





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (9): 4294-4302.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.09.014
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
PAN Yandi( ), ZHANG Tingting, FANG Rendong, PENG Lianci*(
), ZHANG Tingting, FANG Rendong, PENG Lianci*( )
)
Received:2024-11-18
Online:2025-09-23
Published:2025-09-30
Contact:
PENG Lianci
E-mail:pydi123@163.com;penglianci@swu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
PAN Yandi, ZHANG Tingting, FANG Rendong, PENG Lianci. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Host Defense Peptides against Microorganisms[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4294-4302.
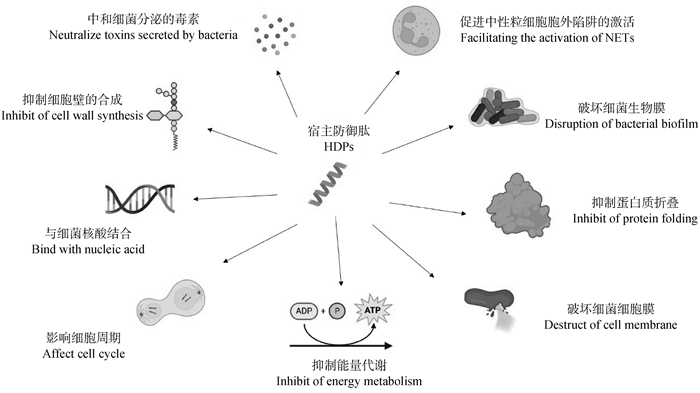
Fig. 1
Molecular mechanisms of antimicrobial activity mediated by host defense peptides The molecular mechanisms of host defense peptides against bacterial action include directly disrupting bacterial cell membrane, inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, disrupting bacterial biofilms, neutralizing bacterial toxins, affecting intracellular nucleic acid and protein synthesis, cell cycle, and energy metabolism processes, as well as forming "NETs""
| 1 |
MOOKHERJEE N , ANDERSON M A , HAAGSMAN H P , et al. Antimicrobial host defence peptides: functions and clinical potential[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2020, 19 (5): 311- 332.
doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0058-8 |
| 2 |
HUAN Y C , KONG Q , MOU H J , et al. Antimicrobial peptides: Classification, design, application and research progress in multiple fields[J]. Front Microbiol, 2020, 11, 582779.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.582779 |
| 3 | ZHANG Q Y , YAN Z B , MENG Y M , et al. Antimicrobial peptides: mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential[J]. Mil Med Res, 2021, 8 (1): 48. |
| 4 |
CARDOSO M H , DE LA FUENTE-NUNEZ C , SANTOS N C , et al. Influence of antimicrobial peptides on the bacterial membrane curvature and vice versa[J]. Trends Microbiol, 2024, 32 (7): 624- 627.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2024.04.012 |
| 5 |
XU D , LU W Y . Defensins: A double-edged sword in host immunity[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11, 764.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00764 |
| 6 |
GAO X H , DING J Q , LIAO C B , et al. Defensins: The natural peptide antibiotic[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2021, 179, 114008.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.114008 |
| 7 |
SCHLIEVERT P M , KILGORE S H , BECK L A , et al. Host cationic antimicrobial molecules inhibit S. aureus exotoxin production[J]. mSphere, 2023, 8 (1): e0057622.
doi: 10.1128/msphere.00576-22 |
| 8 | LIN Y B , SANSON M A , VEGA L A , et al. ExPortal and the LiaFSR regulatory system coordinate the response to cell membrane stress in Streptococcus pyogenes[J]. Mbio, 2020, 11 (5): e01804- 20. |
| 9 |
WANG H Y , CHEN X C , YAN Z H , et al. Human neutrophil peptide 1 promotes immune sterilization in vivo by reducing the virulence of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and increasing the ability of macrophages[J]. Biotechnol Appl Biochem, 2022, 69 (5): 2091- 2101.
doi: 10.1002/bab.2270 |
| 10 |
KLING C , SOMMER A , ALMEIDA-HERNANDEZ Y , et al. Inhibition of pertussis toxin by human α-defensins-1 and-5: differential mechanisms of action[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (13): 10557.
