





畜牧兽医学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 5683-5696.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.11.027
章蓓雯1,2( ), 李鸿喜1,2, 翁成桢1,2, 黄欣欣1,2, 李晓冰2, 邱龙新2, 陈洪博2,*(
), 李鸿喜1,2, 翁成桢1,2, 黄欣欣1,2, 李晓冰2, 邱龙新2, 陈洪博2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-29
出版日期:2025-11-23
发布日期:2025-11-27
通讯作者:
陈洪博
E-mail:1092796034@qq.com;lyxy_vet@163.com
作者简介:章蓓雯(2000-),女,福建大田人,硕士生,主要从事中西兽医结合与保健研究,E-mail:1092796034@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Beiwen1,2( ), LI Hongxi1,2, WENG Chengzhen1,2, HUANG Xinxin1,2, LI Xiaobing2, QIU Longxin2, CHEN Hongbo2,*(
), LI Hongxi1,2, WENG Chengzhen1,2, HUANG Xinxin1,2, LI Xiaobing2, QIU Longxin2, CHEN Hongbo2,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-29
Online:2025-11-23
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
CHEN Hongbo
E-mail:1092796034@qq.com;lyxy_vet@163.com
摘要:
旨在通过网络药理学、分子对接及试验验证相结合共同探究鬼针草对鸡细菌性腹泻的治疗作用机制。本研究利用中药系统药理学分析平台(TCMSP)检索鬼针草药理成分和靶点,GeneCards、OMIM、DisgeNET数据库分析细菌性腹泻相关靶点基因并利用Venny数据库确定交集靶点。Cytoscape 3.10.2软件绘制“鬼针草-成分-靶点-腹泻网络图”;利用STRING数据库构建蛋白互作网络(PPI),并鉴定核心基因;利用DAVID数据库进行GO富集和KEGG通路富集分析;采用AutoDock用于分子对接验证;建立鸡大肠杆菌腹泻模型,观察其肠道组织形态影响及ELISA验证靶蛋白含量。鬼针草治疗鸡细菌腹泻的主要活性成分为:木犀草素、金鸡菊甙、6, 7-二羟基苯并呋喃和槲皮素,对应215个靶点基因;去除重复后与疾病共交集82个靶点,以白细胞介素-6 (interleukin-6, IL-6)、白细胞介素-1β (Interleukin-1 beta,IL-1β)、胱天蛋白酶3 (Caspase-3,CASP3)、基质金属蛋白酶(Matrix metalloproteinase-9,MMP9)和缺氧诱导因子1亚基α (Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, HIF-1α)为关键核心靶点;GO功能富集分析显示鬼针草主要作用靶点涉及凋亡过程、炎症反应等;KEGG通路富集分析显示鬼针草主要作用靶点富集在HIF-1α、C型凝集素受体、IL-17、TNF等信号通路;分子对接结果表明鬼针草主要活性成分与关键靶点具有良好的连接活性。组织切片和ELISA结果显示,鬼针草显著缓解了肠道组织损伤,并显著降低了空肠中IL-6、IL-1β、CASP3、MMP9和HIF-1α蛋白水平(P < 0.05、P < 0.01或P < 0.000 1)。通过网络药理学和试验验证发现,鬼针草可能通过调节IL-6、IL-1β、CASP3、MMP9和HIF-1α表达量来调控肠道炎症的发生发展,进而影响HIF-1α、IL-17、TNF等信号通路,为深入进行鬼针草治疗鸡细菌性腹泻的作用机制研究提供新思路与新方法。
中图分类号:
章蓓雯, 李鸿喜, 翁成桢, 黄欣欣, 李晓冰, 邱龙新, 陈洪博. 基于网络药理学和试验验证分析鬼针草治疗鸡细菌性腹泻的作用机制[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(11): 5683-5696.
ZHANG Beiwen, LI Hongxi, WENG Chengzhen, HUANG Xinxin, LI Xiaobing, QIU Longxin, CHEN Hongbo. The Mechanism of Bidens pilosa L. in the Treatment of Bacterial Diarrhea in Poultry based on Network Pharmacological Analysis and Experimental Verification[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5683-5696.
