





畜牧兽医学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 2893-2905.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.06.032
赵恩浩1( ), 石红梅2, 格桑卓玛3, 索朗斯珠1,*(
), 石红梅2, 格桑卓玛3, 索朗斯珠1,*( ), 贡嘎1,*(
), 贡嘎1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-08
出版日期:2025-06-23
发布日期:2025-06-25
通讯作者:
索朗斯珠,贡嘎
E-mail:3425171673@qq.com;xzslsz@163.com;xzlzgg@163.com
作者简介:赵恩浩(2000-),男,山西临汾人,硕士生, 主要从事高原动物传染病研究,E-mail: 3425171673@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHAO Enhao1( ), SHI Hongmei2, GESANG Zhuoma3, SUOLANG Sizhu1,*(
), SHI Hongmei2, GESANG Zhuoma3, SUOLANG Sizhu1,*( ), GONG Ga1,*(
), GONG Ga1,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-08
Online:2025-06-23
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
SUOLANG Sizhu, GONG Ga
E-mail:3425171673@qq.com;xzslsz@163.com;xzlzgg@163.com
摘要:
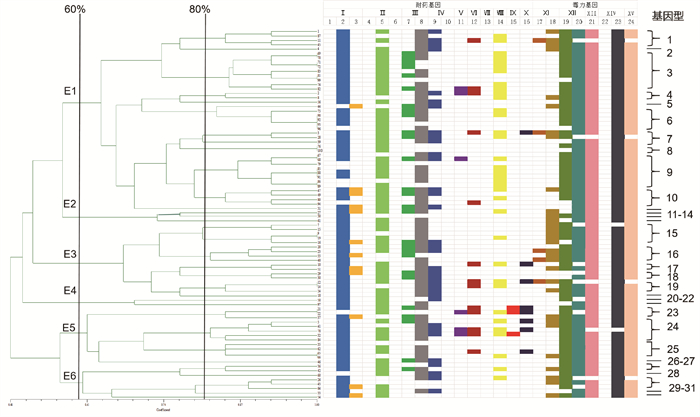
旨在了解甘肃牦牛肺炎克雷伯菌(Klebsiella pneumoniae, Kp)的流行特征、毒力基因、耐药基因、耐药表型以及遗传多样性等情况。本研究从甘肃某屠宰场采集牦牛肺样本156份,通过分离纯化、染色镜检等对肺炎克雷伯菌进行分离鉴定,运用分子生物学手段对分离株的血清型、毒力基因和耐药基因进行检测,并用纸片扩散法对分离株的耐药谱进行检测。结果显示,从156份肺组织样品中分离出84株肺炎克雷伯菌,分离率为53.85%;8种荚膜血清型均未检出,可能是分属其他血清型;毒力基因检测结果显示,菌毛合成相关基因fimH(84.52%)和mrkD(95.23%)、脂多糖相关基因uge(94.05%)、脲酶相关基因ereA(88.10%)、铁摄取系统基因ybtA(97.62%)的检出率较高,其余毒力基因检出率低或未检出;耐药基因检测结果显示,ESBLs类的blaTEM基因(85.71%)、碳青霉烯类VIM基因(79.76%)以及氨基糖苷类的acc(6’)-Ib(77.38%)的检出率较高,其余耐药基因检出率较低或未检出;药敏试验结果显示,分离株对复方新诺明(98.81%)、红霉素(97.62%)、万古霉素(95.24%)和克林霉素(94.05%)高度耐药,对其余药物均有不同程度的耐药;ERIC-PCR结果显示,相似度>60%的可分为一簇,分为E1~E6,其中E1为优势簇,占比50.00%。本研究对甘肃牦牛肺炎克雷伯菌的流行情况、毒力基因、耐药基因、耐药表型等进行了分析研究,对临床和预防的指导用药有一定的参考意义。
中图分类号:
赵恩浩, 石红梅, 格桑卓玛, 索朗斯珠, 贡嘎. 甘肃牦牛源肺炎克雷伯菌的遗传进化、毒力基因及耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(6): 2893-2905.
