





畜牧兽医学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (10): 4863-4876.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.10.009
收稿日期:2025-01-10
出版日期:2025-10-23
发布日期:2025-11-01
通讯作者:
李朋,丁家波
E-mail:17861509833@163.com;lipeng01@caas.cn;dingjiabo@caas.cn
作者简介:王恒泰(1998-), 男, 山东滕州人, 博士生, 主要从事布鲁氏菌逃逸宿主先天免疫的分子机制研究。E-mail: 17861509833@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Hengtai( ), JIANG Hui, LI Peng*(
), JIANG Hui, LI Peng*( ), DING Jiabo*(
), DING Jiabo*( )
)
Received:2025-01-10
Online:2025-10-23
Published:2025-11-01
Contact:
LI Peng, DING Jiabo
E-mail:17861509833@163.com;lipeng01@caas.cn;dingjiabo@caas.cn
摘要:
布鲁氏菌病(brucellosis)是由布鲁氏菌(Brucella spp.)侵染引起的一种人畜共患细菌病, 严重危害人类健康和养殖业发展。布鲁氏菌是一种胞内寄生菌, 逃避宿主天然免疫反应实现胞内寄生是布鲁氏菌毒力的重要体现。脂多糖(LPS)是布鲁氏菌编码的重要毒力因子之一。相较于其他革兰阴性菌, 布鲁氏菌LPS的主要成分、空间结构、连接方式均有不同, 使其表现出特有的低内毒素性, 并且在协助布鲁氏菌逃逸宿主天然免疫系统的识别以及调控免疫应答过程中起关键作用。本文聚焦布鲁氏菌LPS, 对其特殊结构、生物合成过程及其免疫逃逸机制进行综述, 为全面了解布鲁氏菌LPS的生物学功能奠定基础。
中图分类号:
王恒泰, 蒋卉, 李朋, 丁家波. 布鲁氏菌脂多糖的生物合成及其在免疫逃逸中的生物学功能[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(10): 4863-4876.
WANG Hengtai, JIANG Hui, LI Peng, DING Jiabo. Biosynthesis of Brucella Lipopolysaccharides and Their Biological Functions in Immune Evasion[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 4863-4876.
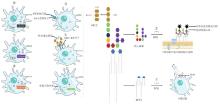
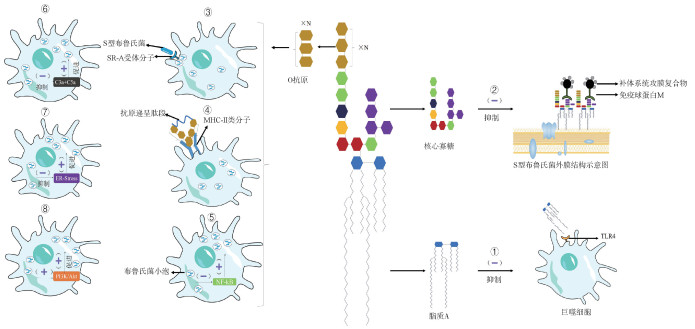
图 2
LPS在S型布鲁氏菌免疫逃逸过程中的作用机制示意图 ①S型布鲁氏菌LPS脂质A的长酰基链抑制宿主TLR4/MD-2的识别和结合;②S型布鲁氏菌LPS的核心寡糖低水平的磷酸化和糖基修饰抑制了补体C1q的结合;③S型布鲁氏菌LPS的O抗原可与宿主细胞膜上的清道夫受体SR-A结合,避免早期与溶酶体融合,保证布鲁氏菌在细胞内的早期存活;④O抗原可通过空间位阻干扰MHC-Ⅱ的递呈过程,降低了抗原呈递的效率;⑤O抗原限制NF-κB信号通路激活,有利于布鲁氏菌在细胞内的存活;⑥O抗原抑制C3转化酶的形成,减少炎性细胞因子的产生、降低补体介导的溶菌作用,有利于布鲁氏菌在细胞内的存活;⑦O抗原抑制ER-Stress信号通路,有利于布鲁氏菌在细胞内的存活;⑧O抗原可以激活巨噬细胞中的PI3K/Akt信号通路,促进被感染的细胞存活,进而有利于布鲁氏菌在细胞内的存活。其中,C3a + C5a是指补体C3片段a和C5片段a是在补体系统激活过程中产生的活性肽;PI3K/Akt是指磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K)和蛋白激酶B(Akt)构成的一个重要的信号通路,调控细胞的生长、代谢和存活等多个生理过程;ER-Stress是指内质网应激,内质网功能受到干扰或损害的状态,作为应对机制,细胞启动一系列适应性机制来恢复内质网的稳态,确保蛋白质正确折叠和细胞功能的正常进行;NF-κB是指一类转录因子,广泛参与细胞的免疫反应、炎症反应、细胞增殖、存活和应激反应等多种生理过程"
| 1 |
HUSSAIN A , HUSSAIN S , CHAUDHRY M , et al. Prevalence and herd-level risk factors associated with Brucella infection in small holders keeping large ruminants[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2025, 183, 105506.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2024.105506 |
| 2 |
QIN Y , ZHOU G , JIAO F , et al. Brucella mediates autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis to escape host killing[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2024, 14, 1408407.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1408407 |
