTTCAGCACCACCCGCCTATG R:ACACCAATACTCAGGAGCAGGATG | ||
| si-SMAD4 | F:CTTCAGCACCACCCGCCTATG R:ACACCAATACTCAGGAGCAGGATG |

Fig. 2
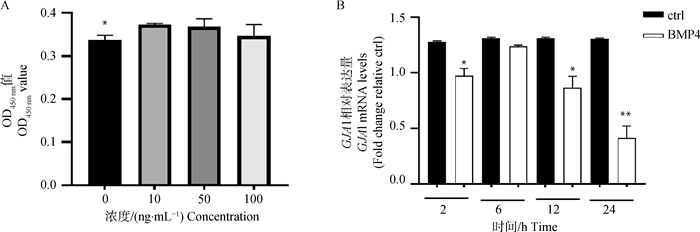
BMP4 downregulates the expression of GJA1 in granulosa cells A. CCK-8 results of treatment with different concentrations of BMP4; B. The mRNA expression levels of GJA1 after treatment with 100 ng·mL-1 BMP4 for different durations. * indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), ** indicate extremely significant differences (P < 0.01), the same as below"
| 1 |
LEI L , WANG Y T , HU D , et al. Astroglial connexin 43-mediated gap junctions and hemichannels: potential antidepressant mechanisms and the link to neuroinflammation[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2023, 43 (8): 4023- 4040.
doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01426-5 |
| 2 |
LI Y T , ACOSTA F M , JIANG J X . Gap junctions or hemichannel-dependent and independent roles of connexins in fibrosis, epithelial-mesenchymal transitions, and wound healing[J]. Biomolecules, 2023, 13 (12): 1796.
doi: 10.3390/biom13121796 |
| 3 |
CHO S J , OH J H , BAEK J , et al. Intercellular cross-talk through lineage-specific gap junction of cancer-associated fibroblasts related to stromal fibrosis and prognosis[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13 (1): 14230.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40957-1 |
| 4 |
SIDELL N , RAJAKUMAR A . Retinoic acid action in cumulus cells: implications for oocyte development and in vitro fertilization[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (3): 1709.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25031709 |
| 5 |
WANG Y , QI J J , YIN Y J , et al. Ferulic acid enhances oocyte maturation and the subsequent development of bovine oocytes[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (19): 14804.
doi: 10.3390/ijms241914804 |
| 6 | MÉNDEZ M S , ARGUDO D E , SORIA M E , et al. Effect of the addition of melatonin in the oocyte maturation and/or vitrification medium on in vitro production of bovine embryos[J]. Rev Investig Vet, 2020, 31 (1): 9. |
| 7 |
EMORI C , SUGIURA K . Role of oocyte-derived paracrine factors in follicular development[J]. Anim Sci J, 2014, 85 (6): 627- 633.
doi: 10.1111/asj.12200 |
| 8 |
WU H C , CHANG H M , YI Y Y , et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 6 affects cell-cell communication by altering the expression of Connexin43 in human granulosa-lutein cells[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2019, 498, 110548.
doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2019.110548 |
| 9 |
CHANG H M , CHENG J C , LEUNG P C K . Theca-derived BMP4 and BMP7 down-regulate connexin43 expression and decrease gap junction intercellular communication activity in immortalized human granulosa cells[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2013, 98 (3): E437- E445.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-3851 |
| 10 |
CHEN Y C , CHANG H M , CHENG J C , et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 up-regulates connexin43 expression in human granulosa cells[J]. Hum Reprod, 2015, 30 (9): 2190- 2201.
doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev175 |
| 11 | WU Y T , CHANG H M , HUANG H F , et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 regulates cell-cell communication by down-regulating connexin43 expression in luteinized human granulosa cells[J]. Mol Hum Reprod, 2017, 23 (3): 155- 165. |
| 12 |
YANG Y , LIANG J , CHEN S Y , et al. O-Fucosylation of BMP1 promotes endometrial decidualization by activating BMP/Smad signaling pathway[J]. Biol Reprod, 2023, 109 (2): 172- 183.
doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioad060 |
| 13 |
CROSS E E , THOMASON R T , MARTINEZ M , et al. Application of small organic molecules reveals cooperative TGFβ and BMP regulation of mesothelial cell behaviors[J]. ACS Chem Biol, 2011, 6 (9): 952- 961.
doi: 10.1021/cb200205z |
| 14 | 龚一鸣, 贾一轩, 李佳骏, 等. 不同FecB基因型和不同直径绵羊卵泡中BMP/SMAD通路活性及蛋白表达差异[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (9): 3957- 3967. |
| GONG Y M , JIA Y X , LI J J , et al. BMP/SMAD pathway activity and protein expression profiles in ovarian follicles with different diameters in diverse FecB genotyped ewes[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (9): 3957- 3967. | |
| 15 | 杨初蕾, 李星瑶, 张译元, 等. 绵羊骨形态发生蛋白受体-1B基因研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2024, 51 (2): 649- 658. |
| YANG C L , LI X Y , ZHANG Y Y , et al. Research progress on bone morphogenetic protein receptor type-1B gene in sheep[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51 (2): 649- 658. | |
| 16 |
XIN X , CHANG H M , LEUNG P C K , et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 6 induces downregulation of pentraxin 3 expression in human granulosa lutein cells in women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. J Assist Reprod Genet, 2024, 41 (1): 31- 48.
doi: 10.1007/s10815-023-02972-z |
| 17 |
YUAN J S , DENG Y , ZHANG Y Y , et al. Bmp4 inhibits goose granulosa cell apoptosis via PI3K/AKT/Caspase-9 signaling pathway[J]. Anim Reprod Sci, 2019, 200, 86- 95.
doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2018.11.014 |
| 18 |
AMPEY B C , AMPEY A C , LOPEZ G E , et al. Cyclic nucleotides differentially regulate Cx43 gap junction function in uterine artery endothelial cells from pregnant ewes[J]. Hypertension, 2017, 70 (2): 401- 411.
doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09113 |
| 19 |
SUGIURA K , SU Y Q , EPPIG J J . Does bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP6) affect female fertility in the mouse?[J]. Biol Reprod, 2010, 83 (6): 997- 1004.
doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.086777 |
| 20 |
LIVAK K J , SCHMITTGEN T D . Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-△△Ct method[J]. Methods, 2001, 25 (4): 402- 408.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 |
| 21 | 闫华, 只达石, 刘锐. 荧光显微镜划痕标记染料示踪技术的改进[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2006, 6 (2): 123. |
| YAN H , ZHI D S , LIU R . Improvement of scratch marking dye tracing technology for fluorescence microscope[J]. Chinese Journal of Contemporary Neurology and Neurosurgery, 2006, 6 (2): 123. | |
| 22 | 颜玉, 鲍秀琦, 薛勇, 等. 应用划痕标记染料示踪技术检测草苁蓉甲醇提取物对大鼠肝癌细胞功能的影响[J]. 黑龙江医药科学, 2011, 34 (5): 3- 4. |
| YAN Y , BAO X Q , XUE Y , et al. Detection of effect of boschniakia rossica extract on rat hepatoma cell function by tracer technique of scratch labeled by dye[J]. Heilongjiang Medicine and Pharmacy, 2011, 34 (5): 3- 4. | |
| 23 |
WU M R , CHEN G Q , LI Y P . TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation, homeostasis and disease[J]. Bone Res, 2016, 4, 16009.
doi: 10.1038/boneres.2016.9 |
| 24 | BRZERT M , KRANC W , NAWROCKI M J , et al. New markers for regulation of transcription and macromolecule metabolic process in porcine oocytes during in vitro maturation[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 21 (3): 1537- 1551. |
| 25 |
CHEN Y C , CHANG H M , CHENG J C , et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 up-regulates connexin43 expression in human granulosa cells[J]. Hum Reprod, 2015, 30 (9): 2190- 2201.
doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev175 |
| 26 |
YAO Y L , REHEMAN A , XU Y F , et al. miR-125b contributes to ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis through targeting BMPR1B, a major gene for sheep prolificacy[J]. Reprod Sci, 2019, 26 (2): 295- 305.