ZHAO Enhao, SHI Hongmei, GESANG Zhuoma, SUOLANG Sizhu, GONG Ga. Genetic Evolution, Virulence Genes, and Drug Resistance Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae from Yak in Gansu Province[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2893-2905.
表 2
K血清型引物参数"
| 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′→3′) Sequence (5′→3′) | 退火温度/℃ Tm | 长度/bp Length |
| K1 | GGTGCTCTTTACATCATTGC | 53 | 1 383 |
| GCAATGGCCATTGCGTTAG | |||
| K2 | GACCCGATATTCATACTTGACAGAG | 54 | 641 |
| CCTGAAGTAAAATCGTTAAATAGATGGC | |||
| K3 | AGGCAATTGACTTTAGGTG | 50 | 547 |
| AGTGAATCAGCCTTCACCT | |||
| K5 | TGGTAGTGATGCTCGCGA | 56 | 280 |
| CCTGAACCCACCCCAATC | |||
| K16 | GTGCTTAACGGAGAACTGAAC | 53 | 922 |
| CCTCACCTGGAAGAAGTGTA | |||
| K20 | CGGTGCTACAGTGCATCATT | 54 | 741 |
| GTTATACGATGCTCAGTCGC | |||
| K54 | CATTAGCTCAGTGGTTGGC | 55 | 881 |
| GCTTGACAAACACCATAGCAG | |||
| K57 | CTCAGGGCTAGAAGTGTCAT | 53 | 547 |
| CACTAACCCAGAAAGTCGAG |
表 3
毒力基因引物参数"
| 类别 Category | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′→3′) Sequence (5′→3′) | 退火温度/℃ Tm | 长度/bp Length |
| 荚膜多糖合成调控基因 Genes regulating capsular polysaccharide synthesis | rmpA | ACTGGGCTACCTCTGCTTCA | 52 | 535 |
| CTTGCATGAGCCATCTTTCA | ||||
| magA | GGTGCTCTTTACATCATTGC | 55 | 1 283 | |
| GCAATGGCCATTTGCGTTAG | ||||
| 菌毛合成相关基因 Genes involved in pilus biosynthesis | fimH | GCTCTGGCCGATACCACCACGG | 55 | 423 |
| GCGAAGTAACGTGCCTGGAACGG | ||||
| mrkD | ATGAAAAAACTGACGCTTTTTATTG | 58 | 963 | |
| TTAATCGTACGTCAGGTTAAAGACC | ||||
| 脲酶相关基因 Urease-related genes | ureA | GCTGACTTAAGAGAACGTTATG | 55 | 337 |
| GATCATGGCGCTACCTCA | ||||
| 脂多糖相关基因 Lipopolysaccharide-related genes | uge | GATCATCCGGTCTCCCTGTA | 55 | 534 |
| TCTTCACGCCTTCCTTCACT | ||||
| wabG | CGGACTGGCAGATCCATATC | 55 | 683 | |
| ACCATCGGCCATTTGATAGA | ||||
| 铁摄取系统 Iron ingestion system | ybtA | ATGACGGAGTCACCGCAAAC | 53 | 960 |
| TTACATCACGCGTTTAAAGG |
表 4
耐药基因引物参数"
| 类别 Category | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′→3′) Sequence (5′→3′) | 退火温度/℃ Tm | 长度/bp Length |
| 超广谱β-内酰胺酶 Extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) | blaSHV | GCCTTTATCGGCCTTCACTCAAG | 55 | 898 |
| TTAGCGTTGCCAGTGCTCGATCA | ||||
| blaTEM | CAGCGGTAAGATCCTTGAGA | 52 | 643 | |
| ACTCCCCGTCGTGTAGATAA | ||||
| blaCTX | AACCGTCACGCTGTTGTTAG | 52 | 766 | |
| TTGAGGCGTGGTGAAGTAAG | ||||
| 碳青霉烯类 Carbopenems | blaOXA | GCGTGGTTAAGGATGAACAC | 52 | 438 |
| CATCAAGTTCAACCCAACCG | ||||
| VIM | GATGGTGTTTGGTCGCATA | 52 | 390 | |
| CGAATGCGCAGCACCAG | ||||
| NDM | GGTTTGGCGATCTGGTTTTC | 55 | 621 | |
| CGGAATGGCTCATCACGATC | ||||
| 喹诺酮类 Quinolones | qnr | ATTTCTCACGCCAGGATTTG | 53 | 516 |
| GATCGGCAAAGGTTAGGTCA | ||||
| gyrA | CGCGTACTATACGCCATGAACGTA | 55 | 420 | |
| ACCGTTGATCACTTCGGTCAGG | ||||
| 氨基糖苷类 Aminoglycoside | acc(3’)-IIa | CGGAAGGCAATAACGGAG | 53 | 740 |
| TCGAACAGGTAGCACTGAG | ||||