| 3 | 王恒泰, 吕浪, 蒋卉, 等. 牛种布鲁氏菌MgtC蛋白在抵抗低Mg2+环境中的生物学功能研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56 (1): 365- 377. |
| WANG H T , LV L , JIANG H , et al. Biological function of MgtC protein in Brucella abortus in response to low Mg2+ environment[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56 (1): 365- 377. | |
| 4 |
LAPAQUE N , MORIYON I , MORENO E , et al. Brucella lipopolysaccharide acts as a virulence factor[J]. Curr Opin Microbiol, 2005, 8 (1): 60- 66.
doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.12.003 |
| 5 |
ZHAO Y , HANNIFFY S , ARCE-GORVEL V , et al. Immunomodulatory properties of Brucella melitensis lipopolysaccharide determinants on mouse dendritic cells in vitro and in vivo[J]. Virulence, 2018, 9 (1): 465- 479.
doi: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1386831 |
| 6 | MARCOS M . Smooth to rough dissociation in Brucella: The missing link to virulence[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2015, 5, 98. |
| 7 | AHMED M E , MOHAMED E I , RAMADAN K M , et al. Evaluation of the immunization of camels with Brucella abortus vaccine (RB51) in Egypt[J]. Open Vet J, 2024, 14 (1): 19- 24. |
| 8 |
CAI G H , GUO C Y , GUO K X , et al. Development of a competitive ELISA based on Brucella neotomae lipopolysaccharide for detecting brucellosis in livestock[J]. Anal Biochem, 2025, 703, 115880.
doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2025.115880 |
| 9 |
FUREVI A , UDEKWU K I , WIDMALM G . Structural elucidation of the O-antigen polysaccharide from Escherichia coli O125ac and biosynthetic aspects thereof[J]. Glycobiology, 2022, 32 (12): 1089- 1100.
doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwac061 |
| 10 |
BROWN H A , VINOGRADOV E , GILBERT M , et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex has a pathway for the biosynthesis of 4-formamido-4, 6-dideoxy-d-glucose[J]. Protein Sci, 2018, 27 (8): 1491- 1497.
doi: 10.1002/pro.3443 |
| 11 |
BUNDLE D R , CHERWONOGRODZKY J W , GINDNEY M A , et al. Definition of Brucella A and M epitopes by monoclonal typing reagents and synthetic oligosaccharides[J]. Infect Immun, 1989, 57 (9): 2829- 2836.
doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2829-2836.1989 |
| 12 |
BUNDLE D R , CHERWONOGRODZKY J W , PERRY M B . Structural elucidation of the Brucella melitensis M antigen by high-resolution NMR at 500 MHz[J]. Biochemistry, 1987, 26 (26): 8717- 8726.
