





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (9): 4472-4490.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.09.028
• Animal Nutrition and Feeds • Previous Articles Next Articles
GUI Ruohong( ), CAO Hongzhan, LIU Songzan, LIU Jixiang, ZHAO Jialong, LU Chunlian*(
), CAO Hongzhan, LIU Songzan, LIU Jixiang, ZHAO Jialong, LU Chunlian*( )
)
Received:2024-10-22
Online:2025-09-23
Published:2025-09-30
Contact:
LU Chunlian
E-mail:a15287132728@163.com;13833038290@163.com
CLC Number:
GUI Ruohong, CAO Hongzhan, LIU Songzan, LIU Jixiang, ZHAO Jialong, LU Chunlian. Effects of Different Dietary Metabolizable Energy and Standard Ileal Digestible Lysine Levels on Performance of High-Producing Lactating Shenxian Sows[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4472-4490.
Table 2
Composition and nutrient levels of basic rations for lactating sows (dry matter basis)"
| 项目Item | 组别Group | |||||
| LL组 | LM组 | LH组 | HL组 | HM组 | HH组 | |
| 原料/% Ingredient | ||||||
| 玉米Corn | 61.94 | 61.81 | 61.79 | 60.50 | 60.40 | 60.00 |
| 小麦麸Wheat bran | 6.06 | 6.66 | 7.24 | 5.93 | 6.52 | 7.45 |
| 大豆粕Soybean meal | 20.49 | 19.65 | 18.80 | 20.80 | 19.96 | 19.04 |
| 玉米胚芽粕Corn germ meal | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 |
| 大豆油Soybean oil | 3.01 | 3.10 | 3.10 | 4.29 | 4.34 | 4.44 |
| L-赖氨酸盐酸盐(98.5%) L-Lysine HCl | 0.12 | 0.39 | 0.66 | 0.11 | 0.39 | 0.66 |
| DL-蛋氨酸(99%) DL-Methionine | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| L-苏氨酸(99%) L-Threonine | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.16 |
| L-色氨酸(99%) L-Tryptophan | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| L-缬氨酸(99%) L-Valine | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.16 |
| 预混料Premix1 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 |
| 合计Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 营养水平/% Nutrient level2 | ||||||
| 代谢能/(MJ·kg-1) Metabolizable energy | 13.45 | 13.46 | 13.45 | 13.72 | 13.72 | 13.72 |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein | 15.78 | 15.64 | 15.59 | 15.75 | 15.56 | 15.70 |
| 钙Calcium | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.79 |
| 磷Phosphorus | 0.59 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 0.57 |
| 总赖氨酸Total Lys | 0.76 | 0.95 | 1.15 | 0.76 | 0.96 | 1.15 |
| 总蛋氨酸Total Met | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.28 |
| 总苏氨酸Total Thr | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.64 |
| 总色氨酸Total Trp | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| 总缬氨酸Total Val | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 |
| 猪标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys | 0.65 | 0.85 | 1.05 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 1.05 |
| 猪标准回肠可消化蛋氨酸SID Met | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| 猪标准回肠可消化苏氨酸SID Thr | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
| 猪标准回肠可消化色氨酸SID Trp | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 |
| 猪标准回肠可消化缬氨酸SID Val | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.74 |
Table 3
Effects of different dietary metabolizable energy and SID lysine levels on performances of lactating sows"
| 项目 Item | 胎次 Parity | 分娩体重/kg IBM | 断奶体重/kg FBM | 体重损失/kg BW loss | 分娩背膘/mm IBF | 断奶背膘/mm FBF | 背膘损失/mm BF loss | 平均日采食量/ (kg·d-1) ADFI | 断奶-发情间隔/d WEI | |
| 组别 Group | LL | 3.10 | 159.69 | 142.88 | 16.81 | 25.67 | 17.44 | 8.23 | 3.65b | 5.90 |
| LM | 3.30 | 156.11 | 140.90 | 15.21 | 25.63 | 18.44 | 7.19 | 3.78a | 5.70 | |
| LH | 3.20 | 155.10 | 139.27 | 15.83 | 24.46 | 16.55 | 7.91 | 3.74ab | 6.00 | |
| HL | 3.20 | 156.16 | 144.63 | 11.53 | 24.30 | 18.36 | 5.94 | 3.71ab | 5.90 | |
| HM | 3.10 | 158.95 | 145.97 | 12.98 | 25.58 | 19.36 | 6.23 | 3.70ab | 5.10 | |
| HH | 2.90 | 155.86 | 142.65 | 13.21 | 24.61 | 17.60 | 7.02 | 3.65b | 6.10 | |
| SEM | 0.10 | 1.36 | 1.36 | 0.43 | 0.70 | 0.74 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.16 | |
| 主效应Main effects | ||||||||||
| 代谢能/(MJ·kg-1) ME | ||||||||||
| 13.46 | 3.20 | 156.96 | 141.02 | 15.95a | 25.25 | 17.48 | 7.78a | 3.72 | 5.87 | |
| 13.72 | 3.07 | 156.99 | 144.42 | 12.57b | 24.83 | 18.44 | 6.40b | 3.68 | 5.70 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸/% SID Lys | ||||||||||
| 0.65 | 3.15 | 157.93 | 143.76 | 14.17 | 24.38 | 17.45 | 7.09 | 3.68 | 5.90 | |
| 0.85 | 3.20 | 157.53 | 143.43 | 14.09 | 25.61 | 18.90 | 6.71 | 3.74 | 5.40 | |
| 1.05 | 3.05 | 155.48 | 140.96 | 14.52 | 25.14 | 17.52 | 7.47 | 3.69 | 6.05 | |
| P值P-value | ||||||||||