| acc(6’)-Ib | ATGACCTTGCGATGCTCTATGA | 54 | 486 | |
| CGAATGCCTGGCGTGTTT | ||||
| 磺胺类 Sulfonamides | Sul 1 | GTGACGGTGTTCGGCATTCT | 58 | 779 |
| TCCGAGAAGGTGATTGCGCT | ||||
| 四环素类 Tetracyclines | tetB | CCTCAGCTTCTCAACGCGTG | 57 | 634 |
| GCACCTTGCTGATGACTCTT | ||||
| 酰胺醇类 Acetamine alcohols | flor | CACGTTGAGCCTCTATAT | 52 | 868 |
| ATGCAGAAGTAGAACGCG | ||||
| 头孢菌素类 Cephalosporins | blaDHA | GCCTGTTTGGTGCTCTGA | 55 | 460 |
| GCACGGTTATACGGCTGA | ||||
| 多黏菌素类 Polymyxins | mcr-1 | AGTCCGTTTGTTCTTGTGGC | 56 | 320 |
| AGATCCTTGGTCTCGGCTTG | ||||
| 大环内酯类 Macrolides | ereA | GCCGGTGCTCATGAACTTGAG | 57 | 419 |
| CGACTCTATTCGATCAGAGGC |
表 5
药敏纸片信息"
| 药物种类 Drug types | 药物名称 Drug name | 药品规格/(μg·片-1) Specifications | 抑菌圈直径判断标准/mm Criteria for determining the inhibitory diameter | ||
| 耐药Resistent | 中介Intermedia | 敏感Senstive | |||
| β-内酰胺类β-lactamase | 氨苄西林 | 10 | < 13 | 13~17 | >17 |
| 羧苄西林 | 100 | < 19 | 19~23 | >23 | |
| 哌拉西林 | 100 | < 17 | 17~21 | >21 | |
| 头孢氨苄 | 30 | < 14 | 14~18 | >18 | |
| 头孢唑林 | 30 | < 14 | 14~18 | >18 | |
| 头孢拉定 | 30 | < 14 | 14~18 | >18 | |
| 头孢呋辛 | 30 | < 14 | 14~18 | >18 | |
| 头孢他啶 | 30 | < 14 | 14~18 | >18 | |
| 头孢曲松 | 30 | < 14 | 14~23 | >23 | |
| 头孢哌酮 | 30 | < 15 | 15~21 | >21 | |
| 氨基糖苷类Aminoglycoside | 丁胺卡那 | 30 | < 14 | 14~17 | >17 |
| 庆大霉素 | 30 | < 12 | 12~15 | >15 | |
| 卡那霉素 | 10 | < 13 | 13~18 | >18 | |
| 新霉素 | 30 | < 12 | 12~17 | >17 | |
| 四环素类Tetracyclines | 四环素 | 30 | < 14 | 14~19 | >19 |
| 多西环素 | 30 | < 12 | 12~16 | >16 | |
| 米诺环素 | 30 | < 12 | 12~16 | >16 | |
| 大环内酯类Macrolides | 红霉素 | 15 | < 13 | 13~23 | >23 |
| 麦迪霉素 | 30 | < 13 | 13~18 | >18 | |
| 喹诺酮类Quinolones | 诺氟沙星 | 10 | < 12 | 12~17 | >17 |
| 氧氟沙星 | 5 | < 12 | 12~16 | >16 | |
| 环丙沙星 | 5 | < 15 | 15~21 | >21 | |
| 糖肽类Glycopeptides | 万古霉素 | 30 | < 14 | 14~17 | >17 |
| 多黏菌素b | 7.5 | < 8 | 8~12 | >12 | |
| 磺胺类Sulfonamides | 复方新诺明 | 23.75 | < 23 | 23~32 | >32 |
| 硝基咪唑类Nitroimidazole class | 呋喃唑酮 | 300 | < 14 | 14~17 | >17 |
| 酰胺醇类Acetamine alcohols | 氯霉素 | 30 | < 12 | 12~18 | >18 |
| 林可胺类Linkomide | 克林霉素 | 2 | < 14 | 14~21 | >21 |

图 7
肺炎克雷伯菌的ERIC-PCR聚类分析图 Ⅰ.超广谱β-内酰胺酶;Ⅱ.碳青霉烯类;Ⅲ.喹诺酮类;Ⅳ.氨基糖苷类;Ⅴ.磺胺类;Ⅵ.四环素类;Ⅶ.酰胺醇类;Ⅷ.头孢菌素类;Ⅸ.多黏菌素类;Ⅹ.大环内酯类;XI.荚膜多糖合成调控基因;XII.菌毛合成相关基因;XIII.脲酶相关基因;XIV.脂多糖相关基因;XV.铁摄取系统;1.blaSHV;2.blaTEM;3.blaOXA;4.blaCTX;5.VIM;6.NDM;7.qnr;8.acc(6’)-Ib;9.gyrA;10.acc(3)-IIa;11.Sul 1;12.tetB;13.flor;14.blaDHA;15.mcr-1;16.ereA;17.rmpA;18.magA;19.fimH;20.mrkD;21.uerA;22.uge;23.wabG;24.ybtA"
| 1 | 王蔚莎, 叶龙, 张妮, 等. 2012—2023年某医院耐碳青霉烯类肺炎克雷伯菌感染流行特征分析[J]. 中国消毒学杂志, 2024, 41 (6): 436-439, 443. |
| WANG W S , YE L , ZHANG N , et al. Analysis of the epidemic characteristics of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in a hospital from 2012 to 2023[J]. Chinese Journal of Disinfection, 2024, 41 (6): 436-439, 443. | |
| 2 | 李学英. 大熊猫源肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定及其部分生物学特性研究[D]. 成都: 西南民族大学, 2022. |
