





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (8): 3516-3525.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.08.024
• Animal Biotechnology and Reproduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
Tong ZHAO1( ), Wenzhe YANG1, Feilong PAN1, Shuchen ZHAO1,2, Kexiang LIU1,2, Zhanjun LÜ1,2, Lijia ZHAO1,2,*(
), Wenzhe YANG1, Feilong PAN1, Shuchen ZHAO1,2, Kexiang LIU1,2, Zhanjun LÜ1,2, Lijia ZHAO1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-11-03
Online:2024-08-23
Published:2024-08-28
Contact:
Lijia ZHAO
E-mail:ZT215926@163.com;ljzhao@neau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Tong ZHAO, Wenzhe YANG, Feilong PAN, Shuchen ZHAO, Kexiang LIU, Zhanjun LÜ, Lijia ZHAO. Bisphenol A Inhibits Testosterone Synthesis in TM3 Cells by Upregulating Apoa1 Gene Expression[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3516-3525.
Table 1
Primers sequence for real-time PCR"
| 引物名称 Primer name | 基因编号 Accession No. | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequence | 产物长度/bp Product length |
| Apoa1 | NM_009692.4 | F: CAAAGACAGCGGCAGAGACT R: AGTTTTCCAGGAGATTCAGGTTCA | 83 |
| Apoa2 | NM_013474.2 | F: GAATCGCAGCACTGTTCCTA R: GTCTCTTAACCAAAGCTCCTTCC | 107 |
| Apoc3 | NM_001289755.1 | F: GAACAAGCCTCCAAGACGGT R: GTTGGTTGGTCCTCAGGGTT | 173 |
| Gapdh | NM_001289726 | F: GCCTCCTCCAATTCAACCCT R: CCCAATACGGCCAAATCCGT | 145 |

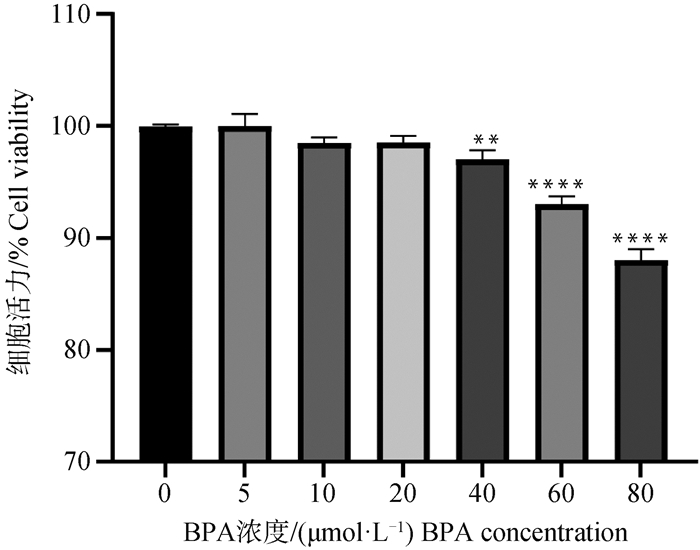
Fig. 1
Effect of different concentration(0-80 μmol ·L-1)of BPA treatment for 24 h on the cell viability of TM3 cells Asterisks on the bar indicate significant differences between CON and BPA-treated groups, * represents P < 0.05, ** represents P < 0.01, *** represents P < 0.001, **** represents P < 0.0001. The same as below"
| 1 |
LIGUORI F , MORENO-MARRODAN C , BARBARO P .Biomass-derived chemical substitutes for bisphenol A: recent advancements in catalytic synthesis[J].Chem Soc Rev,2020,49(17):6329-6363.
doi: 10.1039/D0CS00179A |
| 2 | 王浩. 双酚A类物质在市政污水处理厂中的去除机理及人体暴露分析[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2021. |
| WANG H. Bisphenol A and its analogues: removal mechanisms in municipal wastewater treatment plants and human exposure analysis[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 3 |
BHANDARI R K , DEEM S L , HOLLIDAY D K , et al.Effects of the environmental estrogenic contaminants bisphenol A and 17α-ethinyl estradiol on sexual development and adult behaviors in aquatic wildlife species[J].Gen Comp Endocrinol,2015,214,195-219.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.09.014 |
| 4 |
THAYUMANAVAN G , JEYABALAN S , FULORIA S , et al.Silibinin and naringenin against bisphenol A-induced neurotoxicity in zebrafish model-potential flavonoid molecules for new drug design, development, and therapy for neurological disorders[J].Molecules,2022,27(8):2572.
