





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 5464-5474.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.11.010
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Liuzhe1,2( ), ZHAO Jianan1,2, ZHANG Liqiong1,2, ZHANG Yurong2, TANG Lu2, LI Junliang2,*(
), ZHAO Jianan1,2, ZHANG Liqiong1,2, ZHANG Yurong2, TANG Lu2, LI Junliang2,*( ), GUO Huihui1,*(
), GUO Huihui1,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-20
Online:2025-11-23
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
LI Junliang, GUO Huihui
E-mail:1035282238@qq.com;1018761709@qq.com;aLaddin111@163.com
CLC Number:
ZHANG Liuzhe, ZHAO Jianan, ZHANG Liqiong, ZHANG Yurong, TANG Lu, LI Junliang, GUO Huihui. Construction of XIST Gene Knockout Fibroblast Cell Line from Huaxi Cattle Using CRISPR-Cas12i Technology[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5464-5474.
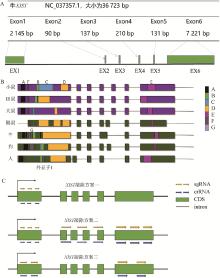
Fig. 1
XIST gene related information and gene knockout strategy A. XIST gene size and the size and location of each chromosome.B. A-F on vertical coordinate represents 7 repeat sequences of the XIST gene, the locations of repeated sequences in mice, voles, rats, moles, cattle, dogs and humans are showed in the figure, and the location of exon 1.C. Three knockout schemes of XIST gene were designed: One was the knockout of the first exon; The second is the knockout of all exons in segments; The third option is the knockout of the entire XIST gene"
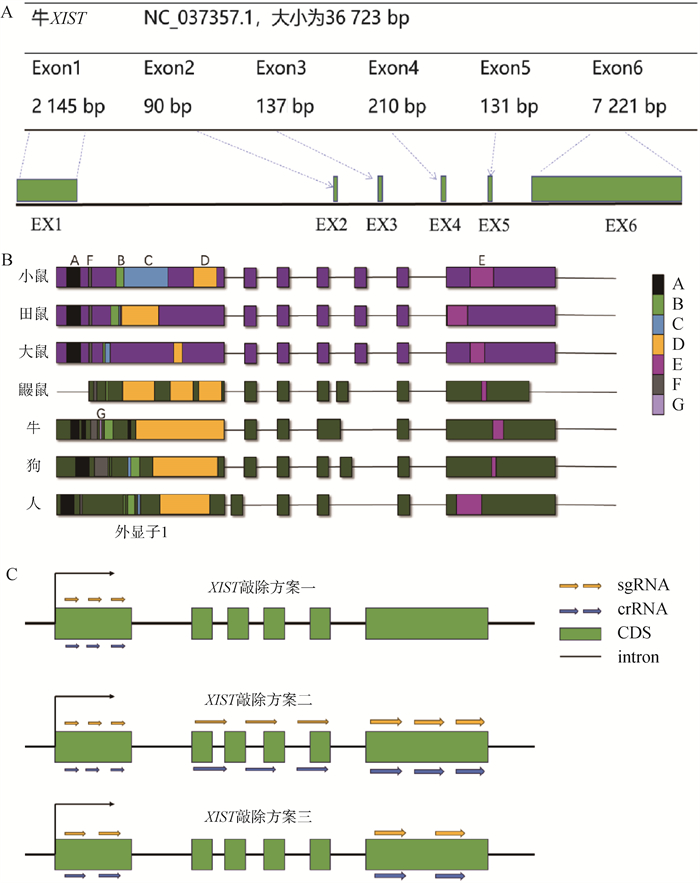
Table 1
sgRNA designed for XIST gene target sites"
| sgRNA名称 sgRNA name | sgRNA序列 sgRNA sequence | |
| 1-1 | acggTTAAAGCGCTGCACTTTGCT | aaaaAGCAAAGTGCAGCGCTTTAA |
| 1-2 | acggACAGACACGAACCCATTGAA | aaaaTTCAATGGGTTCGTGTCTGT |
| 1-3 | acggAAGTCATGGCTCCTGGACTA | aaaaTAGTCCAGGAGCCATGACTT |
| 1-4 | acggCTGGAACATTTTCCAGACCC | aaaaGGGTCTGGAAAATGTTCCAG |
| 1-5 | acggCCATACTAGTCACTTAAGGC | aaaaGCCTTAAGTGACTAGTATGG |
| 1-6 | acggCTAGTGTTCGATTTCAGCCT | aaaaAGGCTGAAATCGAACACTAG |
| 1-7 | acggCTCAAGAGGAACACCTACCC | aaaaGGGTAGGTGTTCCTCTTGAG |
| 1-8 | acggATGGGTTTTCATATTTGGGT | aaaaACCCAAATATGAAAACCCAT |
| 1-9 | acggATCTGATACCAATGCCCTTT | aaaaAAAGGGCATTGGTATCAGAT |
| 1-10 | acggTCAGGCAGGGGCTCTCATAT | aaaaATATGAGAGCCCCTGCCTGA |
| 2-1 | acggATTAAAATGGGCAGTGAGAG | aaaaCTCTCACTGCCCATTTTAAT |
| 2-2 | acggTATAGAACTTGGAGATCGTG | aaaaCACGATCTCCAAGTTCTATA |
| 2-3 | acggCTCACAGCTTGTTTCCCCCA | aaaaTGGGGGAAACAAGCTGTGAG |
| 2-4 | acggCCTCCAGTCAGTCAGACAAA | aaaaTTTGTCTGACTGACTGGAGG |
| 2-5 | acggAGAAACAAGAAGGCTCAGGA | aaaaTCCTGAGCCTTCTTGTTTCT |
| 2-6 | acggGTGTAATCCTATGAGCATTA | aaaaTAATGCTCATAGGATTACAC |
| 2-7 | acggGTGTGGGATGATGTATAGTG | aaaaCACTATACATCATCCCACA |
| 2-8 | acggACAGTTGGTTTCACTAAAGC | aaaaGCTTTAGTGAAACCAACTGT |
| 2-9 | acggGTTTCACTAAAGCAACTCAA | aaaaTTGAGTTGCTTTAGTGAAAC |
| 2-10 | acggCTTTAGTGAAACCAACTGTT | aaaaAACAGTTGGTTTCACTAAAG |
| X-3-1 | acggATGGGGGAAAAATTGTGGTA | aaaaTACCACAATTTTTCCCCCAT |