doi: 10.1177/1933719118770544 |
| 27 | TALHOUK R , TARRAF C , KOBROSSY L , et al. Modulation of Cx43 and gap junctional intercellular communication by androstenedione in rat polycystic ovary and granulosa cells in vitro[J]. J Reprod Infertil, 2012, 13 (1): 21- 32. |
| 28 | MOHAN JEENA L , KUMAR D , RAHANGDALE S , et al. Transcriptional profile of cumulus associated GJA1, PTX3, PRSS35, and SERPINE2 genes with oocytes and embryonic development in water buffalo[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2022, 49 (7): 6285- 6293. |
| 29 | DA SILVA A M S , BRUNO J B , DE LIMA L F , et al. Connexin 37 and 43 gene and protein expression and developmental competence of isolated ovine secondary follicles cultured in vitro after vitrification of ovarian tissue[J]. Theriogenology, 2016, 85 (8): 1457- 1467. |
| 30 |
LI Y X , CHANG H M , SUNG Y W , et al. Betacellulin regulates gap junction intercellular communication by inducing the phosphorylation of connexin 43 in human granulosa-lutein cells[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2023, 16 (1): 103.
doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01185-3 |
| 31 | KIM J E , LEE M Y , KANG M J , et al. Establishment of a useful in vitro decidual induction model using eCG-primed nonpregnant mouse endometrial stromal cells[J]. Biol Reprod, 2022, 107 (6): 1464- 1476. |
| 32 | ZHENG X M , JING H , GAO S Q , et al. LH upregulates connexin 43 expression in granulosa cells by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway[J]. Reprod Fertil Dev, 2021, 33 (3): 239- 244. |
| 33 | WU C H , YANG J G , YANG J J , et al. Androgen excess down-regulates connexin43 in a human granulosa cell line[J]. Fertil Steril, 2010, 94 (7): 2938- 2941. |
| 34 | SANTOS J D R , BATISTA R I T P , MAGALHÃES L C , et al. Overexpression of hyaluronan synthase 2 and gonadotropin receptors in cumulus cells of goats subjected to one-shot eCG/FSH hormonal treatment for ovarian stimulation[J]. Anim Reprod Sci, 2016, 170, 15- 24. |
| 35 | MCGINNIS L K , KINSEY W H . Role of focal adhesion kinase in oocyte-follicle communication[J]. Mol Reprod Dev, 2015, 82 (2): 90- 102. |
| 36 | SHEN P L , XU J , WANG P , et al. A new three-dimensional glass scaffold increases the in vitro maturation efficiency of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) oocyte via remodelling the extracellular matrix and cell connection of cumulus cells[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2020, 55 (2): 170- 180. |
| 37 | YANG Y H , KANNO C , SAKAGUCHI K , et al. Extension of the culture period for the in vitro growth of bovine oocytes in the presence of bone morphogenetic protein-4 increases oocyte diameter, but impairs subsequent developmental competence[J]. Anim Sci J, 2017, 88 (11): 1686- 1691. |
| 38 | NAKAJIMA K , KIDANI T , MIURA H . Molecular profiling of bone remodeling occurring in musculoskeletal tumors[J]. J Orthop Res, 2021, 39 (7): 1402- 1410. |
| 39 | TASCA A , ASTLEFORD K , BLIXT N C , et al. SMAD1/5 signaling in osteoclasts regulates bone formation via coupling factors[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13 (9): e0203404. |
| 40 |
LI Y X , CHANG H M , ZHU H , et al. EGF-like growth factors upregulate pentraxin 3 expression in human granulosa-lutein cells[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2024, 17 (1): 97.
doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01404-5 |
| 41 | JI J H , ZHOU Y J , LI Z P , et al. Impairment of ovarian follicular development caused by titanium dioxide nanoparticles exposure involved in the TGF-β/BMP/Smad pathway[J]. Environ Toxicol, 2023, 38 (1): 185- 192. |
| [1] | CHU Yijian, CUI Jiuzeng, LI Zengkai, ZHANG Lei, CHU Tingting, HUANG Yanping, SONG Yuxuan. Comparative Study on Vaginal Microorganisms in Pre-endometrial Receptivity and Endometrial Receptivity of Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 689-699. |
| [2] | WANG Xiaofei, WANG Bosen, WEI Mengyao, JIANG Luyao, XU Ganggang, LIU Jiaxin, MA Yingtian, WANG Li, SONG Yuxuan, ZHANG Lei. Study on the Role of Ewe's Milk in Ameliorating Pathological Changes in the Liver and Kidney of Mice in a Diabetes Model [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 870-882. |
| [3] | LI Wei, WU Xilong, ZHAO Xingrui, XU Lanjiao, YANG Xiaobin, SONG Xiaozhen. Effects of Chinese Medicine Jianpisiwei Formulas on Growth Performance, Rumen Fermentation and Microbiota Composition of Weaned Hu Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 466-478. |
| [4] | Yuhang JIA, Liangfu GUO, Runan ZHANG, Ayong ZHAO, Yufang LIU, Mingxing CHU. miR-127 Regulated the Proliferation and Differentiation of Sheep Skeletal Myoblasts and Its Transcription Factor PAX3 Screening [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3864-3875. |
| [5] | Yiming GONG, Yixuan JIA, Jiajun LI, Xiangyu WANG, Xiaoyun HE, Mingxing CHU, Ran DI. BMP/SMAD Pathway Activity and Protein Expression Profiles in Ovarian Follicles with Different Diameters in Diverse FecB Genotyped Ewes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3957-3967. |
| [6] | Peng SHEN, Yi WANG, Weijie REN, Yongchun YANG, Houhui SONG, Zhiliang WANG. Meta Analysis of Immune Antibody Monitoring for Lumpy Skin Disease [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3649-3658. |
| [7] | Ting WANG, Yuanqing ZHANG, Yibo YAN, Mingjun SHANGGUAN, Hongyu GUO, Zhiwu WANG. The Genetic Structure Analysis and the Comparative Analysis of Selection Signals in 'Tezanghan' Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2913-2926. |
| [8] | Mingliang HE, Xiaoyang LÜ, Yongqing JIANG, Zhenghai SONG, Yeqing WANG, Huiguo YANG, Shanhe WANG, Wei SUN. Function Analysis of SOX18 in Hu Sheep Hair Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells Based on Transcriptome Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2409-2420. |
| [9] | Chang LIU, Kexing HAO, Yan CHEN, Weibin ZENG, Hengbin YU, Lei CHEN, Jing WANG, Guangdong HU. Effects of Interference with PPARγ Gene on Proliferation, Apoptosis, Migration and Lipid Accumulation of Trophoblast Cells in Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2421-2430. |
| [10] | Ying CHEN, Dayong CHEN, Riga WU, Chunjuan QIU, Lihong FAN, Meirong BAO, Yuan YUE, Hongyan LIANG, Jiaxin ZHANG, Jianhui TIAN, Lei AN, Liqin WANG. Influence of Meat Sheep Varieties on the Scale Application of in vitro Embryo Production Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2451-2459. |
| [11] | Zhibin LUO, Huimin OU, Jianzhong LI, Zhiliang TAN, Jinzhen JIAO. Effects of Low Protein Diet Supplemented with Rumen-protected Amino Acids on Growth Performance, Nutrient Apparent Digestibility and Meat Quality of Hulun Buir Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2498-2509. |
| [12] | PENG Peiya, CHEN Yuhan, YANG Long, WANG Ming, ZHAO Ruiting, HE Jun, YIN Yulong, LIU Mei. Research Progress of Copy Number Variation in Livestock [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1356-1369. |
| [13] | ZHANG Shaohua, WANG Shuai, ZOU Yang, LIU Zhongli, CAI Xuepeng. Advances in Detection Approaches for Ovine Haemonchosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1499-1510. |
| [14] | YANG Yang, YU Qian, LIU Yucheng, YANG Hua, ZHAO Zhuo, WANG Limin, ZHOU Ping, YANG Qingyong, DAI Rong. Identification and Tissue Expression Analysis of the Sheep MYL Gene Family [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1551-1564. |
| [15] | CHANG Xindan, HU Fan, WU Zhiwu, YE Bingsen, LIU Tiehai, LIN Jie, HE Zhixiong, TAN Zhiliang. Effect of High Proportion Rumen Bypass Fat Diet on Feeding Behavior of Growing Mutton Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1077-1084. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||