表 1
鬼针草主要活性成分信息"
| 分子编号 Mol ID | 活性成分 Active ingredients | 类药性/% OB | 药动学参数 DL | 分子量 MW |
| MOL000006 | 木犀草素 | 36.16 | 0.25 | 286.25 |
| MOL000098 | 槲皮素 | 46.43 | 0.28 | 302.25 |
| MOL006436 | 奥卡宁 | 98.81 | 0.2 | 288.27 |
| MOL006438 | (2E)-2-(3, 4dihydroxybenzylidene)-6, 7-dihydroxy-benzofuran-3-one | 39.48 | 0.25 | 286.25 |
| MOL006441 | 鬼针草酚葡糖苷 | 55.9 | 0.61 | 458.51 |
| MOL006442 | 金鸡菊甙 | 57.1 | 0.21 | 274.24 |
表 2
鬼针草治疗鸡细菌性腹泻的核心靶点筛选结果"
| 基因 Gene | 靶点名称 Target Name | 基因 Gene | 靶点名称 Target Name | |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 | EGF | Epidermal growth factor | |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta | EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor | |
| CASP3 | Caspase-3 | CCND1 | G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 | |
| MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 | PPARG | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma | |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha | HMOX1 | Heme oxygenase 1 | |
| TGFB1 | Transforming growth factor beta-1 | VCAM1 | Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 | |
| PTGS2 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 | CASP8 | Caspase-8 | |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 | AKT1 | AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 | |
| STAT1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-alpha/beta | CDK2 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 |
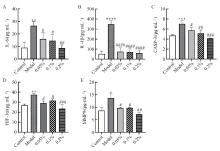
图 9
各组空肠中IL-6、IL-1β、CASP3、MMP9、HIF-1α水平 与空白组相比,*.P < 0.05,**.P < 0.01,***.P < 0.001,****.P < 0.000 1;与模型组相比,治疗组#.P < 0.05,##.P < 0.01,###.P < 0.001,####.P < 0.000 1;Compared with the blank group,*.P < 0.05,**.P < 0.01,***.P < 0.001,****.P < 0.000 1;compared with the model group, the treatment group #.P < 0.05,##.P < 0.01,###.P < 0.001,####.P < 0.000 1"
| 1 | 王旭贞,芦洪江,郝松华,等.白头翁汤预防禽大肠杆菌病作用机制的研究[J].中国预防兽医学报,2024,46(7):674-682. |
| WANGX Z,LUH J,HAOS H,et al.Study on the mechanism of Baitouweng Decoction in preventing avian colibacillosis[J].Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine,2024,46(7):674-682. | |
| 2 | 任涌志,高凌飞,王小婷,等.车前草水提物抗腹泻作用的研究[J].黑龙江畜牧兽医,2016(18):168-170. |
| RENY Z,GAOL F,WANGX T,et al.Study on the anti-diarrhea effect of plantain water extract[J].Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine,2016(18):168-170. | |
| 3 |
POHKARELP,DHAKALS,DOZOISC M.The diversity of Escherichia coli pathotypes and vaccination strategies against this versatile bacterial pathogen[J].Microorganisms,2023,11(2):344.
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020344 |
| 4 |
DHAMAK,CHAKRABORTYS,VERMAA K,et al.Fungal/mycotic diseases of poultry-diagnosis, treatment and control: a review[J].Pak J Biol Sci,2013,16(23):1626-1640.
doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2013.1626.1640 |
| 5 |
WANGS,PENGQ,JIAH M,et al.Prevention of Escherichia coli infection in broiler chickens with Lactobacillus plantarum B1[J].Poult Sci,2017,96(8):2576-2586.
doi: 10.3382/ps/pex061 |
| 6 |
HABIBAUE,KHANA,MMBAGAEJ,et al.Use of antibiotics in poultry and poultry farmers-a cross-sectional survey in Pakistan[J].Front Public Health,2023,11,1154668.
doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1154668 |
| 7 |
ABD EL-HACKME,EL-SAADONYMT,SALEMHM,et al.Alternatives to antibiotics for organic poultry production: types, modes of action and impacts on bird's health and production[J].Poult Sci,2022,101(4):101696.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101696 |
| 8 |
RODRÍGUEZ-MESAX M,CONTRERAS BOLAÑOSL A,MEJÍAA,et al.Immunomodulatory properties of natural extracts and compounds derived from Bidens pilosa L.: Literature review[J].Pharmaceutics,2023,15(5):1491.