doi: 10.1021/bi00400a034 |
| 13 |
WANG J , MA W , FANG Y , et al. Core oligosaccharide portion of lipopolysaccharide plays important roles in multiple antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2021, 65 (10): e0034121.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.00341-21 |
| 14 |
BAI Q , LI H , WU X , SHAO J , et al. Comparative analysis of the main outer membrane proteins of Brucella in the diagnosis of brucellosis[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021, 560, 126- 131.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.04.127 |
| 15 |
FERGUSON G P , DATTA A , BAUMGARTNER J , et al. Similarity to peroxisomal-membrane protein family reveals that Sinorhizobium and Brucella BacA affect lipid-A fatty acids[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2004, 101 (14): 5012- 5017.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307137101 |
| 16 | MORIYÓN I , LÓPEZ-GOÑI I . Structure and properties of the outer membranes of Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis[J]. Int Microbiol, 1998, 1 (1): 19- 26. |
| 17 |
FONTANA C , CONDE-ÁLVAREZ R , STÁHLE J , et al. Structural studies of lipopolysaccharide-defective mutants from Brucella melitensis identify a core oligosaccharide critical in virulence[J]. J Biol Chem, 2016, 291 (14): 7727- 7741.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.701540 |
| 18 |
KAWAHARA K . Variation, modification and engineering of lipid A in endotoxin of gram-negative bacteria[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (5): 2281.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22052281 |
| 19 |
MORENO E , STACKEBRANDT E , DORSCH M , et al. Brucella abortus16S rRNA and lipid A reveal a phylogenetic relationship with members of the alpha-2 subdivision of the class proteobacteria[J]. J Bacteriol, 1990, 172 (7): 3569- 3576.
doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3569-3576.1990 |
| 20 |
ROJAS N , FREER E , WEINTRAUB A , et al. Immunochemical identification of Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide epitopes[J]. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol, 1994, 1 (2): 206- 213.
doi: 10.1128/cdli.1.2.206-213.1994 |
| 21 |
ZHANG J D , WANG Q , HU H X , et al. Brucella lipopolysaccharide deficiency with lipid A induces robust T cells immune response[J]. Mol Immunol, 2025, 182, 11- 19.
doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2025.03.006 |
| 22 |
CASABUONO A C , CZIBENERr C , DEL GIUDICE MG , et al. New features in the lipid A structure of Brucella suis and Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide[J]. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom, 2017, 28 (12): 2716- 2723.
doi: 10.1007/s13361-017-1805-x |
| 23 |
REEVES P R , HOBBS M , VALVANO M A , et al. Bacterial polysaccharide synthesis and gene nomenclature[J]. Trends Microbiol, 1996, 4 (12): 495- 503.
doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(97)82912-5 |
| 24 | 张敏, 刘宗平, 于圣青. 布鲁氏菌脂多糖及其突变株的研究进展[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2013, 21 (3): 80- 86. |
| ZHANG M , LIU Z P , YU S Q . Research progress on Brucella lipopolysaccharides and its mutant strains[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2013, 21 (3): 80- 86. | |
| 25 |
MORONA R , STROEHER U H , KARAGEORGOS L E , et al. A putative pathway for biosynthesis of the O-antigen component, 3-deoxy-L-glycero-tetronic acid, based on the sequence of the vibrio cholerae O1 rfb region[J]. Gene, 1995, 166 (1): 19- 31.
doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00588-9 |
| 26 | 易德武. 羊种布鲁氏菌015株gmd、per和manb缺失株的构建及诊断抗原反应原性评价研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2015. |
| YI D W. Construction of gmd, per, and manb deletion mutants of Brucella ovis strain 015 and evaluation of diagnostic antigen reactogenicity[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2015. (in Chinese) | |
| 27 | 徐锦凤, 王震, 马旭升, 等. 布鲁氏菌脂多糖蛋白ManB和GMD的免疫原性比较[C]//中国兽医病理学2017年学术研讨会暨兽医病理学分会第九次全国会员代表大会. 锦州, 2017. |
| XU J F, WANG Z, MA X S, et al. Comparative immunogenicity of Brucella lipopolysaccharide proteins ManB and GMD[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 Academic Symposium on Veterinary Pathology and the 9th National Member Congress of the Veterinary Pathology Branch. Jinzhou, Liaoning, China, 2017. (in Chinese) | |
| 28 | CHAUDHURI P, SAMINATHAN M, ALI S A, et al. Immunization with Brucella abortus S19Δper conferred protection in water buffaloes against virulent challenge with B. abortus strain S544[J]. Vaccines (Basel), 2021, 9(12): 1423. |
| 29 | HANWEI J, NIE X, ZHU H, et al. miR-146b-5p plays a critical role in the regulation of autophagy in Δper Brucella melitensis-infected RAW264.7 cells[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 1953242. |
| 30 |
RIEGERT A S , CHANTIGIAN D P , THODEN J B , et al. Biochemical characterization of WbkC, an N-formyltransferase from Brucella melitensis[J]. Biochemistry, 2017, 56 (28): 3657- 3668.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00494 |
| 31 | DABRAL N, JAIN-GUPTA N, SELEEM M N, et al. Overexpression of Brucella putative glycosyltransferase WbkA in B. abortus RB51 leads to production of exopolysaccharide[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2015, 5: 54. |
| 32 |
LI Z Q , SHI J X , FU W D , et al. A Brucella melitensis M5-90 wboA deletion strain is attenuated and enhances vaccine efficacy[J]. Mol Immunol, 2015, 66 (2): 276- 283.
doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.04.004 |
| 33 |
VEMULAPALLI R , HE Y , BUCCOLO L S , et al. Complementation of Brucella abortus RB51 with a functional wboA gene results in O-antigen synthesis and enhanced vaccine efficacy but no change in rough phenotype and attenuation[J]. Infect Immun, 2000, 68 (7): 3927- 3932.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.7.3927-3932.2000 |
| 34 |
WANG X R , YAN G M , ZHANG R , et al. Immunogenic response induced by wzm and wzt gene deletion mutants from Brucella abortus S19[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2014, 9 (2): 653- 658.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1810 |
| 35 |
ALAIMO C , CATREIN I , MORF L , et al. Two distinct but interchangeable mechanisms for flipping of lipid-linked oligosaccharides[J]. Embo J, 2006, 25 (5): 967- 976.
doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601024 |
| 36 | 王秀然. 布鲁氏菌wzm/wzt基因对其毒力、免疫原性及蛋白质表达影响的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014. |
| WANG X R. The role of wzm/wzt gene on virulence, immunologicity, and protein expression of Brucella[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2014. (in Chinese) | |
| 37 |
CARDOSO P G , MACEDO G C , AZEVEDO V , et al. Brucella spp noncanonical LPS: structure, biosynthesis, and interaction with host immune system[J]. Microb Cell Fact, 2006, 5, 13.
doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-5-13 |
| 38 |
CZIBENER C , REY SERANTES D A , ROMANI A M , et al. Bm delta-pgm, a vaccine for the control of Brucella melitensis with cross-species protective properties[J]. Vaccine, 2023, 41 (23): 3534- 3543.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.04.076 |
| 39 |
UGALDE J E , CZIBENER C , FELDMAN M F , et al. Identification and characterization of the Brucella abortus phosphoglucomutase gene: role of lipopolysaccharide in virulence and intracellular multiplication[J]. Infect Immun, 2000, 68 (10): 5716- 5723.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.10.5716-5723.2000 |
| 40 |
ZHANG Y , LI T , ZHANG J , et al. The Brucella melitensis M5-90 phosphoglucomutase (PGM) mutant is attenuated and confers protection against wild-type challenge in BALB/c mice[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2016, 32 (4): 58.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2015-6 |
| 41 |
ZHANG J , YIN S , YI D , et al. The Brucella melitensis M5-90ΔmanB live vaccine candidate is safer than M5-90 and confers protection against wild-type challenge in BALB/c mice[J]. Microb Pathog, 2017, 112, 148- 155.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.09.016 |
| 42 |
ZYGMUNT M S , BLASCO J M , LETESSON J J , et al. DNA polymorphism analysis of Brucella lipopolysaccharide genes reveals marked differences in O-polysaccharide biosynthetic genes between smooth and rough Brucella species and novel species-specific markers[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2009, 9, 92.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-92 |
| 43 |
MONREAL D , GRILLÓ M J , GONZÁLEZ D , Et al . Characterization of Brucella abortus O-polysaccharide and core lipopolysaccharide mutants and demonstration that a complete core is required for rough vaccines to be efficient against Brucella abortus and Brucella ovis in the mouse model[J]. Infect Immun, 2003, 71 (6): 3261- 3271.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.6.3261-3271.2003 |
| 44 |
WEN L , ZHENG Y , LI T , et al. Enzymatic synthesis of 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO) and its application for LPS assembly[J]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2016, 26 (12): 2825- 2828.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.04.061 |
| 45 |
ELAMIN A A , STEINICKE S , OEHLMANN W , et al. Novel drug targets in cell wall biosynthesis exploited by gene disruption in Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12 (10): e0186801.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186801 |