| 代谢能ME | 0.518 | 0.993 | 0.227 | < 0.001 | 0.772 | 0.534 | 0.005 | 0.093 | 0.597 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys | 0.831 | 0.748 | 0.670 | 0.888 | 0.832 | 0.624 | 0.424 | 0.104 | 0.217 | |
| 代谢能*标准回肠可消化赖氨酸ME*SID Lys | 0.710 | 0.643 | 0.888 | 0.210 | 0.896 | 0.999 | 0.402 | 0.025 | 0.618 | |
Table 4
Effects of different dietary metabolizable energy and SID lysine levels on reproduce performances of lactating sows and growth performance of piglets"
| 项目Item | 窝产仔数/头 Litter zize at born | 断奶活仔数/头 Litter size at weaning | 哺乳期成活率/% Survival rate | 仔猪平均日增重/kg ADG | |
| 组别 Group | LL | 12.60 | 10.00 | 79.60 | 0.18 |
| LM | 12.40 | 11.00 | 88.85 | 0.19 | |
| LH | 13.00 | 11.10 | 86.01 | 0.19 | |
| HL | 12.70 | 10.80 | 85.16 | 0.18 | |
| HM | 13.00 | 12.00 | 92.69 | 0.20 | |
| HH | 12.30 | 11.10 | 90.49 | 0.19 | |
| SEM | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.92 | 0.00 | |
| 主效应Main effects | |||||
| 代谢能/(MJ·kg-1) ME | |||||
| 13.46 | 12.67 | 10.70b | 84.82b | 0.18b | |
| 13.72 | 12.67 | 11.30a | 89.45a | 0.19a | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸/% SID Lys | |||||
| 0.65 | 12.65 | 10.40b | 82.38b | 0.18b | |
| 0.85 | 12.70 | 11.50a | 90.77a | 0.19a | |
| 1.05 | 12.65 | 11.10a | 88.25a | 0.19ab | |
| P值P-value | |||||
| 代谢能ME | 1.000 | 0.014 | 0.004 | 0.037 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys | 0.990 | 0.001 | < 0.001 | 0.018 | |
| 代谢能*标准回肠可消化赖氨酸ME*SID Lys | 0.272 | 0.199 | 0.898 | 0.700 | |
Table 5
Effect of different dietary ME and SID lysine levels on the apparent digestibility of nutrients in lactating sows %"
| 项目Item | 干物质DM | 粗蛋白CP | 粗脂肪EE | 粗灰分Ash | 总能GE | 钙Ca | 磷P | |
| 组别Group | LL | 76.57d | 78.15 | 77.82 | 35.52 | 78.46 | 49.91 | 42.52 |
| LM | 76.97d | 80.97 | 79.09 | 38.84 | 79.99 | 50.77 | 43.56 | |
| LH | 77.02d | 81.21 | 79.26 | 36.68 | 78.77 | 51.24 | 42.61 | |
| HL | 80.25a | 81.21 | 81.10 | 37.14 | 81.46 | 54.57 | 44.65 | |
| HM | 79.24b | 82.48 | 80.41 | 37.88 | 80.75 | 54.54 | 42.47 | |
| HH | 78.35c | 81.94 | 79.33 | 36.35 | 80.60 | 55.36 | 41.75 | |
| SEM | 0.21 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.44 | 0.23 | 1.32 | 1.09 | |
| 主效应Main effects | ||||||||
| 代谢能/(MJ·kg-1) ME | ||||||||
| 13.46 | 76.85b | 80.11b | 78.72b | 37.02 | 79.07b | 50.64 | 42.90 | |
| 13.72 | 79.28a | 81.88a | 80.28a | 37.13 | 80.94a | 54.82 | 42.96 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸/% SID Lys | ||||||||
| 0.65 | 78.41 | 79.68b | 79.46 | 36.33 | 79.96 | 52.24 | 43.58 | |
| 0.85 | 78.10 | 81.73a | 79.75 | 38.36 | 80.37 | 52.65 | 43.02 | |
| 1.05 | 77.69 | 81.58a | 79.30 | 36.52 | 79.69 | 53.30 | 42.18 | |
| P值P-value | ||||||||
| 代谢能ME | < 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.038 | 0.901 | < 0.001 | 0.127 | 0.979 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys | 0.077 | 0.025 | 0.876 | 0.121 | 0.331 | 0.949 | 0.879 | |
| 代谢能*标准回肠可消化赖氨酸ME*SID Lys | 0.002 | 0.351 | 0.205 | 0.462 | 0.061 | 0.991 | 0.812 | |
Table 6
Effect of different dietary ME and SID lysine levels on milk composition in lactating sows mg ·mL-1"
| 项目Item | 初乳Colostrum | 常乳Milk | ||||||
| 乳糖 Lactose | 乳脂 Fat | 乳蛋白 Protein | 乳糖 Lactose | 乳脂 Fat | 乳蛋白 Protein | |||
| 组别Group | LL | 2.93 | 28.33 | 27.87 | 2.81 | 33.12 | 22.44 | |
| LM | 2.83 | 28.80 | 27.43 | 2.91 | 32.80 | 24.20 | ||
| LH | 3.01 | 28.84 | 28.15 | 2.92 | 31.52 | 22.98 | ||
| HL | 3.01 | 29.38 | 27.95 | 2.98 | 34.82 | 23.22 | ||
| HM | 2.92 | 29.45 | 27.64 | 2.98 | 35.18 | 23.97 | ||
| HH | 2.94 | 29.16 | 27.51 | 3.02 | 34.42 | 22.98 | ||
| SEM | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.13 | ||
| 主效应Main effect | ||||||||
| 代谢能/(MJ·kg-1) ME | ||||||||
| 13.46 | 2.92 | 28.66 | 27.82 | 2.88b | 32.48b | 23.21 | ||
| 13.72 | 2.96 | 29.33 | 27.70 | 2.99a | 34.80a | 23.39 | ||
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸/% SID Lys | ||||||||
| 0.65 | 2.97 | 28.86 | 27.91 | 2.89 | 33.97 | 22.83b | ||
| 0.85 | 2.87 | 29.13 | 27.54 | 2.95 | 33.99 | 24.09a | ||
| 1.05 | 2.97 | 29.00 | 27.83 | 2.97 | 32.97 | 22.98b | ||
| P值P-value | ||||||||
| 代谢能ME | 0.469 | 0.176 | 0.744 | 0.035 | < 0.001 | 0.310 | ||
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys | 0.168 | 0.902 | 0.673 | 0.470 | 0.161 | < 0.001 | ||
| 代谢能*标准回肠可消化赖氨酸ME*SID Lys | 0.365 | 0.828 | 0.587 | 0.685 | 0.600 | 0.063 | ||
Table 7
Effects of different dietary ME and SID lysine levels on serum glycolipid metabolic indices in lactating sows mmol ·L-1"
