





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 1549-1560.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.04.008
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
XING Jingyi1,2( ), GUO Xiaomeng2,3, WANG Meng2,4, GUAN Xin2,4, QIU Liang2,4,*(
), GUO Xiaomeng2,3, WANG Meng2,4, GUAN Xin2,4, QIU Liang2,4,*( ), LI Anqi1,*(
), LI Anqi1,*( ), ZHANG Qingli1,2,3,4, HUANG Jie2,3
), ZHANG Qingli1,2,3,4, HUANG Jie2,3
Received:2024-06-12
Online:2025-04-23
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
QIU Liang, LI Anqi
E-mail:xing-jingyi@foxmail.com;qiuliang@ysfri.ac.cn;anqi826523329@163.com
CLC Number:
XING Jingyi, GUO Xiaomeng, WANG Meng, GUAN Xin, QIU Liang, LI Anqi, ZHANG Qingli, HUANG Jie. Advances in Diagnostic Methods of Infection with Decapod Iridescent Virus 1[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1549-1560.

Fig. 1
Clinical signs of DIV1-infected shrimp a. Penaeus vannamei infected with DIV1 showed symptoms of empty stomach and gut, and pale hepatopancreas; b. Some dead Penaeus vannamei and P. monodon showed clinical signs of black spots on the abdominal carapace (black arrows)[23]; c. Exopalaemon carinicauda infected with DIV1 showed clinical signs of empty stomach and gut, pale hepatopancreas and slightly turbid white hematopoietic tissue(ST. Stomach; HP. Hepatopancreas; MG. Midgut; HM. Hematopoietic tissue)[6]; d. Symptoms of diseased Macrobrachium rosenbergii (blue arrows indicate "white head" and white arrows indicate a pale hepatopancreas)[5]; e. P. monodon infected with DIV1 by intramuscular injection show obvious clinical signs of black body[23]"

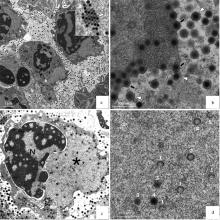
Fig. 3
TEM of hematopoietic tissue of naturally infected M. rosenbergii samples[5] a. Large numbers of virions in hematopoietic tissue; b. DIV1 budded and acquired an envelope from the plasma membrane; c. DIV1 replication and assembly in hematopoietic cells; d. The stages of nucleocapsid assembly, which are indicated with numbers 1-3, and a complete nucleocapsid is indicated with number 4. The capsids at stage 2 and 3 should have a small opening at one vertex but may not be visible in the picture due to the ultrathin section. N. Nucleus; *. A large electron-lucent virogenic stroma; White arrows. Paracrystalline array of viral particles; Black arrows. Budding virions; White triangles. Budded virions that acquired an envelope"
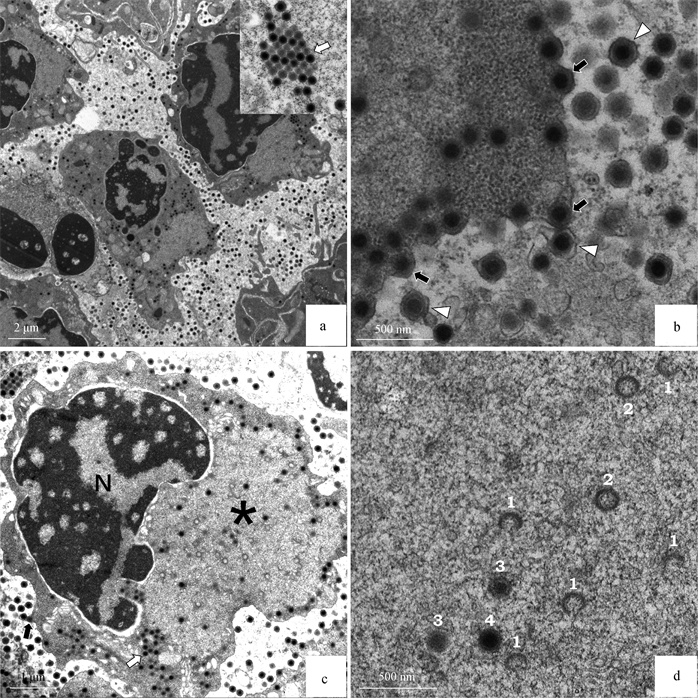
Table 1
Comparison of various DIV1 detection methods"
| 诊断/检测技术 Diagnostic/ Testing technology | 检测靶标 Detection target | 定性/定量 Qualitative/ Quantitative | 特异性 Specificity | WOAH试验验证所处阶段 Stage of WOAH test validation | 最低检出限 Limit of detection (LOD) | 弊端 Disadvantage | 适用场景 Applicable Scenarios | 检测温度 Detection temperature | 参考文献 References |