doi: 10.3390/molecules27082572 |
| 5 |
LOUP B , POUMEROL E , JOUNEAU L , et al.BPA disrupts meiosis I in oogonia by acting on pathways including cell cycle regulation, meiosis initiation and spindle assembly[J].Reprod Toxicol,2022,111,166-177.
doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2022.06.001 |
| 6 |
DIRINCK E , JORENS P G , COVACI A , et al.Obesity and persistent organic pollutants: possible obesogenic effect of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls[J].Obesity (Silver Spring),2011,19(4):709-714.
doi: 10.1038/oby.2010.133 |
| 7 | SERGEEV A V , CARPENTER D O .Residential proximity to environmental sources of persistent organic pollutants and first-time hospitalizations for myocardial infarction with comorbid diabetes mellitus: a 12-year population-based study[J].Int J Occup Med Environ Health,2010,23(1):5-13. |
| 8 | 王敏. 雌激素受体α在双酚A引起肝细胞脂质沉积中的作用[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2023. |
| WANG M. The role of estrogen receptor α in Bisphenol A-induced lipid deposition in hepatocytes[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 9 |
KIM N , NAKAMURA H , MASAKI H , et al.Effect of lipid metabolism on male fertility[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2017,485(3):686-692.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.103 |
| 10 |
SU X , PENG D Q .The exchangeable apolipoproteins in lipid metabolism and obesity[J].Clin Chim Acta,2020,503,128-135.
doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.01.015 |
| 11 | 颜丽, 何津春, 王志禄, 等.载脂蛋白与家族性高胆固醇血症家系成员冠心病患病关系的研究[J].兰州大学学报: 医学版,2016,42(5):31-35. |
| YAN L , HE J C , WANG Z L , et al.Research on relationship between apolipoprotein and coronary heart disease in family members with familial hypercholesterolemia[J].Journal of Lanzhou University: Medical Sciences,2016,42(5):31-35. | |
| 12 | 尹凯. ABCA1介导载脂蛋白A1调节巨噬细胞炎症反应及其机制[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学, 2012. |
| YIN K. Effect and mechanism of apolipoprotein A-I on macrophages inflammatory response via an ABCA1-dependent manner[D]. Hengyang: University of South China, 2012. (in Chinese) | |
| 13 |
ZHANG Y Y , YUAN C , GAO J C , et al.Testicular transcript responses in rare minnow Gobiocypris rarus following different concentrations bisphenol A exposure[J].Chemosphere,2016,156,357-366.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.006 |
| 14 | 吕友缘, 于春晓, 管庆波.代谢综合征对男性睾酮水平的影响及其机制的研究进展[J].老年医学研究,2022,3(3):42-46. |
| LV Y Y , YU C X , GUAN Q B .Research progress on the effect of metabolic syndrome on male testosterone level and its mechanism[J].Geriatrics Research,2022,3(3):42-46. | |
| 15 |
ZHOU J Z , ZHANG Y W , ZENG L , et al.Paternal cadmium exposure affects testosterone synthesis by reducing the testicular cholesterol pool in offspring mice[J].Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,2022,242,113947.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113947 |
| 16 |
BERNECIC N C , DE GRAAF S P , LEAHY T , et al.HDL mediates reverse cholesterol transport from ram spermatozoa and induces hyperactivated motility[J].Biol Reprod,2021,104(6):1271-1281.
doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioab035 |
| 17 |
CORONA G , MAGGI M .The role of testosterone in male sexual function[J].Rev Endocr Metab Disord,2022,23(6):1159-1172.
doi: 10.1007/s11154-022-09748-3 |
| 18 |
JAMBOR T , KNIZATOVA N , GREIFOVA H , et al.Toxicity of bisphenol A and its replacements in the mice Leydig cells in vitro[J].Physiol Res,2023,72(1):71-86.
doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934989 |
| 19 |
LI C M , ZHANG L L , MA T T , et al.Bisphenol A attenuates testosterone production in Leydig cells via the inhibition of NR1D1 signaling[J].Chemosphere,2021,263,128020.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128020 |
| 20 |
LAN H C , WU K Y , LIN I W , et al.Bisphenol A disrupts steroidogenesis and induces a sex hormone imbalance through c-Jun phosphorylation in Leydig cells[J].Chemosphere,2017,185,237-246.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.004 |
| 21 |
QIAN W Y , ZHU J Y , MAO C F , et al.Involvement of CaM-CaMKⅡ-ERK in bisphenol A-induced Sertoli cell apoptosis[J].Toxicology,2014,324,27-34.
doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2014.06.001 |
| 22 |
COCHRAN B J , ONG K L , MANANDHAR B , et al.APOA1:a protein with multiple therapeutic functions[J].Curr Atheroscler Rep,2021,23(3):11.
doi: 10.1007/s11883-021-00906-7 |
| 23 |
MARZAL-CASACUBERTA A , BLANCO-VACA F , ISHIDA B Y , et al.Functional lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency and high density lipoprotein deficiency in transgenic mice overexpressing human apolipoprotein A-Ⅱ[J].J Biol Chem,1996,271(12):6720-6728.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.12.6720 |
| 24 |
SILBERNAGEL G , SCHARNAGL H , KLEBER M E , et al.Common APOC3 variants are associated with circulating ApoC-Ⅲ and VLDL cholesterol but not with total apolipoprotein B and coronary artery disease[J].Atherosclerosis,2020,311,84-90.
doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2020.08.017 |
| 25 | SHI J F , LI Y K , REN K , et al.Characterization of cholesterol metabolism in Sertoli cells and spermatogenesis (Review)[J].Mol Med Rep,2018,17(1):705-713. |
| 26 |
ZHANG Y Y , ZHANG M , ZHU Z , et al.Bisphenol A regulates apolipoprotein A1 expression through estrogen receptors and DNA methlylation and leads to cholesterol disorder in rare minnow testis[J].Aquat Toxicol,2021,241,105999.
doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2021.105999 |
| 27 | GAO Z S , LIU S H , TAN L , et al.Testicular toxicity of bisphenol compounds: homeostasis disruption of cholesterol/testosterone via PPARα activation[J].Sci Total Environ,2022,836,155628. |
| 28 | LAN H C , LIN I W , YANG Z J , et al.Low-dose bisphenol A activates Cyp11a1 gene expression and corticosterone secretion in adrenal gland via the JNK signaling pathway[J].Toxicol Sci,2015,148(1):26-34. |
| 29 | HINFRAY N , NÓBREGA R H , CAULIER M , et al.Cyp17a1 and Cyp19a1 in the zebrafish testis are differentially affected by oestradiol[J].J Endocrinol,2013,216(3):375-388. |
| 30 | CHEN W T , LAU S W , FAN Y Q , et al.Juvenile exposure to bisphenol A promotes ovarian differentiation but suppresses its growth-Potential involvement of pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone[J].Aquat Toxicol,2017,193,111-121. |
| 31 | 韩思兰. 鱼类脂滴自噬与脂滴水解在脂代谢调控中的互作机制研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2021. |
| HAN S L. The interaction between lipophagy and lipolysis in regulation of lipid metabolism in fish[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 32 | MONDUL A M , SELVIN E , ROHRMANN S , et al.Association of serum cholesterol and cholesterol-lowering drug use with serum sex steroid hormones in men in NHANES Ⅲ[J].Cancer Causes Control,2010,21(10):1575-1583. |
| 33 | 赵为民, 杨建英, 代涛, 等.小鼠睾丸间质细胞体外原代培养方法的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(46):8665-8667. |
| ZHAO W M , YANG J Y , DAI T , et al.Establishment of a method for primary culture of mouse Leydig cells in vitro[J].Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2011,15(46):8665-8667. | |
| 34 | 邹治然, 王雪婷, 朱俐.低氧对原代睾丸间质细胞和细胞系TM3、MLTC-1中核呼吸因子1与睾酮合成的影响[J].南通大学学报: 医学版,2017,37(5):395-399. |