| 46 | SOLER-LLORÉNS P , GIL-RAMÍREZ Y , ZABALZA-BARANGUÁ A , et al. Mutants in the lipopolysaccharide of Brucella ovis are attenuated and protect against B. ovis infection in mice[J]. Vet Res, 2014, 45, 72. |
| 47 |
GIL-RAMÍREZ Y , CONDE-ÁLVAREZ R , PALACIOS-CHAVES L , et al. The identification of wadB, a new glycosyltransferase gene, confirms the branched structure and the role in virulence of the lipopolysaccharide core of Brucella abortus[J]. Microb Pathog, 2014, 73, 53- 59.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2014.06.002 |
| 48 |
SALVADOR-BESCÓS M , GIL-RAMÍREZ Y , ZÚÑIGA-RIPA A , et al. WadD, a new Brucella lipopolysaccharide core glycosyltransferase identified by genomic search and phenotypic characterization[J]. Front Microbiol, 2018, 9, 2293.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02293 |
| 49 |
IZQUIERDO L , ABITIU N , CODERCH N , et al. The inner-core lipopolysaccharide biosynthetic waaE gene: function and genetic distribution among some Enterobacteriaceae[J]. Microbiology (Reading), 2002, 148, 3485- 3496.
doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-11-3485 |
| 50 | HONE D M , POWELL J , CROWLEY R W , et al. Lipopolysaccharide from an Escherichia coli htrB msbB mutant induces high levels of MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta secretion without inducing TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta[J]. J Hum Virol, 1998, 1 (4): 251- 256. |
| 51 | EMIOLA A , GEORGE J , ANDREWS S S . A complete pathway model for lipid A biosynthesis in Escherichia coli[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 10 (4): e0121216. |
| 52 |
ZHAO M , ZHU Y , WANG H , et al. Efficient production of N-acetylneuraminic acid in Escherichia coli based on the UDP-N-acetylglucosamine biosynthetic pathway[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2023, 71 (28): 10701- 10709.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c02432 |
| 53 |
BRANDTZAEG P . Host response to Neisseria meningitidis lacking lipopolysaccharides[J]. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther, 2003, 1 (4): 589- 596.
doi: 10.1586/14787210.1.4.589 |
| 54 |
SHARMA S , BANERJEE T , YADAV G , et al. Mutations at novel sites in pmrA/B and lpxA/D genes and absence of reduced fitness in colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from a tertiary care hospital, India[J]. Microb Drug Resist, 2021, 27 (5): 628- 636.
doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0023 |
| 55 |
KUMAR PAL S , KUMAR S . LpxC (UDP-3-O-(R-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase) inhibitors: A long path explored for potent drug design[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 234, 122960.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.179 |
| 56 |
KRAUSE K M , HAGLUND C M , HEBNER C , et al. Potent LpxC inhibitors with in vitro activity against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2019, 63 (11): e00977-19.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.00977-19 |
| 57 |
BARTLING C M , RAETZ C R . Crystal structure and acyl chain selectivity of Escherichia coli LpxD, the N-acyltransferase of lipid A biosynthesis[J]. Biochemistry, 2009, 48 (36): 8672- 8683.
doi: 10.1021/bi901025v |
| 58 |
ALTINOK I , OZTURK R C , KAHRAMAN U C , et al. Protection of rainbow trout against yersiniosis by lpxD mutant Yersinia ruckeri[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 2016, 55, 21- 27.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.04.018 |
| 59 |
BOHL H O , SHI K , LEE J K , et al. Crystal structure of lipid A disaccharide synthase LpxB from Escherichia coli[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9 (1): 377.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02712-9 |
| 60 |
METZGER L E , RAETZ C R . Purification and characterization of the lipid A disaccharide synthase (LpxB) from Escherichia coli, a peripheral membrane protein[J]. Biochemistry, 2009, 48 (48): 11559- 11571.