| 外观症状 Appearance symptom | - | 定性 | - | 无 | - | 依赖专业人员 | 实验室/现场 | - | - |
| 组织病理学 Histopathology | - | 定性 | - | 无 | - | 步骤繁琐、依赖专业人员 | 实验室 | - | - |
| 透射电镜 TEM | - | 定性 | - | 无 | - | 人员 | 实验室 | - | - |
| 原位杂交检测技术(ISH) In situ hybridization | MCP | 定性 | - | 无 | - | 步骤繁琐、依赖设备和人员 | 实验室 | 需要高温变性DNA | [ |
| [ | |||||||||
| 原位地高辛标记的环介导等温扩增ISDL | DNA-依赖的RNA聚合酶Ⅱ的第二大亚基 | 定性 | - | 无 | - | 步骤繁琐、依赖设备和人员 | 实验室 | 需要高温变性DNA | [ |
| [ | |||||||||
| PCR | MCP | 定性 | - | 无 | - | 依赖设备 | 实验室 | 变温 | [ |
| 套式PCR Nested PCR | ATPase | 定性 | 强 | 阶段1 | 36 fg样品总DNA | 依赖设备 | 实验室 | 变温 | [ |
| 半嵌套式PCR Semi-nested PCR | MCP ATPase | 定性 | 强 | 阶段1 阶段1 | 1.0×101拷贝·反应-1 | 依赖设备 | 实验室 | 变温 | [ |
| TaqMan qPCR | ATPase | 定量 | 强 | 阶段2 | 4拷贝·反应-1 | 依赖设备 | 实验室 | 变温 | [ |
| TaqMan qPCR | MCP | 定量 | 强 | 阶段2 | 1.2拷贝·反应-1 | 依赖设备 | 实验室 | 变温 | [ |
| TaqMan qPCR | 11L | 定量 | 强 | 阶段2 | 1.0拷贝·反应-1 | 依赖设备 | 实验室 | 变温 | [ |
| TaqMan qPCR | ATPase | 定量 | 强 | 阶段2 | 9.5×101拷贝·反应-1 | 依赖设备 | 实验室 | 变温 | [ |
| SYBR Green qPCR | 51R | 定量 | 强 | 阶段2 | 3.1拷贝·反应-1 | 依赖设备 | 实验室 | 变温 | [ |
| 105R | 阶段2 | 2.2拷贝·反应-1 | |||||||
| 114R | 阶段2 | 8.6拷贝·反应-1 | |||||||
| 124R | 阶段2 | 2.9拷贝·反应-1 | |||||||
| MCP | 定量 | 强 | 阶段2* | 1.24×102拷贝·反应-1 | 依赖设备 | 实验室 | 变温 | [ | |
| Eva Green qPCR | MCP | 定量 | 强 | 阶段2 | 1.0×102拷贝·反应-1 | 容易因核酸染料非特异地与DNA结合,造成假阳性 | 实验室 | 变温 | [ |
| LAMP | MCP | 定量 | 强 | 阶段2* | 3.54×102拷贝·反应-1 | 容易因非特异性扩增导致假阳性 | 实验室/现场 | 64.4 ℃ | [ |
| qLAMP | ATPase | 定量 | 强 | 阶段2 | 3.8×102拷贝·反应-1 | 对目标DNA定量的准确性略低于qPCR | 实验室/ 现场 | 63 ℃ | [ |
| LAMP、LAMP-dye、LAMP-LFD | DNA-依赖的RNA聚合酶Ⅱ的第二大亚基 | 定性 | 强 | 阶段1 | 3.95×103拷贝·反应-1 | 灵敏度较低 | 实验室/现场 | 60 ℃ | [ |
| LAMP Micro-detection Slide | ATPase | 定性 | 强 | 阶段2 | 1.7×102拷贝·反应-1 | 可能出现假阴性结果 | 实验室/现场 | 65 ℃ | [ |
| RPA | ATPase | 定性 | 强 | 阶段2* | 1.4×101拷贝·反应-1 | 试剂成本高于qPCR | 实验室/现场 | 30 ℃ | [ |
| RPA | ATPase | 定性 | 强 | 阶段2 | 8拷贝·反应-1 | 试剂成本高于qPCR | 实验室/现场 | 37 ℃ | [ |
| Real-time RPA | MCP | 定性 | 强 | 阶段1 | 1.1×101拷贝·反应-1 | 试剂成本高于qPCR | 实验室/现场 | 39 ℃ | [ |
| Real-time RPA | MCP | 定性 | 强 | 阶段2* | 2.3×101拷贝·反应-1 | 试剂成本高于qPCR | 实验室/现场 | 39 ℃ | [ |
| qRPA | ATPase | 定量 | 强 | 阶段1 | 2拷贝·反应-1 | 试剂成本高于qPCR | 实验室 | 42 ℃ | [ |
| DIV1-RPA-SYBR Green I | 定性 | 阶段1 | 2.0×103拷贝·反应-1 | 实验室/现场 | |||||
| 间接酶联免疫吸附试验(间接ELISA) Indirect ELISA | ORF064L | 定量 | 强 | 阶段2 | 5 ng·mL-1 | 步骤繁琐,成本较高 | 实验室/现场 | 常温 | [ |
| 点印迹试验 Dot blot test | 阶段2 | 6.25 ng·点-1 | |||||||
| 1 |
STENTIFORDG D.Histological intersex (ovotestis) in the European lobster Homarus gammarus and a commentary on its potential mechanistic basis[J].Dis Aquat Org,2012,100(2):185-190.
doi: 10.3354/dao02455 |
