





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 1594-1607.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.04.011
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
JI Xing( ), LI Jun, WANG Ran, HE Tao*(
), LI Jun, WANG Ran, HE Tao*( )
)
Received:2024-04-16
Online:2025-04-23
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
HE Tao
E-mail:jixing@jaas.ac.cn;vethetao@163.com
CLC Number:
JI Xing, LI Jun, WANG Ran, HE Tao. Research Progress on Virulence Regulation and Antivirulence Drugs of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1594-1607.

Fig. 1
The main virulence factor regulatory system of S. aureus The three primary virulence factor regulatory systems in Staphylococcus aureus are the Two-Component Regulatory System (TCS), the AGR quorum sensing system, and the SarA family of proteins along with other auxiliary regulatory factors. These three virulence factor regulatory systems can independently or interactively (through activation/antagonism) regulate the expression of related virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus"
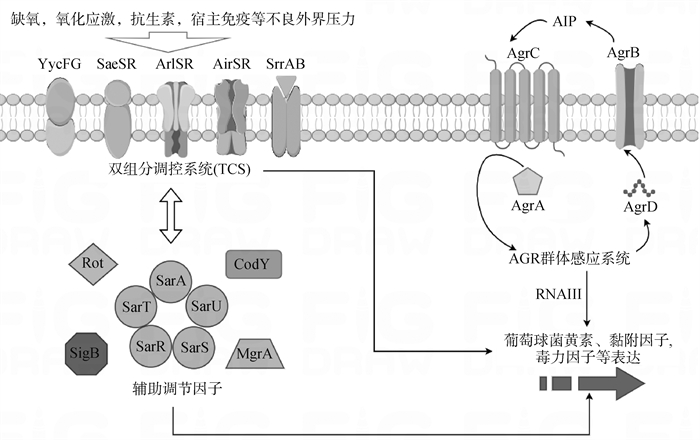
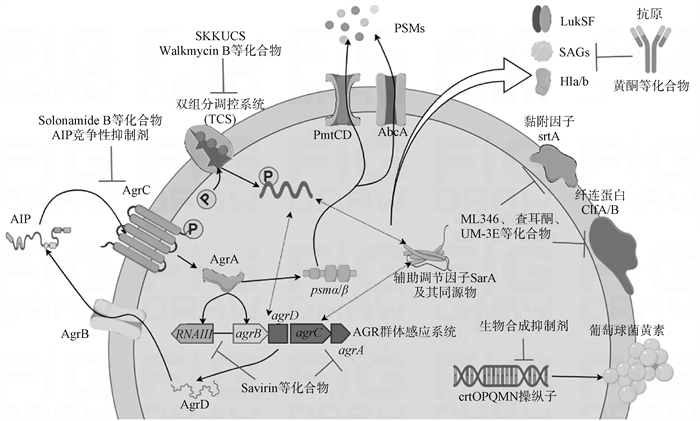
Fig. 2
S. aureus virulence regulatory network and mechanism of action of antivirulence drugs The virulence regulation of Staphylococcus aureus mainly includes the AGR quorum sensing system, the Two-Component Regulatory System (TCS), and the auxiliary regulator SarA and its homologs. These three components can form activation or inhibition regulatory networks to jointly regulate the expression of pore-forming toxins, PSMs (phenol-soluble modulins), secreted proteins, and other virulence factors. Current antitoxin drugs primarily include natural or synthetically produced compounds that can directly target pore-forming toxins, staphyloxanthin, adhesion factors, biofilms, and virulence factor regulatory systems"
| 1 | 田洪亮, 徐刘溢, 彭练慈, 等. 金黄色葡萄球菌病防治研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 2023, 63 (12): 4441- 4450. |
| TIAN H L , XU L Y , PENG L C , et al. Research progress in prevention and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2023, 63 (12): 4441- 4450. | |
| 2 |
CHEUNG G Y C , BAE J S , OTTO M . Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Virulence, 2021, 12 (1): 547- 569.
doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1878688 |
| 3 |
DEHBANIPOUR R , GHALAVAND Z . Anti-virulence therapeutic strategies against bacterial infections: recent advances[J]. Germs, 2022, 12 (2): 262- 275.
doi: 10.18683/germs.2022.1328 |
| 4 |
GOULIAN M . Two-component signaling circuit structure and properties[J]. Curr Opin Microbiol, 2010, 13 (2): 184- 189.
doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.01.009 |
| 5 | ZHENG L , YAN M , FAN F , et al. The essential walk histidine kinase and WalrK regulator differentially mediate autolysis of Staphylococcus aureus RN4220[J]. J Nat Sci, 2015, 1 (6): e111. |
| 6 |
DOBIHAL G S , BRUNET Y R , FLORES-KIM J , et al. Homeostatic control of cell wall hydrolysis by the WalRK two-component signaling pathway in Bacillus subtilis[J]. Elife, 2019, 8, e52088.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.52088 |
| 7 |
DUBRAC S , MSADEK T . Identification of genes controlled by the essential YycG/YycF two-component system of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J. Bacteriol, 2004, 186 (4): 1175- 1181.