| LI X Y. Isolation and identification of Giant panda source Klebsiella pneumoniae and some biological characteristics[D]. Chengdu: Southwest University for Nationalities, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 3 | 陈悦, 陈景燕, 马春霞, 等. 高毒力肺炎克雷伯菌感染的研究进展[J]. 宁夏医学杂志, 2024, 46 (6): 546- 550. |
| CHEN Y , CHEN J Y , MA C X , et al. Progress in highly virulent K. pneumoniae infection[J]. Ningxia Medical Journal, 2024, 46 (6): 546- 550. | |
| 4 |
NJEUNA A , FOUNOU L L , FOUNOU R C , et al. High prevalence and genetic diversity of multidrug resistant and extended spectrum ß-lactamase producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in mothers and neonates in a Cameroonian labour ward[J]. Am J Infect Control, 2024, 52 (11): 1273- 1282.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2024.06.002 |
| 5 | MANIKANDAN P , ALOYUNI S , OTHAIM A A , et al. Prevalence and antimicrobial mechanism of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and its molecular properties[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 2024, 36 (8): 10328. |
| 6 | 田李均. 肺炎克雷伯菌的临床特征及高毒力菌株的耐药机制研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2017. |
| TIAN L J. Clinical characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae and drug resistance mechanisms of highly virulent strains[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2017. (in Chinese) | |
| 7 | 丘江, 张洁, 孙杨, 等. 多重耐药肺炎克雷伯菌62种耐药基因元件的检测与gyrA基因突变的发现[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2019, 35 (6): 539- 544. |
| QIU J , ZHANG J , SUN Y , et al. Detection of 62 drug-resistant gene elements in multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and discovery of gyrA gene mutations[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoonosis, 2019, 35 (6): 539- 544. | |
| 8 |
张凯川, 王晋宇, 李守军, 等. 广东省羊源肺炎克雷伯菌遗传进化与毒力基因及耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (1): 328- 337.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.01.030 |
|
ZHANG K C , WANG J Y , LI S J , et al. Genetic evolution and virulence genes and drug resistance analysis of sheep source Klebsiella pneumoniae in Guangdong Province[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (1): 328- 337.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.01.030 |
|
| 9 | 徐睿, 赖华敏, 欧正阳, 等. 福建省莆田地区猪源肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定及耐药情况检测[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2023 (15): 72-77, 136. |
| XU R , LAI H M , OU Z Y , et al. Isolation, identification and resistance detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Putian, Fujian Province[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2023 (15): 72-77, 136. | |
| 10 |
赵菲菲, 李杰, 韩宁, 等. 分离自屠宰场的肺炎克雷伯菌的耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (7): 3044- 3053.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.07.035 |
|