| 2 | 2023年全国渔业经济统计公报[J]. 中国水产, 2024(7): 12-13. |
| National statistical bulletin on the fisheries economy, 2023[J]. China Fisheries, 2024(7): 12-13. (in Chinese) | |
| 3 |
XUL M,WANGT T,LIF,et al.Isolation and preliminary characterization of a new pathogenic iridovirus from redclaw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus[J].Dis Aquat Org,2016,120(1):17-26.
doi: 10.3354/dao03007 |
| 4 |
QIUL,CHENM M,WANX Y,et al.Characterization of a new member of Iridoviridae, Shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus (SHIV), found in white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei)[J].Sci Rep,2017,7(1):11834.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10738-8 |
| 5 |
QIUL,CHENX,ZHAOR H,et al.Description of a natural infection with Decapod iridescent virus 1 in farmed giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii[J].Viruses,2019,11(4):354.
doi: 10.3390/v11040354 |
| 6 |
CHENX,QIUL,WANGH L,et al.Susceptibility of Exopalaemon carinicauda to the infection with Shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus (SHIV 20141215), a strain of Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1)[J].Viruses,2019,11(4):387.
doi: 10.3390/v11040387 |
| 7 |
QIUL,CHENX,GAOW,et al.Confirmation of susceptibility of swimming crab to infection with Decapod iridescent virus 1[J].Aquaculture,2022,548,737607.
doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737607 |
| 8 |
QIUL,GUOX M,FENGY H,et al.Susceptibility of kuruma shrimp to the infection with Decapod iridescent virus 1[J].Front Mar Sci,2023,10,1114123.
doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1114123 |
| 9 |
SRISALAJ,SANGUANRUTP,THAIUED,et al.Infectious myonecrosis virus (IMNV) and Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) detected in captured, wild Penaeus monodon[J].Aquaculture,2021,545,737262.
doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737262 |
| 10 | 邱亮, 董宣, 万晓媛, 等. 2019年虾虹彩病毒病状况分析[M]//农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站. 2020我国水生动物重要疫病状况分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2020: 185-200. |
| QIU L, DONG X, WAN X Y, et al. Analysis of iridescent viral disease of shrimp (SHID) in 2019[M]//Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, National Fisheries Technology Extension Center. 2020 Analysis of Major Aquatic Animal Diseases in China. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2020: 185-200. (in Chinese) | |
| 11 |
QIUL,CHENX,GAOW,et al.Molecular epidemiology and histopathological study of a natural infection with Decapod iridescent virus 1 in farmed white leg shrimp, Penaeus vannamei[J].Aquaculture,2021,533,736105.
doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.736105 |
| 12 | 邱亮, 董宣, 万晓媛, 等. 2018年虾虹彩病毒病状况分析[M]//农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站, 中国水产学会. 2019我国水生动物重要疫病状况分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2019: 189-207. |
| QIU L, DONG X, WAN X Y, et al. Analysis of iridescent viral disease of shrimp (SHID) in 2018[M]//Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, National Fisheries Technology Extension Center, China Society of Fisheries. 2019 Analysis of Major Aquatic Animal Diseases in China. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2019: 189-207. (in Chinese) | |
| 13 | 邱亮, 董宣, 万晓媛, 等. 2017年虾虹彩病毒病(SHID)分析[M]//农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站. 2017年我国水生动物重要疫病病情分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2018: 187-204. |
| QIU L, DONG X, WAN X Y, et al. Analysis of iridescent viral disease of shrimp (SHID) in 2017[M]//Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, National Fisheries Technology Extension Center. Analysis of Important Diseases of Aquatic Animals in China in 2017. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2018: 187-204. (in Chinese) | |
| 14 |
潘长坤,袁会芳,王甜甜,等.红螯螯虾虹彩病毒在两种螃蟹内的研究[J].应用海洋学学报,2017,36(1):82-86.
doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2017.01.010 |
|
PANC K,YUANH F,WANGT T,et al.Study of Cherax quadricarinatus iridescent virus in two crabs[J].Journal of Applied Oceanography,2017,36(1):82-86.
doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2017.01.010 |
|
| 15 | CHINCHAR V G, YANG F, HUANG J, et al. One new genus with one new species in the subfamily Betairidovirinae[EB/OL]. (2018-09-21). https://ictv.global/filebrowser/download/4955. |
| 16 | KINGA M Q,ADAMSM J,CARSTENSE B,et al.Virus taxonomy: ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses[M].Amsterdam:Elsevier,2011. |
| 17 |
LIF,XUL M,YANGF.Genomic characterization of a novel iridovirus from redclaw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus: evidence for a new genus within the family Iridoviridae[J].J Gen Virol,2017,98(10):2589-2595.
doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000904 |
| 18 |
QIUL,CHENM M,WANGR Y,et al.Complete genome sequence of Shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus (SHIV) isolated from white leg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei[J].Arch Virol,2018,163(3):781-785.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-017-3642-4 |
| 19 | 邱亮, 董宣, 万晓媛, 等. 2022年十足目虹彩病毒病状况分析[M]//农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站. 2023我国水生动物重要疫病状况分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2023. |
| QIU L, DONG X, WAN X Y, et al. Analysis of infection with Decapod iridescent virus 1 (IDIV1) in 2022[M]//Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, National Fisheries Technology Extension Center. 2023 Analysis of Major Aquatic Animal Diseases in China. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 20 | 邱亮, 董宣, 万晓媛, 等. 2021年十足目虹彩病毒病状况分析[M]//农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站. 2022我国水生动物重要疫病状况分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2022: 161-174. |
| QIU L, DONG X, WAN X Y, et al. Analysis of infection with Decapod iridescent virus 1 (IDIV1) in 2021[M]//Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, National Fisheries Technology Extension Center. 2022 Analysis of Major Aquatic Animal Diseases in China. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2022: 161-174. (in Chinese) | |
| 21 | 邱亮, 董宣, 万晓媛, 等. 2020年虾虹彩病毒病状况分析[M]//农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站. 2021我国水生动物重要疫病状况分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2021: 182-196. |
| QIU L, DONG X, WAN X Y, et al. Analysis of iridescent viral disease of shrimp (SHID) in 2020[M]//Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, National Fisheries Technology Extension Center. 2021 Analysis of Major Aquatic Animal Diseases in China. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2021: 182-196. (in Chinese) | |
| 22 |
许昊川,徐胜威,王雯琼,等.2020年浙江省宁波市南美白对虾虾苗主要病原携带情况调查[J].中国动物检疫,2021,38(9):29-32, 39.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2021.09.008 |
|
XUH C,XUS W,WANGW Q,et al.Investigation on major pathogens carried by shrimp seeds of Penaeus vannamei in Ningbo City of Zhejiang Province in 2020[J].China Animal Health Inspection,2021,38(9):29-32, 39.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2021.09.008 |
|
| 23 |
HEZ H,CHENX Y,ZHAOJ C,et al.Establishment of infection mode and Penaeus monodon hemocytes transcriptomics analysis under Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) challenge[J].Aquaculture,2021,542,736816.
doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736816 |
| 24 |
LIAOX Z,WANGC G,WANGB,et al.Comparative Transcriptome analysis of Litopenaeus vannamei reveals that triosephosphate isomerase-like genes play an important role during Decapod iridescent virus 1 infection[J].Front Immunol,2020,11,1904.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01904 |
| 25 |
SOTO-RODRIGUEZS A,GOMEZ-GILB,LOZANO-OLVERAR,et al.Field and experimental evidence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus as the causative agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease of cultured shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in Northwestern Mexico[J].Appl Environ Microbiol,2015,81(5):1689-1699.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.03610-14 |
| 26 |
FLEGELT W.Historic emergence, impact and current status of shrimp pathogens in Asia[J].J Invertebr Pathol,2012,110(2):166-173.
doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2012.03.004 |
| 27 |
LIAOX Z,HEJ G,LIC Z.Decapod iridescent virus 1:an emerging viral pathogen in aquaculture[J].Rev Aquacult,2022,14(4):1779-1789.
doi: 10.1111/raq.12672 |
| 28 | SANGUANRUTP,THAIUED,THAWONSUWANJ,et al.The lymphoid organ (LO) is an additional, prime target for Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) in Penaeus vannamei[J].Aquaculture,2021,547,737482. |
| 29 | 王甜甜. 红螯螯虾虹彩病毒(CQIV)与白斑综合症病毒(WSSV)感染的组织细胞特异性以及感染途径的研究[D]. 厦门: 国家海洋局第三海洋研究所, 2016. |
| WANG T T. Research on the tissues/cell tropism and transmission of Cherax quadricarinatus iridovirus (CQIV) and white spot syndrome virus (WSSV)[D]. Xiamen: Third Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, 2016. (in Chinese) | |
| 30 | 邱亮. 养殖对虾的病毒宏基因组分析及虾血细胞虹彩病毒(Shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus, SHIV)的分子流行病学研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2018. |
| QIU L. Viral metagenomics analysis of farmed shrimp and molecular epidemiological study of Shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus (SHIV)[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2018. (in Chinese) | |
| 31 |
QIUL,CHENM M,WANX Y,et al.Detection and quantification of Shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus by TaqMan probe based real-time PCR[J].J Invertebr Pathol,2018,154,95-101.
doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2018.04.005 |
| 32 |
QIUL,CHENX,GUOX M,et al.A TaqMan probe based real-time PCR for the detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1[J].J Invertebr Pathol,2020,173,107367.
doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2020.107367 |
| 33 |
GONGH Y,LIQ Y,ZHANGH,et al.Development and comparison of qPCR and qLAMP for rapid detection of the Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1)[J].J Invertebr Pathol,2021,182,107567.
doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2021.107567 |
| 34 | 邹莹,郭晓萌,万晓媛,等.十足目虹彩病毒(DIV1)环介导等温扩增(LAMP)检测方法的建立及应用[J].渔业科学进展,2020,41(6):156-164. |
| ZOUY,GUOX M,WANX Y,et al.Establishment and application of the LAMP detection method for decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1)[J].Progress in Fishery Sciences,2020,41(6):156-164. | |
| 35 |
CHENZ W,HUANGJ,ZHANGF,et al.Detection of Shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus by recombinase polymerase amplification assay[J].Mol Cell Probes,2020,49,101475.
doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2019.101475 |
| 36 |
GUOX M,XINGJ Y,LIA Q,et al.Establishment of a real-time PCR for the detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1)[J].J Fish Dis,2024,47(6):e13926.
doi: 10.1111/jfd.13926 |
| 37 |
SELLARSM J,FRANZL,MOSERR J.Development of new real-time PCR methods for detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1 in shrimp[J].J World Aquacult Soc,2023,54(1):167-180.
doi: 10.1111/jwas.12885 |
| 38 |
XUT,TANR X,ZHUY T,et al.Establishment of a SYBR Green I-based real-time PCR for the detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1[J].J Invertebr Pathol,2023,201,107998.
doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2023.107998 |
| 39 |
DONGX,CHENY J,LOUH Y,et al.Development of a melting curve-based triple Eva green real-time PCR assay for simultaneous detection of three shrimp pathogens[J].Animals,2024,14(4):592.