doi: 10.1128/JB.186.4.1175-1181.2004 |
| 8 |
WU S , QIN B , DENG S , et al. CodY is modulated by YycF and affects biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13, 967567.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.967567 |
| 9 |
WU S , ZHANG J , PENG Q , et al. The role of Staphylococcus aureus YycFG in gene regulation, biofilm organization and drug resistance[J]. Antibiotics (Basel), 2021, 10 (12): 1555.
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10121555 |
| 10 |
DELAUNÉ A , DUBRAC S , BLANCHET C , et al. The WalKR system controls major staphylococcal virulence genes and is involved in triggering the host inflammatory response[J]. Infect Immun, 2012, 80 (10): 3438- 3453.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.00195-12 |
| 11 |
GIRAUDO A T , RASPANTI C G , CALZOLARI A , et al. Characterization of a Tn551-mutant of Staphylococcus aureus defective in the production of several exoproteins[J]. Can J Microbiol, 1994, 40 (8): 677- 681.
doi: 10.1139/m94-107 |
| 12 | LIU Q , YEO W , BAE T . The SaeRS two-component system of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Genes(Basel), 2016, 7 (10): 81. |
| 13 |
SUN F , LI C , JEONG D , et al. In the Staphylococcus aureus two-component system sae, the response regulator SaeR binds to a direct repeat sequence and DNA binding requires phosphorylation by the sensor kinase SaeS[J]. J Bacteriol, 2010, 192 (8): 2111- 2127.
doi: 10.1128/JB.01524-09 |
| 14 |
MAINIERO M , GOERKE C , GEIGER T , et al. Differential target gene activation by the Staphylococcus aureus two-component system saeRS[J]. J Bacteriol, 2010, 192 (3): 613- 623.
doi: 10.1128/JB.01242-09 |
| 15 |
RAMUNDO M S , BELTRAME C O , BOTELHO A M N , et al. A unique SaeS allele overrides cell-density dependent expression of saeR and lukSF-PV in the ST30-SCCmecIV lineage of CA-MRSA[J]. Int J Med Microbiol, 2016, 306 (6): 367- 380.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2016.05.001 |
| 16 |
BAROJA M L , HERFST C A , KASPER K J , et al. The SaeRS two-component system is a direct and dominant transcriptional activator of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 2016, 198 (19): 2732- 2742.
doi: 10.1128/JB.00425-16 |
| 17 |
KATO F , KADOMOTO N , IWAMOTO Y , et al. Regulatory mechanism for exfoliative toxin production in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Infect Immun, 2011, 79 (4): 1660- 1670.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.00872-10 |
| 18 |
WITTEKIND M A , BRIAUD P , SMITH J L , et al. The small protein ScrA influences Staphylococcus aureus virulence-related processes via the SaeRS system[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2023, 11 (3): e0525522.
doi: 10.1128/spectrum.05255-22 |
| 19 |
FOURNIER B , HOOPER D C . A new two-component regulatory system involved in adhesion, autolysis, and extracellular proteolytic activity of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 2000, 182 (14): 3955- 3964.
doi: 10.1128/JB.182.14.3955-3964.2000 |
| 20 |
WALKER J N , CROSBY H A , SPAULDING A R , et al. The Staphylococcus aureus ArlRS two-component system is a novel regulator of agglutination and pathogenesis[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2013, 9 (12): e1003819.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003819 |
| 21 |
RADIN J N , KELLIHER J L , PÁRRAGA SOLÓRZANO P K , et al. The two-component system ArlRS and alterations in metabolism enable Staphylococcus aureus to resist calprotectin-induced manganese starvation[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2016, 12 (11): e1006040.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006040 |
| 22 | PÁRRAGA SOLÓRZANO P K , YAO J , ROCK C O , et al. Disruption of glycolysis by nutritional immunity activates a Two-Component System that coordinates a metabolic and antihost response by Staphylococcus aureus[J]. MBio, 2019, 10 (4): e01321- 19. |
| 23 |
CROSBY H A , TIWARI N , KWIECINSKI J M , et al. The Staphylococcus aureus ArlRS two-component system regulates virulence factor expression through MgrA[J]. Mol Microbiol, 2020, 113 (1): 103- 122.
doi: 10.1111/mmi.14404 |
| 24 |
CROSBY H A , SCHLIEVERT P M , MERRIMAN J A , et al. The Staphylococcus aureus global regulator MgrA modulates clumping and virulence by controlling surface protein expression[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2016, 12 (5): e1005604.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005604 |
| 25 |
SUN F , JI Q , JONES M B , et al. AirSR, a[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134 (1): 305- 314.