| X-3-2 | acggCAAAGATGGACATGTTTAAA | aaaaTTTAAACATGTCCATCTTTG |
| X-3-3 | acggCTAGAGTAATGGCCAGTGTA | aaaaTACACTGGCCATTACTCTAG |
| X-3-4 | acggCATTACAGGTTTATTTCCTC | aaaaGAGGAAATAAACCTGTAATG |
| X-3-5 | acggTGTGACTTCCATTACAGGTT | aaaaAACCTGTAATGGAAGTCACA |
| C-3-1 | acggAGGCACATGAGATAATATGA | aaaaTCATATTATCTCATGTGCCT |
| C-3-2 | acggCATTAATCTCACATCTCATC | aaaaGATGAGATGTGAGATTAATG |
| C-3-3 | acggGCTTCACAAATAGACAAGTC | aaaaGACTTGTCTATTTGTGAAGC |
| C-3-4 | acggCATAAGTTCAACTGACACAA | aaaaTTGTGTCAGTTGAACTTATG |
| C-3-5 | acggCCAAAAGGTTGTTCACGTGA | aaaaTCACGTGAACAACCTTTTGG |

Fig. 2
Efficiency identification and cutting efficiency of sgRNA after electrotransfection A. sgRNA efficiency after electrotransfection, dark blue represents GFP negative cells, pink represents GFP positive cells. The conversion efficiency is 43.3%. B. The sgRNA sites of the 3 knockout models, red is the PAM region, scheme one is to knockout the first exon; The second is to knockout all exons in segments; The third option is to knockout the entire XIST gene. C. The successful knockout zone and knockout efficiency statistics of each sgRNA. D. The 5 off-target sites predicted by sgRNA, namely OT1, OT2, OT3, OT4 and OT5, the knockout effect of off-target sites was verified. E. The mismatch site was verified by T7E1, and no cutting site was found"

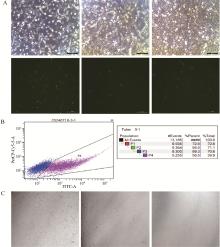
Fig. 3
Identification of electrotransfection efficiency and monoclonal cell line culture A. Expression of GFP fluorescent protein 24 h after electrotransfection, green is GFP fluorescence expression (100X). B. The efficiency of sgRNA after electrotransfection was 39.9%, with dark blue representing GFP negative cells and pink representing GFP positive cells. C. Cell status in 48-and 24-well plates of cultured monoclones (100X)"

Table 3
Monoclonal culture and identification 板·个-1"
| 华西牛XIST敲除 XIST knockout in Huaxi cattle | 96孔板数量 Number of 96-well plates | 48孔板数量 Number of 48-well plates | 24孔板数量 Number of 24-well plates | 筛选单克隆数 Monoclonal numbers | 验证成功 Successful authentication |
| 284方案一284 option one | 15 | 16 | 16 | 320 | 5 |
| 284方案二284 option two | 15 | 7 | 6 | 165 | 1 |
| 284方案三284 option three | 15 | 6 | 6 | 73 | 0 |

Fig. 4
Genotype identification and knockout efficiency of monoclonal cell lines A. M. DNA molecular weight standard; 250-500 bp white bands are homozygous knockout cell lines, marked by red arrows. The 2 000 bp white bands represent cell lines that were not successfully knocked out. B. M. DNA molecular weight standard; The first 5 DNA bands represent homozygous knockout cell lines, and the last DNA band represents heterozygous knockout cell lines. C. Sequencing of homozygous mutant cell lines, red is the knockout region, the results are consistent with PCR identification"

| 1 |
LYON M F . Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.)[J]. Nature, 1961, 190 (4773): 372- 373.
