





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (9): 4491-4506.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.09.029
• Animal Nutrition and Feeds • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIA Chunqiu( ), MIAO Shu, LI Zhiqing, LIU Lei, WAN Fachun*(
), MIAO Shu, LI Zhiqing, LIU Lei, WAN Fachun*( ), SHEN Weijun*(
), SHEN Weijun*( )
)
Received:2024-10-24
Online:2025-09-23
Published:2025-09-30
Contact:
WAN Fachun, SHEN Weijun
E-mail:xiachunqiu2022@163.com;wanfc@sina.com;shenweijun@hunan.edu.cn
CLC Number:
XIA Chunqiu, MIAO Shu, LI Zhiqing, LIU Lei, WAN Fachun, SHEN Weijun. Valine Regulates Bovine Myoblast Proliferation through the AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4491-4506.
Table 1
Primer information sequence of qRT-PCR"
| 基因 Gene | 引物序列(5′→ 3′) Primer sequence | 产物长度/bp Length |
| 配对盒7 Paired box 7(PAX7) | F:AGCCGAGTGCTCAGAATCAA R:TCCAGACGGTTCCCTTTGTC | 131 |
| 细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶 Cyclin-dependent kinase 1(CDK1) | F:CGGATAAAGCCGGGGTCTAC R:TGGCTACCACTTGGCCTGTA | 132 |
| 增殖细胞核抗原 Proliferating cell nuclear antigen(PCNA) | F:TGCAGATGTACCCCTTGTTGT R:CATCCTCGATCTTGGGAGCC | 83 |
| 哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白 Mammalian target of Rapamycin(mTOR) | F:GCTGCATGGGGTTTAGGTCA R:GATGCACTGTTGTGCCAAGG | 138 |
| AMP依赖的蛋白激酶 Adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase(AMPK) | F:TCGGCAAAGTGAAGATTGGAGA R:TCCAACAACATCTAAACTGCGA | 98 |
| 甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶 Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase(GAPDH) | F:AGGTCGGAGTGAACGGATTC R:ATGGCGACGATGTCCACTTT | 85 |
Fig. 2
Effect of Val on the viability of bovinemyoblasts A.Light microscopy of bovine myoblasts at different concentrations (0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 1 mmol ·L-1) Val treatment for 24 h (40×), Scale bar=100 μm; B.Statistical chart of CCK-8 cell viability. *, ** and *** represent P < 0.05, P < 0.01 and P < 0.001, respectively, the same as below"
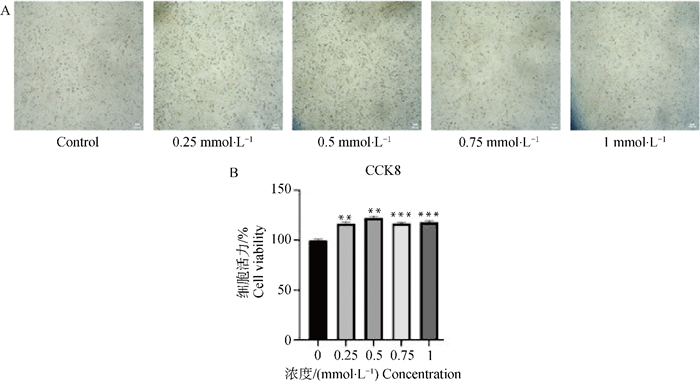
Fig. 7
Effect of Val on protein expression of AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway-related factor proteins in bovine myoblasts A.Changes in protein expression levels of AMPK and mTOR after Val addition; B.Gray value analysis of mTOR protein expression level after Val addition; C.Gray value analysis of AMPK protein expression level after Val addition"
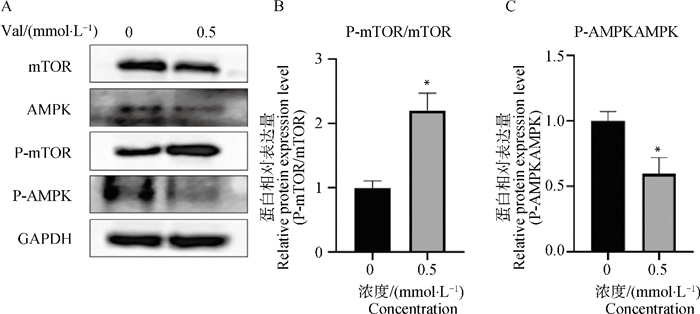
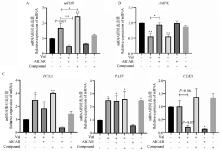
Fig. 8