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051491 |
| 9 |
RABET,VAN STADENJ.Antibacterial activity of South African plants used for medicinal purposes[J].J Ethnopharmacol,1997,56(1):81-87.
doi: 10.1016/S0378-8741(96)01515-2 |
| 10 | LIANGY C,LINC J,YANGC Y,et al.Toxicity study of Bidens pilosa in animals[J].Tradit Complement Med,2019,10(2):150-157. |
| 11 |
SHENA Z,LIX,HUW,CHENF H.Total flavonoids of Bidens bipinnata L. ameliorate experimental adjuvant-induced arthritis through induction of synovial apoptosis[J].BMC Complement Altern Med,2015,15(1):437.
doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0962-3 |
| 12 |
CHUNGC Y,YANGW C,LIANGC L,et al.Cytopiloyne, a polyacetylenic glucoside from Bidens pilosa, acts as a novel anticandidal agent via regulation of macrophages[J].Ethnopharmacol,2016,184,72-80.
doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.02.036 |
| 13 | BASTOSC C C,ÁVILAP H M,FILHOE X D S,et al.Use of Bidens pilosa L. (Asteraceae) and Curcuma longa L. (Zingiberaceae) to treat intestinal mucositis in mice: Toxico-pharmacological evaluations[J].Toxicol Rep,2015,3,279-287. |
| 14 |
HORIUCHIM,WACHIH,SEYAMAY.Effects of Bidens pilosa L. var. radiata Scherff on experimental gastric lesion[J].Nat Med,2010,64(4):430-435.
doi: 10.1007/s11418-010-0426-5 |
| 15 |
CHANGC L,CHUNGC Y,KUOC H,et al.Beneficial effect of Bidens pilosa on body weight gain, food conversion ratio, gut bacteria and Coccidiosis in chickens[J].PLoS One,2016,11(1):e0146141.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146141 |
| 16 | SHERMAN B T, HAO M, QIU J, et al. DAVID: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update)[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 23 March 2022, 50(W1): W216-W221. |
| 17 |
ZHANGL,YANGZ,LIX,et al.Anti-atherosclerotic effects of naringenin and quercetin from Folium Artemisiae argyi by attenuating interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β)/matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9): Network pharmacology-based analysis and validation[J].BMC Complement Med Ther,2023,23(1):378.
doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04223-1 |
| 18 |
张旭梅,魏玉荣,许丞惠,等.基于网络药理学和试验验证分析小檗碱治疗鸡沙门菌感染的作用机制[J].畜牧兽医学报,2023,54(8):3557-3570.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.08.039 |
|
ZHANGX M,WEIY R,XUC H,et al.Based on network pharmacology and experimental verification, the mechanism of berberine in the treatment of Salmonella infection in chickens was analyzed[J].Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2023,54(8):3557-3570.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.08.039 |
|
| 19 | HANJ,HOUJ,LIUY,et al.Using network pharmacology to explore the mechanism of panax notoginseng in the treatment of myocardial fibrosis[J].Diabetes Res,2022,2022,8895950. |
| 20 |
ZHANGR,LIZ,GUX,et al.Probiotic Bacillus subtilis LF11 protects intestinal epithelium against Salmonella infection[J].Front Cell Infect Microbiol,2022,12,837886.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.837886 |
| 21 |
QUAGLIOA E V,CRUZV M,ALMEIDA-JUNIORL D,et al.Bidens pilosa (Black Jack) standardized extract ameliorates acute TNBS-induced intestinal inflammation in rats[J].Planta Med,2020,86(5):319-330.
doi: 10.1055/a-1089-8342 |
| 22 |
MEMONF U,YANGY,LVF,et al.Effects of probiotic and Bidens pilosa on the performance and gut health of chicken during induced Eimeria tenella infection[J].Appl Microbiol,2021,131(1):425-434.
doi: 10.1111/jam.14928 |
| 23 |
巩志国,赵佳敏,顾柏臣,等.基于网络药理学分析党参减轻大肠杆菌感染小鼠急性肺损伤的作用机制[J].畜牧兽医学报,2023,54(8):3571-3581.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.08.040 |
|
GONGZ G,ZHAOJ M,GUB C,et al.Based on network pharmacology, the mechanism of Codonopsis pilosula in alleviating acute lung injury in mice infected with E.coli[J].Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2023,54(8):3571-3581.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.08.040 |
|
| 24 |
HUANGL,KIMM Y,CHOJ Y.Immunopharmacological activities of Luteolin in chronic diseases[J].Int J Mol Sci,2023,24(3):2136.
doi: 10.3390/ijms24032136 |
| 25 |
QIW,QIW,XIONGD,et al.Quercetin: Its antioxidant mechanism, antibacterial properties and potential application in prevention and control of toxipathy[J].Molecules,2022,27(19):6545.
doi: 10.3390/molecules27196545 |
| 26 |
HUSSAINM S,GUPTAG,GOYALA,et al.From nature to therapy: Luteolin's potential as an immune system modulator in inflammatory disorders[J].Biochem Mol Toxicol,2023,37(11):e23482.