| 项目Item | 葡萄糖 GLU | 总胆固醇 TC | 甘油三酯 TG | 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇 HDL-C | 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇 LDL-C | 游离脂肪酸 NEFA | |
| 组别 Group | LL | 3.48 | 2.11 | 0.50 | 0.80 | 0.87 | 0.22 |
| LM | 3.58 | 2.06 | 0.57 | 0.82 | 0.69 | 0.24 | |
| LH | 3.36 | 2.12 | 0.44 | 0.82 | 0.71 | 0.26 | |
| HL | 3.54 | 2.11 | 0.65 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.20 | |
| HM | 3.72 | 2.18 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.73 | 0.19 | |
| HH | 3.63 | 2.24 | 0.63 | 0.86 | 0.94 | 0.21 | |
| SEM | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.01 | |
| 主效应Main effect | |||||||
| 代谢能/(MJ·kg-1) ME | |||||||
| 13.46 | 3.47 | 2.10 | 0.50b | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.24 | |
| 13.72 | 3.63 | 2.18 | 0.64a | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.20 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸/% SID Lys | |||||||
| 0.65 | 3.51 | 2.11 | 0.57 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.21 | |
| 0.85 | 3.65 | 2.12 | 0.61 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.21 | |
| 1.05 | 3.49 | 2.18 | 0.54 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.24 | |
| P值P-value | |||||||
| 代谢能ME | 0.073 | 0.275 | 0.002 | 0.377 | 0.255 | 0.088 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys | 0.257 | 0.678 | 0.371 | 0.989 | 0.189 | 0.628 | |
| 代谢能*标准回肠可消化赖氨酸ME*SID Lys | 0.599 | 0.785 | 0.549 | 0.955 | 0.326 | 0.903 | |
Table 8
Effect of different dietary ME and SID lysine levels on serum nitrogen metabolism indexes in lactating sows"
| 项目 Item | 总蛋白/ (g·L-1) TP | 白蛋白/ (g·L-1) ALB | 尿素氮/ (mmol·L-1) BUN | 肌酐/ (μmol·L-1) CRE | 谷丙转氨酶/ (U·L-1) ALT | 谷草转氨酶/ (U·L-1) AST | 碱性磷酸酶/ (U·L-1) AKP | |
| 组别 Group | LL | 79.51a | 34.78 | 4.07 | 97.44 | 89.84 | 47.36 | 35.13 |
| LM | 80.07a | 37.50 | 3.99 | 94.10 | 87.79 | 47.08 | 35.81 | |
| LH | 75.89b | 33.85 | 4.05 | 92.38 | 84.85 | 45.86 | 36.55 | |
| HL | 77.24b | 31.04 | 4.28 | 90.42 | 87.58 | 47.34 | 37.25 | |
| HM | 77.18b | 36.18 | 3.73 | 89.97 | 85.77 | 45.13 | 38.35 | |
| HH | 79.07a | 34.50 | 3.92 | 85.84 | 82.47 | 43.27 | 37.73 | |
| SEM | 0.30 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 1.19 | 0.88 | 0.50 | 0.61 | |
| 主效应Main effect | ||||||||
| 代谢能/(MJ·kg-1) ME | ||||||||
| 13.46 | 78.49 | 35.38 | 4.04 | 94.64a | 87.50 | 46.77 | 35.83 | |
| 13.72 | 77.83 | 33.91 | 3.98 | 88.74b | 85.28 | 45.25 | 37.78 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸/% SID Lys | ||||||||
| 0.65 | 78.38 | 32.91b | 4.18a | 93.93 | 88.71 | 47.35 | 36.19 | |
| 0.85 | 78.63 | 36.84a | 3.86b | 92.04 | 86.78 | 46.10 | 37.08 | |
| 1.05 | 77.48 | 34.18b | 3.99ab | 89.11 | 83.66 | 44.57 | 37.14 | |
| P值P-value | ||||||||
| 代谢能ME | 0.165 | 0.156 | 0.568 | 0.013 | 0.200 | 0.126 | 0.125 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys | 0.119 | 0.009 | 0.048 | 0.230 | 0.061 | 0.075 | 0.786 | |
| 代谢能*标准回肠可消化赖氨酸ME*SID Lys | < 0.001 | 0.223 | 0.157 | 0.859 | 0.996 | 0.538 | 0.902 | |
Table 9
Effect of different dietary ME and SID lysine levels on serum individual AA concentrations in lactating sows μg· mL-1"
| 项目Item | Asp | Glu | His | Ser | Arg | Gly | Thr | Pro | Ala | Val | Met | Cys | Ile | Leu | Phe | Lys | Tyr | |
| 组别 Group | LL | 6.83 | 27.52 | 8.59 | 18.09 | 59.20 | 70.80 | 41.78 | 33.89 | 38.72 | 39.07 | 3.09cd | 0.66 | 11.50 | 25.04 | 13.02 | 68.56 | 7.34 |
| LM | 5.19 | 24.16 | 7.06 | 13.66 | 46.58 | 72.27 | 29.02 | 28.14 | 31.28 | 25.29 | 2.57d | 0.47 | 8.42 | 17.44 | 11.72 | 58.67 | 7.00 | |
| LH | 5.89 | 26.18 | 7.79 | 13.41 | 28.31 | 57.27 | 38.94 | 30.01 | 36.67 | 36.99 | 4.78a | 0.49 | 10.50 | 18.70 | 9.23 | 60.22 | 6.63 | |
| HL | 6.24 | 27.44 | 8.62 | 15.55 | 61.10 | 72.56 | 36.47 | 29.45 | 38.98 | 37.87 | 4.06ab | 0.69 | 11.22 | 25.53 | 14.99 | 64.86 | 7.38 | |
| HM | 5.11 | 24.05 | 7.03 | 13.29 | 44.76 | 64.23 | 29.36 | 27.98 | 30.03 | 29.83 | 2.81d | 0.43 | 9.87 | 18.56 | 9.83 | 56.63 | 6.25 | |
| HH | 4.87 | 23.96 | 7.01 | 13.17 | 18.37 | 59.41 | 34.97 | 30.44 | 33.57 | 32.19 | 3.85bc | 0.51 | 9.64 | 19.23 | 10.11 | 60.89 | 7.29 | |
| SEM | 0.25 | 0.77 | 0.24 | 0.48 | 3.73 | 1.66 | 1.41 | 0.79 | 1.18 | 1.29 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.77 | 0.58 | 1.14 | 0.34 | |
| 主效应Main effect | ||||||||||||||||||
| 代谢能/(MJ·kg-1) ME | ||||||||||||||||||
| 13.46 | 5.97 | 25.95 | 7.81 | 15.05 | 44.70 | 66.78 | 36.58 | 30.68 | 35.56 | 33.78 | 3.48 | 0.54 | 10.14 | 20.39 | 11.33 | 6.62 | 6.99 | |