Effects of AMPK inhibitors, activators and Val on the proliferation of bovine myoblasts and the mRNA expression of factors related to the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway A.Changes in mRNA expression levels of mTOR after the addition of AMPK inhibitors, activators, and Val; B.Changes in mRNA expression levels of AMPK after the addition of AMPK inhibitors, activators, and Val; C.Changes in mRNA expression levels of PAX7, CDK1 and PCNA after addition of AMPK inhibitors, activators, and Val"
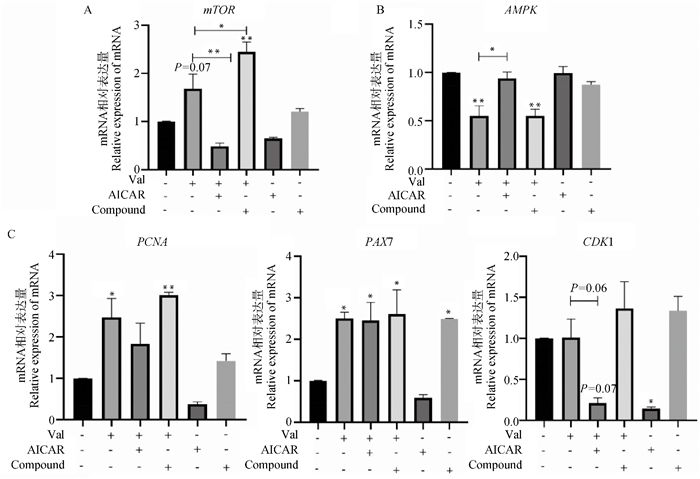
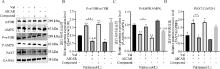
Fig. 9
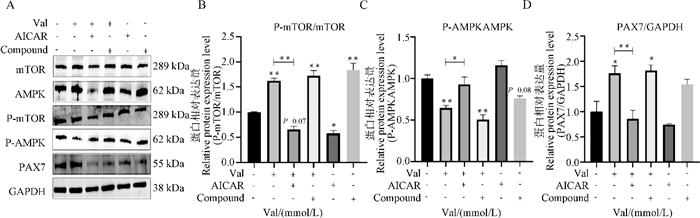
Effects of AMPK inhibitors, activators and Val on the proliferation of bovine myoblasts and the expression of AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway-related factor proteins A.Changes in protein expression levels of PAX7, AMPK and mTOR after the addition of AMPK inhibitors, activators and Val; B.Gray value analysis of mTOR protein expression level after addition of AMPK inhibitors, activators and Val; C.Gray value analysis of AMPK protein expression level after addition of AMPK inhibitor, activator and Val; D.Grayscale analysis of PAX7 protein expression levels after the addition of AMPK inhibitors, activators and Val"
| 1 | 曹兵海, 曹建民, 李俊雅, 等. 2023年度肉牛牦牛产业与技术发展报告[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2024, 60 (3): 335- 338. |
| CAO B H , CAO J M , LI J Y , et al. 2023 Annual report on the development of the beef cattle and yak industry and technology[J]. China Journal of Animal Husbandry, 2024, 60 (3): 335- 338. | |
| 2 | 其达拉图. 有关肉牛养殖和管理[J]. 吉林畜牧兽医, 2020, 41 (2): 88- 89. |
| QI D L T . Regarding beef cattle breeding and management[J]. Jilin Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 41 (2): 88- 89. | |
| 3 | 赵畅. 牛肉进口对我国牛肉市场的影响研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2023. |
| ZHAO C. Research on the impact of beef import on china 's beef market[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 4 | SPENCER R J , KETEL C R , PENNER G B , et al. Association of a variant upstream of growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11) on carcass traits in crossbred beef cattle[J]. Transl Anim Sci, 2023, 7 (1) |
| 5 | ZHANG Z , HE Z , PANG W . The role and regulatory mechanism of tissue and organ crosstalk on skeletal muscle development: a review[J]. Chin J Biotechnol, 2023, 39 (4): 1502- 1513. |
| 6 |
OKSBJERG N , GONDRET F , VESTERGAARD M . Basic principles of muscle development and growth in meat-producing mammals as affected by the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system[J]. Domest Anim Endocrinol, 2004, 27 (3): 219- 240.
doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2004.06.007 |
| 7 | HERNÁNDEZ-HERNÁNDEZ J M, GARCÍA-GONZÁLEZ E G, BRUN C E, et al. The myogenic regulatory factors, determinants of muscle development, cell identity and regeneration[C]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2017, 72: 10-18. |
| 8 |
BRAUN T , GAUTEL M . Transcriptional mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle differentiation, growth and homeostasis[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2011, 12 (6): 349- 361.
doi: 10.1038/nrm3118 |
| 9 |
ZHANG D , ZHANG X , LIU Z , et al. Diosmin promotes myogenesis via activating the Akt/FOXO1 pathway to facilitate the proliferation of C2C12 myoblasts[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2023, 71 (49): 19705- 19716.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c04828 |
| 10 |
GUAN L , CAO Z , PAN Z , et al. Butyrate promotes C2C12 myoblast proliferation by activating ERK/MAPK pathway[J]. Mol Omics, 2023, 19 (7): 552- 559.
doi: 10.1039/D2MO00256F |
| 11 |
LIU S , LIU Z , WANG P , et al. Estrogen-mediated oar-miR-485-5p targets PPP1R13B to regulate myoblast proliferation in sheep[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 236, 123987.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123987 |
| 12 |
WANG Z , CAI D , LI K , et al. Transcriptome analysis of the inhibitory effect of cycloleucine on myogenesis[J]. Poult Sci, 2022, 101 (12): 102219.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102219 |
| 13 | AOYAMA S , KIM H K , HIROOKA R , et al. Distribution of dietary protein intake in daily meals influences skeletal muscle hypertrophy via the muscle clock[J]. Cell Rep, 2021, 36 (1) |
| 14 | KASPY M S , HANNAIAN S J , BELL Z W , et al. The effects of branched-chain amino acids on muscle protein synthesis, muscle protein breakdown and associated molecular signalling responses in humans: an update[J]. Nutr Res Rev, 2023, 1- 36. |
| 15 | 黄璇, 蒋桂韬, 李闯, 等. 饲粮支链氨基酸比例对攸县麻鸭生长性能、血清生化指标和肠道发育的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34 (9): 5759- 5766. |
| HUANG X , JIANG G T , LI C , et al. Effects of dietary branched-chain amino acid ratio on growth performance, serum biochemical indexes and intestinal development of youxian duck[J]. Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34 (9): 5759- 5766. | |
| 16 | 董贤文. 提高蛋氨酸和支链氨基酸对奶牛乳腺上皮细胞酪蛋白合成调控通路的影响[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2017. |
| DONG X W. Effect of methionine and branched-chain amino acids on the regulation pathway of casein synthesis in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese) | |
| 17 |
CORZO A , KIDD M T , DOZIER Ⅲ W A , et al. Marginality and needs of dietary valine for broilers fed certain all-vegetable diets[J]. J Appl Poult Res, 2007, 16 (4): 546- 554.
