





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 2978-2989.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.06.040
• Clinical Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Chenlei( ), GUO Xinrui, HE Haiyang, LIU Yang, MA Baohua*(
), GUO Xinrui, HE Haiyang, LIU Yang, MA Baohua*( ), PENG Sha*(
), PENG Sha*( )
)
Received:2024-10-18
Online:2025-06-23
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
MA Baohua, PENG Sha
E-mail:2023050669@nwafu.edu.cn;mabh@nwsuaf.edu.cn;pengshacxh@nwsuaf.edu.cn
CLC Number:
WANG Chenlei, GUO Xinrui, HE Haiyang, LIU Yang, MA Baohua, PENG Sha. The Therapeutic Effect of Exosomes from Canine Adipose Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Overexpressing Klotho on Acute Kidney Injury in Canines[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2978-2989.
Table 1
Gene and primer sequence"
| 基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′→3′) Forward primers | 下游引物(5′→3′) Reverse primers |
| Canine-Keap1 | AGGTCTTCCACGCCTGTATCA | CATCACCTGCGTGGGCTTA |
| Canine-Nrf2 | CTACTCCCAGGTTCCCCACAT | GAACGGCAAGAGTCTGAGGTG |
| Klotho | CGGATATCTTATCTAGAAGCTTCGAAAT- GTGTGGAATGCGGC | TCGACGCGGCCGCTCGAGGGCTCCCGCAGCATGCTA |
| GADPH | TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC | GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
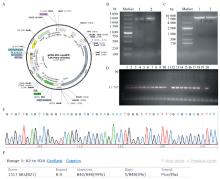
Fig. 1
Construction and identification of EF1-KL recombinant plasmid A. EF1-KL recombinant plasmid map; B. Detection of Klotho gene in PCR products by agarose gel electrophoresis; C. Detection of pCDH-EF1-copGFP-T2A-PURO vector plasmid after double enzyme digestion by agarose gel electrophoresis; D. Detection of EF1-KL recombinant plasmid in PCR product of bacterial fluid by agarose gel electrophoresis; E. EF1-KL recombinant plasmid sequencing the peak figure; F. Comparative identification of EF1-KL recombinant plasmid sequences"
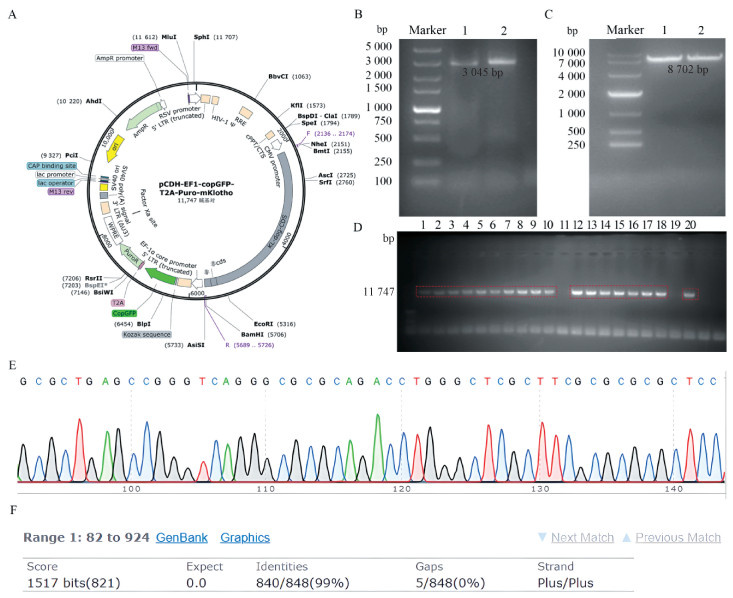

Fig. 3
Identification of Exos derived from KL-cADMSCs A. Western blot detection of exosomes marker proteins CD63 and Alix; B. Detection of KL-Exos particle size distribution using nano laser particle size analyzer; C. The shape of KL-Exos were observed under transmission electron microscope, the scale bar was 100 nm"