doi: 10.3390/ijms241310557 |
| 11 |
VARNEY K M , BONVIN A , PAZGIER M , et al. Turning defense into offense: Defensin mimetics as novel antibiotics targeting lipid Ⅱ[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2013, 9 (11): e1003732.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003732 |
| 12 |
AWANG T , CHAIRATANA P , PONGPRAYOON P . Molecular dynamics simulations of human α-defensin 5 (HD5) crossing gram-negative bacterial membrane[J]. Plos One, 2023, 18 (11): e0294041.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294041 |
| 13 |
FU J , ZONG X , JIN M L , et al. Mechanisms and regulation of defensins in host defense[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8 (1): 300.
doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01553-x |
| 14 |
CHAIRATANA P , NOLAN E M . Human α-defensin 6: A small peptide that self-assembles and protects the host by entangling microbes[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2017, 50 (4): 960- 967.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00653 |
| 15 |
AKAHOSHI D T , NATWICK D E , YUAN W R , et al. Flagella-driven motility is a target of human Paneth cell defensin activity[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2023, 19 (2): e1011200.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011200 |
| 16 |
KUDRYASHOVA E , QUINTYN R , SEVEAU S , et al. Human defensins facilitate local unfolding of thermodynamically unstable regions of bacterial protein toxins[J]. Immunity, 2014, 41 (5): 709- 721.
doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.10.018 |
| 17 |
FUSCO A , SAVIO V , PERFETTO B , et al. Antimicrobial peptide human β-defensin-2 improves in vitro cellular viability and reduces pro-inflammatory effects induced by enteroinvasive Escherichia coli in Caco-2 cells by inhibiting invasion and virulence factors' expression[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12, 1009415.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1009415 |
| 18 |
GAO X H , FENG J H , WEI L N , et al. Defensins: A novel weapon against Mycobacterium tuberculosis?[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 127, 111383.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111383 |
| 19 |
ANDRÉS M T , FIERRO P , ANTUÑA V , et al. The antimicrobial activity of human defensins at physiological non-permeabilizing concentrations is caused by the inhibition of the plasma membrane H-ATPases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (13): 7335.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25137335 |
| 20 |
HUANG C , YANG X , HUANG J , et al. Porcine beta-defensin 2 provides protection against bacterial infection by a direct bactericidal activity and alleviates inflammation via interference with the TLR4/NF-κB pathway[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10, 1673.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01673 |
| 21 |
DASH R , BHATTACHARJYA S . Thanatin: An emerging host defense antimicrobial peptide with multiple modes of action[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (4): 1522.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22041522 |
| 22 | LI B , ZHANG L , WANG L , et al. Antimicrobial activity of yak beta-defensin 116 against Staphylococcus aureus and its role in gut homeostasis[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 253 (Pt 2): 126761. |
| 23 |
HUANG W P , BALIGA C , VáZQUEZ-LASLOP N , et al. Sequence diversity of apidaecin-like peptides arresting the terminating ribosome[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2024, 52 (15): 8967- 8978.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae567 |
| 24 |
LAUER S M , REEPMEYER M , BERENDES O , et al. Multimodal binding and inhibition of bacterial ribosomes by the antimicrobial peptides Api137 and Api88[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15 (1): 3945.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48027-4 |
| 25 |
WANG Y , SONG Y C , YAN S A , et al. Antimicrobial properties and mode of action of cryptdin-4, a mouse α-defensin regulated by peptide redox structures and bacterial cultivation conditions[J]. Antibiotics (Basel), 2023, 12 (6): 1047.
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12061047 |
| 26 |
PASTUSZAK K , KOWALCZYK B , TARASIUK J , et al. Insight into the mechanism of interactions between the LL-37 peptide and model membranes of Legionella gormanii bacteria[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (15): 12039.
doi: 10.3390/ijms241512039 |
| 27 | PALUSIŃSKA-SZYSZ M , JURAK M , GISCH N , et al. The human LL-37 peptide exerts antimicrobial activity against Legionella micdadei interacting with membrane phospholipids[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids, 2022, 1867 (6): 159138. |
| 28 |
ZHANG R , XU L J , DONG C M . Antimicrobial peptides: An overview of their structure, function and mechanism of action[J]. Protein Pept Lett, 2022, 29 (8): 641- 650.
doi: 10.2174/0929866529666220613102145 |
| 29 |
LU Y , XIANG F , XU L Y , et al. The protective role of chicken cathelicidin-1 against Streptococcus suis serotype 2 in vitro and in vivo[J]. Vet Res, 2023, 54 (1): 65.
