





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 2510-2518.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.06.022
• Animal Nutrition and Feeds • Previous Articles Next Articles
Sijia LIU1,2( ), Nan ZHENG1, Jiaqi WANG1, Shengguo ZHAO1,*(
), Nan ZHENG1, Jiaqi WANG1, Shengguo ZHAO1,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-04
Online:2024-06-23
Published:2024-06-28
Contact:
Shengguo ZHAO
E-mail:liusijia1214@163.com;zhaoshengguo1984@163.com
CLC Number:
Sijia LIU, Nan ZHENG, Jiaqi WANG, Shengguo ZHAO. Effects of Red Clover Extract on Microbial Diversity and Urea Decomposition in Rumen Fermentation of Dairy Cows in vitro[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2510-2518.
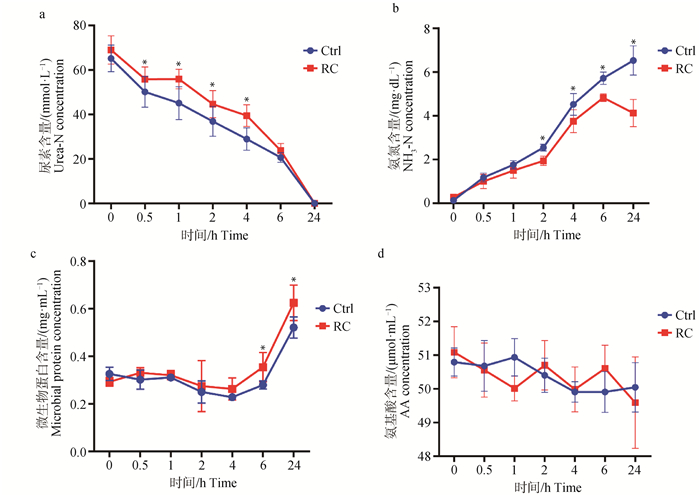
Fig. 1
Effects of red clover extract on nitrogen metabolism a. Urea content; b. NH3-N content; c. Microbial protein content; d. Total free amino acid content. * indicates significant differences between treatments (P < 0.05); Ctrl. Control group; RC. Supplement red clover extract treatment group; The error bar indicates the SEM; The same as below"
| 1 |
KERTZ A F . Review: urea feeding to dairy cattle: a historical perspective and review[J]. Prof Anim Sci, 2010, 26 (3): 257- 272.
doi: 10.15232/S1080-7446(15)30593-3 |
| 2 |
HAILEMARIAM S , ZHAO S G , HE Y , et al. Urea transport and hydrolysis in the rumen: a review[J]. Anim Nutr, 2021, 7 (4): 989- 996.
doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2021.07.002 |
| 3 | 刘思佳. 奶牛瘤胃中活性尿素分解菌群多样性分析[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020. |
| LIU S J. Diversity analyze of active ureolytic bacterial community in the rumen of dairy cows[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 4 | GETAHUN D , ALEMNEH T , AKEBEREGN D , et al. Urea metabolism and recycling in ruminants[J]. Biomed J Sci Tech Res, 2019, 20 (1): 14790- 14796. |
| 5 |
SOUZA V C , AGUILAR M , VAN AMBURGH M , et al. Milk urea nitrogen variation explained by differences in urea transport into the gastrointestinal tract in lactating dairy cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2021, 104 (6): 6715- 6726.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-19787 |
| 6 |
WAGNER J J , ENGLE T E , BRYANT T C . The effect of rumen degradable and rumen undegradable intake protein on feedlot performance and carcass merit in heavy yearling steers[J]. J Anim Sci, 2010, 88 (3): 1073- 1081.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2009-2111 |
| 7 |
CECONI I , RUIZ-MORENO M J , DILORENZO N , et al. Effect of urea inclusion in diets containing corn dried distillers grains on feedlot cattle performance, carcass characteristics, ruminal fermentation, total tract digestibility, and purine derivatives-to-creatinine index[J]. J Anim Sci, 2015, 93 (1): 357- 369.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2014-8214 |
| 8 |
ZHAO S G , WANG J Q , ZHENG N , et al. Reducing microbial ureolytic activity in the rumen by immunization against urease therein[J]. BMC Vet Res, 2015, 11, 94.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-015-0409-6 |
| 9 |
ZHANG Z Y , LI M , ZHANG X Y , et al. A novel urease inhibitor of ruminal microbiota screened through molecular docking[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (17): 6006.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21176006 |
| 10 |
HE Y , ZHANG X Y , LI M , et al. Coptisine: a natural plant inhibitor of ruminal bacterial urease screened by molecular docking[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2022, 808, 151946.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151946 |
| 11 |
GUTIERREZ-BAÑUELOS H , ANDERSON R C , CARSTENS G E , et al. Effects of nitroethane and monensin on ruminal fluid fermentation characteristics and nitrocompound-metabolizing bacterial populations[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2008, 56 (12): 4650- 4658.