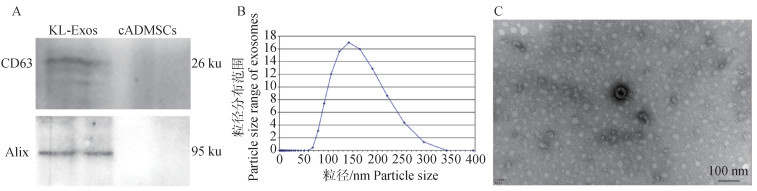
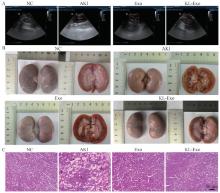
Fig. 5
Kidney B-ultrasound results, appearance, and histopathological changes in canine of different treatment groups A. B-Ultrasonography images of kidney in different treatment groups; B. Morphology of kidney in different treatment groups; C. HE staining of kidney tissue in different treatment groups, renal tubular dilation (a), necrosis and shedding of renal tubular epithelial cells (b), inflammatory cell infiltration (c), venous thrombosis (d), vacuolar degeneration (e), scale bars were all 50 μm"
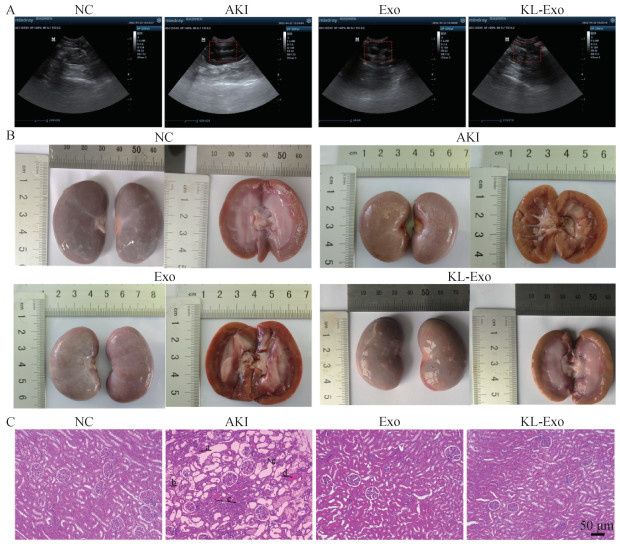
Fig. 6
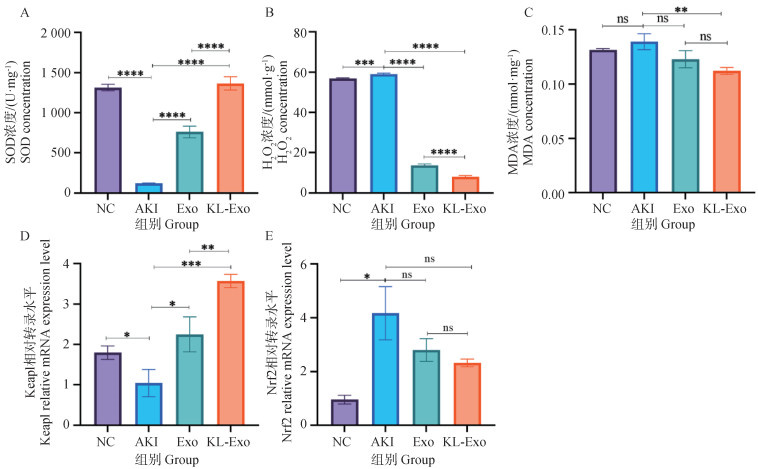
Detection of oxidative stress-related indicators and key factors in the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in the kidneys A. Content of SOD (U·mg-1); B. Content of H2O2 (mmol·g-1); C. Content of MDA (nmol·mg-1); D. Relative expression level of Keap1 mRNA; E. Relative expression level of Nrf2 mRNA. *. P < 0.05;**. P < 0.01;***. P < 0.001;****. P < 0.000 1; ns. No significant difference"
| 1 | CHEW D J, DIBARTOLA S P, SCHENCK P A. Canine and feline nephrgy and urlogy[M]. LAI Y Z, CHEN S D, Translate. Second Edition. Taipei, China: Elsevier Taiwan LLC, 2013: 63-93. |
| 2 |
LO FURNO D , MANNINO G , GIUFFRIDA R . Functional role of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of chronic neurodegenerative diseases[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233 (5): 3982- 3999.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.26192 |
| 3 |
TENCHOV R , SASSO J M , WANG X , et al. Exosomes-nature's lipid nanoparticles, a rising star in drug delivery and diagnostics[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16 (11): 17802- 17846.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c08774 |
| 4 | 杨汴蕾, 李秋柏, 陈智超. 间充质干细胞临床应用中的血栓栓塞风险及机制[J]. 临床血液学杂志, 2023, 36 (5): 378-381, 386. |
| YANG B L , LI Q B , CHEN Z C . Thromboembolic risk and mechanism in the clinical application of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Journal of Clinical Hematology, 2023, 36 (5): 378-381, 386. | |
| 5 |
刘健, 陈志伟, 王英洁, 等. 儿童造血干细胞移植后急性肾损伤相关危险因素的回顾性研究[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2022, 24 (10): 1136- 1142.
doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2205007 |
|
LIU J , CHEN Z W , WANG Y J , et al. Retrospective study on risk factors associated with acute kidney injury after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children[J]. Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics, 2022, 24 (10): 1136- 1142.
doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2205007 |
|
| 6 |
PAPADOPOULOS K S , PIPERI C , KORKOLOPOULOU P . Clinical applications of adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC) exosomes in tissue regeneration[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (11): 5916.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25115916 |
| 7 |
BUNGGULAWA E J , WANG W , YIN T Y , et al. Recent advancements in the use of exosomes as drug delivery systems[J]. J Nanobiotechnol, 2018, 16 (1): 81.
doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0403-9 |
| 8 |
GRANGE C , PAPADIMITRIOU E , DIMUCCIO V , et al. Urinary extracellular vesicles carrying Klotho improve the recovery of renal function in an acute tubular injury model[J]. Mol Ther, 2020, 28 (2): 490- 502.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.11.013 |
| 9 |
MARTIN-VIRGALA J , FERNANDEZ-VILLABRILLE S , MARTIN-CARRO B , et al. Serum and urinary soluble α-Klotho as markers of kidney and vascular impairment[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15 (6): 1470.
doi: 10.3390/nu15061470 |
| 10 |
MATTINZOLI D , MOLINARI P , ROMERO-GONZALEZ G , et al. Is there a role in acute kidney injury for FGF23 and Klotho?[J]. Clin Kidney J, 2023, 16 (10): 1555- 1562.
doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad093 |
| 11 |
李清茹, 王一帆, 陈冠廷, 等. 细胞外囊泡治疗急性肾损伤临床前研究的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27 (24): 3926- 3936.
doi: 10.12307/2023.701 |
|
LI Q R , WANG Y F , CHEN G T , et al. Meta-analysis of preclinical studies of extracellular vesicles in acute kidney injury[J]. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27 (24): 3926- 3936.
doi: 10.12307/2023.701 |
|
| 12 |
WEI Y , FANG J , CAI S , et al. Primordial germ cell-like cells derived from canine adipose mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Cell Prolif, 2016, 49 (4): 503- 511.
doi: 10.1111/cpr.12271 |
| 13 | 何文来. 脂肪间充质干细胞对犬肾损伤治疗作用探究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. |
| HE W L. Therapeutic effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on kidney injury in dogs[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 14 | 张慧敏. 犬脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体对犬皮肤损伤治疗作用探究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2023. |
| ZHANG H M. The therapeutic effect of canine adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on canine skin injury[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 15 |
ROSS L . Acute kidney injury in dogs and cats[J]. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract, 2022, 52 (3): 659- 672.
doi: 10.1016/j.cvsm.2022.01.005 |
| 16 |
CHAN M J , CHEN Y C , FAN P C , et al. Predictive value of urinary aquaporin 2 for acute kidney injury in patients with acute decompensated heart failure[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10 (3): 613.
doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030613 |
| 17 |
KHWAJA A . KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury[J]. Nephron Clin Pract, 2012, 120 (4): c179- c184.
doi: 10.1159/000339789 |
| 18 |
HE W , QIN D , LI B , et al. Immortalized canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress in mice and dogs[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2021, 136, 39- 50.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2021.02.001 |
| 19 |
WANG Y , CHEN X D , CAO W , et al. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: pathological and therapeutic implications[J]. Nat Immunol, 2014, 15 (11): 1009- 1016.