doi: 10.1021/bi901750f |
| 61 |
EMPTAGE R P , PEMBLE C W , YORK J D , et al. Mechanistic characterization of the tetraacyldisaccharide-1-phosphate 4'-kinase LpxK involved in lipid A biosynthesis[J]. Biochemistry, 2013, 52 (13): 2280- 2290.
doi: 10.1021/bi400097z |
| 62 |
WEI J R , RICHIE D L , MOSTAFAVI M , et al. LpxK is essential for growth of Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606: Relationship to toxic accumulation of lipid A pathway intermediates[J]. mSphere, 2017, 2 (4): e00199-17.
doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00199-17 |
| 63 |
WU J , JIANG L , SHAO Q , et al. Comparison of the safety and efficacy of the wild-type and lpxL/lpxM mutant inactivated vaccine against the avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O1, O2, and O78 challenge[J]. Vaccine, 2024, 42 (10): 2707- 2715.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.03.038 |
| 64 |
GORZELAK P , KLEIN G , RAINA S . Molecular basis of essentiality of early critical Steps in the lipopolysaccharide biogenesis in Escherichia coli K-12: Requirement of MsbA, Cardiolipin, LpxL, LpxM and GcvB[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (10): 5099.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22105099 |
| 65 |
ZHU L , LI Y , WANG J , et al. Identification of two secondary acyltransferases of lipid A in Pseudomonas putida KT2442[J]. J Appl Microbiol, 2017, 123 (2): 478- 490.
doi: 10.1111/jam.13499 |
| 66 |
FISSEHA M , CHEN P , BRANDT B , et al. Characterization of native outer membrane vesicles from lpxL mutant strains of Neisseria meningitidis for use in parenteral vaccination[J]. Infect Immun, 2005, 73 (7): 4070- 4080.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.7.4070-4080.2005 |
| 67 |
OKUDA S , SHERMAN D J , SILHAVY T J , et al. Lipopolysaccharide transport and assembly at the outer membrane: the PEZ model[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2016, 14 (6): 337- 345.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.25 |
| 68 |
SALMON-DIVON M , KORNSPAN D . Transcriptomic analysis of smooth versus rough Brucella melitensis Rev.1 vaccine strains reveals insights into virulence attenuation[J]. Int J Med Microbiol, 2020, 310 (1): 151363.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2019.151363 |
| 69 |
MANTEROLA L , MORIYóN I , MORENO E , et al. The lipopolysaccharide of Brucella abortus BvrS/BvrR mutants contains lipid A modifications and has higher affinity for bactericidal cationic peptides[J]. J Bacteriol, 2005, 187 (16): 5631- 5639.
doi: 10.1128/JB.187.16.5631-5639.2005 |
| 70 |
FERNANDEZ-PRADA C M , NIKOLICH M , VEMULAPALLI R , et al. Deletion of wboA enhances activation of the lectin pathway of complement in Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis[J]. Infect Immun, 2001, 69 (7): 4407- 4416.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4407-4416.2001 |
| 71 |
KIM S , WATARAI M , SUZUKI H , et al. Lipid raft microdomains mediate class A scavenger receptor-dependent infection of Brucella abortus[J]. Microb Pathog, 2004, 37 (1): 11- 19.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2004.04.002 |
| 72 |
ZHANG M , HAN X , LIU H , et al. Inactivation of the ABC transporter ATPase gene in Brucella abortus strain 2308 attenuated the virulence of the bacteria[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2013, 164 (3-4): 322- 329.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.02.017 |
| 73 |
PEI J , TURSE J E , FICHT T A . Evidence of Brucella abortus OPS dictating uptake and restricting NF-kappaB activation in murine macrophages[J]. Microbes Infect, 2008, 10 (6): 582- 590.
doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2008.01.005 |
| 74 |
LI P , TIAN M , BAO Y , et al. Brucella rough mutant induce macrophage death via activating IRE1α pathway of endoplasmic reticulum stress by enhanced T4SS secretion[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2017, 7, 422.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00422 |
| 75 |
刘爱军, 黄晓兵, 张传亮, 等. 布鲁氏菌与宿主天然免疫信号通路相互作用的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56 (4): 1561- 1574.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.04.009 |
|
LIU A J , HUANG X B , ZHANG C L , et al. Progress on the interactions of Brucella with host innate immunity signaling pathways[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56 (4): 1561- 1574.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.04.009 |
|
| 76 |
EISENSCHENK F C , HOULE J J , HOFFMANN E M . Mechanism of serum resistance among Brucella abortus isolates[J]. Vet Microbiol, 1999, 68 (3-4): 235- 244.