doi: 10.1021/jf800756c |
| 12 |
PATRA A K , SAXENA J . Dietary phytochemicals as rumen modifiers: a review of the effects on microbial populations[J]. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2009, 96 (4): 363- 375.
doi: 10.1007/s10482-009-9364-1 |
| 13 |
赵玉超, 余诗强, 蒋林树. 生物类黄酮调控瘤胃微生态系统的作用——聚焦甲烷减排[J]. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34 (9): 5452- 5465.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2022.09.002 |
|
ZHAO Y C , YU S Q , JIANG L S . Roles of bioflavonoids in regulating rumen microecosystems: focus on methane emission reduction[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34 (9): 5452- 5465.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2022.09.002 |
|
| 14 |
MA J , ZHENG Y M , TANG W J , et al. Dietary polyphenols in lipid metabolism: a role of gut microbiome[J]. Anim Nutr, 2020, 6 (4): 404- 409.
doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.08.002 |
| 15 | STEINSHAMN H . Effect of forage legumes on feed intake, milk production and milk quality-a review[J]. Anim Sci Pap Rep, 2010, 28 (3): 195- 206. |
| 16 |
ZHAN J S , LIU M M , SU X S , et al. Effects of alfalfa flavonoids on the production performance, immune system, and ruminal fermentation of dairy cows[J]. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci, 2017, 30 (10): 1416- 1424.
doi: 10.5713/ajas.16.0579 |
| 17 |
WEATHERBURN M W . Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia[J]. Anal Chem, 1967, 39 (8): 971- 974.
doi: 10.1021/ac60252a045 |
| 18 | JIN D , ZHAO S G , ZHENG N , et al. Differences in ureolytic bacterial composition between the rumen digesta and rumen wall based on ureC gene classification[J]. Front Microbiol, 2017, 8, 385. |
| 19 |
CALLAHAN B J , MCMURDIE P J , ROSEN M J , et al. DADA2:high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data[J]. Nat Methods, 2016, 13 (7): 581- 583.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3869 |
| 20 |
WANG Q , GARRITY G M , TIEDJE J M , et al. Naïve bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2007, 73 (16): 5261- 5267.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00062-07 |
| 21 |
JIN D , ZHAO S G , ZHENG N , et al. Urea metabolism and regulation by rumen bacterial urease in ruminants-a review[J]. Ann Anim Sci, 2018, 18 (2): 303- 318.
doi: 10.1515/aoas-2017-0028 |
| 22 |
WANG R , WANG M , UNGERFELD E M , et al. Nitrate improves ammonia incorporation into rumen microbial protein in lactating dairy cows fed a low-protein diet[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2018, 101 (11): 9789- 9799.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-14904 |
| 23 |
TROYER A F , STOEHR H , Willet M . Hays, great benefactor to plant breeding and the founder of our association[J]. J Hered, 2003, 94 (6): 435- 441.
