





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (10): 4690-4699.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.10.040
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yongqing LIU( ), Gang ZHANG, Yanling XIONG, Zhongxin SUN, Fan GAO, Ting LIU, Hui LI*(
), Gang ZHANG, Yanling XIONG, Zhongxin SUN, Fan GAO, Ting LIU, Hui LI*( )
)
Received:2023-11-07
Online:2024-10-23
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Hui LI
E-mail:2231514747@qq.com;hli23@gzu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Yongqing LIU, Gang ZHANG, Yanling XIONG, Zhongxin SUN, Fan GAO, Ting LIU, Hui LI. Effects of Heat Stress on Duodenal Mucosal Structure, HIF-1 and Its Related Protein Expression in Congjiang Xiang Pigs[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4690-4699.
Table 1
Primers sequences for qRT-PCR"
| 基因名称 Gene name | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequence(5′→3′) | 产物大小/bp Product size | 退火温度/℃ Annealing temperature | 登录号 Accesion No. |
| PHD-2 | F:TCATGAGCAGCATGGACGAC | 117 | 63 | XM_021073581.1 |
| R:CGTAACCTGTTCCGTTGCC | ||||
| HIF-1α | F: TCCTTCGATCAGTTGTCACCATTGG | 89 | 64 | NM_001123124.1 |
| R: GGCATTGGAGTGGGCTGGAATAC | ||||
| HSP90 | F: CAGAGGCGGACAAGAACGACAAG | 116 | 63 | NM_213973.2 |
| R: GATCCTGTTGGCGTGCGTCTG | ||||
| β-actin | F: TCTGGCACCACACCTTCT | 114 | 60 | XM_021086047.1 |
| R: TGATCTGGGTCATCTTCTCAC |
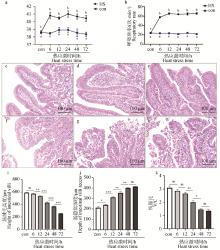
Fig. 1
Effect of heat stress to intestinal villi structure (200×) a. Rectal temperature; b. Respiratory rate; c. Duodenum histology structure of control group; d. Duodenum histology of group HS 6h; e. Duodenum histology of group HS 12h; f. Duodenum histology of group HS 24h; g. Duodenum histology of group HS 48h; h. Duodenum histology of group HS 72h; i. Height of duodenum intestinal villi; j. Depth of duodenum intestinal crypt; k. Ratio of villi height and gland depth (V/C). ns. No statistical difference; *, **, ***. Represent P < 0.05, P < 0.01, P < 0.001, respectively. The same as below"
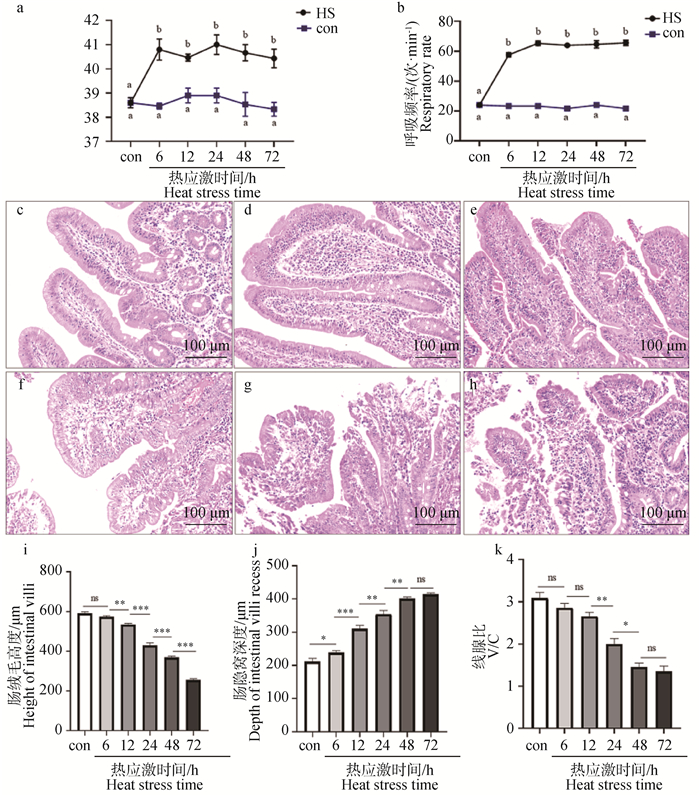

Fig. 3
Effect of heat stress on goblet cell number in duodenal mucosac(200×) a. Intestinal mucosa of control group, goblet cell appears blue; b. Intestinal mucosa goblet cells of group HS 6h; c. Intestinal mucosa goblet cells of group HS 12h; d. Intestinal mucosa goblet cells of group HS 24h; e. Intestinal mucosa goblet cells of group HS 48h; f. Intestinal mucosa goblet cells of group HS 72h;g. Changes in the number of intestinal mucosa goblet cells"

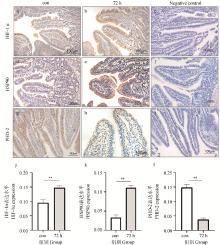
Fig. 5
Localization of HIF-1α, HSP90 and PHD-2 under heat stress(200×) a-b. Localization of HIF-1α in the duodenal; c. HIF-1α negative control; c-d. Localization of HSP90 in the duodenal; f. HSP90 negative control; g-h. Localization of PHD-2 in the duodenal; i. PHD-2 negative control. The positive expression is shown in brown in a~i. j. HIF-1α expression level; k. HSP90 expression level; l. PHD-2 expression level"


Fig. 6
Effect of heat stress to HIF-1α, HSP90 and PHD-2 expression a-c. Relative expression of HIF-1α、HSP90 and PHD-2 mRNA in control group and different HS treatment group; d. Representative Western blot bands of HIF-1α、HSP90 and PHD-2 in control group and different HS treatment group; e-g. Relative expression of HIF-1α、HSP90 and PHD-2 in control group and different HS treatment group"

| 1 | GHULAM MOHYUDDIN S , KHAN I , ZADA A , et al. Influence of heat stress on intestinal epithelial barrier function, tight junction protein, and immune and reproductive physiology[J]. BioMed Res Int, 2022, 2022, 8547379. |
| 2 | HAO Y , FENG Y J , LI J L , et al. Role of MAPKs in HSP70's protection against heat stress-induced injury in rat small intestine[J]. BioMed Res Int, 2018, 2018, 1571406. |
