





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 5635-5648.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.11.023
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Zhikang1( ), ZHOU Keke2, CHEN Zhaoguo2, MI Rongsheng2, HUANG Yan2, ZHU Qi2, GONG Haiyan2,*(
), ZHOU Keke2, CHEN Zhaoguo2, MI Rongsheng2, HUANG Yan2, ZHU Qi2, GONG Haiyan2,*( ), LIU Wei1,*(
), LIU Wei1,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-19
Online:2025-11-23
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
GONG Haiyan, LIU Wei
E-mail:huaerL@stu.hunau.edu.cn;gonghaiyan@shvri.ac.cn;weiliupro@163.com
CLC Number:
LI Zhikang, ZHOU Keke, CHEN Zhaoguo, MI Rongsheng, HUANG Yan, ZHU Qi, GONG Haiyan, LIU Wei. The Dynamic Analysis on the Infectivity of Babesia microti in Rats, Rabbits and Sheep[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5635-5648.
Table 1
Primer sequences of nested PCR and fluorescence quantitative PCR"
| 引物Primer | 序列(5′→3′)Sequence |
| Bab-1-F | AATTACCCAATCCTGACACAGG |
| Bab-1-R | TTTCGCAGTAGTTCGTCTTTAACA |
| Bab-2-F | GACACAGGGAGGTAGTGACAAGA |
| Bab-2-R | CCCAACTGCTCCTATTAACCATTAC |
| Bm-RF | CAGGGAGGTAGTGACAAGAAATAACA |
| Bm-RR | GGTTTAGATTCCCATCATTCCAAT |
| Bm-Probe | 6FAM-TACAGGGCTTAAAGTCTMGBNFQ[ |
| BmSA1-F | ATGGTGTCATTCAAACCAAC |
| BmSA1-R | TTAGAATAGAAACATAGCGA |
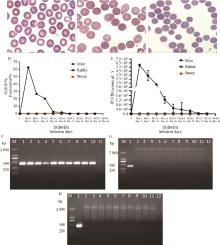
Fig. 1
Investigation of B. microti in the blood of three kinds of animals post-inoculation A-C. Blood smear of mice (A), rabbits (B) and sheep (C) infected with B. microti (Giemsa staining, ×1 000); D. Curve of infection rate investigated under microscopy; E. Curve of B.microti specific gene copys investigated using Q-PCR analysis; G-H: Nested PCR amplification of B. microti in the blood DNA samples from mice (F), rabbits (G) and sheep (H)(M. DL2000 DNA marker; 1. Positive control; 2-10. Day 4-36 post-infection (dpi) with 4 day intervals; 11. Negative control; 12. ddH2O)"