doi: 10.1186/s13567-023-01199-1 |
| 30 |
XIA R , XIAO H Z , XU M , et al. Insight into the inhibitory activity and mechanism of bovine cathelicidin BMAP 27 against Salmonella Typhimurium[J]. Microb Pathog, 2024, 187, 106540.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106540 |
| 31 |
OVERHAGE J , CAMPISANO A , HÄUSSLER S , et al. Human host defense peptide LL-37 prevents bacterial biofilm formation[J]. Infect Immun, 2008, 76 (9): 4176- 4182.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.00318-08 |
| 32 |
LIN M F , TSAI P W , CHEN J Y , et al. OmpA binding mediates the effect of antimicrobial peptide LL-37 on Acinetobacter baumannii[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10 (10): e0141107.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141107 |
| 33 |
LIN M F , LIN Y Y , LAN C Y . Characterization of biofilm production in different strains of Acinetobacter baumanni and the effects of chemical compounds on biofilm formation[J]. PeerJ, 2020, 8, e9020.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.9020 |
| 34 |
ZHANG L , WU W K K , GALLO R L , et al. Critical role of antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin for controlling Helicobacter pylori survival and infection[J]. J Immunol, 2016, 196 (4): 1799- 1809.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500021 |
| 35 |
SOUNDRARAJAN N , SOMASUNDARAM P , KIM D , et al. Effective healing of Staphylococcus aureus-infected wounds in pig cathelicidin protegrin-1-overexpressing transgenic mice[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (14): 11658.
doi: 10.3390/ijms241411658 |
| 36 |
HE Y M , RUAN S M , LIANG G Z , et al. A nonbactericidal anionic antimicrobial peptide provides prophylactic and therapeutic efficacies against bacterial infections in mice by immunomodulatory-antithrombotic duality[J]. J Med Chem, 2024, 67 (9): 7487- 7503.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00342 |
| 37 |
LU Y , TIAN H L , CHEN R Q , et al. Synergistic antimicrobial effect of antimicrobial peptides CATH-1, CATH-3, and PMAP-36 with erythromycin against bacterial pathogens[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13, 953720.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.953720 |
| 38 |
CATTEAU L , IGLESIAS Y D , TSUNEMOTO H , et al. Nafcillin augmentation of daptomycin and cathelicidin LL-37 killing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis: Foundations of successful therapy of endocarditis[J]. Int J Antimicrob Agents, 2023, 61 (6): 106758.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106758 |
| 39 |
FARZI N , OLOOMI M , BAHRAMALI G , et al. Antibacterial properties and efficacy of LL-37 fragment GF-17D3 and scolopendin A2 peptides against resistant clinical strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumannii in vitro and in vivo model studies[J]. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins, 2024, 16 (3): 796- 814.
doi: 10.1007/s12602-023-10070-w |
| 40 |
YE Z F , FU L , LI S Y , et al. Synergistic collaboration between AMPs and non-direct antimicrobial cationic peptides[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15 (1): 7319.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51730-x |
| 41 |
ZHAI Y J , FENG Y , MA X , et al. Defensins: defenders of human reproductive health[J]. Hum Reprod Update, 2023, 29 (1): 126- 154.
doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmac032 |
| 42 |
CHANG T L , VARGAS J , DELPORTILLO A , et al. Dual role of α-defensin-1 in anti-HIV-1 innate immunity[J]. J Clin Invest, 2005, 115 (3): 765- 773.
doi: 10.1172/JCI21948 |
| 43 |
MAITI B K . Potential role of peptide-based antiviral therapy against SARS-CoV-2 infection[J]. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci, 2020, 3 (4): 783- 785.
doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.0c00081 |
| 44 |
GULATI N M , MIYAGI M , WIENS M E , et al. alpha-defensin HD5 stabilizes Human Papillomavirus 16 capsid/core interactions[J]. Pathog Immun, 2019, 4 (2): 196- 234.
doi: 10.20411/pai.v4i2.314 |
| 45 | KEIKHA M , KAMALI H , GHAZVINI K , et al. Antimicrobial peptides: natural or synthetic defense peptides against HBV and HCV infections[J]. Virus Dis, 2022, 33 (4): 445- 455. |
| 46 |
ROY M , LEBEAU L , CHESSA C , et al. Comparison of anti-viral activity of frog skin anti-microbial peptides temporin-sha and K3 SHa to LL-37 and temporin-Tb against herpes simplex virus type 1[J]. Viruses, 2019, 11 (1): 77.