doi: 10.1021/ja2071835 |
| 26 | HALL J W , YANG J , GUO H , et al. The AirSR two-component system contributes to Staphylococcus aureus survival in human blood and transcriptionally regulates sspABC operon[J]. Front Microbiol, 2015, 6, 682. |
| 27 |
SUN H , YANG Y , XUE T , et al. Modulation of cell wall synthesis and susceptibility to vancomycin by the two-component system AirSR in Staphylococcus aureus NCTC8325[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2013, 13, 286.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-286 |
| 28 | HALL J W , YANG J , GUO H , et al. The Staphylococcus aureus AirSR two-component system mediates reactive oxygen species resistance via transcriptional regulation of Staphyloxanthin production[J]. Infect Immun, 2017, 85 (2): e00838- 16. |
| 29 |
TIWARI N , LÓPEZ-REDONDO M , MIGUEL-ROMERO L , et al. The SrrAB two-component system regulates Staphylococcus aureus pathogenicity through redox sensitive cysteines[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2020, 117 (20): 10989- 10999.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1921307117 |
| 30 |
THROUP J P , ZAPPACOSTA F , LUNSFORD R D , et al. The srhSR gene pair from Staphylococcus aureus: genomic and proteomic approaches to the identification and characterization of gene function[J]. Biochemistry, 2001, 40 (34): 10392- 10401.
doi: 10.1021/bi0102959 |
| 31 |
YARWOOD J M , MCCORMICK J K , SCHLIEVERT P M . Identification of a novel two-component regulatory system that acts in global regulation of virulence factors of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 2001, 183 (4): 1113- 1123.
doi: 10.1128/JB.183.4.1113-1123.2001 |
| 32 |
WHITE M J , BOYD J M , HORSWILL A R , et al. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C contributes to survival of Staphylococcus aureus USA300 in human blood and neutrophils[J]. Infect Immun, 2014, 82 (4): 1559- 1571.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.01168-13 |
| 33 |
BLEUL L , FRANCOIS P , WOLZ C . Two-Component systems of S. aureus: signaling and sensing mechanisms[J]. Genes (Basel), 2021, 13 (1): 34.
doi: 10.3390/genes13010034 |
| 34 | LE K Y , OTTO M . Quorum-sensing regulation in staphylococci-an overview[J]. Front Microbiol, 2015, 6, 1174. |
| 35 | JENUL C , HORSWILL A R . Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus virulence[J]. Microbiol. Spectr, 2019, 7 (2) |
| 36 |
VINODHINI V , KAVITHA M . Deciphering agr quorum sensing in Staphylococcus aureus: insights and therapeutic prospects[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2024, 51 (1): 155.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08930-3 |
| 37 |
BALABAN N , GOLDKORN T , GOV Y , et al. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis via target of RNAIII-activating Protein (TRAP)[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276 (4): 2658- 2667.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005446200 |
| 38 |
BOISSET S , GEISSMANN T , HUNTZINGER E , et al. Staphylococcus aureus RNAIII coordinately represses the synthesis of virulence factors and the transcription regulator Rot by an antisense mechanism[J]. Genes Dev, 2007, 21 (11): 1353- 1366.
doi: 10.1101/gad.423507 |
| 39 |
LE HUYEN K B , GONZALEZ C D , PASCREAU G , et al. A small regulatory RNA alters Staphylococcus aureus virulence by titrating RNAIII activity[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49 (18): 10644- 10656.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab782 |
| 40 | WILLIAMS P , HILL P , BONEV B , et al. Quorum-sensing, intra-and inter-species competition in the staphylococci[J]. Microbiology (Reading), 2023, 169 (8): 001381. |
| 41 |
CHEUNG G Y C , JOO H , CHATTERJEE S S , et al. Phenol-soluble modulins--critical determinants of staphylococcal virulence[J]. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 2014, 38 (4): 698- 719.
doi: 10.1111/1574-6976.12057 |
| 42 |
CHEUNG A L , NISHINA K A , TROTONDA M P , et al. The SarA protein family of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2008, 40 (3): 355- 361.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.10.032 |
| 43 |
MANNA A C , BAYER M G , CHEUNG A L . Transcriptional analysis of different promoters in the sar locus in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 1998, 180 (15): 3828- 3836.
doi: 10.1128/JB.180.15.3828-3836.1998 |
| 44 |
CHAN P F , FOSTER S J . Role of SarA in virulence determinant production and environmental signal transduction in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 1998, 180 (23): 6232- 6241.
doi: 10.1128/JB.180.23.6232-6241.1998 |
| 45 |
STERBA K M , MACKINTOSH S G , BLEVINS J S , et al. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus SarA binding sites[J]. J Bacteriol, 2003, 185 (15): 4410- 4417.
