





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 4980-4991.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.11.017
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
Huan WANG1( ), Taoyu CHEN1, Hui WU2, Yong MENG1, Shiyuan LI1, Hejie QIAN1, Shihua NIU1, Churiga MAN1, Qiaoling CHEN1, Hongyan GAO1, Li DU1, Fengyang WANG1, Si CHEN1,*(
), Taoyu CHEN1, Hui WU2, Yong MENG1, Shiyuan LI1, Hejie QIAN1, Shihua NIU1, Churiga MAN1, Qiaoling CHEN1, Hongyan GAO1, Li DU1, Fengyang WANG1, Si CHEN1,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-14
Online:2024-11-23
Published:2024-11-30
Contact:
Si CHEN
E-mail:772101737@qq.com;chensi.ruth@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
Huan WANG, Taoyu CHEN, Hui WU, Yong MENG, Shiyuan LI, Hejie QIAN, Shihua NIU, Churiga MAN, Qiaoling CHEN, Hongyan GAO, Li DU, Fengyang WANG, Si CHEN. Polymorphism Analysis of the ATG16L2 Gene Promoter Region in Hainan Black Goat[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 4980-4991.
Table 1
Primers information of ATG16L2 gene in Hainan Black goat"
| 名称Name | 上游引物(5′→3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′→3′) Reverse primer | 产物长度/bp Length | 退火温度/℃ Annealing temperature |
| P1 | TGGGCAGGAGCCAGACTAAGC | AAGGGGATGGTACGCATGGAG | 668 | 63.2 |
| P2 | CGGCTAGCGGAAATCCTGACCCCAATATGAC | CAGCTGATTTCATCGAGCAAACCCC | 847 | 62.0 |
| P3 | GGCTAGCGCTCCACTGAATCACTCCTT | TCTGGACCAGGCGGTGCACTAAACT | 658 | 62.0 |
| P4 | GGCTAGCGCTGCCTGGTATCCGTTTC | CCTCGAGATAGGGCCTTTTGCGTTCGATCC | 729 | 62.0 |
| P5 | CAGCAGCATACACGCTCCTGCG | GCTGAGCCGGCCAGCAGCT | 294 | 66.6 |
| P6 | ATCCTGACCCCAATATGACTC | ATGGTACGCATGGAGGATC | 198 | 55.3 |
| P7 | ATTGGTCATCACTTCATGGCTTTCT | CATATTGTCAAGGCTTTGCCTTCAT | 317 | 60.0 |
Table 2
Softwares for bioinformatics analysis of the ATG16L2 promoter region"
| 软件分析Software analysis | 网站Website |
| 启动子序列的特征分析Characteristic analysis of promoter sequences | |
| 重复元件分析Repeat element analysis | |
| 顺式作用元件分析Analysis of cis-acting elements | |
| CpG岛位点分析CpG island site analysis | |
| 转录因子结合预测Transcription factor binding prediction | |
| 转录因子结合预测Transcription factor binding prediction |
Table 3
The similarity of the ATG16L2 gene between Hainan Black goats and different species"
| 物种Species | 相似性/% Similarity | 物种Species | 相似性/% Similarity | |
| 羚羊Budorcas taxicolor | 99.03 | 绵羊Ovis aries | 98.64 | |
| 普通牛Bos taurus | 96.81 | 瘤牛Bos indicus | 91.61 | |
| 猪Sus scrofa | 86.87 | 马Equus caballus | 86.51 | |
| 雪貂Mustela putorius furo | 82.71 | 老虎Panthera tigris | 80.35 | |
| 骆驼Camelus dromedarius | 76.47 | 双峰驼Camelus bactrianus | 74.47 | |
| 蓝鲸Balaenoptera musculus | 71.44 | 人Homo sapiens | 68.23 | |
| 狗Canis lupus familiaris | 64.19 | 羊驼Vicugna pacos | 62.73 | |
| 鸭嘴兽Ornithorhynchus anatinus | 62.44 | 大熊猫Ailuropoda melanoleuca | 61.76 | |
| 家鼠Mus musculus | 53.87 | 鸡Gallus gallus | 42.02 | |
| 斑马鱼Danio rerio | 38.34 |
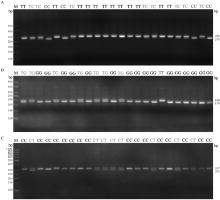
Fig. 5
Electrophoresis of PCR-RFLP detection of SNP sites in the promoter region of the ATG16L2 gene in Hainan Black goat A. The SNP1 site is digested with the restriction enzyme Pvu Ⅱ; B. The SNP2 site is digested with the restriction enzyme BamH Ⅰ; C. The SNP3 site is digested with the restriction enzyme Nde Ⅰ"

