





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 335-342.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.01.031
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Xingyue1( ), YANG Zhiyuan2(
), YANG Zhiyuan2( ), LIN Jian2, ZHANG Zixuan1, ZHOU Yuting1, CHENG Huimin2, LIU Yuehuan2, HU Ge1,*(
), LIN Jian2, ZHANG Zixuan1, ZHOU Yuting1, CHENG Huimin2, LIU Yuehuan2, HU Ge1,*( )
)
Received:2024-02-27
Online:2025-01-23
Published:2025-01-18
Contact:
HU Ge
E-mail:idwxy99@163.com;yangzy88@126.com;bnhuge@126.com
CLC Number:
WANG Xingyue, YANG Zhiyuan, LIN Jian, ZHANG Zixuan, ZHOU Yuting, CHENG Huimin, LIU Yuehuan, HU Ge. Development and Application of a Real-time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR Detection Method for Pigeon Circovirus[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 335-342.
Table 1
Information of primers"
| 引物名称 Primers | 引物序列(5'→3') Primer sequences (5'→3') | 产物大小/bp Product size (bp) |
| CV-F | 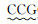 | 530 |
| CV-R | 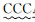 | |
| qCap-F | GGTTGCTGCTGTCTGGTTTG | 158 |
| qCap-R | AGACCTTCCAGCAAGTGACG | |
| Cap-F | GCGAAGCGACTACACTCGAA | 911 |
| Cap-R | ACTAATCCGCGACTTGGAGC |
Table 2
Reference strains"
| 登录号 Accession No. | 分离国家 Country | 宿主 Host | 提交年份 Year | 长度/nt Length/nt | Cap基因位置 Position of Cap gene |
| AF252610.1 | 德国 | 鸽 | 2000 | 2 037 | 1 166-1 987 |
| NC-002361.1 | 德国 | 鸽 | 2000 | 2 037 | 1 166-1 987 |
| AJ298229 | 英国 | 鸽 | 2001 | 2 037 | 1 166-1 987 |
| DQ915960 | 法国 | 鸽 | 2006 | 2 037 | 1 166-1 987 |
| DQ915956 | 比利时 | 鸽 | 2006 | 2 038 | 1 167-1 988 |
| DQ915961.1 | 美国 | 鸽 | 2006 | 2 037 | 1 166-1 987 |
| EU840176 | 美国 | 鸽 | 2008 | 2 041 | 1 167-1 988 |
| KF738870.1 | 波兰 | 鸽 | 2013 | 2 037 | 1 166-1 987 |
| LC035390.1 | 日本 | 鸽 | 2015 | 2 041 | 1 166-1 987 |
| KX108803.1 | 中国 | 鸽 | 2016 | 2 037 | 1 166-1 987 |
| KX108815.1 | 中国 | 鸽 | 2016 | 2 037 | 1 166-1 987 |
| KX108817.1 | 中国 | 鸽 | 2016 | 2 031 | 1 166-1 981 |
| KY114965.1 | 巴西 | 鸽 | 2016 | 2 041 | 1 167-1 991 |
| KX431143 | 中国 | 鸽 | 2016 | 2 034 | 1 165-1 980 |
| MF136692.1 | 澳大利亚 | 鸽 | 2017 | 2 037 | 1 166-1 987 |
| MF621931.1 | 巴西 | 鸽 | 2017 | 2 038 | 1 120-1 941 |
| MW181957.1 | 中国 | 鸽 | 2020 | 2 042 | 1 166-1 987 |
| MW656169.1 | 波兰 | 鸽 | 2021 | 2 043 | 1 174-1 995 |
| OL901206.1 | 中国 | 鸽 | 2021 | 2 037 | 1 166-1 987 |
| ON598390.1 | 中国 | 鸽 | 2022 | 2 032 | 1 166-1 978 |
| OQ184742.1 | 中国 | 鸽 | 2023 | 2 037 | 1 166-1 987 |
| OR573846.1 | 中国 | 鸽 | 2023 | 2 036 | 1 165-1 986 |
| OR611917.1 | 中国 | 鸽 | 2023 | 2 037 | 1 165-1 983 |
| HQ738642 | 尼日利亚 | 鸡 | 2010 | 2 036 | 1 125-1 946 |
| OK094643.1 | 中国 | 鸭 | 2021 | 1 994 | 1 157-1 930 |
| OQ744003.1 | 泰国 | 鸭 | 2023 | 1 996 | 1 160-1 933 |
| MN171332.1 | 中国 | 鹅 | 2018 | 1 822 | 1 009-1 761 |
| MN420497.1 | 中国 | 鸡 | 2019 | 2 001 | 1 135-2 001 |
Table 3
The results of samples collected from Northern and Northwest China for detection of PiCV"
| 地区 Sampling area | 鸽 Pigeon | 采样场点数 Site | 采样时间(月/年) Date | 样本数量 Numbers | PCR(阳性/样品) PCR (Positive/total) | qPCR(阳性/样品) qPCR (Positive/total) |