doi: 10.3390/ani14040592 |
| 40 |
NAIKP,JAITPALS,SHETTYP,et al.An integrated one-step assay combining thermal lysis and loop-mediated isothermal DNA amplification (LAMP) in 30 min from EE. coli and M. smegmatis cells on a paper substrate[J].Sens Actuators B: Chem,2019,291,74-80.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.044 |
| 41 |
SHIRATOK.Detecting amplicons of loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].Microbiol Immunol,2019,63(10):407-412.
doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12734 |
| 42 |
LIC,JIANGK T,QIUL,et al.Establishment of two visual interpretation methods of DIV1 LAMP amplification products[J].J Virol Methods,2023,322,114806.
doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2023.114806 |
| 43 |
CAOZ,DONGX,ZOUP Z,et al.Development of a cost-efficient micro-detection slide system for the detection of multiple shrimp pathogens[J].Anal Biochem,2020,599,113735.
doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2020.113735 |
| 44 |
PIEPENBURGO,WILLIAMSC H,STEMPLED L,et al.DNA detection using recombination proteins[J].PLoS Biol,2006,4(7):e204.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040204 |
| 45 |
XIAX M,YUY X,WEIDMANNM,et al.Rapid detection of shrimp white spot syndrome virus by real time, isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification assay[J].PLoS One,2014,9(8):e104667.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104667 |
| 46 |
XIAX M,YUY X,HUL H,et al.Rapid detection of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) by real-time, isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification assay[J].Arch Virol,2015,160(4):987-994.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-015-2357-7 |
| 47 | MANIMOZHIE,PORKODIM,MARTINAP,et al.An emerging shrimp pathogen: Decapod iridescent virus (DIV1)[J].Pharm Innov J,2021,SP-10(11):850-854. |
| 48 | 尹伟力,吴葳,刘晓静,等.重组酶快速检测十足目虹彩病毒1方法的建立[J].水产科学,2021,40(2):267-272. |
| YINW L,WUW,LIUX J,et al.Rapid detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) by recombinase polymerase amplification[J].Fisheries Science,2021,40(2):267-272. | |
| 49 |
TONGG X,YINW L,WUX Q,et al.Rapid detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) by recombinase polymerase amplification[J].J Virol Methods,2022,300,114362.
doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114362 |
| 50 |
HUANGQ J,CHENY,LIUH,et al.Establishment of a real-time recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) for the detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1)[J].J Virol Methods,2022,300,114377.
doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114377 |
| 51 |
XUY J,WANGY,HUJ J,et al.Development and visualization improvement for the rapid detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) in Penaeus vannamei based on an isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification assay[J].Viruses,2022,14(12):2752.
doi: 10.3390/v14122752 |
| 52 | 张徐俞,黄俊,杨稳,等.重组酶聚合酶扩增结合CRISPR-Cas12a快速检测十足目虹彩病毒1方法的建立[J].微生物学通报,2021,48(12):4980-4988. |
| ZHANGX Y,HUANGJ,YANGW,et al.Rapid detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1 by recombinase polymerase amplification combined with CRISPR-Cas12a[J].Microbiology China,2021,48(12):4980-4988. | |
| 53 | CHENJ L,WANGW,ZHENGQ,et al.Shark-derived single-domain antibodies for the detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1[J].Aquacult Rep,2023,30,101597. |
| 54 | Principles and methods of validation of diagnostic assays for infectious diseases[M]//WOAH. Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals. Paris: Office International des epizooties, 2021: 11-26. |
| [1] | ZHANG Yue, RU Yi, HAO Rongzeng, YANG Rui, ZHAO Longhe, LI Yajun, YANG Yang, ZHANG Rong, JIANG Chenghui, ZHENG Haixue. Preparation and Immunogenicity Evaluation of African Swine Fever Virus H108R Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1344-1354. |
| [2] | MA Xiaoli, LI Duan, ZENG Daoping, LIU Yanling, WANG Xiaomin, PENG Guoliang, SONG Changxu, WANG Lei, XU Zheng. Establishment of a Fully Automated Chemiluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay for Detecting Antibodies against African Swine Fever Virus p72 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1355-1365. |