Table 4
SNP sites population genetics analysis in the promoter region of the ATG16L2 gene in Hainan Black goat"
| SNP位点SNP site | 基因型频率(样本数) Genotype frequency (sample number) | 等位基因频率Allele frequency | Ho | He | Ne | PIC | χ2 (HWE) |
| SNP1 (g.30667970T>C) | TT:0.365(73) | T:0.575 | 0.511 | 0.489 | 1.956 | 0.369 | 3.957 (P>0.05) |
| TC:0.420(84) | C:0.425 | ||||||
| CC:0.215(43) | |||||||
| SNP2 (g.30668540T>C) | GG:0.505(101) | G:0.723 | 0.599 | 0.401 | 1.669 | 0.321 | 1.439 (P>0.05) |
| TG:0.435(87) | T:0.278 | ||||||
| TT:0.060(12) | |||||||
| SNP3 (g.30668664C>T) | CC:0.800(160) | C:0.900 | 0.820 | 0.180 | 1.220 | 0.164 | 2.469 (P>0.05) |
| CT:0.200(40) | T:0.100 | ||||||
| TT:0.000(0) |
| 1 |
RIZZOLLO F , MORE S , VANGHELUWE P , et al. The lysosome as a master regulator of iron metabolism[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2021, 46 (12): 960- 975.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.07.003 |
| 2 |
ALBANO G D , MONTALBANO A M , GAGLIARDO R , et al. Autophagy/mitophagy in airway diseases: impact of oxidative stress on epithelial cells[J]. Biomolecules, 2023, 13 (8): 1217.
doi: 10.3390/biom13081217 |
| 3 |
ALULA K M , THEISS A L . Autophagy in Crohn's disease: converging on dysfunctional innate immunity[J]. Cells, 2023, 12 (13): 1779.
doi: 10.3390/cells12131779 |
| 4 |
CHEN L , YANG L M , LI Y Y , et al. Autophagy and inflammation: regulatory roles in viral infections[J]. Biomolecules, 2023, 13 (10): 1454.
doi: 10.3390/biom13101454 |
| 5 | HU J T , ZHAO W , NIU L L , et al. Gene organization and characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Hainan black goat (Capra hircus)[J]. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal, 2016, 27 (3): 1656- 1657. |
| 6 |
WANG D F , ZHOU L L , ZHOU H L , et al. Effects of nutrition level of concentrate-based diets on growth performance and carcass characteristics of Hainan black goats[J]. Trop Anim Health Prod, 2014, 46 (5): 783- 788.
doi: 10.1007/s11250-014-0565-x |
| 7 |
SHI L G , ZHANG Y , WU L L , et al. Moderate coconut oil supplement ameliorates growth performance and ruminal fermentation in Hainan black goat kids[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2020, 7, 622259.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.622259 |
| 8 |
WANG D Y , YUAN T L , LIU J M , et al. ATG16L2 inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation through promoting ATG5-12-16L1 complex assembly and autophagy[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2022, 52 (8): 1321- 1334.
doi: 10.1002/eji.202149764 |
| 9 |
MO Y J , ZHANG W , WEN Q W , et al. Corrigendum to "Genetic association analysis of ATG16L1 rs2241880, rs6758317 and ATG16L2 rs11235604 polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Chinese population"[Int. Immunopharmacol. 93 (2021) 107378][J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 104, 108511.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108511 |
| 10 |
LUU L D W , POPPLE G , TSANG S P W , et al. Genetic variants involved in innate immunity modulate the risk of inflammatory bowel diseases in an understudied Malaysian population[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 37 (2): 342- 351.
