





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (9): 4077-4090.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.09.032
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lu PENG( ), Heng ZHANG(
), Heng ZHANG( ), Siqi PANG, Zhulin QIAO, Xiaofen ZHANG, Chen TAN, Yunfeng SONG, Rui ZHOU, Lu LI*(
), Siqi PANG, Zhulin QIAO, Xiaofen ZHANG, Chen TAN, Yunfeng SONG, Rui ZHOU, Lu LI*( )
)
Received:2023-11-20
Online:2024-09-23
Published:2024-09-27
Contact:
Lu LI
E-mail:penglu1998@webmail.hzau.edu.cn;zhangheng666@webmail.hzau.edu.cn;lilu@mail.hzau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Lu PENG, Heng ZHANG, Siqi PANG, Zhulin QIAO, Xiaofen ZHANG, Chen TAN, Yunfeng SONG, Rui ZHOU, Lu LI. Screening of Trivalent Inactivated Vaccine Candidate Strains of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2, 3 and 9 Using Galleria mellonella and Mice Infection Models[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4077-4090.
Table 1
PCR primers"
| 引物Primers | 引物序列(5′→3′) Sequence | 产物大小/bp Product |
| cps2I-F | TTCGTATTAACTTACTTGGCGT | 363 |
| cps2I-R | TAAATCCCCATATGCCAAATCC | |
| cps3L-F | ACATCCATTGCAGGAGTAGT | 210 |
| cps3L-R | TGCAGTTCCAAAATTCTTCGT | |
| cps9J-F | TCCCTTTAATTTCACAGGCAAT | 409 |
| cps9J-R | CTGTCAAAGAATTGAATCCCAC | |
| gapdh-F | CACACTTGTTGAAATATGACAC | 571 |
| gapdh-R | AGCACCGTCAAGTTTACC | |
| sly-F | GCAGAAGGGACAACTGTAGAAG | 443 |
| sly-R | GCACTGCTATTATGGACTGTTGA | |
| fbps-F | CAAGGTTTGGGTCGGGATA | 720 |
| fbps-R | CCCGTCTGTTGCCAAGTAA | |
| orf2-F | CAAGTGTATGTGGATGGG | 858 |
| orf2-R | ATCCAGTTGACACGTGCA | |
| mrp-F | GGTATACCTTGCTGGTACGGTTC | 532 |
| mrp-R | AGTCTCTACAGCTGTAGCTGG | |
| 89K-F | GATATCGCCACTATGGTATC | 720 |
| 89K-R | GATTGTGGACCATGCTCTTTAG | |
| gdh-F | GCAGCGYAYYCYGYCAAACG | 688 |
| gdh-R | CCATGGACAGATAAAGATGG | |
| epf-F | ACAAAGGCGTAGGTTCAATC | 269 |
| epf-R | CGGCATCAAGAATGTCTTTG |
Table 2
Inactivated vaccine immunization program and immune dose"
| 组别Group | 免疫剂量Immune dose | 数量Quantity | 免疫方式Vaccination method | 攻毒菌株/剂量Challenge strain/dose | 攻毒方式Challenge method |
| SS1803免疫组 SS1803 | 4×107 CFU | 6 | 肌肉注射Intramuscular injection | SS1803: 5×107 CFU | 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection |
| SS1803免疫组 SS1803 | 8×107 CFU | 6 | 肌肉注射Intramuscular injection | SS1803: 5×107 CFU | 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection |
| SS1803024免疫组 SS1803024 | 2×108 CFU | 6 | 肌肉注射Intramuscular injection | SS1803024: 1.7×108 CFU | 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection |
| SS1803024免疫组 SS1803024 | 5×108 CFU | 6 | 肌肉注射Intramuscular injection | SS1803024: 1.7×108 CFU | 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection |
| SS1696免疫组 SS1696 | 1×108 CFU | 6 | 肌肉注射Intramuscular injection | SS1696: 1.5×107 CFU | 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection |
| SS1696免疫组 SS1696 | 5×108 CFU | 6 | 肌肉注射Intramuscular injection | SS1696: 1.5×107 CFU | 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection |
| 三价苗免疫组 TIV | 2×107 CFU SS1803+1.5×108 CFU SS1803024+3×107 CFU SS1696 | 18 | 肌肉注射Intramuscular injection | SS1803: 5×107 CFU SS1803024: 1.7×108 CFU SS1696: 1.5×107 CFU | 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection |
| 阴性对照组 Negative | PBS | 18 | 肌肉注射Intramuscular injection | SS1803: 5×107 CFU SS1803024: 1.7×108 CFU SS1696: 1.5×107 CFU | 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection |
Table 3
Screening results of S.suis serotype 3, 9 strains on Galleria mellonella %"
| 血清3型菌株Serotype 3 strains | 第一轮死亡率(n=10) Mortality rate of first round experiment | 第二轮死亡率(n=10) Mortality rate of second round experiment | 血清9型菌株Serotype 9 strains | 第一轮死亡率(n=10) Mortality rate of first round experiment | 第二轮死亡率(n=10) Mortality rate of second round experiment | |
| SS1761 | 60 | 80 | SS1802036 | 60 | 50 | |
| SS1804125 | 100 | 60 | SS1807065 | 80 | 80 | |
| SS1730 | 10 | 10 | SS1823 | 30 | 40 | |
| SS1767 | 20 | 20 | SS1805031 | 90 | 70 | |
| SS1766 | 30 | 40 | SS1805032 | 60 | 40 | |
| SS1968 | 10 | 10 | SS1804104 | 90 | 90 | |
| SS1803024 | 100 | 60 | SS1804097 | 30 | 20 | |
| SS1803025 | 70 | 60 | SS1407 | 0 | 10 | |
| SS2214 | 30 | 10 | SS1904022 | 10 | 10 | |
| SS1703 | 40 | 30 | SS1681 | 40 | 20 | |
| SS1804072 | 40 | 10 | SS1696 | 80 | 80 | |
| SS1808002 | 30 | 20 | SS1697 | 70 | 60 | |
| 生理盐水组Normal saline group | 0 | 0 | SS1807038 | 40 | 20 | |
| SS1807035 | 80 | 80 | ||||
| 空白对照组Blank control group | 0 | 0 | SS1807091 | 30 | 30 | |
| SS1807090 | 30 | 0 | ||||
| 生理盐水组Normal saline group | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 空白对照组Blank control group | 0 | 0 |

Fig. 2
Growth characteristics and identification of virulence factors of SS serotype 2, 3 and 9 strains A, D, G. OD600 nm value of SS1803, SS1803024, SS1696; B, E, H. Bacterial count of SS1803, SS1803024, SS1696; C, F, I. Virulence factor identification of SS1803, SS1803024, SS1696: M. 5 000 DNA marker; 1. gapdh gene; 2. sly gene; 3. fbps gene; 4. orf2 gene; 5. mrp gene; 6. 89K gene; 7. gdh gene; 8. epf gene"
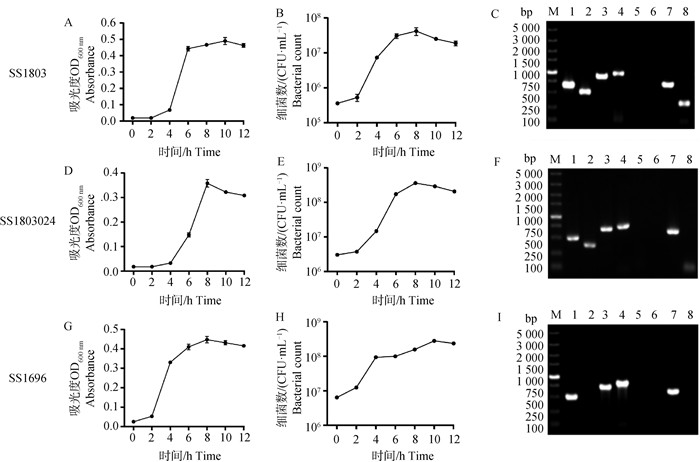

Fig. 7
Determination of inflammatory cytokines in serum of mice at 12 and 24 h after challenge(n=6) A, B, C. IL-6 levels in serum of mice after SS1803、SS1803024、SS1696 challenge; D, E, F. IL-12 levels in serum of mice after SS1803, SS1803024, SS1696 challenge. *. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001; ****. P < 0.000 1;ns. P > 0.05"
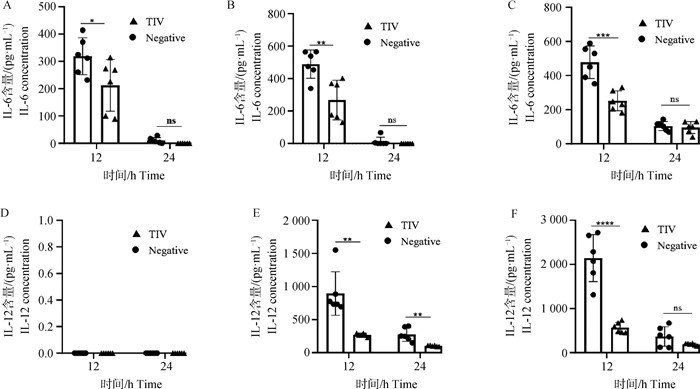

Fig. 8
Pathological histological sections of brain, spleen, lung and kidneys of mice after challenge(200× and 100×) A. Control group of SS1803 challenge; B. TIV group of SS1803 challenge; C. Control group of SS1803024 challenge; D. TIV group of SS1803024 challenge; E. Control group of SS1696 challenge; F. TIV group of SS1696 challenge; G. Blank group(bar: 200 μm, 100 μm). Brain tissue sections: red arrows indicate neuronal cell degeneration with pyknotic hyperchromatic nuclei; green arrows indicate mild