doi: 10.1128/JB.185.15.4410-4417.2003 |
| 46 |
LOUGHRAN A J , ATWOOD D N , ANTHONY A C , et al. Impact of individual extracellular proteases on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation in diverse clinical isolates and their isogenic sarA mutants[J]. Microbiologyopen, 2014, 3 (6): 897- 909.
doi: 10.1002/mbo3.214 |
| 47 |
ANDREY D O , RENZONI A , MONOD A , et al. Control of the Staphylococcus aureus toxic shock tst promoter by the global regulator SarA[J]. J Bacteriol, 2010, 192 (22): 6077- 6085.
doi: 10.1128/JB.00146-10 |
| 48 | ORIOL C , CENGHER L , MANNA A C , et al. Expanding the Staphylococcus aureus SarA regulon to small RNAs[J]. MSystems, 2021, 6 (5): e0071321. |
| 49 |
MANNA A , CHEUNG A L . Characterization of sarR, a modulator of sar expression in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Infect Immun, 2001, 69 (2): 885- 896.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.2.885-896.2001 |
| 50 |
REYES D , ANDREY D O , MONOD A , et al. Coordinated regulation by AgrA, SarA, and SarR to control agr expression in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 2011, 193 (21): 6020- 6031.
doi: 10.1128/JB.05436-11 |
| 51 |
MANNA A C , CHEUNG A L . SarU, a SarA homolog, is repressed by SarT and regulates virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Infect Immun, 2003, 71 (1): 343- 353.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.1.343-353.2003 |
| 52 |
SCHMIDT K A , MANNA A C , GILL S , et al. SarT, a repressor of alpha-hemolysin in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Infect Immun, 2001, 69 (8): 4749- 4758.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.8.4749-4758.2001 |
| 53 |
XUE T , ZHANG X , SUN H , et al. ArtR, a novel sRNA of Staphylococcus aureus, regulates α-toxin expression by targeting the 5' UTR of sarT mRNA[J]. Med Microbiol Immunol, 2014, 203 (1): 1- 12.
doi: 10.1007/s00430-013-0307-0 |
| 54 |
TEGMARK K , KARLSSON A , ARVIDSON S . Identification and characterization of SarH1, a new global regulator of virulence gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Mol Microbiol, 2000, 37 (2): 398- 409.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02003.x |
| 55 |
SCHMIDT K A , MANNA A C , CHEUNG A L . SarT influences SarS expression in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Infect Immun, 2003, 71 (9): 5139- 5148.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5139-5148.2003 |
| 56 |
ANDERSON E E , DYZENHAUS S , ILMAIN J K , et al. SarS is a repressor of Staphylococcus aureus bicomponent pore-forming Leukocidins[J]. Infect Immun, 2023, 91 (4): e0053222.
doi: 10.1128/iai.00532-22 |
| 57 |
MCNAMARA P J , MILLIGAN-MONROE K C , KHALILI S , et al. Identification, cloning, and initial characterization of rot, a locus encoding a regulator of virulence factor expression in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 2000, 182 (11): 3197- 3203.
doi: 10.1128/JB.182.11.3197-3203.2000 |
| 58 |
TSENG C W , STEWART G C . Rot repression of enterotoxin B expression in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 2005, 187 (15): 5301- 5309.
doi: 10.1128/JB.187.15.5301-5309.2005 |
| 59 |
SAÏD-SALIM B , DUNMAN P M , MCALEESE F M , et al. Global regulation of Staphylococcus aureus genes by Rot[J]. J Bacteriol, 2003, 185 (2): 610- 619.
doi: 10.1128/JB.185.2.610-619.2003 |
| 60 | MANNA A C , RAY B . Regulation and characterization of rot transcription in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Microbiology (Reading), 2007, 153 (Pt 5): 1538- 1545. |
| 61 |
BENSON M A , LILO S , NYGAARD T , et al. Rot and SaeRS cooperate to activate expression of the staphylococcal superantigen-like exoproteins[J]. J Bacteriol, 2012, 194 (16): 4355- 4365.
doi: 10.1128/JB.00706-12 |
| 62 |
LUONG T T , DUNMAN P M , MURPHY E , et al. Transcription profiling of the MgrA regulon in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 2006, 188 (5): 1899- 1910.
doi: 10.1128/JB.188.5.1899-1910.2006 |
| 63 |
GUPTA R K , LUONG T T , LEE C Y . RNAIII of the Staphylococcus aureus agr system activates global regulator MgrA by stabilizing mRNA[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2015, 112 (45): 14036- 14041.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1509251112 |
| 64 |
POHL K , FRANCOIS P , STENZ L , et al. CodY in Staphylococcus aureus: a regulatory link between metabolism and virulence gene expression[J]. J Bacteriol, 2009, 191 (9): 2953- 2963.