doi: 10.1093/jhered/esg099 |
| 24 |
FLYTHE M , KAGAN I . Antimicrobial effect of red clover (Trifolium pratense) phenolic extract on the ruminal hyper ammonia-producing bacterium, Clostridium sticklandii[J]. Curr Microbiol, 2010, 61 (2): 125- 131.
doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9586-5 |
| 25 |
LIU S J , ZHANG Z Y , HAILEMARIAM S , et al. Biochanin A inhibits ruminal nitrogen-metabolizing bacteria and alleviates the decomposition of amino acids and urea in vitro[J]. Animals, 2020, 10 (3): 368.
doi: 10.3390/ani10030368 |
| 26 |
COLEMAN G S , SANDFORD D C . The uptake and utilization of bacteria, amino acids and nucleic acid components by the rumen ciliate eudiplodinium maggii[J]. J Appl Bacteriol, 1979, 47 (3): 409- 419.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01201.x |
| 27 |
VANHATALO A , KUOPPALA K , AHVENJÄRVI S , et al. Effects of feeding grass or red clover silage cut at two maturity stages in dairy cows.1.Nitrogen metabolism and supply of amino acids[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2009, 92 (11): 5620- 5633.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2009-2249 |
| 28 |
CHOWDHURY M R , WILKINSON R G , SINCLAIR L A . Feeding lower-protein diets based on red clover and grass or alfalfa and corn silage does not affect milk production but improves nitrogen use efficiency in dairy cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2023, 106 (3): 1773- 1789.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2022-22607 |
| 29 |
BRODERICK G A . Utilization of protein in red clover and alfalfa silages by lactating dairy cows and growing lambs[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2018, 101 (2): 1190- 1205.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13690 |
| 30 |
SALAMI S A , VALENTI B , LUCIANO G , et al. Dietary cardoon meal modulates rumen biohydrogenation and bacterial community in lambs[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 16180.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95691-3 |
| 31 |
DAO T K , DO T H , LE N G , et al. Understanding the role of Prevotella genus in the digestion of lignocellulose and other substrates in vietnamese native goats' rumen by metagenomic deep sequencing[J]. Animals, 2021, 11 (11): 3257.
doi: 10.3390/ani11113257 |
| 32 |
BETANCUR-MURILLO C L , AGUILAR-MARÍN S B , JOVEL J . Prevotella: a key player in ruminal metabolism[J]. Microorganisms, 2022, 11 (1): 1.
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010001 |
| 33 |
ACCETTO T , AVGUŠTIN G . The diverse and extensive plant polysaccharide degradative apparatuses of the rumen and hindgut Prevotella species: a factor in their ubiquity?[J]. Syst Appl Microbiol, 2019, 42 (2): 107- 116.
doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2018.10.001 |
| 34 |
KOVATCHEVA-DATCHARY P , NILSSON A , AKRAMI R , et al. Dietary fiber-induced improvement in glucose metabolism is associated with increased abundance of Prevotella[J]. Cell Metab, 2015, 22 (6): 971- 982.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.10.001 |
| 35 |
NATIVIDAD J M , LAMAS B , PHAM H P , et al. Bilophila wadsworthia aggravates high fat diet induced metabolic dysfunctions in mice[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9 (1): 2802.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05249-7 |
| 36 |
OLSON C A , IÑIGUEZ A J , YANG G E , et al. Alterations in the gut microbiota contribute to cognitive impairment induced by the ketogenic diet and hypoxia[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2021, 29 (9): 1378- 1392.e6.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.07.004 |
| [1] | Zhibin LUO, Huimin OU, Jianzhong LI, Zhiliang TAN, Jinzhen JIAO. Effects of Low Protein Diet Supplemented with Rumen-protected Amino Acids on Growth Performance, Nutrient Apparent Digestibility and Meat Quality of Hulun Buir Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2498-2509. |