doi: 10.3382/japr.2007-00025 |
| 18 |
SARTORI T , SANTOS A C A , DASILVA R O , et al. Branched chain amino acids improve mesenchymal stem cell proliferation, reducing nuclear factor kappa B expression and modulating some inflammatory properties[J]. J Nutr, 2020, 78, 110935.
doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.110935 |
| 19 |
JIAN H , XU Q , WANG X , et al. Amino acid and fatty acid metabolism disorders trigger oxidative stress and inflammatory response in excessive dietary valine-induced NAFLD of laying hens[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9, 849767.
doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.849767 |
| 20 |
XU Y T , MA X K , WANG C L , et al. Effects of dietary valine: lysine ratio on the performance, amino acid composition of tissues and mRNA expression of genes involved in branched-chain amino acid metabolism of weaned piglets[J]. Asian Australas J Anim Sci, 2018, 31 (1): 106.
doi: 10.5713/ajas.17.0148 |
| 21 |
AMIRDAHRI S , JANMOHAMMADI H , TAGHIZADEH A , et al. Valine requirement of female Cobb broilers from 8 to 21 days of age[J]. J Appl Poult Res, 2020, 29 (4): 775- 785.
doi: 10.1016/j.japr.2020.04.005 |
| 22 | 王立. 外源缬氨酸影响小鼠脂肪沉积的机制研究[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2023. |
| WANG L. Study on the mechanism of exogenous valine affecting fat deposition in mice[D]. Jingzhou: Yangtze University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 23 |
KITA K , MAKINO R . Influence of valine analogues on protein synthesis of chicken embryo myoblasts[J]. J Poult Sci, 2014, 51 (2): 191- 194.
doi: 10.2141/jpsa.0130162 |
| 24 |
DUAN Y , ZENG L , LI F , et al. Effect of branched-chain amino acid ratio on the proliferation, differentiation, and expression levels of key regulators involved in protein metabolism of myocytes[J]. J Nutr, 2017, 36, 8- 16.
doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2016.10.016 |
| 25 |
ZHANG J , HE W , YI D , et al. Regulation of protein synthesis in porcine mammary epithelial cells by L-valine[J]. Amino Acids, 2019, 51, 717- 726.
doi: 10.1007/s00726-019-02709-2 |
| 26 |
TANG S , XIE J , WU W , et al. High ammonia exposure regulates lipid metabolism in the pig skeletal muscle via mTOR pathway[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2020, 740, 139917.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139917 |
| 27 |
苗舒, 安济山, 王祚, 等. 亮氨酸通过PI3K-AKT信号通路促进牛成肌细胞的增殖[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (1): 142- 152.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.01.015 |
|
MIAO S , AN J S , WANG Z , et al. Leucine promotes the proliferation of bovine myoblasts through PI3K-AKT signaling pathway[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (1): 142- 152.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.01.015 |
|
| 28 |
冯铭, 伊旭东, 庞卫军. 肠道微生物通过骨骼肌纤维类型、肌内脂肪含量和骨骼肌代谢调控猪肉质研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (6): 2304- 2312.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.06.003 |
|
FENG M , YI X D , PANG W J . Research progress on intestinal microbes regulating pork quality through skeletal muscle fiber type, intramuscular fat content and skeletal muscle metabolism[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (6): 2304- 2312.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.06.003 |
|
| 29 |
ZHAO Z , GUO D , WEI Y , et al. Integrative ATAC-seq and RNA-seq analysis of the longissimus dorsi muscle of gannan yak and jeryak[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (11): 6029.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25116029 |
| 30 |
CHEN B , WANG Y , HOU D , et al. Transcriptome-based identification of the muscle tissue-specific expression gene CKM and its regulation of proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation in chicken primary myoblasts[J]. Animals, 2023, 13 (14): 2316.