| 3 | 郑文亚, 李国生, 刘犇, 等. 运输应激对山羊小肠形态和热休克蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2021, 57 (12): 207- 212. |
| ZHENG W Y , LI G S , LIU B , et al. Effects of transport stress on small intestine morphology and heatshock protein expression in goats[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2021, 57 (12): 207- 212. | |
| 4 | 武亚南, 石玉祥, 张永英, 等. 活化Nrf2缓解热应激致肉鸡心肌细胞氧化损伤的研究[J]. 2020, 56(2): 17-22. |
| WU Y N, SHI Y X, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Sstudy on Nrf2 activation alleviating heat stress-induced oxidative damage in broiler cardiomyocytes[J]. 2019, 56(2): 17-22. (in Chinese) | |
| 5 | 熊云霞, 王丽, 易宏波, 等. 热应激对猪禽肠道健康的影响及其机制研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2020, 56 (2): 17- 22. |
| XIONG Y X , WANG L , YI H B , et al. Research progress on effects of heat stress on intestinal health of poultry and pigs and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2020, 56 (2): 17- 22. | |
| 6 |
CUI Y J , ZHOU X , CHEN L Y , et al. Crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress in heat exposure-induced apoptosis is dependent on the ATF4-CHOP-CHAC1 signal pathway in IPEC-J2 cells[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2021, 69 (51): 15495- 15511.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c03361 |
| 7 |
DENG C C , ZHANG J P , HUO Y N , et al. Melatonin alleviates the heat stress-induced impairment of Sertoli cells by reprogramming glucose metabolism[J]. J Pineal Res, 2022, 73 (3): e12819.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12819 |
| 8 |
KERBER E L , PADBERG C , KOLL N , et al. The importance of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF-1 and HIF-2) for the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (22): 8551.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21228551 |
| 9 | FERNÁNDEZ-TORRES J , ZAMUDIO-CUEVAS Y , MARTÍNEZ-NAVA G A , et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors (HIFs) in the articular cartilage: a systematic review[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2017, 21 (12): 2800- 2810. |
| 10 | CAOMENGBING , ZONGCHAO , ZHUANGYANRONG , et al. Modeling of heat stress in sows part 2: comparison of various thermal comfort indices[J]. Animals, 2021, 11 (6): 1498. |
| 11 | 朱海波. 慢性热应激对肉鸡肠道黏膜屏障功能的影响[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2020. |
| ZHU H B. Effect of chronic heat stress on intestinal mucosal barrier function in broilers[D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 12 | GABLER N K , KOLTES D , SCHAUMBERGER S , et al. Diurnal heat stress reduces pig intestinal integrity and increases endotoxin translocation[J]. Transl Anim Sci, 2018, 2 (1): 1- 10. |
| 13 | 刘凤丹, 张蓉, 陈光吉, 等. 环境温度和饲粮金荞麦提取物对蛋鸡肝脏超微结构及线粒体抗氧化功能的影响[J/OL]. 中国饲料: 1-8[2023-10-31]. https://doi.org/10.15906/j.cnki.cn11-2975/s.2023050037-08. |
| LIU F D, ZHANG R, CHEN G J, et al. Effects of ambient temperature and dietary FagoPyrum dibotrys hara extract on liver ultrastructure and mitochondrial antioxidant function of laying hens[J/OL]. China Feed: 1-8[2023-10-31]. https://doi.org/10.15906/j.cnki.cn11-2975/s.2023050037-08. (in Chinese) | |
| 14 | 周慧爽, 李艳君, 林树乾, 等. 热应激对鸡肠道屏障的损伤研究进展[J/OL]. 中国畜牧杂志: 1-10[2023-10-29]. https://doi.org/10.19556/j.0258-7033.20230203-08. |
| ZHOU H S, LI Y J, LIU S Q, et al. Research progress on heat stress on intestinal barrier injury in poultry[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science: 1-10[2023-10-29]. https://doi.org/10.19556/j.0258-7033.20230203-08. (in Chinese) | |
| 15 | 邓谭杰, 荀文娟, 侯冠彧, 等. 热应激对鸡肠黏膜屏障的影响及其营养调控研究进展[J]. 中国家禽, 2023, 45 (5): 92- 99. |
| DENG T J , XUN W J , HOU G Y , et al. Research progress on the effect of heat stress on intestinal mucosal barrier and nutritional manipulation in chickens[J]. China Poultry, 2019, 45 (5): 92- 99. | |
