





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 5875-5887.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.11.043
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
HU Ximin( ), LUORENG Zhuoma, ZHOU Ran, LI Yuhang, WANG Xingping*(
), LUORENG Zhuoma, ZHOU Ran, LI Yuhang, WANG Xingping*( )
)
Received:2025-02-11
Online:2025-11-23
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
WANG Xingping
E-mail:huximin0808@163.com;wxp@nxu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
HU Ximin, LUORENG Zhuoma, ZHOU Ran, LI Yuhang, WANG Xingping. Role of lncRNA PFN1-AS1 in the Inflammatory Response of Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5875-5887.
Table 1
The primer sequences used for qRT-PCR"
| 基因名 Gene name | 基因登录号 GenBank ID | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequences | 产物长度/bp Product length |
| lncRNAPFN1-AS1 | PQ628053 | F: GAATAAAGCCCGCCCTAG R: GAGTGCCTGCCAATCATACA | 187 |
| IL-6 | NM_173923 | F: CACTCCATTCGCTGTCT R: GTGTCTCCTTGCTGCTT | 227 |
| IL-8 | NM_173925.2 | F: ACACATTCCACACCTTTCCAC R: ACCTTCTGCACCCACTTTTC | 149 |
| IL-1β | NM_174093.1 | F: CAACCGTACCTGAACCC R: GACACCACCTGCCTGAA | 110 |
| CDK2 | NM_001014934 | F: GATGGACGGAGCTTGTTATCG R: ATCACACTCACACTGGAGAAGA | 182 |
| CDK4 | NM_001037594.2 | F: CCTTCATGCCAACTGCATCG R: CCAGAGTGTAACAACCACAGGT | 168 |
| PCNA | NM_001034494.1 | F: GAACCTCACCAGCATGTCCA R: ACGTGTCCGCGTTATCTTCA | 86 |
| CASP3 | NM_001077840.1 | F: AAGATTTAGTGCCGATGC R: GACCACCAAGTTCTAGGATA | 175 |
| CASP8 | NM_001045970.2 | F: TCACCCACGGAAACAAGG R: TCGGTCTCAACGGCTACAC | 178 |
| BAX | NM_173894.1 | F: GCAAACTGGTGCTCAAGG R: GCACTCCAGCCACAAAGA | 189 |
| GAPDH | NM_001034034.2 | F: GGCATCGTGGAGGGACTTATG R: CCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTGAG | 186 |
| RPS18 | NM_001033614.2 | F: GTGGTGTTGAGGAAAGCAGACA R: TGATCACACGTTCCACCTCATC | 79 |
| U6 | NM_001075477.2 | F: GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT R: CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT | 89 |
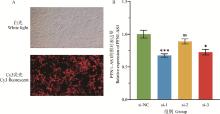
Fig. 6
Interference efficiency of si-PFN1-AS1 A. Transfection efficiency fluorescence plot 100×(White light for all cells, red fluorescence for transfected cells with Cy3 fluorescent tags); B. Results of lncRNA PFN1-AS1 interference efficiency (si-NC was the control group, si-1, si-2, and si-3 were interfering fragments of lncRNA PFN1-AS1).*.P < 0.05, ***.P < 0.001, ns. P>0.05"
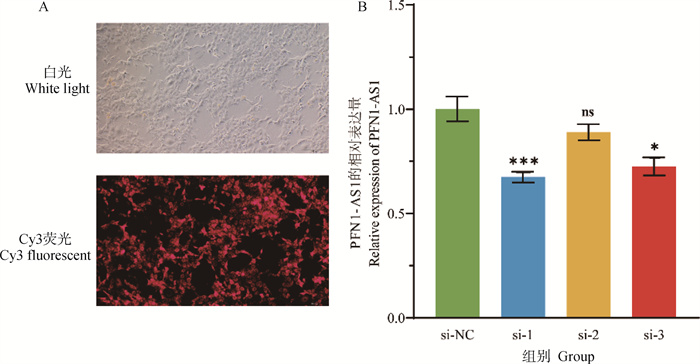
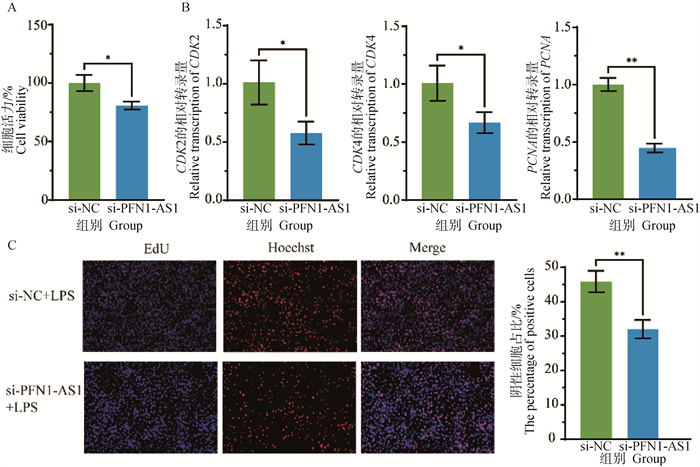
Fig. 8
Effect of interference with lncRNA PFN1-AS1 on the activity and proliferation of inflammatory bMECs A. CCK-8 assay of cell viability; B. Proliferation gene transcription levels; C. EdU assay of cell proliferation100×(All cells were labeled with blue fluorescence of Hoechst; the proliferative cells were labeled with red fluorescence of EdU).*.P < 0.05, **.P < 0.01"
| 1 |
HE W , MA S , LEI L , et al. Prevalence, etiology, and economic impact of clinical mastitis on large dairy farms in China[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2020, 242, 108570.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.108570 |
| 2 |