hemorrhage in brain parenchyma. Spleen tissue sections: red arrows indicate increased multinucleated macrophages; green arrows indicate a small amount of hemosiderin deposition. Lung tissue sections: red arrows indicate alveolar epithelial cell hyperplasia; green arrows indicate a small amount of protein mucus in the bronchial lumen; yellow arrows indicate inflammatory cell infiltration. Kidney tissue sections: red arrows indicate glomerular lobulation; black arrows indicate atrophy and loss of some glomeruli in the cortical area, and the number of mesangial cells in the glomerulus is reduced"

| 1 |
OKURA M , OSAKI M , NOMOTO R , et al. Current taxonomical situation of Streptococcus suis[J]. Pathogens, 2016, 5 (3): 45.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens5030045 |
| 2 |
FENG Y J , ZHANG H M , WU Z W , et al. Streptococcus suis infection: an emerging/reemerging challenge of bacterial infectious diseases?[J]. Virulence, 2014, 5 (4): 477- 497.
doi: 10.4161/viru.28595 |
| 3 |
HAAS B , GRENIER D . Understanding the virulence of Streptococcus suis: a veterinary, medical, and economic challenge[J]. Med Mal Infect, 2018, 48 (3): 159- 166.
doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2017.10.001 |
| 4 |
ATHEY T B T , TEATERO S , LACOUTURE S , et al. Determining Streptococcus suis serotype from short-read whole-genome sequencing data[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2016, 16 (1): 162.
doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0782-8 |
| 5 | GOYETTE-DESJARDINS G , AUGER J P , XU J G , et al. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent-an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2014, 3 (6): e45. |
| 6 |
SEGURA M , ARAGON V , BROCKMEIER S L , et al. Update on Streptococcus suis research and prevention in the era of antimicrobial restriction: 4th international workshop on S. suis[J]. Pathogens, 2020, 9 (5): 374.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens9050374 |
| 7 | YANG H H , HUANG J J , HU X T , et al. Comparative genome analysis of Streptococcus suis serotype 9 isolates from China, The Netherland, and the U. K[J]. Life (Basel), 2021, 11 (12): 1324. |
| 8 | 黄晓慧, 韩雪姣, 刘雪兰, 等. 199株猪链球菌临床分离株血清型、毒力基因及多位点序列分型分析[J]. 微生物学通报, 2022, 49 (10): 4209- 4223. |
| HUANG X H , HAN X J , LIU X L , et al. Serotypes, main virulence genes, and multilocus sequence typing of 199 clinical isolates of Streptococcus suis[J]. Microbiology China, 2022, 49 (10): 4209- 4223. | |
| 9 | 吕若一, 司晓慧, 孙志刚, 等. 猪链球菌耐药现状分析及感染防控措施[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (12): 4920- 4933. |
| LÜ R Y , SI X H , SUN Z G , et al. Drug resistance situation of Streptococcus suis and prevention measures of infections[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (12): 4920- 4933. | |
| 10 |
LIU P , ZHANG Y , TANG H , et al. Prevalence of Streptococcus suis in pigs in China during 2000-2021: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. One Health, 2023, 16, 100513.
doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2023.100513 |
| 11 | 王治方, 白红杰, 徐引弟, 等. 猪链球菌流行优势菌株的调查及耐药性[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2020, 40 (12): 2327- 2332. |
| WANG Z F , BAI H J , XU Y D , et al. Prevalence and drug resistance of Streptococcus suis[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2020, 40 (12): 2327- 2332. | |
| 12 | 刘琪, 王娟, 周如月, 等. 广东地区健康猪群和发病猪群猪链球菌流行病学调查分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2017, 44 (6): 1825- 1831. |
| LIU Q , WANG J , ZHOU R Y , et al. The Streptococcus suis epidemiological analysis of healthy and infected swine in Guangdong province[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 44 (6): 1825- 1831. | |
| 13 | 毛从剑, 曹冶, 于吉锋, 等. 四川部分地区猪链球菌的分离鉴定及其毒力基因型和耐药性研究[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2023, (22): 97-103, 146. |
| MAO C J , CAO Y , YU J F , et al. Isolation and identification of Streptococcus suis in some areas of Sichuan Province and study on its virulence genotype and drug resistance[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2023, (22): 97-103, 146. | |
| 14 |
TANG J S , GUO M R , CHEN M , et al. A link between STK signalling and capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Streptococcus suis[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14 (1): 2480.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38210-4 |
| 15 |
FITTIPALDI N , SEGURA M , GRENIER D , et al. Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis[J]. Future Microbiol, 2012, 7 (2): 259- 279.
doi: 10.2217/fmb.11.149 |
| 16 | TRAM G , JENNINGS M P , BLACKALL P J , et al. Streptococcus suis pathogenesis-A diverse array of virulence factors for a zoonotic lifestyle[J]. Adv Microb Physiol, 2021, 78, 217- 257. |
| 17 |
ZHONG Q , ZHAO Y , CHEN T , et al. A functional peptidoglycan hydrolase characterized from T4SS in 89K pathogenicity island of epidemic Streptococcus suis serotype 2[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2014, 14, 73.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-14-73 |
| 18 |
CORSAUT L , MARTELET L , GOYETTE-DESJARDINS G , et al. Immunogenicity study of a Streptococcus suis autogenous vaccine in preparturient sows and evaluation of passive maternal immunity in piglets[J]. BMC Vet Res, 2021, 17 (1): 72.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-02774-4 |
| 19 | 段倩倩, 毛天骄, 韩业芹, 等. 猪链球菌2型灭活疫苗对小鼠的免疫效果评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020, 32 (4): 577- 585. |
| DUAN Q Q , MAO T J , HAN Y Q , et al. Evaluation of immune efficacy of inactivated Streptococcus suis serotype 2 vaccine in mice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2020, 32 (4): 577- 585. | |
| 20 | 李倩倩, 龙云志, 梁巩, 等. 猪链球菌3型疫苗候选菌株筛选及3+9型二价灭活疫苗对小鼠免疫效果评估[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2022, 49 (6): 2307- 2317. |
| LI Q Q , LONG Y Z , LIANG G , et al. Screening of vaccine candidate strains of Streptococcus suis serotype 3 and evaluation of the immune effect of the bivalent inactivated vaccine Streptococcus suis serotype 3+9 on mice[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 49 (6): 2307- 2317. | |
| 21 |
SCHULTSZ C , JANSEN E , KEIJZERS W , et al. Differences in the population structure of invasive Streptococcus suis strains isolated from pigs and from humans in the Netherlands[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7 (5): e33854.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033854 |
| 22 |
ZHANG B Z , KU X , YU X X , et al. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibilities of bacterial pathogens in Chinese pig farms from 2013 to 2017[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9 (1): 9908.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45482-8 |
| 23 |
BAUMS C G , KOCK C , BEINEKE A , et al. Streptococcus suis bacterin and subunit vaccine immunogenicities and protective efficacies against serotypes 2 and 9[J]. Clin Vaccine Immunol, 2009, 16 (2): 200- 208.
doi: 10.1128/CVI.00371-08 |
| 24 | 赵望, 孙毅, 曾同祥. 大蜡螟作为病原真菌动物实验模型的相关研究[J]. 中国真菌学杂志, 2020, 15 (4): 248- 252. |
| ZHAO W , SUN Y , ZENG T X . The related research of Galleria mellonella as an animal experimental model of pathogenic fungi[J]. Chinese Journal of Mycology, 2020, 15 (4): 248- 252. | |
| 25 |
VELIKOVA N , KAVANAGH K , WELLS J M . Evaluation of Galleria mellonella larvae for studying the virulence of Streptococcus suis[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2016, 16 (1): 291.
doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0905-2 |
| 26 |
YEPES-PÉREZ Y , RODRÍGUEZ-OBEDIENTE K , CAMARGO A , et al. Molecular characterisation of parvorder Platyrrhini IgG sub-classes[J]. Mol Immunol, 2021, 139, 23- 31.
doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.08.012 |
| 27 |
HUNTER C A , JONES S A . IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease[J]. Nat Immunol, 2015, 16 (5): 448- 457.