| [3] | YU Jiangwei, CHENG Huimin, LIN Jian, YANG Baolin, HUANG Cheng, YANG Zhiyuan, HU Ge. Establishment and Application of TaqMan Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Detection Method for Duck Plague Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 765-773. |
| [4] | LIU Jianhua, SA Ruixue, ZHANG Siyu, LI Yintao, DENG Zhichao, JIA Handuo, ZHAO Min, FU Yu, YANG Yiming, RAN Duoliang, JA Erken. Pathogenicity of Equine Herpesvirus Type 1 Isolates to Syrian Golden Hamsters [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 327-334. |
| [5] | ZHANG Su, SUN Lifang, LI Lanlan, WU Linjiao, CHEN Leiqing, WU Yunkun. Research Progress on the Interactions of African Swine Fever Virus Structural Proteins with Host Proteins [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 95-106. |
| [6] | CHEN Xiaoli, ZHOU Jiahao, ZHOU Jing, QU Qian, WANG Zhihua, XIONG Ying, ZHU Yongqi, JIA Weixin, LÜ Weijie, GUO Shining. Effect of Modified Yuyin Decoction on cGAS-STING Pathway of African Swine Fever Virus Infected PAMs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5839-5853. |
| [7] | ZHANG Duo, TENG Man, ZHANG Zhuo, LIU Jinling, ZHENG Luping, GE Siyu, HAN Fang, LUO Qin, CHAI Shujun, ZHAO Dong, YU Zuhua, LUO Jun. Development and Pathogenicity Analysis of a meq-gene-edited Candidate Marek's Disease Vaccine Strain Generated from a Hypervirulent MDV Variant [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5672-5683. |
| [8] | ZHOU Zhiyu, DU Jige, XIN Ruolan, ZHANG Jiawen, PAN Chenfan, YIN Chunsheng, CHEN Xiaoyun, ZHU Zhen. Isolation and Identification of Three Lumpy Skin Disease Viruses in China and Their GPCR Gene Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5620-5630. |
| [9] | Qi ZHANG, Ningning DONG, Xiaomei TAN, Zhengwang SHI, Na LI, Wenqi ZHU, Aoxing TANG, Chuanfeng LI, Jie ZHU, Guangqing LIU, Yan SU, Chunchun MENG. Fusion Expression of African Swine Fever Virus p30 Protein and CRM197 and Evaluation of Its Immunogenicity in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5230-5237. |
| [10] | Ting YOU, Shanhui REN, Meng WANG, Hongqiang ZHANG, Xiaolong GAO, Wei YAO, Hui WANG, Xue YANG, Chunling MA, Minyi LIU, Yuzhe ZHANG, Jinlong WANG, Yuefeng SUN, Haotai CHEN, Guirong WANG. Construction and Replication Ability of the ORF112 Gene Deleted Orf Virus Strain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5200-5210. |
| [11] | Qiuyuan FENG, Hanwei YU, Yunfeng YANG, Hui ZHANG, Weiyi HANWU, Xintong SUN, Xiaolong SHAO, Junlin LIU, Guohua CHEN, Zhizhong JING, Yixia CHEN. Regulation of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway by Goat Poxvirus Ankyin Protein ORF140 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5191-5199. |
| [12] | Yuzhe ZHANG, Shanhui REN, Wei YAO, Zhenli GONG, Hongqiang ZHANG, Minyi LIU, Ting YOU, Xiangwei WANG, Jiyun LI, Xiangping YIN, Yuefeng SUN, Haotai CHEN, Xuerui WAN. Application of the Cre-LoxP System to Construct the Deleted TK Gene of the Lumpy Skin Disease Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4517-4529. |
| [13] | Mengdi WANG, Yumin WANG, Zhen ZHANG, Xiuxiang LU, Heng WANG, Wenjie FAN, Chen YAO, Pengxiang LIU, Yanjie MA, Beibei CHU, Jiang WANG, Guoyu YANG. Effect of TSG101 Gene Knockdown on Proliferation of Pseudorabies Virus in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4110-4120. |
| [14] | Yiqian FU, Dongge LIANG, Mingyang WANG, Jiajia PAN, Yanbin YANG, Lei ZENG, Xiangtao KANG. Construction of Interferon Regulatory Factor Knockdown Cell Line and Its Effect on Pseudorabies Virus Proliferation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4100-4109. |
| [15] | Lu FENG, Hong TIAN, Haixue ZHENG, Zhengwang SHI, Juncong LUO, Xiaoyang ZHANG, Juanjuan WEI, Jing ZHOU, Huancheng LIAO, Wanying WANG. A Detection Method of African Swine Fever Virus based on Enzymatic Recombinase Amplification [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4226-4231. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||