doi: 10.3390/ani13142316 |
| 31 |
ZHENG J , LOU J , LI Y , et al. Satellite cell-specific deletion of Cipc alleviates myopathy in mdx mice[J]. Cell Rep, 2022, 39 (11): 110939.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110939 |
| 32 |
CAO Y , HU G , LONG X , et al. Valine promotes milk synthesis by regulating PKM2 nuclear accumulation and histone H3 acetylation through the TAS1R1-mTOR-DDX39B signaling pathway[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 254, 127786.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127786 |
| 33 |
REZAEI R , WU G . Branched-chain amino acids regulate intracellular protein turnover in porcine mammary epithelial cells[J]. Amino Acids, 2022, 54 (11): 1491- 1504.
doi: 10.1007/s00726-022-03203-y |
| 34 |
KWON H C , JUNG H S , HAN J H , et al. Optimizing hormonal and amino acid combinations for enhanced cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. Anim Biosci, 2023, 36 (11): 1757.
doi: 10.5713/ab.23.0199 |
| 35 | 杜志强, 丁然, 赵素娟, 等. 缬氨酸影响小鼠C2C12细胞脂肪沉积的研究[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2021, 52 (8): 39- 47. |
| DU Z Q , DING R , ZHAO S J , et al. Study on the effect of valine on fat deposition in mouse C2C12 cells[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2021, 52 (8): 39- 47. | |
| 36 | WANG XINLING , XU JIE , ZENG HANFANG . Enhancement of BCAT2-mediated valine catabolism stimulates β-casein synthesis via the AMPK-mTOR signaling axis in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2022, 70 (32): 9898- 9907. |
| 37 | KIM JUNGEUN , LEE JEONG-EUN , LEE JAE-SUNG . Phenylalanine and valine differentially stimulate milk protein synthetic and energy-mediated pathway in immortalized bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. J Anim Technol or JAST, 2020, 6 (2): 263- 275. |
| 38 | 郝怡泓. 支链氨基酸对奶牛乳腺上皮细胞酪蛋白合成的影响[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2023. |
| HAO Y H. Effect of branched-chain amino acids on casein synthesis in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 39 |
GUAN L , TANG Y , LI G , et al. Comprehensive analysis of role of cyclin-dependent kinases family members in colorectal cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12, 921710.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.921710 |
| 40 |
SERPICO A F , PISAURO C , GRIECO D . On the assembly of the mitotic spindle, bistability and hysteresis[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2023, 80 (4): 83.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04727-6 |
| 41 |
XU X , WANG C , YANG J , et al. EZH2 promotes DNA replication by stabilizing interaction of POLδ and PCNA via methylation-mediated PCNA trimerization[J]. Epigenet chromatin, 2018, 11, 1- 14.
doi: 10.1186/s13072-017-0171-z |
| 42 |
SONG J , HAO L , ZENG X , et al. A novel miRNA Y-56 targeting IGF-1R mediates the proliferation of porcine skeletal muscle satellite cells through AKT and ERK pathways[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2022, 9, 754435.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.754435 |
| 43 | WU W , SUN J , JI H , et al. AMP-activated protein kinase in the grass carp ctenopharyngodon idellus: molecular characterization, tissue distribution and mRNA expression in response to overwinter starvation stress[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol, 2020, 246, 110457. |
| 44 |
IHLAMUR M , AKGVL B , ZENGIN Y , et al. The mTOR signaling pathway and mTOR Inhibitors in cancer: next-generation inhibitors and approaches[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2024, 24 (4): 478- 494.
doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230509161645 |
| 45 |
XIE L , LI R , ZHANG J , et al. Methionine promotes milk synthesis through the BRCC36-BRG1-mTOR signaling axis in mammary epithelial cells[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2024, 72 (4): 2135- 2144.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05370 |
| 46 |
TANG B , LUO Z , ZHANG R , et al. An update on the molecular mechanism and pharmacological interventions for ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in autophagy[J]. Cell Signal, 2023, 107, 110665.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110665 |
| 47 | 吴良邦, 葛云林. 薯蓣皂苷通过调控AMPK/mTOR自噬信号通路影响骨肉瘤细胞增殖及侵袭的机制研究[J]. 浙江中西医结合杂志, 2024, 34 (4): 304-309, 316. |
| WU L B , GE Y L . Mechanism of diosgenin affecting the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by regulating AMPK/mTOR autophagy signaling pathway[J]. Zhejiang Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2024, 34 (4): 304-309, 316. | |
| 48 |
LIANG Z , JIN C , BAI H , et al. Low rumen degradable starch promotes the growth performance of goats by increasing protein synthesis in skeletal muscle via the AMPK-mTOR pathway[J]. Anim Nutr, 2023, 13, 1- 8.
doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2022.10.006 |
| 49 |
DU M , SHEN Q W , ZHU M J , et al. Leucine stimulates mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in C2C12 myoblasts in part through inhibition of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase[J]. J Anim Sci, 2007, 85 (4): 919- 927.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2006-342 |
| 50 |
WANG X , XU J , ZENG H , et al. Enhancement of BCAT2-mediated valine catabolism stimulates β-casein synthesis via the AMPK-mTOR signaling axis in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70 (32): 9898- 9907.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c03629 |
| 51 | 林峰, 付新梅, 王超, 等. 3C-like蛋白酶抑制剂的构效关系、分子对接和分子动力学[J]. 物理化学学报, 2016, 32 (11): 2693- 2708. |
| LIN F , FU X M , WANG C , et al. Structure-activity relationship, molecular docking and molecular dynamics of 3C-like protease inhibitors[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2016, 32 (11): 2693- 2708. | |
| 52 |
ZINELDEEN D H , TAHOON N M , SARHAN N I . AICAR ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via modulation of the HGF/NF-κB/SNARK signaling pathway and restores mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticular impairments in high-fat diet-fed rats[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (4): 3367.
doi: 10.3390/ijms24043367 |
| 53 |
KHORRAMINEJAD-SHIRAZI M , SANI M , TALAEI-KHOZANI T , et al. AICAR and nicotinamide treatment synergistically augment the proliferation and attenuate senescence-associated changes in mesenchymal stromal cells[J]. Stem cell res ther, 2020, 11, 1- 17.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1471-y |
| 54 |
GAN W , ZHANG N N , LI L . The regulation mechanism of AMPK/FOXO3 signal pathway in the apoptosis and differentiation of duck myoblasts[J]. Russ J Genet, 2021, 57, 97- 109.
doi: 10.1134/S1022795421010075 |
| 55 | 张娜, 符海鑫, 曹慧, 等. FLCN通过AMPK-mTOR信号轴调节奶牛乳腺上皮细胞能量代谢[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2022, 53 (8): 71- 79. |
| ZHANG N , FU H X , CAO H , et al. FLCN regulates energy metabolism in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells through AMPK-mTOR signaling axis[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2022, 53 (8): 71- 79. | |
| 56 | 蓝日国. 牛磺酸通过AMPK-mTOR调节能量代谢缓解乳房链球菌感染诱导的炎症[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2021. |
| LAN R G. Taurine regulates energy metabolism through AMPK-mTOR and alleviates inflammation induced by Streptococcus mammiae infection[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | CAO Xiaoyao, WANG Congyong, WANG Ting, XIONG Lanling, YU Heyang, WANG Zezhao, GAO Huijiang, LI Junya, ZHU Bo. Estimation of Genetic Parameters and Genetic Progress for Growth and Development Traits in Huaxi Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4355-4368. |