| [2] | LONG Tanghui, ZHOU Jianghui, ZHAN Yanbo, ZHANG Jian, ZHAO Xianghui, LI Yanjiao, OUYANG Kehui, QIU Qinghua. Research Progress on LuxS/AI-2 Quorum Sensing of Rumen Microbe in Ruminants [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1893-1903. |
| [3] | CHANG Xindan, HU Fan, WU Zhiwu, YE Bingsen, LIU Tiehai, LIN Jie, HE Zhixiong, TAN Zhiliang. Effect of High Proportion Rumen Bypass Fat Diet on Feeding Behavior of Growing Mutton Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1077-1084. |
| [4] | ZUO Zizhen, WANG Haibo, CHAI Zhixin, FU Jianhui, ZHANG Xiangfei, LUO Xiaolin, ZHONG Jincheng. Effects of Rumen-protected Methionine on Meat Quality, Volatile Flavor Compounds and Fatty Acid Composition of Yak Semitendinosus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1102-1114. |
| [5] | FAN Dingkun, ZHANG Jixian, FU Yuze, MA Tao, BI Yanliang, ZHANG Naifeng. Research Progress of Ruminant Microbial Culturomics [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 51-58. |
| [6] | WU Zhili, YAO Junhu, LEI Xinjian. Research Progress of Rumen-protected Glucose on Nutritional Regulation in Perinatal Dairy Animals [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3173-3182. |
| [7] | MA Youji, CHEN Pengfei, MA Qing, WU Yi. Effects of Different Exercise Amounts on Rumen Microflora Diversity of Tan Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3393-3405. |
| [8] | XIONG Chengkun, ZHANG Daoliang, YANG Yue, DING Hongyan, ZHAO Jie, LI Yu, WANG Xichun, FENG Shibin, ZHAO Chang, TANG Jishun, WU Jinjie. Effect of Rutin on Rumen Fermentation, Rumen Flora Structure and Antioxidant Properties in Perinatal Hu Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 2898-2909. |
| [9] | WU Yicheng, RAN Tao, ZHOU Chuanshe, TAN Zhiliang. Evaluation of the Viral Community Composition in Goat Rumen Fluid, Based on Metagenomic Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 2932-2941. |
| [10] | ZHAO Wei, Mahmoud M. Abdelsattar, CHAI Jianmin, WANG Xin, DIAO Qiyu, ZHANG Naifeng. Research Progress of Rumen Microbiota Transplantation and Its Application [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 1792-1803. |
| [11] | WANG Weihao, DUAN Yan, WANG Hongdi, DOU Lu, LIU Ting, KANG Letian, SUN Lina, AO Tehenggerile, JIN Ye. Effects of Feeding Regimens on Growth Performance, Slaughter Performance, Meat Quality and Rumen Bacteria Community of Sunit Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 1085-1094. |
| [12] | SUN Meijie, CAO Liwen, ZHENG Wenjin, SHEN Junshi, ZHU Weiyun. Effect of Dietary Urea Supplementation on Liver Ammonia Metabolism in Fattening Hu Lambs Based on Transcriptome Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 1148-1159. |
| [13] | ZHANG Qiqi, WANG Junmei, YUE Ziqi, GUO Yixin, SHI Liyuan, ZHANG Xiaohong, ZOU Huawei, PENG Quanhui, XUE Bai, WANG Lizhi, WANG Zhisheng, HU Rui. Effect of LPS on the Complement C3 Activation and ATP Production in the Rumen Epithelial Cells of Yak [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4664-4675. |
| [14] | CHI Xingzi, LI Yaoxing, WANG Huiting, YAN Ming’en, YANG Shijing, YANG Bowen, SUN Han, GUO Shining, SHI Dayou, WU Li, LIU Cui. Effect of Echinacea purpurea Extract Combined with Sulfasalazine on Immune Imbalance of Th17/Treg in Rats with Damp-Heat Syndrome [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4817-4826. |
| [15] | CHI Xingzi, YANG Shijing, YANG Bowen, SUN Han, YAO Lili, GU Daxing, GUO Shining, SHI Dayou, WU Li, LIU Cui. Effect and Mechanism of Echinacea purpurea Extract in Rats with Dampness-heat Diarrhea [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(1): 380-391. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||