doi: 10.1128/JB.01492-08 |
| 65 |
ROUX A , TODD D A , VELÁZQUEZ J V , et al. CodY-mediated regulation of the Staphylococcus aureus Agr system integrates nutritional and population density signals[J]. J Bacteriol, 2014, 196 (6): 1184- 1196.
doi: 10.1128/JB.00128-13 |
| 66 |
IBBERSON C B , JONES C L , SINGH S , et al. Staphylococcus aureus hyaluronidase is a CodY-regulated virulence factor[J]. Infect Immun, 2014, 82 (10): 4253- 4264.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.01710-14 |
| 67 |
MONTGOMERY C P , BOYLE-VAVRA S , ROUX A , et al. CodY deletion enhances in vivo virulence of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clone USA300[J]. Infect Immun, 2012, 80 (7): 2382- 2389.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.06172-11 |
| 68 |
MAJERCZYK C D , DUNMAN P M , LUONG T T , et al. Direct targets of CodY in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 2010, 192 (11): 2861- 2877.
doi: 10.1128/JB.00220-10 |
| 69 |
BISCHOFF M , ENTENZA J M , GIACHINO P . Influence of a functional sigB operon on the global regulators sar and agr in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 2001, 183 (17): 5171- 5179.
doi: 10.1128/JB.183.17.5171-5179.2001 |
| 70 |
SENN M M , GIACHINO P , HOMEROVA D , et al. Molecular analysis and organization of the sigmaB operon in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Bacteriol, 2005, 187 (23): 8006- 8019.
doi: 10.1128/JB.187.23.8006-8019.2005 |
| 71 |
GULDIMANN C , BOOR K J , WIEDMANN M , et al. Resilience in the face of uncertainty: Sigma factor B fine-tunes gene expression to support homeostasis in Gram-Positive bacteria[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2016, 82 (15): 4456- 4469.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00714-16 |
| 72 |
ENTENZA J , MOREILLON P , SENN M M , et al. Role of sigmaB in the expression of Staphylococcus aureus cell wall adhesins ClfA and FnbA and contribution to infectivity in a rat model of experimental endocarditis[J]. Infect Immun, 2005, 73 (2): 990- 998.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.2.990-998.2005 |
| 73 |
ANDREY D O , JOUSSELIN A , VILLANUEVA M , et al. Impact of the regulators SigB, Rot, SarA and sarS on the toxic shock tst promoter and TSST-1 expression in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10 (8): e0135579.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135579 |
| 74 |
KUSCH K , HANKE K , HOLTFRETER S , et al. The influence of SaeRS and σ(B) on the expression of superantigens in different Staphylococcus aureus isolates[J]. Int J Med Microbiol, 2011, 301 (6): 488- 499.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2011.01.003 |
| 75 |
AHMAD-MANSOUR N , LOUBET P , POUGET C , et al. Staphylococcus aureus toxins: An update on their pathogenic properties and potential treatments[J]. Toxins, 2021, 13 (10): 677.
doi: 10.3390/toxins13100677 |
| 76 |
KONG C , NEOH H , NATHAN S . Targeting Staphylococcus aureus toxins: A potential form of anti-virulence therapy[J]. Toxins, 2016, 8 (3): 72.
doi: 10.3390/toxins8030072 |
| 77 | MAGYARICS Z , LESLIE F , BARTKO J , et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-ascending-dose study of the penetration of a monoclonal antibody combination (ASN100) targeting Staphylococcus aureus cytotoxins in the lung epithelial lining fluid of healthy volunteers[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2019, 63 (8): e00350- 19. |
| 78 |
LAVENTIE B , RADEMAKER H J , SALEH M , et al. Heavy chain-only antibodies and tetravalent bispecific antibody neutralizing Staphylococcus aureus leukotoxins[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011, 108 (39): 16404- 16409.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102265108 |
| 79 |
CARDOT-MARTIN E , CASALEGNO J S , BADIOU C , et al. α-Defensins partially protect human neutrophils against Panton-Valentine leukocidin produced by Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Lett Appl Microbiol, 2015, 61 (2): 158- 164.
doi: 10.1111/lam.12438 |
| 80 |
DROZDOWSKI B , ZHOU Y , KLINE B , et al. Generation and characterization of high affinity human monoclonal antibodies that neutralize staphylococcal enterotoxin B[J]. J Immune Based Ther Vaccines, 2010, 8, 9.
doi: 10.1186/1476-8518-8-9 |
| 81 |
VARSHNEY A K , WANG X , SCHARFF M D , et al. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B-specific monoclonal antibody 20B1 successfully treats diverse Staphylococcus aureus infections[J]. J Infect Dis, 2013, 208 (12): 2058- 2066.
doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit421 |
| 82 |
YANG X , BUONPANE R A , MOZA B , et al. Neutralization of multiple staphylococcal superantigens by a single-chain protein consisting of affinity-matured, variable domain repeats[J]. J Infect Dis, 2008, 198 (3): 344- 348.
doi: 10.1086/589776 |
| 83 | FENG J , SUN D , WANG L , et al. Biochanin a as an α-hemolysin inhibitor for combating methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2021, 38 (1): 6. |
| 84 |
REN X , GUO X , LIU C , et al. Natural flavone hispidulin protects mice from Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia by inhibition of α-hemolysin production via targeting AgrA(C)[J]. Microbiol Res, 2022, 261, 127071.
doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127071 |
| 85 |
AKSOY C S , AVCI F G , UGUREL O M , et al. Potentiating the activity of berberine for Staphylococcus aureus in a combinatorial treatment with thymol[J]. Microb Pathog, 2020, 149, 104542.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104542 |
| 86 |
ZHANG M , LI H , AGYEKUMWAA A K , et al. Effects of citronellal on growth and enterotoxins production in Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213[J]. Toxicon, 2022, 213, 92- 98.
doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2022.04.016 |
| 87 |
ELMESSERI R A , SALEH S E , ELSHERIF H M , et al. Staphyloxanthin as a potential novel target for deciphering promising anti-Staphylococcus aureus agents[J]. Antibiotics (Basel), 2022, 11 (3): 298.
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11030298 |
| 88 |
LIN F , LIU C , LIU Y , et al. Mechanism of action and inhibition of dehydrosqualene synthase[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010, 107 (50): 21337- 21342.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010907107 |
| 89 |
CHEN F , DI H , WANG Y , et al. Small-molecule targeting of a diapophytoene desaturase inhibits S. aureus virulence[J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2016, 12 (3): 174- 179.
doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2003 |
| 90 | GAO P , DAVIES J , KAO R Y T . Dehydrosqualene desaturase as a novel target for anti-virulence therapy against Staphylococcus aureus[J]. MBio, 2017, 8 (5): e01224- 17. |
| 91 |
RAO L , XU Y , SHEN L , et al. Small-molecule compound SYG-180-2-2 attenuates Staphylococcus aureus virulence by inhibiting hemolysin and staphyloxanthin production[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12, 1008289.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1008289 |
| 92 |
ELMESSERI R A , SALEH S E , GHOBISH S A , et al. Diclofenac and meloxicam exhibited anti-virulence activities targeting Staphyloxanthin production in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Antibiotics (Basel), 2023, 12 (2): 277.
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020277 |
| 93 |
TON-THAT H , MAZMANIAN S K , FAULL K F , et al. Anchoring of surface proteins to the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus. Sortase catalyzed in vitro transpeptidation reaction using LPXTG peptide and NH(2)-Gly(3) substrates[J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275 (13): 9876- 9881.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.13.9876 |
| 94 |
YUE C , YUAN Z , XU G , et al. Structure-guided design, synthesis, and antivirulence assessment of covalent Staphylococcus aureus ortase a inhibitors[J]. J Med Chem, 2024, 67 (2): 1127- 1146.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01615 |
| 95 |
YANG T , ZHANG T , GUAN X , et al. Tideglusib and its analogues as inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus SrtA[J]. J Med Chem, 2020, 63 (15): 8442- 8457.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00803 |
| 96 |
SONG W , WANG L , ZHAO Y , et al. Hibifolin, a natural sortase a inhibitor, attenuates the pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus and enhances the antibacterial activity of Cefotaxime[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2022, 10 (4): e0095022.
doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00950-22 |
| 97 |
ZHANG B , TENG Z , LI X , et al. Chalcone attenuates Staphylococcus aureus virulence by targeting sortase A and Alpha-Hemolysin[J]. Front Microbiol, 2017, 8, 1715.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01715 |
| 98 |
SONG W , WANG L , JIN M , et al. Punicalagin, an inhibitor of Sortase A, is a promising therapeutic drug to combat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2022, 66 (6): e0022422.