doi: 10.1111/jgh.15752 |
| 11 | MA T , WU S , YAN W , et al. A functional variant of ATG16L2 is associated with Crohn's disease in the Chinese population[J]. Colorectal Dis, 2016, 18 (11): O420- O426. |
| 12 | MOLINEROS J E , YANG W L , ZHOU X J , et al. Confirmation of five novel susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and integrated network analysis of 82 SLE susceptibility loci[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2017, 26 (6): 1205- 1216. |
| 13 |
ZHONG C H , WANG Y Y , LIU C P , et al. A novel single-nucleotide polymorphism in WNT4 promoter affects its transcription and response to FSH in chicken follicles[J]. Genes (Basel), 2022, 13 (10): 1774.
doi: 10.3390/genes13101774 |
| 14 |
LI K Y , LIU Y F , HE X Y , et al. A novel SNP in the promoter region of IGF1 associated with Yunshang black goat kidding number via promoting transcription activity by SP1[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10, 873095.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.873095 |
| 15 |
ZHANG P , FU Y , ZHANG R , et al. Association of KCTD15 gene with fat deposition in pigs[J]. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl), 2022, 106 (3): 537- 544.
doi: 10.1111/jpn.13587 |
| 16 | WANG P , LI W T , LIU Z Y , et al. Analysis of the association of two SNPs in the promoter regions of the PPP2R5C and SLC39A5 genes with litter size in Yunshang black goats[J]. Animals (Basel), 2022, 12 (20): 2801. |
| 17 |
MAŃKOWSKA A , BRYM P , SOBIECH P , et al. Promoter polymorphisms in STK35 and IFT27 genes and their associations with boar sperm freezability[J]. Theriogenology, 2022, 189, 199- 208.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.06.023 |
| 18 |
ROY J , ANAND K , MOHAPATRA S , et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in piRNA-pathway genes: an insight into genetic determinants of human diseases[J]. Mol Genet Genomics, 2020, 295 (1): 1- 12.
doi: 10.1007/s00438-019-01612-5 |
| 19 |
WORKU D , GOWANE G , VERMA A . Genetic variation in promoter region of the bovine LAP3 gene associated with estimated breeding values of milk production traits and clinical mastitis in dairy cattle[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18 (5): e0277156.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277156 |
| 20 | ANJUM K H , NADEEM A , JAVED M , et al. Genomic and computational analysis of novel SNPs in TNP1 gene promoter region of Bos indicus breeding bulls[J]. Genet Res (Camb), 2022, 2022, 9452234. |
| 21 | YUAN Z H , GE L , SU P W , et al. NCAPG regulates myogenesis in sheep, and SNPs located in its putative promoter region are associated with growth and development traits[J]. Animals (Basel), 2023, 13 (20): 3173. |
| 22 |
WORKU D , GOWANE G , ALEX R , et al. Inputs for optimizing selection platform for milk production traits of dairy Sahiwal cattle[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17 (5): e0267800.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267800 |
| 23 |
WORKU D , GOWANE G R , MUKHERJEE A , et al. Associations between polymorphisms of LAP3 and SIRT1 genes with clinical mastitis and milk production traits in Sahiwal and Karan Fries dairy cattle[J]. Vet Med Sci, 2022, 8 (6): 2593- 2604.
doi: 10.1002/vms3.924 |
| 24 |
HAN Y C , TAN T , LI Z X , et al. Identification of selection signatures and loci associated with important economic traits in Yunan black and Huainan pigs[J]. Genes (Basel), 2023, 14 (3): 655.