ZHAO F F , LI J , HAN N , et al. Analysis of drug resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from slaughterhouses[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (7): 3044- 3053.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.07.035 |
|
| 11 | 李花. 肝脓肿肺炎克雷伯菌血清分型及毒力基因的研究[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2018. |
| LI H. Serotyping and virulence genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae in liver abscess[D]. Shenyang: China Medical University, 2018. (in Chinese) | |
| 12 |
王佳宁, 张自强, 孔德婧, 等. 家兔肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (12): 5198- 5206.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.12.029 |
|
WANG J N , ZHANG Z Q , KONG D J , et al. Isolation and identification of K. pneumoniae in rabbits[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (12): 5198- 5206.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.12.029 |
|
| 13 | 贡嘎, 格桑卓玛, 左伟, 等. 西藏部分地区牦牛源肺炎克雷伯菌的分离、鉴定、毒力及耐药基因分析[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2021, 41 (1): 102- 109. |
| GONG G , GESANG Z M , ZUO W , et al. Isolation, identification, virulence and drug resistance gene analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae in some parts of Tibet[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 41 (1): 102- 109. | |
| 14 | 吴香云. 湖北地区奶牛乳房炎源肺炎克雷伯菌毒力和耐药分子特征研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2022. |
| WU X Y. Study on virulence and drug resistance of dairy cow mastitis source Klebsiella pneumoniae in Hubei province[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 15 | 崔琦. 奶牛乳房炎源性肺炎克雷伯菌MrkD基因原核表达以及对乳腺上皮细胞黏附的研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2021. |
| CUI Q. Prokaryotic expression of MrkD gene in Kbsiella pneumoniae and adhesion to mammary epithelial cells[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 16 | 买尔哈巴·吾斯曼. 国内部分地区奶牛乳腺炎源肺炎克雷伯菌生物学特性研究[D]. 塔里木: 塔里木大学, 2022. |
| MAIERHABA W S M. Research on the biological characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae in some areas of China[D]. Tarim: Tarim University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 17 |
张自强, 王佳佳, 任玉莹, 等. 兔源支气管败血波氏杆菌和肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定及其对抗菌药物的敏感性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2021, 52 (8): 2254- 2264.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.08.018 |
|
ZHANG Z Q , WANG J J , REN Y Y , et al. Isolation and identification of B. septicus and K. pneumoniae and its sensitivity to antimicrobial agents[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52 (8): 2254- 2264.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.08.018 |
|
| 18 | 隋明, 王静霞, 唐贤华, 等. 四川地区牦牛源肺炎克雷伯氏菌的分离鉴定及其耐药性分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2019, 46 (6): 1816- 1824. |