doi: 10.1128/aac.00224-22 |
| 99 |
WANG L , WANG G , QU H , et al. Taxifolin, an inhibitor of sortase A, interferes with the adhesion of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcal aureus[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12, 686864.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.686864 |
| 100 | SEETHALAKSHMI P S , RAJEEV R , KIRAN G S , et al. Promising treatment strategies to combat Staphylococcus aureus biofilm infections: an updated review[J]. Biofouling, 2020, 36 (10): 1159- 1181. |
| 101 |
FELIPE V , BRESER M L , BOHL L P , et al. Chitosan disrupts biofilm formation and promotes biofilm eradication in Staphylococcus species isolated from bovine mastitis[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2019, 126, 60- 67.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.159 |
| 102 |
KONG C , CHEE C , RICHTER K , et al. Suppression of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and virulence by a benzimidazole derivative, UM-C162[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8 (1): 2758.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21141-2 |
| 103 | YAP C H , TAY S T , CHEE C F . Indole derivative (um-3e) as an antimicrobial and antivirulence strategy for the prevention of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm-associated infections[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2023, 130, S115- S116. |
| 104 |
KUMAR P , LEE J , BEYENAL H , et al. Fatty acids as antibiofilm and antivirulence agents[J]. Trends Microbiol, 2020, 28 (9): 753- 768.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.03.014 |
| 105 |
SELVARAJ A , VALLIAMMAI A , MUTHURAMALINGAM P , et al. Carvacrol Targets SarA and CrtM of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to mitigate biofilm formation and staphyloxanthin synthesis: An in vitro and in vivo approach[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5 (48): 31100- 31114.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c04252 |
| 106 |
VIJAYAKUMAR K , BHARATHIDASAN V , MANIGANDAN V , et al. Quebrachitol inhibits biofilm formation and virulence production against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Microb Pathog, 2020, 149, 104286.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104286 |
| 107 |
ZHENG J , SHANG Y , WU Y , et al. Diclazuril inhibits biofilm formation and hemolysis of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. ACS Infect Dis, 2021, 7 (6): 1690- 1701.
doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00030 |
| 108 | WANG H , SHI Y , CHEN J , et al. The antiviral drug efavirenz reduces biofilm formation and hemolysis by Staphylococcus aureus[J]. J Med Microbiol, 2021, 70 (10) |
| 109 |
ZHENG J , SHANG Y , WU Y , et al. Loratadine inhibits Staphylococcus aureus virulence and biofilm formation[J]. IScience, 2022, 25 (2): 103731.
doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103731 |
| 110 |
NIELSEN A , MÅNSSON M , BOJER M S , et al. Solonamide B inhibits quorum sensing and reduces Staphylococcus aureus mediated killing of human neutrophils[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9 (1): e84992.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084992 |
| 111 |
SULLY E K , MALACHOWA N , ELMORE B O , et al. Selective chemical inhibition of agr quorum sensing in Staphylococcus aureus promotes host defense with minimal impact on resistance[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2014, 10 (6): e1004174.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004174 |
| 112 |
DALY S M , ELMORE B O , KAVANAUGH J S , et al. ω-Hydroxyemodin limits Staphylococcus aureus quorum sensing-mediated pathogenesis and inflammation[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2015, 59 (4): 2223- 2235.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.04564-14 |
| 113 | BROWN M M , KWIECINSKI J M , CRUZ L M , et al. Novel peptide from commensal staphylococcus simulans blocks methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus quorum sensing and protects host skin from damage[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2020, 64 (6) |
| 114 |
ALONZO F R . Toward uncovering the complexities of bacterial interspecies communication and competition on the skin[J]. MBio, 2022, 13 (4): e0132022.
doi: 10.1128/mbio.01320-22 |
| 115 |
LIN H , SONG L , ZHOU S , et al. A hybrid antimicrobial peptide targeting Staphylococcus aureus with a dual function of inhibiting quorum sensing signaling and an antibacterial effect[J]. J Med Chem, 2023, 66 (24): 17105- 17117.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c02027 |
| 116 |
MAHDALLY N H , GEORGE R F , KASHEF M T , et al. Staquorsin: A novel Staphylococcus aureus agr-mediated quorum sensing inhibitor impairing virulence in vivo without notable resistance development[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12, 700494.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.700494 |
| 117 |
LEE J , KIM Y , LEE J . Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and virulence factor production by petroselinic acid and other unsaturated c18 fatty acids[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2022, 10 (3): e0133022.
doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01330-22 |
| 118 |
PARSONS J B , KUKULA M , JACKSON P , et al. Perturbation of Staphylococcus aureus gene expression by the enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase inhibitor AFN-1252[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2013, 57 (5): 2182- 2190.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.02307-12 |
| 119 |
LONG D R , MEAD J , HENDRICKS J M , et al. 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid inhibits methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus survival and attenuates virulence gene expression[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2013, 57 (1): 241- 247.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.01023-12 |
| 120 |
ARYA R , KIM T , YOUN J W , et al. Identification of an antivirulence agent targeting the master regulator of virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2023, 13, 1268044.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1268044 |
| 121 |
DUFRESNE K , DIMAGGIO D J , MADUTA C S , et al. Discovery of an anti-virulence compound that targets the Staphylococcus aureus SaeRS two-component system to inhibit toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1) production[J]. J Biol Chem, 2024, 300 (7): 107455.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107455 |
| 122 |
GAO P , WEI Y , HOU S , et al. SaeR as a novel target for antivirulence therapy against Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2023, 12 (2): 2254415.