| 北京市 | 肉鸽 | 1 | 11/2022 | 35 | 29/35 | 33/35 |
| 信鸽 | 2 | 06/2023 | 20 | 2/20 | 2/20 | |
| 山西省 | 信鸽 | 1 | 07/2023 | 9 | 9/9 | 9/9 |
| 河北省 | 信鸽 | 1 | 10/2022 | 64 | 44/64 | 62/64 |
| 陕西省 | 信鸽 | 1 | 06/2023 | 7 | 4/7 | 7/7 |
| 新疆 | 信鸽 | 1 | 10/2022 | 2 | 1/2 | 2/2 |
| 内蒙古 | 信鸽 | 2 | 08/2023 | 6 | 6/6 | 6/6 |
| 甘肃省 | 信鸽 | 1 | 07/2023 | 4 | 3/4 | 4/4 |
| 总计 | - | 10 | - | 147 | 98/147 | 125/147 |
| 1 |
SANTOS H M , TSAI C Y , CATULIN G E M , et al. Common bacterial, viral, and parasitic diseases in pigeons (Columba livia): a review of diagnostic and treatment strategies[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2020, 247, 108779.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2020.108779 |
| 2 |
WOODS L W , LATIMER K S , NIAGRO F D , et al. A retrospective study of circovirus infection in pigeons: nine cases (1986-1993)[J]. J Vet Diagn Invest, 1994, 6 (2): 156- 164.
doi: 10.1177/104063879400600205 |
| 3 |
ABADIE J , NGUYEN F , GROIZELEAU C , et al. Pigeon circovirus infection: pathological observations and suggested pathogenesis[J]. Avian Pathol, 2001, 30 (2): 149- 158.
doi: 10.1080/03079450124811 |
| 4 | 王浩然. 鸽圆环病毒分子流行病学调查及检测方法的建立[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021. |
| WANG H R. Molecular epidemiological investigation and establishment of diagnostic technique on pigeon circovirus[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 5 |
WANG H R , GAO H , JIANG Z W , et al. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of pigeon circovirus from racing pigeons in Northern China[J]. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23 (1): 290.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08425-8 |
| 6 |
TODD D . Avian circovirus diseases: lessons for the study of PMWS[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2004, 98 (2): 169- 174.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2003.10.010 |
| 7 |
李晓波, 王吉, 王莎莎, 等. 鸽圆环病毒荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立及应用[J]. 实验动物科学, 2022, 39 (4): 28- 32.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6179.2022.04.006 |
|
LI X B , WANG J , WANG S S , et al. Establishment and application of fluorescent quantitative PCR assay for pigeon circovirus[J]. Laboratory Animal Science, 2022, 39 (4): 28- 32.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6179.2022.04.006 |
|
| 8 |
日孜瓦古·努尔东, 米晓云, 魏玉荣, 等. 鸽圆环病毒Cap及Rep基因的克隆与进化分析[J]. 塔里木大学学报, 2020, 32 (1): 1- 6.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0568.2020.01.001 |
|
RIZIWAGU·NUERDONG , MI X Y , WEI Y R , et al. Cloning and phylogenetic analysis of Cap and Rep genes of pigeon circovirus[J]. Journal of Tarim University, 2020, 32 (1): 1- 6.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0568.2020.01.001 |
|
| 9 |
SILVA B B I , URZO M L R , ENCABO J R , et al. Pigeon circovirus over three decades of research: bibliometrics, scoping review, and perspectives[J]. Viruses, 2022, 14 (7): 1498.