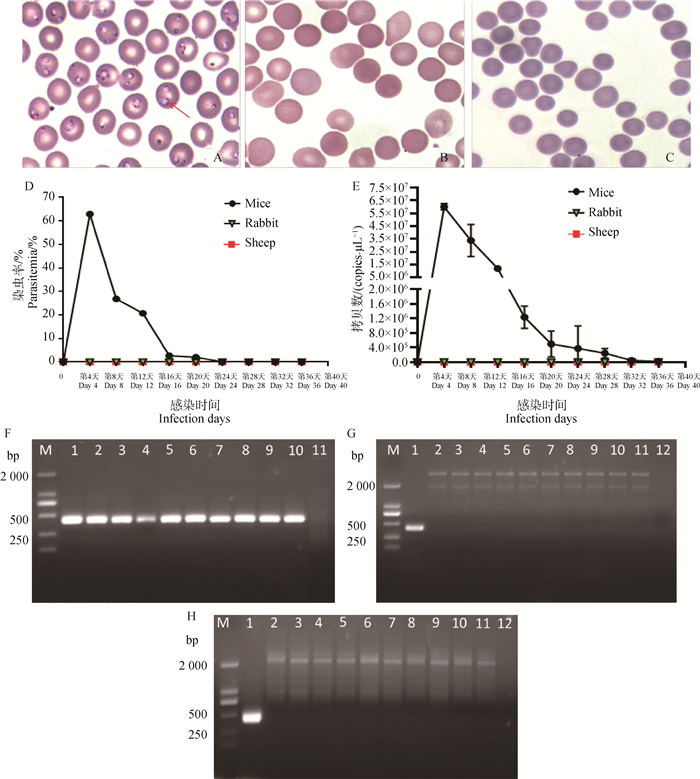
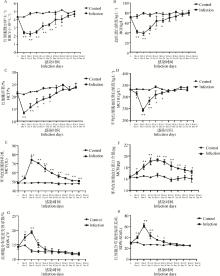
Fig. 4
Curves of RBC associated parameters in B.microti-infected mice A. The number of RBCs; B. The concentration of Hemoglobin (HGB); C. Hematocrit (HCT); D. The mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC); E. The mean corpuscular volume (MCV); F. The mean corpuscular hemoglobin content (MCH); G. RBC distribution width-variation coefficient (RDW-CV); H. RBC distribution width-standard deviation (RDW-SD). Control. The control group; Infection. The infection group; Student's T-test: *. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01"
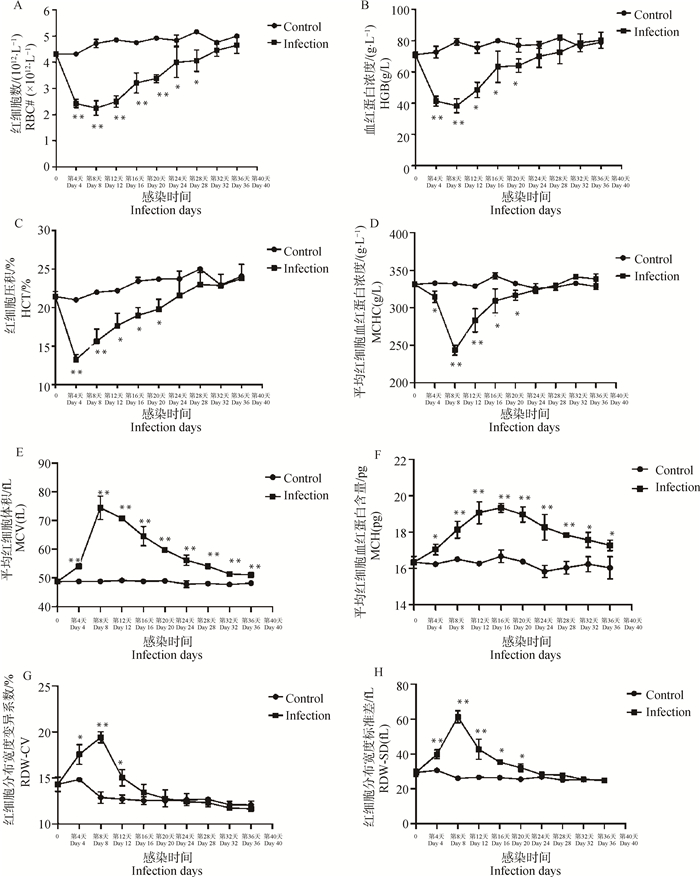
Fig. 5
Curves of platelet parameters in B.microti-infected mice A. The number of platelet (PLT); B. Plateletcrit (PCT%); C.The mean platelet volume (MPV); D. The platelet distribution width (PDW). Control. The control group; Infection. The infection group; Student's T-test: *. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01"
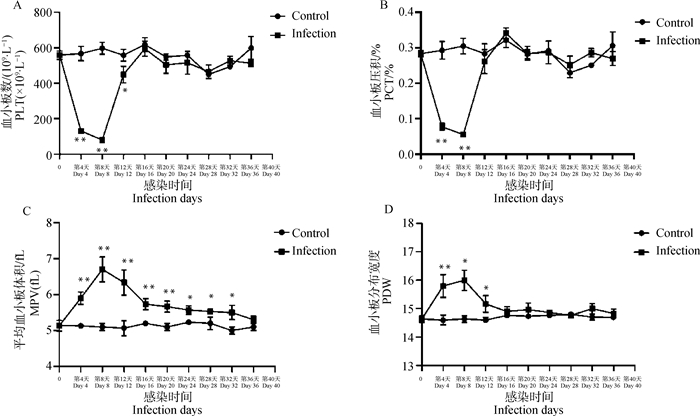
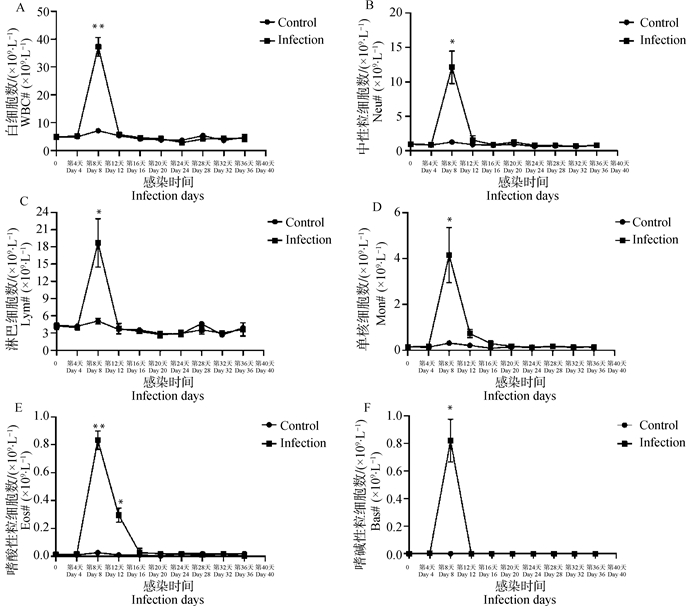
Fig. 6
Curves of parameters associated with white cells in B.microti-infected mice A. The number of white blood cells (WBC); B. The number of neutrophils (Neu); C. The number of lymphocytes (Lym); D. The number of monocytes (Mon); E. The number of eosinophil (Eos); F. The number of basophil (Bas). Control. The control group; Infection. The infection group; Student's T-test: *. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01"