| 13.72 | 5.41 | 25.15 | 7.55 | 14.00 | 41.41 | 65.40 | 33.60 | 29.29 | 34.19 | 33.30 | 3.58 | 0.54 | 10.24 | 21.11 | 11.64 | 6.96 | 6.97 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸/% SID Lys | ||||||||||||||||||
| 0.65 | 6.54 | 27.48 | 8.60a | 16.82a | 60.15a | 71.68a | 39.12a | 31.67 | 38.85a | 38.47a | 3.58b | 0.67a | 11.36a | 25.28a | 14.00a | 66.71a | 7.36 | |
| 0.85 | 5.15 | 24.11 | 7.04b | 13.48b | 45.67b | 68.25a | 29.19b | 28.06 | 30.65b | 27.56b | 2.69c | 0.45b | 9.14b | 18.00b | 10.77b | 57.65b | 6.62 | |
| 1.05 | 5.38 | 25.07 | 7.40b | 13.29b | 23.34c | 58.34b | 36.96a | 30.23 | 35.12ab | 34.59a | 4.32a | 0.50b | 10.07b | 18.97b | 9.67b | 60.56b | 6.96 | |
| P值P-value | ||||||||||||||||||
| 代谢能ME | 0.255 | 0.612 | 0.553 | 0.202 | 0.574 | 0.625 | 0.244 | 0.378 | 0.542 | 0.821 | 0.684 | 0.940 | 0.830 | 0.547 | 0.757 | 0.405 | 0.980 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys | 0.058 | 0.212 | 0.018 | 0.002 | < 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.008 | 0.178 | 0.018 | 0.001 | < 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | < 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.701 | |
| 代谢能*标准回肠可消化赖氨酸ME*SID Lys | 0.733 | 0.817 | 0.709 | 0.438 | 0.696 | 0.257 | 0.635 | 0.388 | 0.825 | 0.214 | 0.007 | 0.774 | 0.126 | 0.970 | 0.284 | 0.671 | 0.719 | |
Table 10
Alpha diversity index of faecal microflora"
| 项目 Item | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | |
| 组别 Group | LL | 624.86 | 6.30 | 0.96 |
| LM | 713.46 | 5.72 | 0.91 | |
| LH | 646.77 | 6.48 | 0.96 | |
| HL | 504.58 | 5.11 | 0.86 | |
| HM | 752.79 | 5.66 | 0.87 | |
| HH | 662.28 | 5.54 | 0.86 | |
| SEM | 23.73 | 0.17 | 0.02 | |
| 主效应Main effects | ||||
| 代谢能/(MJ·kg-1) ME | ||||
| 13.46 | 661.70 | 6.17a | 0.94a | |
| 13.72 | 639.88 | 5.44b | 0.86b | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸/% SID Lys | ||||
| 0.65 | 564.72b | 5.71 | 0.91 | |
| 0.85 | 733.12a | 5.69 | 0.89 | |
| 1.05 | 654.52ab | 6.01 | 0.91 | |
| P值P-value | ||||
| 代谢能ME | 0.583 | 0.038 | 0.031 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys | 0.009 | 0.680 | 0.783 | |
| 代谢能*标准回肠可消化赖氨酸ME*SID Lys | 0.225 | 0.354 | 0.721 | |

Fig. 1
Effect of dietary ME and SID Lys levels on the faecal microbiota of lactating sows A. Venn diagram of faecal microbial diversity; B. Principal coordinate analysis of BrayeCurtis distances of the fecal samples from six treatments; C. Analysis of microbial abundance of sows at the phylum level (Top 10); D. Analysis of microbial abundance in sows at the genus level (Top 20); E. The KEGG function classification of faecal flora (Top 20)"
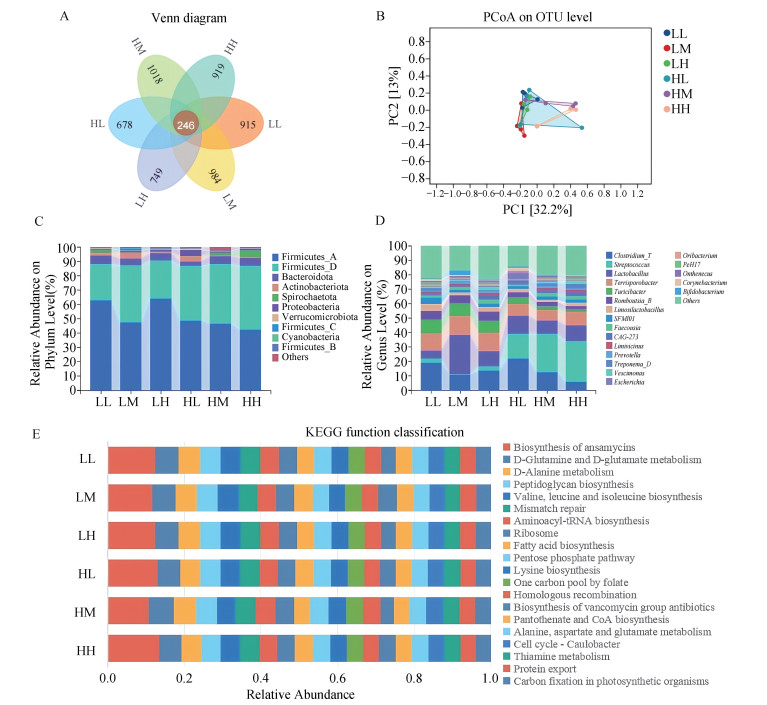
Table 11
Flora composition of sows ' faeces as organisms at the phylum level (top 5 of relative abundance) %"
| 项目 Item | 厚壁菌门A Firmicutes_A | 厚壁菌门D Firmicutes_D | 拟杆菌门 Bacteroidota | 放线菌门 Actinobacteriota | 螺旋体门 Spirochaetota | |
| 组别 Group | LL | 63.12 | 25.29 | 5.81 | 1.93 | 2.06 |
| LM | 47.40 | 40.21 | 4.68 | 4.01 | 0.43 | |
| LH | 64.24 | 26.81 | 4.61 | 0.82 | 0.75 | |
| HL | 48.66 | 38.56 | 2.62 | 4.10 | 0.15 | |
| HM | 46.71 | 41.69 | 5.55 | 0.31 | 2.02 | |
| HH | 42.41 | 44.79 | 5.44 | 0.67 | 4.79 | |
| SEM | 3.35 | 3.57 | 0.67 | 0.58 | 0.69 | |
| 主效应Main effects | ||||||
| 代谢能/(MJ·kg-1) ME | ||||||
| 13.46 | 58.26 | 30.77 | 5.03 | 2.25 | 1.08 | |
| 13.72 | 45.93 | 41.68 | 4.54 | 1.69 | 2.32 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸/% SID Lys | ||||||
| 0.65 | 55.89 | 31.92 | 4.21 | 3.01 | 1.10 | |
| 0.85 | 47.06 | 40.95 | 5.12 | 2.16 | 1.22 | |
| 1.05 | 53.33 | 35.80 | 5.03 | 0.74 | 2.77 | |
| P值P-value | ||||||
| 代谢能ME | 0.072 | 0.150 | 0.731 | 0.613 | 0.382 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys | 0.529 | 0.604 | 0.853 | 0.254 | 0.557 | |
| 代谢能*标准回肠可消化赖氨酸ME*SID Lys | 0.415 | 0.640 | 0.430 | 0.113 | 0.237 | |
Table 12
Flora composition of sows ' faeces as organisms at the genus level (top 6 of relative abundance) %"
| 项目 Item | 梭菌属 Clostridium_T | 乳酸杆菌属 Lactobacillus | 链球菌属 Streptococcus | 特里斯孢子杆菌属 Terrisporobacter | 苏黎世杆菌属 Turicibacter | 罗姆布茨菌属 Romboutsia_B | |
| 组别Group | LL | 19.19 | 5.65 | 2.88 | 11.88 | 9.70 | 5.62 |
| LM | 11.05 | 27.08 | 0.33 | 13.33 | 8.78 | 5.47 | |
| LH | 13.88 | 10.26 | 2.97 | 12.83 | 8.48 | 6.30 | |
| HL | 22.02 | 12.26 | 17.32 | 8.49 | 4.38 | 3.44 | |
| HM | 12.86 | 9.41 | 26.32 | 7.20 | 2.56 | 2.82 | |
| HH | 6.11 | 10.57 | 28.28 | 9.74 | 1.66 | 2.03 | |
| SEM | 1.84 | 2.40 | 4.47 | 1.13 | 0.84 | 0.48 | |
| 主效应Main effect | |||||||
| 代谢能/(MJ·kg-1) ME | |||||||
| 13.46 | 14.71 | 14.33 | 2.06b | 12.68 | 8.99a | 5.79a | |