doi: 10.3390/v14071498 |
| 10 |
ZHANG Z C , DAI W , WANG S H , et al. Epidemiology and genetic characteristics of pigeon circovirus (PiCV) in eastern China[J]. Arch Virol, 2015, 160 (1): 199- 206.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-014-2255-4 |
| 11 | 韩晓语, 杨俊杰, 赵洪哲, 等. 鸽圆环病毒Cap基因SYBR Green Ⅰ荧光定量PCR方法的建立及应用[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2024, 32 (3): 95- 101. |
| HAN X Y , YANG J J , ZHAO H Z , et al. Development and application of SYBR green Ⅰ fluorescent quantitative PCR for detection of Cap Gene of pigeon circovirus[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Parasitology, 2024, 32 (3): 95- 101. | |
| 12 | 栗文文, 袁海霞, 徐雅萍, 等. 鸽圆环病毒研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2011, 38 (8): 236- 238. |
| LI W W , YUAN H X , XU Y P , et al. Pigeon circovirus research progress[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2011, 38 (8): 236- 238. | |
| 13 |
NATH B K , DAS S , DAS T , et al. Development and applications of a TaqMan based quantitative real-time PCR for the rapid detection of Pigeon circovirus (PiCV)[J]. J Virol Methods, 2022, 308, 114588.
doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2022.114588 |
| 14 |
MANKERTZ A , HATTERMANN K , EHLERS B , et al. Cloning and sequencing of columbid circovirus (CoCV), a new circovirus from pigeons[J]. Arch Virol, 2000, 145 (12): 2469- 2479.
doi: 10.1007/s007050070002 |
| 15 | 兰世捷, 苗艳, 陈亮, 等. 鸽圆环病毒和鸽疱疹病毒双重PCR检测方法的建立及初步应用[J]. 中国家禽, 2022, 44 (4): 113- 116. |
| LAN S J , MIAO Y , CHEN L , et al. Establishment and preliminary application of double PCR detection method for pigeon circovirus and pigeon herpesvirus[J]. China Poultry, 2022, 44 (4): 113- 116. | |
| 16 |
HATTERMANN K , SOIKE D , GRUND C , et al. A method to diagnose Pigeon circovirus infection in vivo[J]. J Virol Methods, 2002, 104 (1): 55- 58.
doi: 10.1016/S0166-0934(02)00038-1 |
| 17 | 亓玉卓, 梁琳, 朱亚丽, 等. 鸽圆环病毒SYBR GreenⅠ荧光定量PCR方法的建立及应用[J]. 中国家禽, 2021, 43 (3): 22- 27. |
| QI Y Z , LIANG L , ZHU Y L , et al. Development and application of SYBR green Ⅰ real-time PCR for detection of pigeon circovirus[J]. China Poultry, 2021, 43 (3): 22- 27. | |
| 18 | 郭学波, 赵承锋, 吴瑶, 等. 鸽圆环病毒TaqMan荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立及初步应用[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2024, 54 (2): 169- 173. |
| GUO X B , ZHAO C F , WU Y , et al. Establishment and application of PCR assay for detect of pigeon circovirus[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2024, 54 (2): 169- 173. | |
| 19 |
ZHANG Z C , LU C P , WANG Y , et al. Molecular characterization and epidemiological investigation of Pigeon circovirus isolated in eastern China[J]. J Vet Diagn Invest, 2011, 23 (4): 665- 672.
doi: 10.1177/1040638711407878 |
| 20 |
SAHINDOKUYUCU I , YAZICI Z , BARRY G . A retrospective molecular investigation of selected pigeon viruses between 2018-2021 in Turkey[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17 (8): e0268052.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268052 |
| 21 |
NATH B K , DAS S , TIDD N , et al. Lesions and viral loads in racing pigeons naturally coinfected with pigeon circovirus and columbid alphaherpesvirus 1 in Australia[J]. J Vet Diagn Invest, 2023, 35 (3): 278- 283.
doi: 10.1177/10406387231156839 |
| 22 |
STENZEL T A , PESTKA D , TYKAŁOWSKI B , et al. Epidemiological investigation of selected pigeon viral infections in Poland[J]. Vet Rec, 2012, 171 (22): 562.