doi: 10.1038/ni.3002 |
| 20 |
YAMANAKA S . Pluripotent stem cell-based cell therapy-promise and challenges[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2020, 27 (4): 523- 531.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.09.014 |
| 21 |
TIWARI P , YADAV K , SHUKLA R P , et al. Extracellular vesicles-powered immunotherapy: unleashing the potential for safer and more effective cancer treatment[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2024, 756, 110022.
doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2024.110022 |
| 22 |
LI X , LIAO J , SU X , et al. Human urine-derived stem cells protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model via exosomal miR-146a-5p which targets IRAK1[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10 (21): 9561- 9578.
doi: 10.7150/thno.42153 |
| 23 |
ÇAM S B , ÇIFTCI E , GÜRBÜZ N , et al. Allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate human hypoxic AKI-on-a-Chip within a tight treatment window[J]. Stem Cell Res Therap, 2024, 15 (1): 105.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03674-8 |
| 24 |
CAO J Y , WANG B , TANG T T , et al. Exosomal miR-125b-5p deriving from mesenchymal stem cells promotes tubular repair by suppression of p53 in ischemic acute kidney injury[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11 (11): 5248- 5266.
doi: 10.7150/thno.54550 |
| 25 |
KOIKE M , SATO T , SHIOZAKI Y , et al. Involvement of α-klotho in growth hormone (GH) signaling[J]. J Clin Biochem Nutrit, 2024, 74 (3): 221- 229.
doi: 10.3164/jcbn.23-127 |
| 26 | GUO Y, WAN F, SHI Y P, et al. Association between renal α-klotho and renal pathology among patients with chronic kidney disease[M/OL]. Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis: Official Peer-reviewed Journal of The International Society for Apheresis, the Japanese Society for Apheresis, the Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy, 2024. |
| 27 |
MORENO J A , IZQUIERDO M C , SANCHEZ-NINO M D , et al. The inflammatory cytokines TWEAK and TNFα reduce renal klotho expression through NFκB[J]. J Am Societ Nephrol, 2011, 22 (7): 1315- 1325.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010101073 |
| 28 |
CUI W , LENG B , WANG G . Klotho protein inhibits H2O2-induced oxidative injury in endothelial cells via regulation of PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways[J]. Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 2019, 97 (5): 370- 376.
doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2018-0277 |
| 29 |
邓阳, 肖亦莎, 李昕, 等. 氨基糖苷类抗生素治疗药物监测及其毒理机制研究进展[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2019, 33 (12): 1085- 1092.
doi: 10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2019.12.010 |
|
DENG Y , XIAO Y S , LI X , et al. Progress in the monitoring of aminoglycoside antibiotics and their toxicological mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2019, 33 (12): 1085- 1092.
doi: 10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2019.12.010 |
|
| 30 | 陈梦鹿. KIM-1、NGAL在氨基糖苷类药物致肾毒性模型中的表达[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2014. |
| CHEN M L. Expression of KIM-1 and NGAL in aminoglycoside induced nephrotoxicity model[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese) | |
| 31 |
陆江, 朱道仙, 刘莉, 等. 青蒿琥酯通过Keap1/Nrf2通路抑制氧化应激改善犬急性肾损伤的体内外分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (7): 2343- 2353.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.07.031 |
|
LU J , ZHU D X , LIU L , et al. In vitro and in vivo analysis of artesunate inhibiting oxidative stress through Keap1/Nrf2 pathway to improve acute kidney injury in canines[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (7): 2343- 2353.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.07.031 |
|
| 32 |
XIAO J L , LIU H Y , SUN C C , et al. Regulation of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling in health and diseases[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2024, 51 (1): 809.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09771-4 |
| [1] | JIANG Lin, ZHANG Yaohui, LI Jing, ZHANG Xiaojing. Application of Imaging Techniques in the Diagnosis of Common Cardiac Diseases in Dogs and Cats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2103-2111. |