| 13.72 | 13.67 | 10.75 | 23.97a | 8.48 | 2.87b | 2.76b | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys/% | |||||||
| 0.65 | 20.61a | 8.96 | 10.10 | 10.18 | 7.04 | 4.53 | |
| 0.85 | 11.96b | 18.24 | 13.32 | 10.27 | 5.67 | 4.15 | |
| 1.05 | 10.00b | 10.42 | 15.63 | 11.28 | 5.07 | 4.16 | |
| P值P-value | |||||||
| 代谢能ME | 0.760 | 0.424 | 0.019 | 0.088 | < 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| 标准回肠可消化赖氨酸SID Lys | 0.043 | 0.204 | 0.869 | 0.913 | 0.382 | 0.902 | |
| 代谢能*标准回肠可消化赖氨酸ME*SID Lys | 0.384 | 0.090 | 0.826 | 0.843 | 0.869 | 0.530 | |
| 1 | Denmark Pig Research Center. Landsgennemsnit for produktivitet i griseproduktionen[EB/OL]. [June 23, 2023]. https://svineproduktion.dk/Viden/Paa-kontoret/Oekonomi_ledelse/Produktionsstyring_og_okonomi/Landsgennemsnit. |
| 2 |
TOKACH M D , MENEGAT M B , GOURLEY K M , et al. Review: Nutrient requirements of the modern high-producing lactating sow, with an emphasis on amino acid requirements[J]. Animal, 2019, 13 (12): 2967- 2977.
doi: 10.1017/S1751731119001253 |
| 3 |
NOBLET J , ETIENNE M . Effect of energy level in lactating sows on yield and composition of milk and nutrient balance of piglets[J]. J Anim Sci, 1986, 63 (6): 1888- 1896.
doi: 10.2527/jas1986.6361888x |
| 4 |
DOURMAD J Y , NOBLET J , ÉTIENNE M . Effect of protein and lysine supply on performance, nitrogen balance, and body composition changes of sows during lactation[J]. J Anim Sci, 1998, 76 (2): 542- 550.
doi: 10.2527/1998.762542x |
| 5 |
PEDERSEN T F , CHANG C Y , TROTTIER N L , et al. Effect of dietary protein intake on energy utilization and feed efficiency of lactating sows[J]. J Anim Sci, 2019, 97 (2): 779- 793.
doi: 10.1093/jas/sky462 |
| 6 | NRC . Nutrient Requirements of Swine: Eleventh Revised Edition[M]. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2012. |
| 7 | DOURMAD J , GAUTHIER R , GAILLARD C . Évolution des concepts nutritionnels et des méthodes d 'alimentation des truies reproductrices: historique et perspectives[J]. INRAE Productions Animales, 2021, 34 (2): 111- 126. |
| 8 |
HUBER L A , RUDAR M , TROTTIER N L , et al. Whole-body nitrogen utilization and tissue protein and casein synthesis in lactating primiparous sows fed low- and high-protein diets[J]. J Anim Sci, 2018, 96 (6): 2380- 2391.
doi: 10.1093/jas/sky047 |
| 9 |
GOURLEY K M , SWANSON A J , ROYALL R Q , et al. Effects of timing and size of meals prior to farrowing on sow and litter performance[J]. Transl Anim Sci, 2020, 4 (2): 724- 736.
doi: 10.1093/tas/txaa066 |
| 10 |
MORALES J J , LOEZA R , ANGELES A A , et al. Effect of high-energy diets on the performance of lactating sows in tropical climate[J]. J Appl Anim Res, 2009, 36 (2): 175- 178.
doi: 10.1080/09712119.2009.9707054 |
| 11 |
ZHAO P Y , ZHANG Z F , LAN R X , et al. Effect of lysophospholipids in diets differing in fat contents on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, milk composition and litter performance of lactating sows[J]. Animal, 2017, 11 (6): 984- 990.
doi: 10.1017/S1751731116002238 |
| 12 |
KIM K , CHOI Y , HOSSEINDOUST A , et al. Evaluation of high nutrient diets and additional dextrose on reproductive performance and litter performance of heat-stressed lactating sows[J]. Anim Sci J, 2019, 90 (9): 1212- 1219.
doi: 10.1111/asj.13214 |
| 13 |
HONG J , FANG L H , KIM Y Y . Effects of dietary energy and lysine levels on physiological responses, reproductive performance, blood profiles, and milk composition in primiparous sows[J]. J Anim Sci Technol, 2020, 62 (3): 334- 347.
doi: 10.5187/jast.2020.62.3.334 |
| 14 |
XUE L , PIAO X , LI D , et al. The effect of the ratio of standardized ileal digestible lysine to metabolizable energy on growth performance, blood metabolites and hormones of lactating sows[J]. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2012, 3 (1): 11.
doi: 10.1186/2049-1891-3-11 |
| 15 | PEDERSEN T F , BRUUN T S , FEYERA T , et al. A two-diet feeding regime for lactating sows reduced nutrient deficiency in early lactation and improved milk yield[J]. Livest Sci, 2016, 191 (9): 165- 173. |
| 16 |
SHI M , ZANG J , LI Z , et al. Estimation of the optimal standardized ileal digestible lysine requirement for primiparous lactating sows fed diets supplemented with crystalline amino acids[J]. Anim Sci J, 2015, 86 (10): 891- 896.
doi: 10.1111/asj.12377 |
| 17 |
HOJGAARD C K , BRUUN T S , THEIL P K . Optimal lysine in diets for high-yielding lactating sows1[J]. J Anim Sci, 2019, 97 (10): 4268- 4281.