doi: 10.1038/190372a0 |
| 2 |
BROWN S D . XIST and the mapping of the X chromosome inactivation centre[J]. Bioessays, 1991, 13 (11): 607- 612.
doi: 10.1002/bies.950131112 |
| 3 |
WUTZ A , GRIBNAU J . X inactivation Xplained[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2007, 17 (5): 387- 393.
doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2007.08.001 |
| 4 |
LEE J T , BARTOLOMEI M S . X-inactivation, imprinting, and long noncoding RNAs in health and disease[J]. Cell, 2013, 152 (6): 1308- 1323.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.016 |
| 5 |
TONGE P D , NAGY A . Extinction of Xist improves cloning[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2010, 7 (5): 550- 552.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.10.003 |
| 6 |
WANG X , QU J , LI J , et al. Epigenetic reprogramming during somatic cell nuclear transfer: recent progress and future directions[J]. Front Genet, 2020, 11, 205.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00205 |
| 7 |
GAO R , WANG C , GAO Y , et al. Inhibition of aberrant DNA re-methylation improves post-implantation development of somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2018, 23 (3): 426- 435.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.07.017 |
| 8 |
LONG C R , WESTHUSIN M E , GOLDING M C . Reshaping the transcriptional frontier: epigenetics and somatic cell nuclear transfer[J]. Mol Reprod Dev, 2014, 81 (2): 183- 193.
doi: 10.1002/mrd.22271 |
| 9 |
MATOBA S , LIU Y , LU F , et al. Embryonic development following somatic cell nuclear transfer impeded by persisting histone methylation[J]. Cell, 2014, 159 (4): 884- 895.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.055 |
| 10 |
TYUMENTSEVA M , TYUMENTSEV A , AKIMKIN V . CRISPR/Cas9 landscape: Current state and future perspectives[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (22): 16075.
doi: 10.3390/ijms242216075 |
| 11 |
MCGAW C , GARRITY A J , MUNOZ G Z , et al. Engineered Cas12i2 is a versatile high-efficiency platform for therapeutic genome editing[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13 (1): 2833.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30465-7 |
| 12 | RANANAWARE S R , MEISTER K S , SHOEMAKER G M , et al. PAM-free diagnostics with diverse type Ⅴ CRISPR-Cas systems[J]. medRxiv[Preprint], 2024, 2024.05.02.24306194. |
| 13 |
BAI R , GUO W , ZHANG T , et al. Single-cut gene therapy in a one-step generated rhesus monkey model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Cell Rep Med, 2025, 6 (4): 102037.
doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102037 |
| 14 | CHEN Y , HU Y , WANG X , et al. Synergistic engineering of CRISPR-Cas nucleases enables robust mammalian genome editing[J]. Innovation (Camb), 2022, 3 (4): 100264. |
| 15 |
SWIECH L , HEIDENREICH M , BANERJEE A , et al. In vivo interrogation of gene function in the mammalian brain using CRISPR-Cas9[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2015, 33 (1): 102- 106.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.3055 |
| 16 |
GUO C , MA X , GAO F , et al. Off-target effects in CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2023, 11, 1143157.
doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1143157 |
| 17 |
LIAO H , WU J , VANDUSEN N J , et al. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated homology-directed repair for precise gene editing[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2024, 35 (4): 102344.
doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102344 |
| 18 |
YAN W X , HUNNEWELL P , ALFONSE L E , et al. Functionally diverse type Ⅴ CRISPR-Cas systems[J]. Science, 2019, 363 (6422): 88- 91.
doi: 10.1126/science.aav7271 |
| 19 |
REN J , HAI T , CHEN Y , et al. Improve meat production and virus resistance by simultaneously editing multiple genes in livestock using Cas12i[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2024, 67 (3): 555- 564.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-023-2407-0 |
| 20 |
LEE K , UH K , FARRELL K . Current progress of genome editing in livestock[J]. Theriogenology, 2020, 150, 229- 235.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.01.036 |
| 21 |
BOGLIOTTI Y S , WU J , VILARINO M , et al. Efficient derivation of stable primed pluripotent embryonic stem cells from bovine blastocysts[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018, 115 (9): 2090- 2095.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716161115 |
| 22 |
KIM D , KIM J , HUR J K , et al. Genome-wide analysis reveals specificities of Cpf1 endonucleases in human cells[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2016, 34 (8): 863- 868.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.3609 |
| 23 |
DOENCH J G , FUSI N , SULLENDER M , et al. Optimized sgRNA design to maximize activity and minimize off-target effects of CRISPR-Cas9[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2016, 34 (2): 184- 191.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.3437 |
| 24 |
ZETSCHE B , GOOTENBERG J S , ABUDAYYEH O O , et al. Cpf1 is a single RNA-guided endonuclease of a class 2 CRISPR-Cas system[J]. Cell, 2015, 163 (3): 759- 771.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.038 |
| 25 | DUAN Z , LIANG Y , SUN J , et al. An engineered Cas12i nuclease that is an efficient genome editing tool in animals and plants[J]. Innovation (Camb), 2024, 5 (2): 100564. |
| 26 |
HURET C , FERRAYÉ L , DAVID A , et al. Altered X-chromosome inactivation predisposes to autoimmunity[J]. Sci Adv, 2024, 10 (18): eadn6537.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adn6537 |
| 27 | HAUTH A , PANTEN J , KNEUSS E , et al. Escape from X inactivation is directly modulated by levels of Xist non-coding RNA[J]. bioRxiv[Preprint], 2024, 2024.02.22.581559. |
| 28 |
INOUE K , KOHDA T , SUGIMOTO M , et al. Impeding Xist expression from the active X chromosome improves mouse somatic cell nuclear transfer[J]. Science, 2010, 330 (6003): 496- 499.
doi: 10.1126/science.1194174 |
| 29 |
DONG Y , WU X , PENG X , et al. Knockdown of YY1 Inhibits XIST Expression and Enhances Cloned Pig Embryo Development[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (23): 14572.
doi: 10.3390/ijms232314572 |
| 30 |
AKSIT M A , YU B , ROELEN B A J , et al. Silencing XIST on the future active X: Searching human and bovine preimplantation embryos for the repressor[J]. Eur J Hum Genet, 2024, 32 (4): 399- 406.
doi: 10.1038/s41431-022-01115-9 |
| 31 |
YU B , VAN TOL H T A , STOUT T A E , et al. Initiation of X chromosome inactivation during bovine embryo development[J]. Cells, 2020, 9 (4): 1016.