| [2] | ZHAO Ying, WANG Jinglei, WANG Meng, WANG Libin, ZHANG Qian, LI Zhijie, MA Xin, YU Sijiu, PAN Yangyang. Preparation and Characterization of Forsythiaside A and Kaempferol Encapsulated in Milk-derived Exosomes and Evaluation of Anti-inflammatory Effects in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2481-2495. |
| [3] | HE Haiyang, MA Baohua, PENG Sha. Research Progress on the Role and Mechanism of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Exosomes in Animal Acute Renal Injury [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 115-125. |
| [4] | Yingguang LÜ, Guangming JIAO, Jinfang SANG, Zhipeng KOU, Tao LIU, Yue WANG, Xiangyu LU, Chenxi PIAO, Yajun MA, Jiantao ZHANG, Hongbin WANG. The Effect of Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells on the Healing Process of Autologous Skin Transplantation in Bama Miniature Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3193-3204. |
| [5] | LIU Yangguang, ZHANG Huibin, WEN Haoyu, XIE Fan, ZHAO Shiming, DING Yueyun, ZHENG Xianrui, YIN Zongjun, ZHANG Xiaodong. SNP/Indel Screening Analysis of Porcine Ovarian Granulosa Cells Treated with Follicular Fluid Exosomes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 576-586. |
| [6] | LIU Xinxin, ZHOU Enyou, AN Zhiyuan, CAI Chunxia, ZHANG Lujie, LI Jianzeng, LI Zhuanjian, YAN Fengbin, KANG Xiangtao, GAO Yanling, HAN Ruili. Effects of Exosomes from Different Sources on Bone Development and Bone Diseases [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 419-426. |
| [7] | WANG Xinxin, LIN Shumei, ZHAO Dongdong, WANG Xuesheng. Role of Exosomes Secreted by Alveolar Epithelial Cells in Regulating Macrophage Polarization in Acute Lung Injury [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 71-78. |
| [8] | JIAO Guangming, LÜ Yingguang, SANG Jinfang, KOU Zhipeng, LIU Tao, WANG Yue, LU Xiangyu, PIAO Chenxi, MA Yajun, ZHANG Jiantao, WANG Hongbin. Effect of Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Combination with Methylprednisolone on Allogeneic Skin Grafts in Minipigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3533-3545. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jiabin, XU Zhao, ZHOU Guangyu, ZHANG Mengdi, FU Yang, LIU Jiaqi, ZHOU Donghai. Effects of Electroacupuncture Therapy on Renal Function, Calcium and Phosphorus Metabolism, Antioxidant Capacity and NRF2 Signaling Pathway in AKI Dogs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(2): 803-815. |
| [10] | YUAN Yue, HE Chuqiao, SHU Zongtao, SHI Chaoying, LI Xiaokun, YANG Deji, YAO Dawei. Imaging Manifestations of Multi-Sequence Scanning and Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Acute Edematous Pancreatitis in Canines [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4777-4785. |
| [11] | GUO Xinyu, WANG Haotian, ZHANG Xuemei, WANG Xiaolong, LI Heping, YANG Yanbin, ZHONG Kai. Study on the Regulation of Macrophage Polarization by Exosomes Derived from Cow Milk [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4754-4765. |
| [12] | LU Jiang, ZHU Daoxian, LIU Li, HAO Fuxing, WU Zhi, FU Hongqing. Artesunate Improves Acute Renal Injury in Dogs by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress Via Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in vitro and in vivo [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(7): 2343-2353. |
| [13] | KUANG Jingjing, HE Yanjuan, HU Qun, GU Ting, WU Zhenfang, CAI Gengyuan, HONG Linjun. Effect of TIMP2 Protein Derived from Porcine Uterine Fluid Exosomes on Embryo Implantation During Early Pregnancy [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(4): 1122-1132. |
| [14] | DING Jun, FU Zilin, HE Junhao, DUAN Xiaowei, MA Lu, BU Dengpan. Research Progress of Milk-derived Exosomes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(4): 1019-1029. |
| [15] | NI Aixin, LI Yunlei, GE Pingzhuang, WANG Panlin, Adamu Mani Isa, SHI Lei, FAN Jing, SUN Yanyan, SUN Hong, MA Hui, CHEN Jilan. Extraction and Protein Profiling of Exosomes Derived from Trichomonas gallinae in Pigeon [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(7): 1737-1747. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||