doi: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2254415 |
| 123 |
OKADA A , IGARASHI M , OKAJIMA T , et al. Walkmycin B targets WalK (YycG), a histidine kinase essential for bacterial cell growth[J]. J Antibiot, 2010, 63 (2): 89- 94.
doi: 10.1038/ja.2009.128 |
| 124 |
KWIECINSKI J M , JELANI D A , FUENTES E J , et al. Therapeutic inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus ArlRS two-component regulatory system blocks virulence[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2022, 66 (7): e0018722.
doi: 10.1128/aac.00187-22 |
| 125 | WANG Z , WANG H , BAI J , et al. The Staphylococcus aureus ArlS kinase inhibitor tilmicosin has potent anti-biofilm activity in both static and flow conditions[J]. Microorganisms, 2024, 12 (2) |
| [1] | YOU Liuchao, YIN Hao, TAO Zhengyu, HUANG Rong, FU Lei, CHU Yuefeng. Research Progress in the Virulence Factors and Intracellular Survival Mechanism of Brucella [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1575-1593. |
| [2] | ZHANG Yanmin, LIU Shuai, TENG Zhanwei, XIE Hongbing, XIA Xiaojing, HE Yonghui, CHANG Meinan. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Functional Oligosaccharides Alleviating Calf Diarrhea [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 979-994. |
| [3] | LI Zhenya, LIU Jie, LI Yun, WANG Fei, KONG Yuanyuan, LI Yong, JIA Rongling. Biological Characteristics and Comparative Genomic Analysis of Virulent and Attenuated Strains of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 851-859. |
| [4] | Qilin WANG, Runlai CAO, Weiyang WANG, Bo ZHANG, Zhijie LIU, Xiaoxu WANG. Isolation, Identification and Drug Resistance Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Aborted Fetuses of Fox [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3640-3648. |
| [5] | Hengjie CUI, Jinlong QIN, Zhihao ZHU, Xue BAO, Shaowen LI, Xianrong MENG. Correlation Analysis of Benzalkonium Bromide Sensitivity and Biofilm Formation Ability in Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3669-3677. |
| [6] | HE Xiaolan, ZHAO Yankun, MENG Lu, LIU Huimin, GAO Jiaojiao, ZHENG Nan. Research Progress in Heteroresistance of Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1432-1445. |
| [7] | SONG Yan, YUAN Yongfeng, QIAN Hongyu, LI Xincan, LUO Hongyan, WANG Zhiying, ZHOU Zuoyong. Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics Analysis of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Isolated from Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 680-687. |
| [8] | WU Zihao, CAI Yilong, TUO Haixin, CHEN Wei. Pathogenicity Analysis of a PVL+ ST22 Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Equine Raw Milk [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 718-726. |
| [9] | LIU Xinhuan, YUN Jialei, MAO Li, LI Jizong, HAO Fei, HE Miaofeng, YANG Leilei, ZHANG Wenwen, CHENG Zilong, SUN Min, LIU Maojun, WANG Shaohui, BAI Juan, LI Wenliang. Isolation, Identification, Virulence Genes and Drug Resistance Analysis of Escherichia coli Isolated from Diarrheal Goat and Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3445-3454. |
| [10] | ZHAO Feifei, LI Jie, HAN Ning, XIE Shiting, ZENG Zhenling. Antibacterial Drug Resistance Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Slaughterhouse [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 3044-3053. |
| [11] | JIANG Meihan, WEI Jintao, GUO Yuming, GUO Shuangshuang, DU Encun. Effects of Essential Oils on Gut Lesions, Carbohydrate Active Enzymes Spectrum and eggNOG Pathways of Intestinal Flora in Broilers Challenged with Clostridium perfringens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2448-2457. |
| [12] | JIANG Zenghai, TENG Lin, HE Anwen, LIU Yanyan, YUE Min, HE Qigai. Genomic Analysis of Salmonella Typhimurium Isolates and Salmonella Serotype 4, [5], 12: i:- Isolates from Pig-borne Food Chain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 1199-1209. |
| [13] | LU Bikai, YUAN Xiufang, XU Lihua, YU Bin, SU Fei, YE Shiyi, CHEN Yijie, JIANG Liming, ZHANG Hui, LI Junxing. Molecular Serotyping and Apx Gene Profile Analysis of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae Isolates [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 1341-1346. |
| [14] | ZHI Yan, MEI Chen, LIU Zhenyi, WUYUN Gerile, WANG Hongjun, HU Ge. Research Progress on the Virulence Factors of Avibacterium paragallinarum [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 4934-4942. |
| [15] | WANG Jianing, ZHANG Ziqiang, KONG Dejing, FENG Caicai, ZHANG Feike, LIU Yumei. Isolation and Identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5198-5206. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||