| SUI M , WANG J X , TANG X H , et al. Isolation and resistance analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Sichuan[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 46 (6): 1816- 1824. | |
| 19 |
王奇林, 曹润来, 王威阳, 等. 狐狸流产胎儿体内肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定及耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (8): 3640- 3648.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.08.035 |
|
WANG Q L , CAO R L , WANG W Y , et al. Isolation, identification and resistance analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae in fox ted fetuses[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (8): 3640- 3648.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.08.035 |
|
| 20 | 陈瑞格, 李赟辉, 项维, 等. 鸽源ST443肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定和生物学特性分析[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2024, 60 (5): 46- 55. |
| CHEN R G , LI Y H , XIANG W , et al. Isolation, identification and biological characterization of pigeon-derived ST443 K. pneumoniae[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 60 (5): 46- 55. | |
| 21 |
DEEKSHA S , SHILPEE P , SRIKRISHNA S , et al. Comparative genomics of an extensively drug resistant strain Klebsiella pneumoniae ⅡTR008 with international high-risk clonal lineage ST147 isolated from river water[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2024, 117 (1): 57.
doi: 10.1007/s10482-024-01955-z |
| 22 | 安舒琦. 吉林省肺炎克雷伯菌临床分离株耐药性及耐药基因研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023. |
| AN S Q. Study on drug resistance and resistance genes of K. pneumoniae clinical isolates in Jilin province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 23 | 周新新, 刘瑞杰, 孙桂芹. 肺炎克雷伯菌临床分布及耐药性分析[J]. 浙江临床医学, 2023, 25 (12): 1844- 1846. |
| ZHOU X X , LIU R J , SUN G Q . Clinical distribution and drug resistance analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae[J]. Zhejiang Clinical Medicine Journal, 2023, 25 (12): 1844- 1846. | |
| 24 |
DIMAITINO V , VENDITTI C , MESSINA F , et al. Screening of Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae strains with multi-drug resistance and virulence profiles isolated from an Italian hospital between 2020 and 2023[J]. Antibiotics (Basel), 2024, 13 (6): 561.
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13060561 |
| 25 |
QIAN J , JIN P , YANG Y , et al. Protein function annotation and virulence factor identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae genome by multiple machine learning models[J]. Microbial pathogenesis, 2024, 193, 106727.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106727 |
| 26 |
李华明, 项维, 卢文兵, 等. 1株猪源ST-35型肺炎克雷伯菌的致病性和药物敏感性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (12): 4356- 4366.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.12.021 |
|
LI H M , XIANG W , LU W B , et al. Pathogenicity and drug susceptibility analysis of one pig-derived ST-35 K. pneumoniae strain[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (12): 4356- 4366.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.12.021 |