doi: 10.1136/vr.100932 |
| 23 | CSÁGOLA A , LŐRINCZ M , TOMBÁCZ K , et al. Genetic diversity of pigeon circovirus in Hungary[J]. Virus Genes, 2012, 44 (1): 75- 79. |
| [1] | Yiming GAO, Guosheng CHEN, Shiting NI, Ze TONG, Haonan WANG, Fan YANG, Lijun YANG, Yupeng MO, Chen TAN. Investigation and Analysis of Infection Status of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in Pigs in Selected Areas of Southern China, 2022 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3064-3074. |
| [2] | LIANG Canxin, ZHENG Xiaoxue, SHU Xueli, ZHOU Wanyi, LIAO Ming, CAO Weisheng. Isolation of ALV-K Associated with Endothelial Hemangioma in Chicken and Analysis of gp85 Gene Evolution [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1127-1136. |
| [3] | SONG Yan, YUAN Yongfeng, QIAN Hongyu, LI Xincan, LUO Hongyan, WANG Zhiying, ZHOU Zuoyong. Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics Analysis of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Isolated from Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 680-687. |
| [4] | ZHOU Zhiyu, DU Jige, XIN Ruolan, ZHANG Jiawen, PAN Chenfan, YIN Chunsheng, CHEN Xiaoyun, ZHU Zhen. Isolation and Identification of Three Lumpy Skin Disease Viruses in China and Their GPCR Gene Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5620-5630. |
| [5] | WANG Zhiyuan, LIU Boqi, XU Zhiying, XU Sijia, XING Jiabao, ZHANG Guihong, WANG Heng, SUN Yankuo. Analysis of ORF5 Gene Variation of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus in Local Regions of China from 2021 to 2022 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(9): 3812-3823. |
| [6] | CHEN Hongjian, CAO Yan, FAN Jie, GAN Rongxuan, SONG Wenbo, YU Shengwei, YANG Ting, ZHAO Yanxia, WEI Chunyan, XIE Rui, HUA Lin, PENG Zhong, WU Bin. Prevalence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Pseudorabies Virus within Pig Slaughterhouses in Hubei Province of China during 2020-2022 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 2972-2981. |
| [7] | CHANG Yiming, TANG Cheng, YUE Hua. Molecular Epidemiological Investigation of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Yaks [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 2030-2041. |
| [8] | WANG Mengjiao, JIANG Qian, MA Xuejun, XIA Ruiyang, GUO Xueping, SUN Lei, ZHONG Qi, MA Xuelian, YAO Gang. Molecular Epidemiological Investigation of Bovine Coronavirus in Calf Diarrhea in Main Cattle Producing Areas of Xinjiang [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5125-5133. |
| [9] | ZHANG Ao, TAN Bin, LIU Kexin, LIU Jiali, ZHANG Shuqin. Genomic Characterization Analysis of a H1N1 Subtype Swine Influenza Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4866-4871. |
| [10] | CHANG Hao, QIU Yingwu, PENG Jie, GAO Qi, SONG Zebu, CHEN Yang, LI Wei, LIN Limiao, CAO Xuezhen, ZHOU Qingfeng, ZHANG Guihong, LI Qunhui, ZHENG Zezhong. Establishment of a Dual Real-time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR Assay for Genotype I ASFV [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4428-4432. |
| [11] | ZHOU Qun, YANG Yuan, SONG Xin, HE Xinyi, CAO Hui, ZHANG Bin. Detection of Feline Parvovirus and Mutation Analysis of VP2 Gene in Chengdu from 2017 to 2021 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(4): 1303-1309. |
| [12] | GUO Yanyan, LIANG Canxin, LI Jinqun, DONG Xinyi, LIAO Ming, CAO Weisheng. Study on Molecular Epidemiology of ALV-K in Guangdong Local Breed Chickens and the Effect of 12 bp Deletion of gag Gene on Virus Replication Ability in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(11): 3956-3966. |
| [13] | CAI Weilong, LI Na, FENG Yaoyu, XIAO Lihua. Advances in Molecular Epidemiology of Giardia duodenalis from Cattle in China [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(2): 300-310. |
| [14] | ZHAO Wenxing, WU Kexin, GUO Ziyu, ZHANG Yunhao, TANG Lihui, LIU Yiling, MO Chonghui, ZHAO Baoyu, LU Hao. Isolation and Identification of Endophytic Fungi in Thermopsis lanceolata [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(10): 2986-2994. |
| [15] | GUO Huifang, LI Ning, WANG Baiyu, QIAO Qilong, HUANG Qing, LI Yongtao, WANG Zeng, ZHAO Jun. Analysis of the Transcription Level of NLRP3 Gene in Fowl Adenovirus Serotype 4 Infected Chicken Tissues by a Real-time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(1): 195-201. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||