doi: 10.1093/jas/skz286 |
| 18 | SILVA G , THOMPSON R , KNOPF B , et al. Effects of metabolizable energy and standardized ileal digestible lysine levels on lactating sow and litter performance[J]. J Anim Sci, 2020, 98 (Suppl 3): 95- 96. |
| 19 | YANG F , ZHANG S , TIAN M , et al. Different sources of high fat diet induces marked changes in gut microbiota of nursery pigs[J]. Front Microbio, 2020, 11 (1): 859. |
| 20 |
田威龙, 司景磊, 刘笑笑, 等. 高脂高糖饮食对小型猪肠道微生物的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (4): 1143- 1153.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.04.014 |
|
TIAN W L , SI J L , LIU X X , et al. Effects of high-fat and high-sugar diet on intestinal microbiota in mini-pigs[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (4): 1143- 1153.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.04.014 |
|
| 21 | ZHAO J , ZHANG X , LIU H , et al. Dietary protein and gut microbiota composition and function[J]. Curr Protein Pept Sci, 2019, 20 (2): 145- 154. |
| 22 | 石岗, 段晓红, 李尚, 等. 深县猪和国外猪种的生产性能比较分析[J]. 猪业科学, 2019, 36 (4): 128- 129. |
| SHI G , DUAN X H , LI S , et al. Comparative analysis of the production performance of Shenxian pigs and foreign pig breeds[J]. Swine Industry Science, 2019, 36 (4): 128- 129. | |
| 23 | 冯韶华, 芦春莲, 苗玉涛, 等. 深县猪研究进展[J]. 猪业科学, 2019, 36 (8): 134- 135. |
| FENG S H , LU C L , MIAO Y T , et al. Research progress on Shenxian pigs[J]. Swine Industry Science, 2019, 36 (8): 134- 135. | |
| 24 | 魏述东, 孙延晓. 莱芜猪选育与饲养管理技术[J]. 猪业科学, 2017, 34 (4): 55- 58. |
| WEI S D , SUN Y X . Laiwu pig breeding and management technology[J]. Swine Industry Science, 2017, 34 (4): 55- 58. | |
| 25 | 黄金秀, 王瑞生, 蒋亚东, 等. 荣昌哺乳母猪标准回肠可消化赖氨酸适宜需要量研究[J]. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30 (7): 2501- 2509. |
| HUANG J X , WANG R S , JIANG Y D , et al. Study on optimal requirement of standard ileal digestible lysine for Rongchang lactating sows[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2018, 30 (7): 2501- 2509. | |
| 26 | 中华人民共和国国家市场监督管理总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 猪营养需要量: GB/T 39235-2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020. |
| Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration. Nutrient requirements of swine: GB/T 39235-2020[S]. Beiing: Standards Press of China, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 27 | AOAC . Official methods of analysis of AOAC international[M]. 17th ed Gaithersburg: AOAC International, 2000. |
| 28 | 赵剑虹. 柱前紫外衍生-高效液相色谱法同时测定血清和饮料中18种游离氨基酸[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2006. |
| ZHAO J H. Determination of 18 free amino acids in serum and drinks by high performance liquid chromatography after ultraviolet derivatization with 2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2006. (in Chinese) | |
| 29 |
YANG Y , HEO S , JIN Z , et al. Effects of dietary energy and lysine intake during late gestation and lactation on blood metabolites, hormones, milk composition and reproductive performance in multiparous sows[J]. Arch Anim Nutr, 2008, 62 (1): 10- 21.
doi: 10.1080/17450390701780227 |
| 30 | PARK M S , YANG Y X , CHOI J Y , et al. Effects of dietary fat inclusion at two energy levels on reproductive performance, milk compositions and blood profiles in lactating sows[J]. Acta Agr Scand A-Anim Sci, 2008, 58 (3): 121- 128. |
| 31 |
KNABE D A , BRENDEMUHL J H , CHIBA L I , et al. Supplemental lysine for sows nursing large litters[J]. J Anim Sci, 1996, 74 (7): 1635- 1640.
doi: 10.2527/1996.7471635x |
| 32 |
LIU B , ZHOU Y , XIA X , et al. Effects of dietary lysine levels on production performance and milk composition of high-producing sows during lactation[J]. Animals, 2020, 10 (11): 1947.
doi: 10.3390/ani10111947 |
| 33 | ESTRADA J , VIER C M , HANSON A , et al. Effects of increasing lactation dietary energy concentration by adding fat during the summer period on sow and litter performance[J]. J Anim Sci, 2022, 100 (3): 120- 121. |
| 34 |
ROONEY H B , O'DRISCOLL K , O'DOHERTY J V , et al. Effect of increasing dietary energy density during late gestation and lactation on sow performance, piglet vitality, and lifetime growth of offspring[J]. J Anim Sci, 2020, 98 (1): skz379.
doi: 10.1093/jas/skz379 |
| 35 |
VADMAND C N , KROGH U , HANSEN C F , et al. Impact of sow and litter characteristics on colostrum yield, time for onset of lactation, and milk yield of sows[J]. J Anim Sci, 2015, 93 (5): 2488- 2500.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2014-8659 |
| 36 |
MOREIRA R H R , PEREZ PALENCIA J Y , MOITA V H C , et al. Variability of piglet birth weights: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr, 2020, 104 (2): 657- 666.
doi: 10.1111/jpn.13264 |
| 37 |
KIM K Y , CHOI Y H , HOSSEINDOUST A , et al. Effects of free feeding time system and energy level to improve the reproductive performance of lactating sows during summer[J]. J Anim Sci Technol, 2020, 62 (3): 356- 364.
doi: 10.5187/jast.2020.62.3.356 |
| 38 |
KIM K Y , CHOI Y H , HOSSEINDOUST A , et al. Evaluation of high nutrient diets and additional dextrose on reproductive performance and litter performance of heat-stressed lactating sows[J]. Anim Sci J, 2019, 90 (9): 1212- 1219.
doi: 10.1111/asj.13214 |
| 39 |
TU P K , LE DUC N , HENDRIKS W H , et al. Effect of dietary lysine supplement on the performance of Mong Cai sows and their piglets[J]. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci, 2010, 23 (3): 385- 395.