|
| 27 | 林楠, 岳广欣, 兰小琴, 等. 中药成分对多药耐药肺炎克雷伯菌的抑菌及耐药逆转作用的体外研究[J]. 中国研究型医院, 2023, 10 (3): 23- 27. |
| LIN N , YUE G X , LAN X Q , et al. In vitro study of antibacterial and resistance reversal of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae[J]. Chinese Research Hospitals, 2023, 10 (3): 23- 27. | |
| 28 | 唐金蓉, 张碟, 李盛. 四种中药单体联合亚胺培南对耐碳青霉烯肺炎克雷伯菌体外抑菌作用研究[J]. 现代检验医学杂志, 2022, 37 (6): 162-165, 197. |
| TANG J R , ZHANG D , LI S . Study on the bacteriostatic effect of four single Chinese medicines combined with imipenem on carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in vitro[J]. Journal of Modern Laboratory Medicine, 2022, 37 (6): 162-165, 197. |
| [1] | 石金川, 孙淼, 孟令浩, 王永强, 耿超, 齐朝鲁蒙, 陈亨利, 王梓, 刘锴. 赛鸽源大肠杆菌耐药性检测及多重耐药菌株的全基因组测序分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(5): 2372-2382. |
| [2] | 廖怡雯, 叶景芬, 武绍碧, 陈世雄, 杨婉, 罗雪, 杨琦. 环介导等温扩增技术的发展及其在耐药基因检测中的应用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(4): 1621-1631. |
| [3] | 杜清洁, 吴礼平, 张帆, 戴鹏秀, 冯献程, 张欣珂. 牙周炎患犬口腔菌群差异性及卟啉单胞菌耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(2): 934-942. |
| [4] | 范维, 刘昕昕, 翟艺禄, 张新玉, 王唯, 付佳棋, 孙福亮. 羊源肺炎克雷伯菌分离鉴定及其外膜囊泡提取方法的建立[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(1): 353-364. |
| [5] | 王奇林, 曹润来, 王威阳, 张博, 刘志杰, 王晓旭. 狐狸流产胎儿体内肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定及耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(8): 3640-3648. |
| [6] | 宋艳, 袁永丰, 钱虹宇, 李鑫灿, 罗洪艳, 王芝英, 周作勇. 羊伪结核棒状杆菌的分离鉴定及部分生物学特性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(2): 680-687. |
| [7] | 吴素娟, 林昌成, 万鹏, 李杰, 陆毅兴, 胡健欣, 彭险峰, 曾振灵. 异丙氧苯胍联合黏菌素对肺炎克雷伯菌体外协同抗菌作用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(12): 5792-5801. |
| [8] | 刘鑫欢, 恽佳蕾, 毛立, 李基棕, 郝飞, 何苗锋, 杨蕾蕾, 张纹纹, 程子龙, 孙敏, 刘茂军, 王少辉, 白娟, 李文良. 羊腹泻样本中大肠杆菌的分离、毒力基因与耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(8): 3445-3454. |
| [9] | 赵菲菲, 李杰, 韩宁, 谢仕廷, 曾振灵. 分离自屠宰场的肺炎克雷伯菌的耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(7): 3044-3053. |
| [10] | 蒋增海, 滕霖, 贺安文, 刘言言, 乐敏, 何启盖. 猪产业链中鼠伤寒沙门菌及沙门菌血清型4,[5],12:i:-基因组学分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(3): 1199-1209. |
| [11] | 王佳宁, 张自强, 孔德婧, 冯彩彩, 张飞可, 刘玉梅. 家兔肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(12): 5198-5206. |
| [12] | 陶洁, 李本强, 程靖华, 石迎, 刘佩红, 刘惠莉. 肉鸽肠道微生物菌群差异分析和抗生素耐药基因预测[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(12): 5293-5300. |
| [13] | 杨梦林, 郑世奇, 彭凯, 王玮, 黄燕华, 彭杰. 鸽源鼠伤寒沙门菌的分离鉴定及致病性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(11): 4880-4888. |
| [14] | 张凯川, 王晋宇, 李守军, 贾坤. 广东省羊源肺炎克雷伯菌遗传进化与毒力基因及耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(1): 328-337. |
| [15] | 王喜, 李珂, 李廷翠, 严红亚, 赵蓉, 常志顺, 廖明, 孙敏华, 信爱国. 75株蛋鸡源沙门菌的MLST分型与耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(5): 1626-1631. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