GAO J , BARKEMA H W , ZHANG L , et al. Incidence of clinical mastitis and distribution of pathogens on large Chinese dairy farms[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2017, 100 (6): 4797- 4806.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-12334 |
| 3 |
ZHOU M , YANG Y , WU M , et al. Role of long polar fimbriae type 1 and 2 in pathogenesis of mammary pathogenic Escherichia coli[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2021, 104 (7): 8243- 8255.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-20122 |
| 4 |
DOGAN B , KLAESSIG S , RISHNIW M , et al. Adherent and invasive Escherichia coli are associated with persistent bovine mastitis[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2006, 116 (4): 270- 282.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2006.04.023 |
| 5 |
GILBERT F B , CUNHA P , JENSEN K , et al. Differential response of bovine mammary epithelial cells to Staphylococcus aureus or Escherichia coli agonists of the innate immune system[J]. Vet Res, 2013, 44 (1): 40- 63.
doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-44-40 |
| 6 |
GONEN E , VALLON-EBERHARD A , ELAZAR S , et al. Toll-like receptor 4 is needed to restrict the invasion of Escherichia coli P4 into mammary gland epithelial cells in a murine model of acute mastitis[J]. Cell Microbiol, 2007, 9 (12): 2826- 2838.
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00999.x |
| 7 |
CORNUT M , BOURDONNAY E , HENRY T . Transcriptional regulation of inflammasomes[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (21): 8087.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21218087 |
| 8 |
GOULART D B , MELLATA M . Escherichia coli mastitis in dairy cattle: Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment challenges[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13, 928346.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.928346 |
| 9 |
XIA X , HOU J , REN P , et al. Coexpression analysis of lncRNAs and mRNAs identifies potential regulatory long noncoding RNAs involved in the inflammatory effects of lipopolysaccharide on bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. BMC Vet Res, 2023, 19 (1): 209- 221.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03780-4 |
| 10 |
LUO H , XU C , LE W , et al. lncRNA CASC11 promotes cancer cell proliferation in bladder cancer through miRNA-150[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120 (8): 13487- 13493.
doi: 10.1002/jcb.28622 |
| 11 |
YAN L , WU X , ZHANG Y , et al. LncRNA ENST00000370438 promotes cell proliferation by upregulating DHCR24 in breast cancer[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2023, 62 (6): 855- 865.
doi: 10.1002/mc.23529 |
| 12 |
WANG J P , HU Q C , YANG J , et al. Differential expression profiles of lncRNA following LPS-induced inflammation in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2021, 8, 758488.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.758488 |
| 13 |
WANG D , YANG H , MA S , et al. Transcriptomic changes and regulatory networks associated with resistance to mastitis in Xinjiang brown cattle[J]. Genes (Basel), 2024, 15 (4): 465- 483.