doi: 10.1038/ni.3153 |
| 28 |
TRINCHIERI G . Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2003, 3 (2): 133- 146.
doi: 10.1038/nri1001 |
| 29 |
DE LA CRUZ DOMÍNGUEZ-PUNARO M , SEGURA M , RADZIOCH D , et al. Comparison of the susceptibilities of C57BL/6 and A/J mouse strains to Streptococcus suis serotype 2 infection[J]. Infect Immun, 2008, 76 (9): 3901- 3910.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.00350-08 |
| 30 | 崔丽荣, 王嘉珍, 李亮, 等. 猪链球菌三价灭活苗的制备及对小鼠免疫效果的评价[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2022, 44 (2): 169- 178. |
| CUI L R , WANG J Z , LI L , et al. Preparation of trivalent inactivated vaccine of Streptococcus suis and evaluation of immune efficacy on mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 44 (2): 169- 178. | |
| 31 |
LI Y A , SUN Y N , FU Y , et al. Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis vector delivering a dual-antigen expression cassette provides mouse cross-protection against Streptococcus suis serotypes 2, 7, 9, and 1/2[J]. Vet Res, 2022, 53 (1): 46.
doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01062-9 |
| 32 |
LI Q , LV Y F , LI Y A , et al. Live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis vector delivering a conserved surface protein enolase induces high and broad protection against Streptococcus suis serotypes 2, 7, and 9 in mice[J]. Vaccine, 2020, 38 (44): 6904- 6913.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.08.062 |
| 33 |
OBRADOVIC M R , CORSAUT L , DOLBEC D , et al. Experimental evaluation of protection and immunogenicity of Streptococcus suis bacterin-based vaccines formulated with different commercial adjuvants in weaned piglets[J]. Vet Res, 2021, 52 (1): 133.
doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-01004-x |
| [1] | Huihui DUAN, Shihang REN, Hongyin ZHANG, Rui YU, Zhonghu LIU, Xiangdang DU, Yanhong SHANG. Horizontal Transfer of Drug Resistance Genes Carried by ICE_Prophage in Streptococcus suis SC124 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3699-3705. |
| [2] | Sijin TIAN, Jiaqi ZHAO, Xiaoming WANG, Liping WANG, Jinhu HUANG. Antimicrobial Resistance of Streptococcus suis in China: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3163-3176. |
| [3] | LI Pengxu, LI Shijing, SUN Jun, XIANG Wei, ZHAO Miaomiao, HOU Tianmu, LI Huaming, GUANG Min, CHEN Ruige, XU Mengran, WU Xiaomin, JIANG Hexiang, LEI Liancheng, ZHANG Fuxian. Molecular Subtyping and Identification of Streptococcus suis Meningitidis Type 2 and Its Biological Characteristics [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1192-1207. |
| [4] | YANG Yanbei, XU Jing, LIU Wanping, TAO Aini, FENG Yulin, SUN Yong, WANG Chuang, LIU Jian. Effects of Low-concentration Azitromycin on Protein Expression, Capsular Polysaccharides and Drug Susceptibility of Streptococcus suis Type 2 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(2): 757-765. |
| [5] | Lü Ruoyi, SI Xiaohui, SUN Zhigang, SHI Xiaomin, LIU Xiaoye. Drug Resistance Situation of Streptococcus suis and Prevention Measures of Infections [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 4920-4933. |
| [6] | ZHANG Shanshan, HE Bin, LI Shuguang, LIU Mingcheng, JIANG Jinqing, HU Jianhe, LEI Liancheng, SHEN Zhiqiang, XIA Xiaojing. Rapid Detection of Streptococcus suis with Visual RPA-LFD Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(2): 538-547. |
| [7] | HAN Xuejiao, LI Liang, ZHAN Songhe, DUAN Qianqian, CUI Lirong, LIU Xuelan, SUN Pei, WEI Jianzhong, LI Yu. Effects of Prophage on Virulence, Environmental Adaptability, Drug Resistance and Metabolic Activity of Streptococcus suis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(1): 290-303. |
| [8] | WANG Antian, HUANG Jing, SONG Bingxiao, SUN Yufan, ZHOU Rui, LI Lu. Evaluation of Therapeutic Effect of Porcine β-defensin-2 on Streptococcus suis Infection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(12): 3160-3170. |
| [9] | LI Wen-chao, GU You-fang, DU Ling, GONG Peng-tao, LI Jian-hua, ZHANG Xi-chen. Immunoprotection of Chickens against Eimeria tenella by Recombinant Serpin Protein Expressed in E. coli [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2013, 44(2): 270-275. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||