| ZOU Z R , WANG X T , ZHU L .Effects of hypoxia on the synthesis of nuclear respiratory factor 1 and testosterone in primary Leydig cells, cell lines TM3 and MLTC-1[J].Journal of Nantong University: Medical Sciences,2017,37(5):395-399. |
| [1] | Shiyuan XU, Liuguang ZHANG, Songqi LIU, Kaihui WU, Chao WANG, Dong WANG, Yunwei PANG. Study on the Effects and Mechanism of ART3 in Regulating Spermatogenesis in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2995-3010. |
| [2] | Yaxuan MENG, Yan LIU, Jing WANG, Guoshun CHEN, Tao FENG. Research Progress in the Effect of Oxidative Stress on Ovarian Function in Female Livestock [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2825-2835. |
| [3] | Kaihui WU, Liuguang ZHANG, Chao WANG, Shiyuan XU, Songqi LIU, Kaimin YUAN, Dong WANG, Yunwei PANG. Study on the Mechanism of Melatonin Relieving Testicular Damage in Mice Induced Busulfan [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2486-2497. |
| [4] | Tingting CHU, Xiaoyu ZHANG, Lei SUN, Jiashun TONG, Lei ZHANG, Yuxuan SONG. Advances in Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Endometrial Fibrosis in Domestic Animals [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2334-2344. |
| [5] | CHEN Hongyu, WEI Yating, LI Ruoxi, GAO Liutao, LIU Shenhe. Advances in Animals Sperm Sexing Techniques [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1370-1380. |
| [6] | WEI Yating, XU Zejun, CHEN Hongyu, WANG Xianwei, CHEN Qixin, LIU Shenhe. Research Progress of Exogenous Vitamin E and Selenium Regulating Semen Quality in Animals [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1389-1400. |
| [7] | ZHONG Zhuxia, HU Xiuzhong, XIANG Min, YU Jie, LIU Chenhui, ZHAO Shenglan, WAN Pingmin, WANG Dingfa, ZHOU Yuan, CHENG Lei. Research Progress on Biological Function and Application of Pregnancy Associated Glycoproteins in Livestock Production [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 874-881. |
| [8] | JIANG Lijun, ZONG Yunhe, LI Yunlei, CHEN Jilan, GENG Zhaoyu, SUN Yanyan, JIN Sihua. Research Progress of Antioxidant Application in Poultry Semen Storage [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 913-923. |
| [9] | WANG Nana, LI Qihan, MA Yuan, JIN Haoyan, HU Yamei, MA Yun, ZHANG Lingkai. Research Progress on TLR7 and TLR8 in Livestock Reproductive Control Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 427-437. |
| [10] | GAO Yawei, PENG Di, SUN Zhaoyang, YAN Ziyue, CUI Kai, MA Zefang. Mining the Molecular Mechanism of Exogenous Melatonin Affecting the Development of Mink Ovary Based on Transcriptome Data [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 607-618. |
| [11] | XIAO Yimei, WANG Shengnan, XU Yuewen, HE Xiaolin, YIN Fuquan. Research on the Influence of Heat Stress on Male Reproduction [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 11-21. |
| [12] | CHEN Siying, SUN Yawen, LI Kang, LIU Shuo, HAO Haisheng, DU Weihua, ZOU Huiying, ZHU Huabin, PANG Yunwei. Application of Microfluidic Technologies in Livestock in vitro Embryo Production [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 4889-4897. |
| [13] | ZHANG Chenyibo, YU Tong, REN Binbin, ZHENG Ruizhi, ZHU Wenzhi, SU Jianmin. Mechanism of Epigenetic Reprogramming of Early Animal Embryos [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 4898-4909. |
| [14] | DU Haidong, NA Renhua. Research Progress on Physiological Metabolism and Microbial Changes of Ruminants During Gestation and Lactation and Their Effects on Offspring Development [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4458-4467. |
| [15] | SHAO Jing, ZHANG Ying, TANG Yu, XU Baozeng. Research Progress of ERM Proteins in Mammalian Oocyte Maturation and Fertilization [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4477-4487. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||