| [2] | HU Jinling, ZHONG Qiqi, HUANG Cheng, LEI Minggang. AKR1B1 Regulates Proliferation and Differentiation of Porcine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells via the AMPK/mTOR/S6 Signaling Pathway [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3722-3733. |
| [3] | WU Silin, YANG Benshun, YE Miaomiao, LIANG Entang, LI Fuqiang, MA Weidong, ZAN Linsen, ZHAO Chunping, YANG Wucai. Effect of Luteolin on Semen Cryopreservation of Qinchuan Bull [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3244-3251. |
| [4] | SHI Shanshan, WAN Qiongfei, XU Yingxin, WANG Qiushuo, ZHANG Linlin, GUO Yiwen, HU Debao, GUO Hong, DING Xiangbin, LI Xin. Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis of miRNAs at Different Developmental Stages of Bovine Skeletal Muscle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2701-2710. |
| [5] | WANG Qinqian, GAO Zhendong, LU Ying, MA Ruoshan, DENG Weidong, HE Xiaoming. Research Progress of Whole Genome Resequencing in Chinese Indigenous Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2026-2037. |
| [6] | YAO Tingting, LI Hao, YAN Huixuan, CAO Yifan, Cirengluobu , Suolangquji , Nimacangjue , ZHAO Li, Danzengluosang , Silangwangmu , Basangzhuzha , CHEN Ningbo. Genetic Diversity of Mitochondrial Genome and Maternal Origin of 10 Cattle Populations in Tibet Autonomous Region [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2194-2202. |
| [7] | ZHAO Wenxuan, GAO Xue, YU Dawei, GAO Chen, LI Junya. Establishment and Pluripotency Analysis of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mengshan Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1731-1743. |
| [8] | LI Xiaotong, WANG Pengyu, FANG Yingyan, YU Hongxi, ZHANG Yi, WANG Yachun, ZHANG Yuanpei, LI Yanqin, JIANG Li. Mining and Functional Verification of Gene Polymorphisms Loci Related to Bull Sperm Freezability [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1981-1988. |
| [9] | HU Xin, YOU Wei, JIANG Fugui, CHENG Haijian, SUN Zhigang, SONG Enliang. Analysis of Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Simmental Cattle Based on Whole Genome Resequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1189-1202. |
| [10] | CHEN Qiong, MAO Shuaixiang, WU Longfei, YANG Chuang, SUN Baoli. lncRNA Expression Characteristics in Semitendinosus Muscle of Leiqiong Cattle and Lufeng Cattle and Its ceRNA Network Analysis in Skeletal Muscle Development and Fat Deposition [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1203-1215. |
| [11] | WANG Yuanqing, WANG Zezhao, ZHU Bo, CHEN Yan, XU Lingyang, ZHANG Lupei, GAO Huijiang, LI Chao, LI Junya, GAO Xue. Comparison of Prediction Accuracy of Genomic Selection for Economically Important Traits in Huaxi Cattle Based on Different Chip Densities [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 591-602. |
| [12] | ZHANG Zhengyu, YANG Peihong, GUO Hong, LI Xin, ZHANG Linlin, GUO Yiwen, HU Debao, DING Xiangbin. Effects of Sirt1 Deacetylase on Proliferation and Differentiation of Bovine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 603-610. |
| [13] | ZHAO Gangkui, GAO Haixu, YIN Siqi, SUN Honghong, XIN Yiran, ZAN Linsen, ZHAO Chunping. The Effects of the SFRP4 Gene on Bovine Preadipocyte Differentiation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 611-620. |
| [14] | WU Shaoqiang, LIU Yufan, WEI Yirong, HUANG Yanna, JIANG Qinyang. Mechanism of Resveratrol Regulating Myofiber Type Transformation through PROX1/SIRT1 Signaling Pathway in Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 201-212. |
| [15] | NIU Yifan, LI Chongyang, ZHANG Peipei, ZHANG Hang, FENG Xiaoyi, YU Zhou, CAO Jianhua, DU Weihua, WAN Pengcheng, MA Youji, ZHAO Xueming. Microamplification System Evaluation of Bovine Biopsied Embryo Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 246-258. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||