doi: 10.3390/v11010077 |
| 47 |
YE C , WAN C , CHEN J , et al. Cathelicidin CATH-B1 inhibits pseudorabies virus infection via direct interaction and TLR4/JNK/IRF3-mediated interferon activation[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97 (7): e0070623.
doi: 10.1128/jvi.00706-23 |
| 48 |
PENG L C , DU W J , BALHUIZEN M D , et al. Antiviral activity of chicken cathelicidin B1 against influenza A virus[J]. Front Microbiol, 2020, 11, 426.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00426 |
| 49 |
VON BECK T , NAVARRETE K , ARCE N A , et al. A wild boar cathelicidin peptide derivative inhibits severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 and its drifted variants[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13 (1): 14650.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41850-7 |
| 50 |
CHENG Y T , SUN F , LI S , et al. Inhibitory activity of a scorpion defensin BmKDfsin3 against hepatitis C virus[J]. Antibiotics (Basel), 2020, 9 (1): 33.
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9010033 |
| 51 |
WANG J , JIANG B Y , WANG K Z , et al. A cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide from Hydrophis cyanocinctus inhibits Zika virus infection by downregulating expression of a viral entry factor[J]. J Biol Chem, 2022, 298 (10): 102471.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102471 |
| 52 |
SCHROEDER B O , WU Z H , NUDING S , et al. Reduction of disulphide bonds unmasks potent antimicrobial activity of human β-defensin 1[J]. Nature, 2011, 469 (7330): 419- 423.
doi: 10.1038/nature09674 |
| 53 |
KAMLI M R , SABIR J S M , MALIK M A , et al. Human β defensins-1, an antimicrobial peptide, kills Candida glabrata by generating oxidative stress and arresting the cell cycle in G0/G1 phase[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 154, 113569.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113569 |
| 54 |
MEMARIANI H , MEMARIANI M . Antibiofilm properties of cathelicidin LL-37: an in-depth review[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2023, 39 (4): 99.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03545-z |
| 55 |
MEMARIANI M , MEMARIANI H . Antifungal properties of cathelicidin LL-37: current knowledge and future research directions[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2024, 40 (1): 34.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03852-5 |
| 56 |
JIN X , LI Q H , SUN J , et al. Porcine β-defensin-2 alleviates AFB1-induced intestinal mucosal injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2023, 262, 115161.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115161 |
| 57 |
HE H R , HUANG X Z , WEN C Y , et al. A novel defensin-like peptide C-13326 possesses protective effect against multidrug-resistant Aeromonas schubertii in hybrid snakehead (Channa maculate ♀×Channa argus ♂)[J]. J Fish Dis, 2024, 47 (4): e13922.
doi: 10.1111/jfd.13922 |
| 58 |
WILLIAMS S A , LAY F T , BINDRA G K , et al. Crocodile defensin (CpoBD13) antifungal activity via pH-dependent phospholipid targeting and membrane disruption[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14 (1): 1170.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36280-y |
| 59 |
CRAUWELS P , BANK E , WALBER B , et al. Cathelicidin contributes to the restriction of Leishmania in human host macrophages[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10, 2697.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02697 |
| 60 | NOGRADO K , ADISAKWATTANA P , REAMTONG O . Antimicrobial peptides: On future antiprotozoal and anthelminthic applications[J]. Acta Trop, 2022, 235, 11. |
| 61 |
MALUF S E , DAL MAS C , OLIVEIRA E B , et al. Inhibition of malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum development by crotamine, a cell penetrating peptide from the snake venom[J]. Peptides, 2016, 78, 11- 16.
doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2016.01.013 |
| 62 |
ULMSCHNEIDER J P , ULMSCHNEIDER M B . Melittin can permeabilize membranes via large transient pores[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15 (1): 7281.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51691-1 |
| 63 |
MEMARIANI H , MEMARIANI M . Melittin as a promising anti-protozoan peptide: current knowledge and future prospects[J]. AMB Express, 2021, 11 (1): 16.
doi: 10.1186/s13568-020-01177-2 |
| 64 |
LI T , REN X , LUO X , et al. A foundation model identifies broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptides against drug-resistant bacterial infection[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15 (1): 7538.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51933-2 |
| 65 |
WHITMORE M , TOBIN I , BURKARDT A , et al. Nutritional modulation of host defense peptide synthesis: A novel host-directed antimicrobial therapeutic strategy?[J]. Adv Nutr, 2024, 15 (9): 100277.
doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2024.100277 |
| [1] | MENG Yaxuan, LIU Yan, WANG Jing, CHEN Guoshun, FENG Tao. Effects of Glucosamine on Serum Anti-oxidation, Inflammatory Indexes and Intestinal Microbes in Weaned Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3908-3921. |
| [2] | XIONG Pingwen, XU Chuanhui, AI Gaoxiang, JI Huayuan, HU Yan, CHEN Jiang, SONG Qiongli, SONG Wenjing, CHEN Xiaolian, CHEN Xiaolian, ZOU Zhiheng, CHEN Hehong. Effects of Golden Buckwheat Stem and Leaf Meal on Nutrient Apparent Digestibility, Serum Biochemical Indices, Fecal Microflora Composition of Gannan Tibetan Sows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3290-3304. |
| [3] | ZHANG Shiqi, ZHENG Nan, WANG Jiaqi, ZHAO Shengguo. Effect of Dietary NFC/NDF Ratio on the Metabolic Flux of Microbial Urea Nitrogen in the Rumen of Dairy Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1302-1312. |
| [4] | SHEN Wenjuan, YANG Zhuo, ZHANG Xinrui, FU Yu, TAO Jinzhong. Research Progress of Microorganisms and Reproductive and Related Diseases in Dairy Cows Reproductive Tract [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 924-932. |
| [5] | ZHU Fang, LI Lulu, ZHAO Hongyi, DONG Yarong, JIANG Yuecai, LI Dengliang, ZHANG Tianliang, XIONG Nannan, CHEN Dekun, MA Wentao, ZHAO Huiying. Treatment Effects of Lactobacillus salivarius on Subclinical Mastitis in Dairy Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5706-5715. |
| [6] | LU Jian, ZHANG Xin, JIANG Dongcai, MA Meng, WANG Qiang, WANG Xingguo, LI Yongfeng, GUO Jun, DOU Taocun, HU Yuping, LI Shangmin, SHAO Dan, QU Liang. Effects of Glycine Manganese on Laying Performance and Gut Microbiota in Aged Laying Hens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 218-231. |
| [7] | FAN Dingkun, ZHANG Jixian, FU Yuze, MA Tao, BI Yanliang, ZHANG Naifeng. Research Progress of Ruminant Microbial Culturomics [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 51-58. |
| [8] | YU Shixiong, WEI Lingyun, XU Tiantian, JIAO Jinzhen, JIANG Linshu, HE Zhixiong. Research Progress of Intestinal Microbial Colonization Pattern in Young Ruminants and Its Nutritional Regulation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 2701-2707. |
| [9] | LU Mengqi, YANG Wengjie, LI Ping, YU Peng, DONG Ling, NIU Xiaoyu, YANG Keli, ZOU Weihua, SONG Hui. Changes of PRRSV Infection on Microorganisms in Lungs and Intestines of Piglets based on 16S rRNA Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(4): 1664-1678. |
| [10] | ZHOU Xuan, XIE Yue, CHEN Shun. The Interactions between Animal-parasitic Nematodes and Their Symbiotic Bacteria [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 914-923. |
| [11] | LI Zhenming, YU Miao, TANG Yantian, LI Yuanfei, LIU Zhichang, RONG Ting, MA Xianyong. Effects of Sodium Humate on Nutrient Apparent Digestibility, Fecal Microorganisms and Their Metabolites in White-feathered Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5091-5100. |
| [12] | DU Haidong, NA Renhua. Research Progress on Physiological Metabolism and Microbial Changes of Ruminants During Gestation and Lactation and Their Effects on Offspring Development [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4458-4467. |
| [13] | HU Liping, SHEN Ziliang, WANG Quan, YU Zitong, ZHANG Qiqi, MAO Yongjiang, YANG Zhangping, ZHANG Huimin. Changes of Rumen Microbe and Milk Fatty Acid Composition during Early Lactation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 3018-3028. |
| [14] | ZHANG Ruixue, LIU Xin, XU Xiaofeng, ZHANG Bo, TANG Yulin, REN Man, GUO Yansheng. Study on the Changes of Rumen Metabolites and Metabolic Pathways in Dairy Cows before and after Parturition [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(11): 3137-3148. |
| [15] | KONG Linglin, WANG Laidi, BAI Hao, JIANG Yong, WANG Zhixiu, WANG Wei, CHEN Guohong, DAI Wangcheng, CHANG Guobin. Effects of Cage Density on Production Performance and Cecal Microorganism of Xueshan Chicken [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(10): 2832-2841. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||