| 16 | YU J , YIN P , LIU F H , et al. Effect of heat stress on the porcine small intestine: a morphological and gene expression study[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol, 2010, 156 (1): 119- 128. |
| 17 | PEARCE S C , SANZ-FERNANDEZ M V , HOLLIS J H , et al. Short-term exposure to heat stress attenuates appetite and intestinal integrity in growing pigs[J]. J Anim Sci, 2014, 92 (12): 5444- 5454. |
| 18 | 许笑. 丁酸梭菌改善坏死性肠炎患鸡肠黏膜屏障机制的初步研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. |
| XU X. Preliminary studies on the roles of Clostridium butyricum for ameliorating gut mucosal barrier of broiler chickens with necrotic enteritis[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 19 | 任书男. 酸马奶源副干酪乳杆菌对E. coli O8所致腹泻模型小鼠肠黏膜屏障的保护作用[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2022. |
| REN S N. Protective effect of Lactobacillus paracasei from koumiss on the intestinal mucosal barrier of diarrhea mouse models caused by E. coli O8[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 20 | 刘帅. 热应激对生长猪肠道健康和HPA轴的影响及机制[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2022. |
| LIU S. Effects of heat stress on intestinal health and HPA axis in growing pigs[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 21 | 段继娇, 谢宇潇, 朱俊红, 等. Occludin基因在猪肠道屏障中的研究进展[J]. 饲料研究, 2023, 46 (18): 140- 144. |
| DUAN J J , XIE Y X , ZHU J H , et al. Research progress of Occludin gene in pig intestinal barrier[J]. Feed Research, 2023, 46 (18): 140- 144. | |
| 22 | 张绍萱. 绿原酸缓解热应激诱发初情期前猪睾丸氧化损伤的多组学研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2022. |
| ZHANG S X. Multi-omics study on chlorogenic acid alleviating heat stressinduced oxidative damage in testes of prepubertal boars[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 23 | CHEN B X , YANG B , ZHU J , et al. Hsp90 relieves heat stress-induced damage in mouse kidneys: involvement of antiapoptotic PKM2-AKT and autophagic HIF-1α signaling[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (5): 1646. |
| 24 | VARASTEH S , BRABER S , AKBARI P , et al. Differences in susceptibility to heat stress along the chicken intestine and the protective effects of galacto-oligosaccharides[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10 (9): e0138975. |
| 25 | HE R J , WANG Z , CUI M , et al. HIF1A Alleviates compression-induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus derived stem cells via upregulating autophagy[J]. Autophagy, 2021, 17 (11): 3338- 3360. |
| 26 | DELBREL E , SOUMARE A , NAGUEZ A , et al. HIF-1α triggers ER stress and CHOP-mediated apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells, a key event in pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8 (1): 17939. |
| 27 | ZHAO X R , LIU L D , LI R , et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α (HIF-1α) induces apoptosis of human uterosacral ligament fibroblasts through the death receptor and mitochondrial pathways[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2018, 24, 8722- 8733. |
| 28 | AGARWAL S , GANESH S . Perinuclear mitochondrial clustering, increased ROS levels, and HIF1 are required for the activation of HSF1 by heat stress[J]. J Cell Sci, 2020, 133 (13): jcs245589. |
| 29 | SINGH D , ARORA R , KAUR P , et al. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor and metabolic pathways: possible targets of cancer[J]. Cell Biosci, 2017, 7, 62. |
| [1] | Yongjie WU, Yinghuan XU, Tengfei LIU, Lin MA, Hong CHEN, Yongping XU. Effect of Scrotal Hyperthermia on Structure and Function of Blood-testis Barrier in Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2973-2982. |