doi: 10.3390/genes14030655 |
| 25 |
YAO D W , GUO D C , ZHANG Y K , et al. Identification of mutations in porcine STAT5A that contributes to the transcription of CISH[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2023, 9, 1090833.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1090833 |
| 26 |
CHEN S , CHAI M L , TIAN C , et al. Genetic variants of fatty acid elongase 6 in Chinese Holstein cow[J]. Gene, 2018, 670, 123- 129.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.073 |
| 27 |
KHOR B , CONWAY K L , OMAR A S , et al. Distinct tissue-specific roles for the disease-associated autophagy genes ATG16L2 and ATG16L1[J]. J Immunol, 2019, 203 (7): 1820- 1829.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800419 |
| 28 |
ZHU Z J , HE M N , ZHANG T , et al. LSD1 promotes the FSH responsive follicle formation by regulating autophagy and repressing Wt1 in the granulosa cells[J]. Sci Bull (Beijing), 2024, 69 (8): 1122- 1136.
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2024.01.015 |
| 29 |
LUO Y B , XU Q , XUE M M , et al. Novel haplotype in the HHEX gene promoter associated with body length in pigs[J]. Genes (Basel), 2023, 14 (2): 511.
doi: 10.3390/genes14020511 |
| 30 | HATTORI N , LIU Y Y , USHIJIMA T . DNA methylation analysis[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2023, 2691, 165- 183. |
| 31 |
LENTJES M H , NIESSEN H E , AKIYAMA Y , et al. The emerging role of GATA transcription factors in development and disease[J]. Expert Rev Mol Med, 2016, 18, e3.
doi: 10.1017/erm.2016.2 |
| 32 |
SCHANG G , ONGARO L , BRÛLÉ E , et al. Transcription factor GATA2 may potentiate follicle-stimulating hormone production in mice via induction of the BMP antagonist gremlin in gonadotrope cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2022, 298 (7): 102072.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102072 |
| 33 |
ROBBINS D J , PAVLETICH T S , PATIL A T , et al. Linking GATA2 to myeloid dysplasia and complex cytogenetics in adult myelodysplastic neoplasm and acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Blood Adv, 2024, 8 (1): 80- 92.
doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023011554 |
| 34 |
ZHANG J Y , HE L , WANG Z W , et al. Decreasing GDF15 promotes inflammatory signals and neutrophil infiltration in psoriasis models[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2023, 143 (3): 419- 430.e8.
doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2022.07.026 |
| 35 |
FABOZZI F , MASTRONUZZI A , CEGLIE G , et al. GATA 2 deficiency: focus on immune system impairment[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13, 865773.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.865773 |
| 36 | MARIN-BEJAR O , ROMERO-MOYA D , RODRIGUEZ-UBREVA J , et al. Epigenome profiling reveals aberrant DNA methylation signature in GATA2 deficiency[J]. Haematologica, 2023, 108 (9): 2551- 2557. |
| 37 |
SETO E , SHI Y , SHENK T . YY1 is an initiator sequence-binding protein that directs and activates transcription in vitro[J]. Nature, 1991, 354 (6350): 241- 245.
doi: 10.1038/354241a0 |
| 38 |
GOPALAKRISHNAN J , TESSNEER K L , FU Y , et al. Variants on the UBE2L3/YDJC autoimmune disease risk haplotype increase UBE2L3 expression by modulating CCCTC-binding factor and YY1 binding[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2022, 74 (1): 163- 173.