doi: 10.3390/genes15040465 |
| 14 | WANG J , WANG X , FENG F , et al. LncRNA HULIB promotes LPS induced inflammatory response in bovine mammary epithelial cells via PP2AB[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 143 (Pt 3): 113496. |
| 15 |
CHU S , ZHAO T , LI M , et al. Long non-coding RNA (CMR) involved in autoprotection in S. aureus mastitis in dairy cows by regulating miR-877/FOXM1[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2024, 278, 116456.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116456 |
| 16 | SUN Y , ZHAO T , MA Y , et al. Multiple roles of LncRNA-BMNCR on cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting miR-145/CBFB axis in BMECs[J]. Vet Q, 2023, 43 (1): 1- 11. |
| 17 |
YANG J , HU Q C , WANG J P , et al. RNA-Seq reveals the role of miR-29c in regulating inflammation and oxidative stress of bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2022, 9, 865415.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.865415 |
| 18 | FENG F , LI Y , WANG J , et al. LncRNA CA12-AS1 targets miR-133a to promote LPS-induced inflammatory response in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 261 (Pt 1): 129710. |
| 19 | 王晋鹏, 罗仍卓么, 李彦霞, 等. lncRNA RRAS2-AS1在LPS诱导奶牛乳腺上皮细胞炎症中的功能[J]. 中国农业科学, 2024, 57 (14): 2874- 2891. |
| WANG J P , LUORENG Z M , LI Y X , et al. Function of lncRNA RRAS2-AS1 in LPS-induced inflammation of bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 57 (14): 2874- 2891. | |
| 20 |
LI Y , REN Q , WANG X , et al. Bta-miR-199a-3p Inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in bovine mammary epithelial cells via the PI3K/AKT/NF-kappa B signaling pathway[J]. Cells, 2022, 11 (21): 3518- 3532.
doi: 10.3390/cells11213518 |
| 21 | LI R , FANG H , SHEN J , et al. Curcumin alleviates LPS-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in bovine mammary epithelial cells via the NFE2L2 signaling pathway[J]. Toxins (Basel), 2021, 13 (3): 1- 15. |
| 22 |
LIU J , GAO Y , ZHANG X , et al. Transcriptome sequencing analysis of bovine mammary epithelial cells induced by lipopolysaccharide[J]. Anim Biotechnol, 2024, 35 (1): 2290527.
doi: 10.1080/10495398.2023.2290527 |
| 23 |
LIN T , BAI X , GAO Y , et al. CTH/H (2) S regulates LPS-induced inflammation through IL-8 signaling in MAC-T cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (19): 11822.
doi: 10.3390/ijms231911822 |
| 24 |
LAI Y C , FUJIKAWA T , MAEMURA T , et al. Inflammation-related microRNA expression level in the bovine milk is affected by mastitis[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12 (5): e0177182.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177182 |
| 25 |
SRIKOK S , PATCHANEE P , BOONYAYATRA S , et al. Potential role of microRNA as a diagnostic tool in the detection of bovine mastitis[J]. Prev Vet Med, 2020, 182, 105101.
doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2020.105101 |
| 26 | JIA L , WANG J , LUORENG Z , et al. Progress in expression pattern and molecular regulation mechanism of lncRNA in bovine mastitis[J]. Animals (Basel), 2022, 12 (9): 1059- 1070. |
| 27 |
WANG H , WANG X , LI X , et al. A novel long non-coding RNA regulates the immune response in MAC-T cells and contributes to bovine mastitis[J]. FEBS J, 2019, 286 (9): 1780- 1795.
doi: 10.1111/febs.14783 |
| 28 |
YANG W , LI X , QI S , et al. lncRNA H19 is involved in TGF-beta1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in bovine epithelial cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. PeerJ, 2017, 5, e3950.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.3950 |
| 29 |
LI X , WANG H , ZHANG Y , et al. Overexpression of lncRNA H19 changes basic characteristics and affects immune response of bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. PeerJ, 2019, 7, e6715.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.6715 |
| 30 |
YI Y , YANG N , YANG Z , et al. LncRNA TM1-3P regulates proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation of fibroblasts in osteoarthritis through miR-144-3p/ONECUT2 axis[J]. Orthop Surg, 2022, 14 (11): 3078- 3091.
doi: 10.1111/os.13530 |
| 31 |
KLEC C , PRINZ F , PICHLER M . Involvement of the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 in carcinogenesis[J]. Mol Oncol, 2019, 13 (1): 46- 60.
doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12404 |
| 32 | MA J , ZHAO N , DU L , et al. Downregulation of lncRNA NEAT1 inhibits mouse mesangial cell proliferation, fibrosis, and inflammation but promotes apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2019, 12 (4): 1174- 1183. |
| 33 | WANG L , QU P , YIN W , et al. Lnc-NEAT1 induces cell apoptosis and inflammation but inhibits proliferation in a cellular model of hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. J Int Med Res, 2021, 49 (3): 1- 11. |
| 34 |
LU J , GU B , LU W , et al. Lnc-ANRIL modulates the immune response associated with NF-kappaB pathway in LPS-stimulated bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. Immun Inflamm Dis, 2023, 11 (12): e1125.