| [2] | Xiaoyi FENG, Peipei ZHANG, Hang ZHANG, Haisheng HAO, Weihua DU, Huabin ZHU, Kai CUI, Xueming ZHAO. Effects of Heat Stress on Epigenetic Modifications and Developmental Competence of Bovine Oocytes and Their Embryos [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2460-2473. |
| [3] | Hang ZHANG, Peipei ZHANG, Baigao YANG, Xiaoyi FENG, Yifan NIU, Zhou YU, Jianhua CAO, Pengcheng WAN, Xueming ZHAO. Combination of IGF1, CoQ10 and MT Alleviated the Effects of Heat Stress on Bovine IVF Blastocysts [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2474-2485. |
| [4] | Ji WANG, Xinyan ZHOU, Fangrui GUO, Qiurong XU, Dongyi WU, Yan MAO, Zhihang YUAN, Jin'e YI, Lixin WEN, Jing WU. Viola yedoensis Makino Improves the Growth Performance, Meat Quality, and Gut Microbiota of Broilers Exposed to Heat Stress [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2761-2774. |
| [5] | WANG Xiao, ZHANG Hao, LUAN Qingjiang, LI Hui, YANG Ding, WANG Tingyue, TIAN Jing, ZHAO Meng, CHEN Lu, TIAN Rugang. A Comprehensive Review of the Impact of Cold and Heat Stress on the Physiological Parameters and Gene Expression in Beef Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 894-904. |
| [6] | HUO Yuannan, QIU Meijia, ZHANG Jiaojiao, YANG Weirong, WANG Xianzhong. Arginine and Its Metabolites Attenuate Heat Stress-induced Apoptosis of Immature Boar Sertoli Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 587-597. |
| [7] | XIAO Yimei, WANG Shengnan, XU Yuewen, HE Xiaolin, YIN Fuquan. Research on the Influence of Heat Stress on Male Reproduction [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 11-21. |
| [8] | ZHANG Hang, YANG Baigao, XU Xi, FENG Xiaoyi, DU Weihua, HAO Haisheng, ZHU Huabin, ZHANG Peipei, ZHAO Xueming. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Heat Stress Affecting the Development of Dairy Cow Embryos [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 2692-2700. |
| [9] | WANG Zixuan, WANG Qiao, ZHANG Jin, Astrid Lissette Barreto Sánchez, ZHENG Maiqing, LI Qinghe, CUI Huanxian, AN Bingxing, ZHAO Guiping, WEN Jie, LI Hegang. Transcriptome Based Screening of Functional Genes Related to Heat Stress Resistance in Beijing You Chickens and Guangming Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 1905-1914. |
| [10] | WANG Han, MENG Lijie, LIU Wenjiao, XU Yongjian, GONG Ting. Effect of TAS1R3 Gene Interference on Autophagy Related Factors in Leydig Cells of Xiang Pig [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(4): 1525-1534. |
| [11] | FENG Xiaoyi, YANG Baigao, HAO Haisheng, DU Weihua, ZHU Huabin, CUI Kai, ZHAO Xueming. Mechanism and Solution of Heat Stress Induced Embryo Quality Decline in Dairy Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 868-876. |
| [12] | HAN Lulu, HAN Deping, ZHAO Qinan, DIAO Qiyu, CUI Kai. Research Progress of Intestinal Injury in Young Farm Animals under Stress Mediated by miRNA [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 877-888. |
| [13] | XUE Hongyan, YANG Mengyu, YANG Huan, DONG Lijun, CAI Xiaqing, ZHAO Zemin, WANG Xianzhong. The Role of ALOX15B-JNK in Heat Stress-induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis of Sertoli Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5056-5065. |
| [14] | CAI Jiawei, ZHANG Chen, JIN Rongshuai, BAO Zhiyuan, ZHANG Xiyu, WANG Fan, ZHAI Pin, ZHAO Bohao, CHEN Yang, TANG Xianwei, WU Xinsheng. Analysis of Testicular Tissue Morphology and Semen Transcriptome of Male Rabbits under Heat Stress [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4653-4663. |
| [15] | ZHOU Wanting, YANG Chen, PENG Cuitian, FU Xinliang, ZHONG Zhuohua, XU Danning, HUANG Yunmao, TIAN Yunbo, LIU Wenjun. Effects of Resveratrol on Anti-oxidation and Anti-apoptosis of Hepatocytes of Ducks on Exposure to Acute Heat Stress [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(1): 239-251. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||