doi: 10.1002/jbt.23482 |
| 27 | 章捷,田由,吴臻斐,等.木犀草素介导PERK/eIF2α/CHOP信号通路改善新生大鼠坏死性小肠结肠炎的作用研究[J].浙江医学,2023,45(21):2248-2254. |
| ZHANGJ,TIANY,WUZ F,et al.The effect of luteolin-mediated PERK/eIF2α/CHOP signaling pathway on improving necrotizing enterocolitis in neonatal rats[J].Zhejiang Medicine,2023,45(21):2248-2254. | |
| 28 |
文安林,杨芸芸,罗永荣,等.黄连防治鸭病毒性肠炎机制的网络药理学分析及动物试验验证[J].畜牧兽医学报,2024,55(7):3225-3233.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.07.040 |
|
WENA L,YANGY Y,LUOY Y,et al.Network pharmacological analysis and animal test verification of the mechanism of Rhizoma Coptidis in preventing and treating duck viral enteritis[J].Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2024,55(7):3225-3233.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.07.040 |
|
| 29 |
XUB,QINW,XUY,et al.Dietary quercetin supplementation attenuates diarrhea and intestinal damage by regulating gut microbiota in weanling piglets retracted in: Oxid Med Cell Longev[J].Oxid Med Cell Longev,2021,2021,6221012.
doi: 10.1155/2021/6221012 |
| 30 |
GONGT,WUD,FENGY,et al.Inhibitory effects of quercetin on porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in vitro and in vivo[J].Virology,2024,589,109923.
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2023.109923 |
| 31 |
OGUNROO B,OFENIFOROE B,FAKAYODEA E.Quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside-rich fraction demonstrated efficacy against infectious, secretory, and osmotic models of diarrhoeal rats[J].Genet Eng Biotechnol,2023,21(1):36.
doi: 10.1186/s43141-023-00489-7 |
| 32 |
ZHANGB,ZHONGQ,LIUN,et al.Dietary glutamine supplementation alleviated inflammation responses and improved intestinal mucosa barrier of LPS-challenged broilers[J].Animals,2022,12(13):1729.
doi: 10.3390/ani12131729 |
| 33 |
DUPAUL-CHICOINEJ,YERETSSIANG,DOIRONK,et al.Control of intestinal homeostasis, colitis, and colitis-associated colorectal cancer by the inflammatory caspases[J].Immunity,2010,32(3):367-378.
doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.02.012 |
| 34 |
ZHANGH,LIUL,JIANGC,et al.MMP9 protects against LPS-induced inflammation in osteoblasts[J].Innate Immun,2020,26(4):259-269.
doi: 10.1177/1753425919887236 |
| 35 |
NIGHOTP,AL-SADIR,RAWATM,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase 9-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability contributes to the severity of experimental DSS colitis[J].Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2015,309(12):G988-G997.
doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00256.2015 |
| 36 |
SINGHALR,SHAHY M.Oxygen battle in the gut: Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in metabolic and inflammatory responses in the intestine[J].Biol Chem,2020,295(30):10493-10505.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.011188 |
| 37 |
KERBERE L,PADBERGC,KOLLN,et al.The importance of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF-1 and HIF-2) for the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease[J].Int J Mol Sci,2020,21(22):8551.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21228551 |
| 38 |
GUC,WUL,LIX.IL-17 family: cytokines, receptors and signaling[J].Cytokine,2013,64(2):477-485.
doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.07.022 |
| 39 |
OWAGAE,HSIEHR H,MUGENDIB,et al.Th17 cells as potential probiotic therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel diseases[J].Int J Mol Sci,2015,16(9):20841-20858.
doi: 10.3390/ijms160920841 |
| 40 |
WENY,WANGH,TIAND,et al.TH17 cell: a double-edged sword in the development of inflammatory bowel disease[J].Therap Adv Gastroenterol,2024,17,17562848241230896.
doi: 10.1177/17562848241230896 |
| 41 |
CǍTANǍC S,BERINDAN NEAGOEI,COZMAV,et al.Contribution of the IL-17/IL-23 axis to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease[J].World J Gastroenterol,2015,21(19):5823-5830.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i19.5823 |
| 42 |
LIY,YUC,ZHUW M,et al.Triptolide ameliorates IL-10-deficient mice colitis by mechanisms involving suppression of IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway and down-regulation of IL-17[J].Mol Immunol,2010,47(15):2467-2474.
doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.06.007 |
| 43 |
VAN LOOG,BERTRANDM J M.Death by TNF: a road to inflammation[J].Nat Rev Immunol,2023,23(5):289-303.
doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00792-3 |
| 44 |
WUY,YANGY,WANGL,et al.Effect of Bifidobacterium on osteoclasts: TNF-α/NF-κB inflammatory signal pathway-mediated mechanism[J].Front Endocrinol (Lausanne),2023,14,1109296.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1109296 |
| 45 |
JIS,ZHANGQ.Momordica charantia polysaccharides alleviate diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome by regulating intestinal inflammation and barrier via NF-κB pathway[J].Allergol Immunopathol (Madr),2022,50(3):62-70.
doi: 10.15586/aei.v50i3.584 |
| 46 |
KULECKAM,ZEBER-LUBECKAN,BAŁABASA,et al.Diarrheal-associated gut dysbiosis in cancer and inflammatory bowel disease patients is exacerbated by Clostridioides difficile infection[J].Front Cell Infect Microbiol,2023,13,1190910.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1190910 |
| 47 | 郭世伟,金晓,徐元庆,等.植物源饲料添加剂缓解家禽大肠杆菌病的研究进展[J].动物营养学报,2023,35(9):5441-5452. |
| GUOS W,JINX,XUY Q,et al.Research progress of plant-derived feed additives to alleviate avian colibacillosis[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2023,35(9):5441-5452. |
| [1] | 王彦博, 张笑梦, 景秀娟, 冯肖艺, 张元庆, 赵学明. 纳米粒子在动物种质资源冷冻保存的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4156-4164. |
| [2] | 王有栋, 曹志平, 李玉茂, 栾鹏, 李辉, 白雪. SNP芯片技术原理及其在鸡遗传育种中的应用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4165-4175. |
| [3] | 潘言迪, 张婷婷, 方仁东, 彭练慈. 动物源宿主防御肽抗微生物作用机制研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4294-4302. |
| [4] | 赵玉洁, 宛宝霞, 王佳奇, 孙思雨, 冷欣阳, 崔一喆. 基于网络药理学分析饲粮添加蒲公英调节鹅免疫因子水平的作用机制[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4698-4707. |
| [5] | 王超慧, 刘筱影, 杨小军, 刘艳利. 甜菜碱缓解油酸诱导鸡胚原代肝细胞脂代谢紊乱及氧化应激的作用机制[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4741-4749. |
| [6] | 李晓蝶, 潘诗琴, 王鲁, 程振涛, 欧德渊, 宋旭琴, 杨剑. 基于网络药理学的中兽药抗炎作用机制研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(8): 3701-3721. |
| [7] | 付伟, 张冉, 丁虹, 臧素敏, 李祥龙, 褚素乔, 刘华格, 周荣艳. 太行鸡与坝上长尾鸡品种区分的分子标记筛选与鉴定[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(8): 3761-3772. |
| [8] | 薛晓晓, 孟令宅, 王素艳, 于蒙蒙, 陈运通, 祁小乐, 李留安, 于晓雪, 高玉龙. B亚型禽偏肺病毒病弱毒疫苗对商品蛋鸡的免疫效果[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(8): 3958-3966. |
| [9] | 赵靖玉, 李丹, 张兵, 张乾义, 张锦华, 宋亚芬, 杨承槐. 鸡传染性支气管炎病毒M41株全基因组序列测定及致病性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(8): 3967-3975. |
| [10] | 袁橙, 袁月, 张清正, 宋小凯, 徐立新, 严若峰, 李祥瑞, 陆明敏. 巨型艾美耳球虫与产气荚膜梭菌共感染致鸡坏死性肠炎模型的评价[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(8): 4120-4128. |
| [11] | 宗云鹤, 杨宇泽, 孙研研, 陈继兰, 李云雷. 赖氨酸乙酰化修饰在鸡精液冷冻中的保护作用及机制研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(7): 3071-3079. |
| [12] | 孙淑佳, 郑嘉祺, 卢姝婉, 刘金松, 姚春雷, 杨彩梅, 许英蕾, 张瑞强. 乳酸菌对黄羽肉鸡生长性能、消化功能和养分利用率的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(7): 3335-3343. |
| [13] | 彭文文, 张美婷, 徐灏铖, 徐保阳, 张玲玲, 杨彩梅. 地衣芽孢杆菌对大肠杆菌攻毒感染肉鸡免疫、抗氧化性能和肠道健康的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(7): 3344-3356. |
| [14] | 陈艳茹, 马小春, 王明慧, 唐瑶瑶, 白露, 赵桂苹, 文杰, 刘冉冉. 白羽肉鸡胸肌意大利面肉和木质肉发生率及其对肉品质影响研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(6): 2672-2684. |
| [15] | 董娇娇, 丁虹, 张寅梁, 张冉, 刘华格, 臧素敏, 张振红, 周荣艳, 李兰会. 鸡白痢沙门菌感染太行鸡盲肠菌群的差异及功能分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(6): 2741-2751. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