doi: 10.1002/iid3.1125 |
| [1] | WEN Xue, XU Wanxue, FU Yitong, YANG Jie, FU Hongyu, FAN Ruifeng. Research Progress on the Relationship between Ferroptosis and Inflammation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3666-3677. |
| [2] | LI Xiaodie, PAN Shiqin, WANG Lu, CHENG Zhentao, OU Deyuan, SONG Xuqin, YANG Jian. Research Progress on the Anti-inflammatory Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine based on Network Pharmacology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3701-3721. |
| [3] | ZHANG Chenmiao, CHEN Bowen, JIANG Linshu, TONG Jinjin. Potential Applications of Nanotechnology-Improved Flavonoids in Animal Health Management [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3107-3115. |
| [4] | GAO Linna, JIANG Yingying, WANG Yue, SHI Qianqian, AN Zhenjiang, WANG Huili, SHEN Yangyang, CHEN Kunlin, ZHANG Leying. Construction of a Whole Genome Knockout Library of bMECs Based on CRISPR/Cas9 Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2711-2723. |
| [5] | LUO Shishi, CHEN Beilei, ZHANG Lei, FENG Qixian, WU Ruisen, CHEN Jiaqi, WANG Yuan, JIAN Zixin, XU Lihui, CHEN Qiuyong, MA Yufang, WANG Quanxi. Radix Pseudostellariae Polysaccharide Regulates Let-7d-3p to Alleviates Inflammatory-induced by Pseudorabies Virus Infection in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2438-2450. |
| [6] | CHEN Zehan, ZHANG Ruoyi, LIN Huiying, ZENG Chunli, LIN Fu, LI Jian. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Chelidonium majus on IPEC-J2 Cells based on HPLC Fingerprint and Network Pharmacology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2466-2480. |
| [7] | ZHAO Ying, WANG Jinglei, WANG Meng, WANG Libin, ZHANG Qian, LI Zhijie, MA Xin, YU Sijiu, PAN Yangyang. Preparation and Characterization of Forsythiaside A and Kaempferol Encapsulated in Milk-derived Exosomes and Evaluation of Anti-inflammatory Effects in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2481-2495. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xiwen, YIN Yue, LI Xiang, WANG Min, WANG Yongfang, JIN Shuning, FENG Xinhui, ZHAO Yurong. Effects of Ursolic Acid on Breast Meat Quality and Wooden Breast of Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 711-721. |
| [9] | LI Fan, SUN Haifeng, SUN Meng, GAO Yanxiao, SUN Yangyang, ZHANG Lujie, BAI Juan, JIANG Ping. Preparation and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Porcine IL-1β Monoclonal Antibody [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 890-899. |
| [10] | LI Xinke, YANG Xue, ZHANG Xuan, MENG Lu, ZHANG Yangdong, WANG Jiaqi, ZHENG Nan. Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids on Liver and Brain Development and Immune Function in Neonatal Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5588-5599. |
| [11] | MA Yue, MIAO Yuhang, DING Tao, XIN Jie, MA Wenyan, LI Yanan, ZHOU Xuezhang, DU Jun. Signaling Pathway Analysis of Ferroptosis Induced by Recombinant Candida krusei 14-3-3 Protein in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5706-5720. |
| [12] | WANG Hengtai, JIANG Hui, LI Peng, DING Jiabo. Biosynthesis of Brucella Lipopolysaccharides and Their Biological Functions in Immune Evasion [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 4863-4876. |
| [13] | Yiqian FU, Dongge LIANG, Mingyang WANG, Jiajia PAN, Yanbin YANG, Lei ZENG, Xiangtao KANG. Construction of Interferon Regulatory Factor Knockdown Cell Line and Its Effect on Pseudorabies Virus Proliferation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4100-4109. |
| [14] | Ling LIU, Wanyu SHI, Xiumei LI, Minghua WANG, Xianghe ZHAI, Weiwei ZHOU. Intervention of Essential Oils from Citrus reticulata Blanco on Lipopolysaccharide- induced Inflammation in RAW264.7 Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4153-4160. |
| [15] | Ya’nan LI, Tianwen MA, Yuhui MA, Chengwei WEI. Bilobalide Regulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis Mediated by AMPK-SIRT3 Positive Feedback Loop and Improves Inflammatory Damage of ATDC5 Chondrocytes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3714-3724. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||