doi: 10.5713/ajas.2010.90318 |
| 40 | 张娜娜, 曹洪战, 芦春莲. 不同能量水平日粮对深县猪生长性能、养分消化率和血液生化指标的影响[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2019, 51 (2): 18- 21. |
| ZHANG N N , CAO H Z , LU C L . Effects of different dietary energy levels on growth performance, nutrient digestibility and blood biochemical parameters of Shenxian pigs[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 51 (2): 18- 21. | |
| 41 | 谭占坤, 张定华, 商鹏, 等. 饲粮能量水平对断奶藏仔猪生产性能、养分消化率和血液生化指标的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30 (07): 1667- 1671. |
| TAN Z K , ZHANG D H , SHANG P , et al. Effect of dietary energy concentration on performance, nutrient digestibility and blood biochemical parameters of Tibetan piglets[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 30 (07): 1667- 1671. | |
| 42 | 杨凯. 日粮消化能、粗蛋白和赖氨酸水平对生长前期昭通乌金猪生长性能和肠道菌群的影响[D]. 昆明: 云南农业大学, 2022. |
| YANG K. Effects of dietary digestible energy、crude protein and lysine levels on growth performance and intestinal microflora of Zhaotong Wujin pigs in early growth stage[D]. Kunmimg: Yunnan Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 43 | 杨佳梦. 饲粮赖氨酸水平对丫杈猪产肉性能和养分消化代谢的影响研究[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2019. |
| YANG J M. Effects of dietary lysine levels on meat production performance, nutrient digestibility and metabolism of Yacha pigs[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese) | |
| 44 | 曾佩玲, 张常明, 王修启, 等. 日粮不同赖氨酸水平对生长猪养分表观消化率、血清氨基酸含量和生化指标的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2009, 24 (S2): 116- 120. |
| ZENG P L , ZHANG C M , WANG X Q , et al. Effects of different dietary lysine levels on apparent nutrient digestibility and serum amino acid concentration and serum biochemical indexes in growing pigs[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2009, 24 (S2): 116- 120. | |
| 45 | 周俊华, 周志扬, 潘天彪, 等. 日粮赖氨酸水平对桂科商品猪生长性能、营养物质表观消化率及血清游离氨基酸的影响[J]. 粮食与饲料工业, 2017 (10): 57-59, 62. |
| ZHOU J H , ZHOU Z Y , PAN T B , et al. Influence of dietary lysine level on growth performance, nutrient apparent digestibility and serum free amino acid in Gui commercial pigs[J]. Cereal & Feed Industry, 2017 (10): 57-59, 62. | |
| 46 |
WIENTJES J G M , SOEDE N M , KNOL E F , et al. Piglet birth weight and litter uniformity: Effects of weaning-to-pregnancy interval and body condition changes in sows of different parities and crossbred lines[J]. J Anim Sci, 2013, 91 (5): 2099- 2107.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2012-5659 |
| 47 | PENG X , YAN C , HU L , et al. Effects of fat supplementation during gestation on reproductive performance, milk composition of sows and intestinal development of their offspring[J]. Animals (Basel), 2019, 9 (4): 125. |
| 48 |
CHE L , HU L , WU C , et al. Effects of increased energy and amino acid intake in late gestation on reproductive performance, milk composition, metabolic, and redox status of sows1[J]. J Anim Sci, 2019, 97 (7): 2914- 2926.
doi: 10.1093/jas/skz149 |
| 49 |
HEO S , YANG Y X , JIN Z , et al. Effects of dietary energy and lysine intake during late gestation and lactation on blood metabolites, hormones, milk composition and reproductive performance in primiparous sows[J]. Can J Anim Sci, 2008, 88 (2): 247- 255.
doi: 10.4141/CJAS07060 |
| 50 | 刘作华. 日粮能量水平对猪肌内脂肪沉积的影响及作用机制研究[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2008. |
| LIU Z H. Effect of dietary energy density on intramuscular fat deposition for pigs and its underlying mechanism[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2008. (in Chinese) | |
| 51 | 袁庆启. 不同精粗比日粮对泌乳中期奶牛脂肪酸代谢和糖代谢及肝脏相关基因表达的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2016. |
| YUAN Q Q. The Effects of different of concentrate to forage ratio on the fatty acid metabolism, glycometabolism and expression of related metabolic genesm in mid-lactating dairy cows[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese) | |
| 52 |
SOLTWEDEL K T , EASTER R A , PETTIGREW J E . Evaluation of the order of limitation of lysine, threonine, and valine, as determined by plasma urea nitrogen, in corn-soybean meal diets of lactating sows with high body weight loss[J]. J Anim Sci, 2006, 84 (7): 1734- 1741.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2005-334 |
| 53 |
COMA J , ZIMMERMAN D R , CARRION D . Lysine requirement of the lactating sow determined by using plasma urea nitrogen as a rapid response criterion[J]. J Anim Sci, 1996, 74 (5): 1056- 1062.
doi: 10.2527/1996.7451056x |
| 54 |
NYBLOM H , BERGGREN U , BALLDIN J , et al. High AST/ALT ratio may indicate advanced alcoholic liver disease rather than heavy drinking[J]. Alcohol Alcohol, 2004, 39 (4): 336- 339.
doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agh074 |
| 55 |
JOHNSTON M E , NELSSEN J L , GOODBAND R D , et al. The effects of porcine somatotropin and dietary lysine on growth performance and carcass characteristics of finishing swine fed to 105 or 127 kilograms[J]. J Anim Sci, 1993, 71 (11): 2986- 2995.
doi: 10.2527/1993.71112986x |
| 56 | 印遇龙. 猪氨基酸营养与代谢[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008. |
| YIN Y L . Amino acid nutrition and metabolism in pig[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008. | |
| 57 | 董志岩, 刘亚轩, 刘景, 等. 不同蛋白质水平的氨基酸平衡日粮对泌乳母猪生产性能、血清指标和乳汁氨基酸含量的影响[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 42 (3): 311- 316. |
| DONG Z Y , LIU Y X , LIU J , et al. Effect of amino acid balanced diets with different protein levels on productive performance, serum indices and amino acid concentrations in milk of lactating sows[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 42 (3): 311- 316. | |
| 58 | 董志岩, 刘亚轩, 方桂友, 等. 不同赖氨酸水平的低蛋白质饲粮对二元母猪生长性能和血清指标的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34 (17): 122- 128. |
| DONG Z Y , LIU Y X , FANG G Y , et al. Different lysine levels affecting productive performance and serum biochemical parameters of two-line crossbred gilts feeding low-protein diets[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 34 (17): 122- 128. | |
| 59 |
LEY R E , TURNBAUGH P J , KLEIN S , et al. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity[J]. Nature, 2006, 444 (7122): 1022- 1023.
doi: 10.1038/4441022a |
| 60 | MACFARLANE G T , MACFARLANE S . Human colonic microbiota: ecology, physiology and metabolic potential of intestinal bacteria[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl, 1997, 222 (32): 3- 9. |
| 61 |
KHANNA S , PARDI D S . IBD poor outcomes after Clostridium difficile infection in IBD[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 9 (6): 307- 308.
doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2012.87 |
| 62 |
GHARIB-NASERI K , KHERAVII S , KEERQIN C , et al. Differential expression of intestinal genes in necrotic enteritis challenged broiler chickens with 2 different Clostridium perfringens strains[J]. Poult Sci, 2021, 100 (3): 100886.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.11.063 |
| 63 | MACFARLANE G T , CUMMINGS J H , ALLISON C . Protein degradation by human intestinal bacteria[J]. J Gen Microbiol, 1986, 132 (6): 1647- 1656. |
| 64 | 吴淑军, 李福昌, 王雪鹏, 等. 日粮能量水平对断奶至3月龄獭兔生长发育、消化代谢、血液生化和盲肠发酵的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2012, 43 (7): 1071- 1078. |
| WU S J , LI F C , WANG X P , et al. Effects of dietary energy levels on growth performance, nutrient metabolism, biochemical parameters and caecum fermentation of Rex rabbits from weaning to 3-month-old[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2012, 43 (7): 1071- 1078. | |
| 65 | 薛星星. "巴×八"二元猪杂交选育及育肥期日粮适宜能蛋比的研究[D]. 西宁: 青海大学, 2022. |
| XUE X X. Study on selection breeding of"Berkshire x Bamei" pigs and suitable energy-protein ratios in fattening diet[D]. Xi 'ning: Qinghai University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 66 |
RAGSDALE S W , PIERCE E . Acetogenesis and the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway of CO2 fixation[J]. Bba-proteins Proteom, 2008, 1784 (12): 1873- 1898.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2008.08.012 |
| 67 |
DUNCAN S H , BARCENILLA A , STEWART C S , et al. Acetate utilization and butyryl coenzyme A (CoA): acetate-CoA transferase in butyrate-producing bacteria from the human large intestine[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2002, 68 (10): 5186- 5190.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.10.5186-5190.2002 |
| 68 | 徐进, 王劼, 舒鼎铭, 等. 丁酸对脂肪代谢的调节及其作用机制[J]. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34 (6): 3495- 3502. |
| XU J , WANG J , SHU D M , et al. Regulation of fatty acid metabolism by butyric acid and its mechanism of action[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34 (6): 3495- 3502. | |
| 69 |
URRUTIA N , BOMBERGER R , MATAMOROS C , et al. Effect of dietary supplementation of sodium acetate and calcium butyrate on milk fat synthesis in lactating dairy cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2019, 102 (6): 5172- 5181.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-16024 |
| 70 |
李常营, 徐兰梦, 黄榆智, 等. 哺乳方式对猪生长、血清生化、肠道微生物及代谢物的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (11): 5147- 5158.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.11.030 |
|
LI C Y , XU L M , HUANG Y Z , et al. Effect of feeding regimes on growth, serum biochemistry, gut microbiota and their metabolites of pigs[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (11): 5147- 5158.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.11.030 |
|
| 71 |
LYNCH J B , GONZALEZ E L , CHOY K , et al. Gut microbiota Turicibacter strains differentially modify bile acids and host lipids[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14 (1): 3669.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39403-7 |
| [1] | ZHENG Yongjie, SUN Tongyu, HU Fengming, WEI Manlin, MA Tao. Research Progress on the Manipulation of Performance, Product Quality and Health Status of Ruminants by Resveratrol [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3631-3639. |
| [2] | YUAN Yue, ZHOU Jianxu, LUO Xiaolin, GUAN Jiuqiang, AN Tianwu, ZHAO Hongwen, BAI Qin, REN Zili, ZHANG Xiangfei, ZHAO Yanling. Effect of Rumen-Protected Fat on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemistry and Slaughter Performance of Fattening Yaks [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3849-3860. |
| [3] | LAN Mingxi, QIN Qing, ZHANG Chongyan, LIU Zhichen, ZHANG Jingwen, ZHAO Dan, WU Danni, QIN Tian, WANG Zhixin, LIU Zhihong. Determination and Analysis of Slaughtering Performance and Meat Quality of Different Parts of Ujumqin Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3177-3187. |
| [4] | HUO Zhen, ZHUANG Lei, ZHOU Wei, WANG Shuaiqin, XIE Ming, HOU Shuisheng, HOU Shuisheng. Effects of Dietary Folic Acid Levels on Production Performance, Plasma Biochemical Indicators and Antioxidant Capacity of Pekin Ducks from 1 to 21 Days of Age [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3327-3334. |
| [5] | SUN Shujia, ZHENG Jiaqi, LU Shuwan, LIU Jinsong, YAO Chunlei, YANG Caimei, XU Yinglei, ZHANG Ruiqiang. Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria on Growth Performance, Digestive Function and Nutrient Utilization of Yellow-feathered Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3335-3343. |
| [6] | CHEN Zhihua, WANG Qi, ZHANG Jin, YANG Liandi, YANG Tianqing, WANG Jing, LONG Dingbiao, HUANG Jinxiu, HUANG Wenming. Effects of Dietary Net Energy and Lysine Levels on Reproductive Performance, Serum Hormone, Lactation Performance and Fecal Flora Diversity of Rongchang Sows in Late Pregnancy [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2801-2815. |
| [7] | LUO Jia, PU Qiang, CHAI Jie, CHEN Li, WANG Jinyong. Biological Effects and Genetic Mechanisms of Intrauterine Heat Stress in Swine [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2004-2014. |
| [8] | MA Yanfen, CHEN Qi, QIAN Zhongli, NI Jia, MENG Hao, GAO Xinkai, WAN Fujun, LIU Xin. Changes and Influencing Factors of Eggshell Quality in Late-phase Laying Hens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2148-2156. |
| [9] | ZHANG Junxing, SHENG Hui, HAN Liyun, ZHANG Hailiang, ZHANG Yi, CAI Bei, MA Yun, WANG Yachun. The Impact of Health Events on Important Economic Traits in Holstein Lactating Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2203-2218. |
| [10] | ZHU Yun, WANG Yuming, SUN Xiaoxiao, CHEN Hui, ZHAO Feng, XIE Jingjing, CHEN Yifan, SA Renna. Effect of the Addition of Corn Gluten Meal to Low-protein Diversified Diet on Growth Performance and Digestive Characteristics of White-feathered Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1802-1812. |
| [11] | WU Xiuju, XIA Pei, LUO Yihao, LUO Jinwei, XUE Mengdi, KE Yanhang, LI Juan, LÜ Jingzhi. Effect of Dietary Lactulose Supplementation on Growth Performance, Serum Parameters and Meat Quality in Meat Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1813-1824. |
| [12] | LIANG Entang, LI Huaxuan, CHEN Shuaicheng, LI Guo, SUN Gege, ZAN Linsen. Effect of Genistein on Semen Cryopreservation of Bull [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 700-710. |
| [13] | LIANG Hui, ZHAO Jing, WANG Yanya, LONG Runze, LIU Xuyang, WU Yingjie, LIU Ning, QIN Yinghe. Effects of Dietary Chlorogenic Acid on Reproductive Performance of Female Rabbits and Growth of Suckling Rabbits under Heat Stress Conditions [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 755-764. |
| [14] | ZHANG Yu, WANG Qiru, SHI Xinchao, GUO Ziming, HE Xin, ZHANG Tie, ZHAO Xinghua. Effects of Magnolol Solid Dispersion on Growth Performance, Serum Antioxidant Capacity and Intestinal Microbiome of Calves [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 943-952. |
| [15] | BAI Guosong, TENG Chunran, WANG Junhong, ZHONG Ruqing, MA Teng, CHEN Liang, ZHANG Hongfu. Effects of Enzymatic Corn Gluten Meal on Growth Performance and Intestinal Microorganisms of Weaned Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 953-968. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||