doi: 10.1002/art.41925 |
| 39 |
KHACHIGIAN L M . The Yin and Yang of YY1 in tumor growth and suppression[J]. Int J Cancer, 2018, 143 (3): 460- 465.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.31255 |
| [1] | Xuanyi WANG, Yawei SUN, Yuwei LONG, Liying WANG, Yuxin ZHOU, Na LI, Xuelian MA, Hongqiong ZHAO, Gang YAO. Correlation Analysis of FOXP3, FSHR, FMR1 Gene Polymorphisms and Reproductive Hormones in Infertile Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2727-2740. |
| [2] | ZHOU Yang, WU Weizi, CAO Weisheng, WANG Fuguang, XU Xiuqiong, ZHONG Wenxia, WU Liyang, YE Jian, LU Shousheng. A Whole Genome Sequencing Method for African Swine Fever Virus based on Nanopore Sequencing Technology was Established [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2080-2089. |
| [3] | CAO Yuzhu, XING Yuxin, MA Chenglin, GUAN Hongbo, JIA Qihui, KANG Xiangtao, TIAN Yadong, LI Zhuanjian, LIU Xiaojun, LI Hong. Biological Characterization of Chicken FGF6 Gene and Association of Its Polymorphisms with Economic Traits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1536-1550. |
| [4] | YANG Yang, YU Qian, LIU Yucheng, YANG Hua, ZHAO Zhuo, WANG Limin, ZHOU Ping, YANG Qingyong, DAI Rong. Identification and Tissue Expression Analysis of the Sheep MYL Gene Family [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1551-1564. |
| [5] | TIAN Rui, XU Sixiang, XIE Feng, LIU Guangjin, WANG Gang, LI Qingxia, DAI Lei, XIE Guoxin, ZHANG Qiongwen, LU Yajing, WANG Guangwen, WANG Jinxiu, ZHANG Wei. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Genome of Clostridium perfringens Isolated from Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1707-1715. |
| [6] | WANG Dongliang, REN Jing, HAO Qinqin, LI Pengfei. Identification and Transcriptional Regulation Analysis of Core Promoter of Bovine CART Gene [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(9): 3689-3699. |
| [7] | DU Xiaodi, HOU Wei, SU Zhonghua, MA Qingmei, HE Xue, HUA Ruiqi, YANG Aiguo, YANG Guangyou. Bioinformatics and Expression Analysis of Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzyme Gene Family of Echinococcus granulosus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2605-2618. |
| [8] | MENG Qiuchi, LU Guangyu, CHEN Dingshuang, LIN Yaqiu, WANG Ruilong, ZHONG Chaosong, WANG Yong, LIU Wei, WANG Youli, LI Yanyan, LI Zhixiong. Goats GPR35 Gene Expression Characteristics Analysis and the Effect on Subcutaneous Fat Cell Differentiation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 4993-5007. |
| [9] | XU Tingting, QI Fenfang, HUANG Shihui, NIU Xi, LI Sheng, RAN Xueqin, WANG Jiafu, XIE Jian. Study of the Polymorphisms of Structural Variation and the Expression of MAP3K4 gene in Xiang Pig [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5046-5055. |
| [10] | SONG Pengyan, WANG Siwei, YUE Qiaoxian, ZHANG Yinliang, CHEN Xiaoyong, ZHOU Rongyan. Identification of oar-miR-200b Promoter and Effects on Mitochondrial Function in Follicular Granulosa Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5066-5076. |
| [11] | CHEN Cheng, QIAO Xibo, SUN Yi, KANG Li, JIANG Yunliang. Study on the Polymorphism and Genetic Effect of the -868 Locus of FSHR Gene on Egg Laying Traits in Langya Chickens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4560-4568. |
| [12] | YANG Yang, ZHOU Ziwei, ZHANG Jingyi, YANG Shuo, WANG Boyu, GE Nan, LIN Ye, HOU Xiaoming. Analysis on SP1 Gene Structure and Its Function on Milk Fat Synthesis in Holstein Dairy Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 2970-2981. |
| [13] | CEN Xin, YANG Tingting, ZHAO Zunfu, WEN Yongping, ZHANG Huanrong. Isolation, Identification, Biological Characteristics and Genome Analysis of a Virulent Salmonella Phage [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(8): 2677-2688. |
| [14] | GAO Dengke, ZHAO Hongcong, DONG Hao, JIN Yaping, CHEN Huatao. The Cloning, Expression Vector Construction and Function Analysis of Goat RORα Gene [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(6): 1779-1794. |
| [15] | WNAG Xuemei, ZHAI Zhe, CHEN Qiaoling, WU Yanru, WU Haotian, HUANG Huixian, LIU Zhiyong, LI Chongrui, MANCHU Riga, WANG Fengyang, DU Li, CHEN Si. Screening and Analysis of Transcriptional Regulatory Elements of MBL2 Gene in Hainan Black Goat [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(6): 1795-1806. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||