doi: 10.1016/S0378-1135(99)00075-9 |
| 77 | HAJIZADEH SISAKHT B , KHALEDI M , AFKHAMI H , et al. Bactericidal activity of serum by Brucella Abortus RB51 outer membrane protein's combined by Brucella Abortus S99 lipopolysaccharide induction[J]. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol, 2024, 16 (3): 187- 192. |
| 78 |
BARQUERO-CALVO E , CHAVES-OLARTE E , WEISS D S , et al. Brucella abortus uses a stealthy strategy to avoid activation of the innate immune system during the onset of infection[J]. PLoS One, 2007, 2 (7): e631.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000631 |
| 79 | 尤留超, 尹号, 陶政宇, 等. 布鲁氏菌毒力因子与胞内存活机制研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56 (4): 1575- 1593. |
| YOU L C , YIN H , TAO Z Y , et al. Research progress in the virulence factors and intracellular survival mechanism of Brucella[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56 (4): 1575- 1593. | |
| 80 |
CAMPOS M A , ROSINHA G M , ALMEIDA I C , et al. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 in induction of cell-mediated immunity and resistance to Brucella abortus infection in mice[J]. Infect Immun, 2004, 72 (1): 176- 186.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.1.176-186.2004 |
| 81 |
SCHMIDINGER B , PETRI K , LETTL C , et al. Helicobacter pylori binds human annexins via lipopolysaccharide to interfere with Toll-like receptor 4 signaling[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2022, 18 (2): e1010326.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010326 |
| 82 |
DUEÑAS A I , ORDUÑA A , CRESPO M S , et al. Interaction of endotoxins with Toll-like receptor 4 correlates with their endotoxic potential and may explain the proinflammatory effect of Brucella spp. LPS[J]. Int Immunol, 2004, 16 (10): 1467- 1475.
doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh148 |
| 83 |
BARQUERO-CALVO E , MORA-CARTíN R , ARCE-GORVEL V , et al. Brucella abortus induces the premature death of human neutrophils through the action of its lipopolysaccharide[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2015, 11 (5): e1004853.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004853 |
| 84 |
LI Z , ZHANG H , ZHANG J , et al. Brucella abortus phosphoglyceromutase and dihydrodipicolinate reductase induce Th1 and Th2-related immune responses[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2018, 34 (2): 22.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-017-2405-4 |
| 85 |
CLOECKAERT A , WEYNANTS V , GODFROID J , et al. O-polysaccharide epitopic heterogeneity at the surface of Brucella spp. studied by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and flow cytometry[J]. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol, 1998, 5 (6): 862- 870.
doi: 10.1128/CDLI.5.6.862-870.1998 |
| 86 |
SURENDRAN N , HILTBOLD E M , HEID B , et al. Role of TLRs in Brucella mediated murine DC activation in vitro and clearance of pulmonary infection in vivo[J]. Vaccine, 2012, 30 (8): 1502- 1512.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.12.036 |
| 87 |
LI X , HE Y . Caspase-2-dependent dendritic cell death, maturation, and priming of T cells in response to Brucella abortus infection[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7 (8): e43512.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043512 |
| 88 |
BARRIONUEVO P , CASSATARO J , DELPINO M V , et al. Brucella abortus inhibits major histocompatibility complex class Ⅱ expression and antigen processing through interleukin-6 secretion via Toll-like receptor 2[J]. Infect Immun, 2008, 76 (1): 250- 262.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.00949-07 |
| 89 |
STRANAHAN L W , ARENAS-GAMBOA A M . When the going gets rough: The significance of Brucella lipopolysaccharide phenotype in host-pathogen interactions[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12, 713157.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.713157 |
| 90 |
IM Y B , PARK W B , JUNG M , et al. Evaluation of Th1/Th2-related immune response against recombinant proteins of Brucella abortus infection in mice[J]. J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2016, 26 (6): 1132- 1139.
doi: 10.4014/jmb.1512.12046 |
| 91 |
SWEENEY R P , LOWARY T L . New insights into lipopolysaccharide assembly and export[J]. Curr Opin Chem Biol, 2019, 53, 37- 43.