doi: 10.3390/cells9041016 |
| 32 |
JALI I , VANAMAMALAI V K , GARG P , et al. Identification and differential expression of long non-coding RNAs and their association with XIST gene during early developmental stages of Bos taurus[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 229, 896- 908.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.221 |
| 33 |
COLAGNURI D , SUNWOO H , WANG D , et al. Xist repeats A and B account for two distinct phases of X inactivation establishment[J]. Dev Cell, 2020, 54 (1): 21- 32.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.05.021 |
| 34 |
LIANG M , ZHANG L , GONG H , et al. Deletion of Xist repeat B disrupts cell cycle and asymmetric cell division through Usp9x hyperactivation in mice[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2025, 53 (5): gkaf142.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf142 |
| 35 |
SHI Y , WANG H , CHAI M , et al. The analysis of X chromosome activity of porcine embryonic stem cells: Study based on parthenogenetic embryonic stem cells with LCDM medium[J]. Theriogenology, 2025, 244, 117479.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2025.117479 |
| 36 | LI Z , SHI J , LIU D , et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated biallelic knockout of IGF1R through microinjection in porcine zygotes[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8 (1): 1- 10. |
| 37 | 邹惠影. 猪XIST表达及X染色体失活规律的研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2016. |
| ZOU H Y. Study on the expression of porcine XIST and the pattern of X chromosome inactivation[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese) | |
| 38 | 余大为. 猪诱导多能干细胞及其核移植胚胎的异常表观重编程研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2015. |
| YU D W. Aberrant epigenetic reprogramming in porcine induced pluripotent stem cells and their nuclear transfer embryos[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | SUN Pinzhi, QU Yingying, ZHANG Qin, YANG Liwen, LI Yange, ZHANG Yiqingqing, ZHANG Yu, LU Hao. Correlation Analysis of the p5cr Gene in Swainsonine Biosynthesis in Metarhizium anisopliae [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4718-4729. |
| [2] | ZHANG Fan, ZENG Wei, ZHOU Ao. Advances in Gene Editing for Disease Resistance Breeding in Livestock and Poultry [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3047-3056. |
| [3] | LI Xiaohan, LI Guiping, HUO Caiyun, ZHANG Qilong, SUN Yingjian, SUN Huiling. Class II CRISPR/Cas Systems and Their Applications in Bacterial Synthetic Biology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1608-1620. |
| [4] | YUE Yibing, LI Junliang, BAO Binwu, GAO Chen, CHEN Yan, ZHU Bo, ZHANG Lupei, WANG Zezhao, GAO Huijiang, GAO Xue, HUANG Yongzhen, LI Junya. Research Progress on OMEGA Gene Editing System: Structure, Function, and Optimization Strategies [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5335-5351. |
| [5] | BAO Binwu, ZOU Huiying, LI Junliang, GAO Chen, GAO Huijiang, DU Zhenwei, ZHANG Boyu, LI Junya, GAO Xue. Research Progress in Gene Editing Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 1-14. |
| [6] | Ruiying LIANG, Jingxia SUO, Lin LIANG, Xianyong LIU, Jiabo DING, Xun SUO, Xinming TANG. Genetic Manipulation of Eimeria: Platform Development, Application, and Perspective [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3362-3373. |
| [7] | Wenwen LIU, Faming DONG, Yanzhen BI. The Development of Multi-Gene Editing Technology and Its Application in Agricultural Biological Germplasm Innovation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3267-3275. |
| [8] | ZHANG Duo, TENG Man, ZHANG Zhuo, LIU Jinling, ZHENG Luping, GE Siyu, HAN Fang, LUO Qin, CHAI Shujun, ZHAO Dong, YU Zuhua, LUO Jun. Development and Pathogenicity Analysis of a meq-gene-edited Candidate Marek's Disease Vaccine Strain Generated from a Hypervirulent MDV Variant [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5672-5683. |
| [9] | Xuefu ZHANG, Yuntong CHEN, Wenrui FAN, Zibo ZHANG, Mengmeng YU, Suyan WANG, Xiaole QI, Liuan LI, Yulong GAO. Construction of Chicken chNHE1 Gene Editing Cell Line and Analysis of Its Resistance to ALV-J Infection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5238-5246. |
| [10] | Xiuhu DING, Zhiping LIN, Fang ZHAO, Kunlin CHEN, Jifeng ZHONG, Yan ZHANG, Yundong GAO, Huixia LI, Huili WANG, Jianli ZHANG, Qiang DING. Highly Efficient BLG Knockout in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells by Using CRISPR/Cas9 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4475-4488. |
| [11] | ZHANG Chenjian, LI Yinxia, DING Qiang, LIU Weijia, WANG Huili, HE Nan, WU Jiashun, CAO Shaoxian. Efficient Preparation of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Goat SOCS2 Gene Edited Embryos [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 129-141. |
| [12] | LIU Ling, WANG Dandan, CUI Kai, MA Yuehui, JIANG Lin. Advances of Disease-Resistant Breeding on Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(2): 434-442. |
| [13] | ZHANG Shuo, ZHOU Yuxiao, WU Haibo, SUO Lun. Dynamics of Gene Editing Consequence Mediated by Long-term CRISPR/Cas9 System [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4196-4208. |
| [14] | ZOU Huiying, LI Junliang, ZHU Huabin. Progress on Research and Application of Prime Editing System [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(11): 3721-3730. |
| [15] | LUO Jun, LIU Jinling, ZHENG Luping, LUO Qin, TENG Man. Recent Advances in Engineering Avian Herpesviruses by CRISPR/Cas9-based Gene Editing Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(10): 3335-3344. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||