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2019.07.004 |
| [1] | 严文岚, 冯宇, 薛天骐, 张子豪, 那仁毕力格, 蒋卉. 野生动物布鲁氏菌病流行现状与分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4253-4266. |
| [2] | 王聪亮, 万仕成, 陈文博, 李剑南, 宋岩峰, 杜晓敏, 刘王叶, 李荣荣, 雷安民, 屈雷, 朱海鲸, 华进联. BLOC1S1基因过表达山羊的生产及生物安全评估[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4328-4340. |
| [3] | 杨文哲, 王锦浩, 赵子琛, 赵彤, 潘飞龙, 陈芳芳, 邵雯琪, 刘克祥, 赵树臣, 赵立佳. 姜黄素影响铁死亡途径缓解LPS诱导牛乳腺上皮细胞炎性反应的分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4730-4740. |
| [4] | 刘爱军, 黄晓兵, 张传亮, 张红丽. 布鲁氏菌与宿主天然免疫信号通路相互作用的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(4): 1561-1574. |
| [5] | 尤留超, 尹号, 陶政宇, 黄蓉, 付磊, 储岳峰. 布鲁氏菌毒力因子与胞内存活机制研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(4): 1575-1593. |
| [6] | 杨晓雯, 宁文晴, 周师众, 袁雅琴, 侯雪新, 丁家波. 一种羊种布鲁氏菌复方新诺明耐药株荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(3): 1465-1472. |
| [7] | 吴婷婷, 关飞虎, 郭嘉, 张璐, 朱德馨, 孙志华, 曹树珠, 徐艺玫, 张辉, 邓兴梅. 布鲁氏菌分泌蛋白BPE005缺失株的构建及其对GPR126/ADGRG6蛋白的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(10): 5104-5114. |
| [8] | 张雲龙, 王靖雷, 朱亚杰, 张明洁, 康澳, 周翔, 魏凯, 曹洪防, 李强, 王勇, 苏峰. RAA-DETECTOR布鲁氏菌核酸快速检测方法的建立及应用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(10): 5115-5124. |
| [9] | 王恒泰, 吕浪, 蒋卉, 程君生, 刘铭赫, 储岳峰, 许健, 李朋, 丁家波. 牛种布鲁氏菌MgtC蛋白在抵抗低Mg2+环境中的生物学功能研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(1): 365-377. |
| [10] | 何松, 汤德元, 曾智勇, 王彬, 黄涛, 毛茵茗, 周飘, 廖正波, 陈旭, 袁盛林, 胡雯雯, 周敏. 日本脑炎病毒免疫逃逸分子机制研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(6): 2368-2378. |
| [11] | 周琦璐, 刘金松, 吴超, 杨彩梅, 刘玉兰, 张瑞强. 单宁酸对脂多糖应激仔猪肝组织的功能、抗氧化能力和炎症应答的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(6): 2519-2529. |
| [12] | 徐朕宇, 邓肖玉, 王月丽, 孙灿, 吴澳迪, 曹剑, 易继海, 王勇, 王震, 陈创夫. 牛种布鲁氏菌A19ΔBtpA缺失株生物学特性及其免疫原性研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(5): 2135-2145. |
| [13] | 赵灿奇, 冯宇, 吕浪, 李彦军, 魏玉磊, 丁家波, 陈祥, 蒋卉. 竞争ELISA和间接ELISA方法应用于牛布鲁氏菌病净化的研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(5): 2146-2153. |
| [14] | 苏依曼, 叶嘉莉, 邱文粤, 章心婷, 庞晓玥, 王荣梅, 唐兆新, 苏荣胜. 积雪草酸通过抑制HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB通路减轻脂多糖诱导肉鸡肾细胞焦亡[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(4): 1777-1786. |
| [15] | 章心婷, 邱文粤, 庞晓玥, 苏依曼, 叶嘉莉, 黄健佳, 周水莲, 唐兆新, 王荣梅, 苏荣胜. 积雪草酸通过抑制氧化应激和铁死亡减轻脂多糖诱导的肉鸡心肌损伤的研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(4): 1787-1799. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