| 1 |
HERSH M H , TIBBETTS M , STRAUSS M , et al. Reservoir competence of wildlife host species for Babesia microti[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2012, 18 (12): 1951- 1957.
doi: 10.3201/eid1812.111392 |
| 2 |
KRAUSE P J . Human babesiosis[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2019, 49 (2): 165- 174.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2018.11.007 |
| 3 |
BLOCH E M , KUMAR S , KRAUSE P J . Persistence of Babesia microti infection in humans[J]. Pathogens, 2019, 8 (3): 102.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens8030102 |
| 4 |
HILDEBRANDT A , GRAY J S , HUNFELD K P . Human babesiosis in Europe: what clinicians need to know[J]. Infection, 2013, 41 (6): 1057- 1072.
doi: 10.1007/s15010-013-0526-8 |
| 5 |
KIM J Y , CHO S H , JOO H N , et al. First case of human babesiosis in Korea: detection and characterization of a novel type of Babesia sp. (KO1) similar to ovine babesia[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2007, 45 (6): 2084- 2087.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.01334-06 |
| 6 |
WESTBLADE L F , SIMON M S , MATHISON B A , et al. Babesia microti: from mice to ticks to an increasing number of highly susceptible humans[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2017, 55 (10): 2903- 2912.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.00504-17 |
| 7 | 周霞, 王慧, 薛靖波, 等. 国内外巴贝虫病流行现状与研究进展[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2019, 31 (1): 63- 70. |
| ZHOU X , WANG H , XUE J B , et al. Epidemic and research progress of babesiosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control, 2019, 31 (1): 63- 70. | |
| 8 |
ANTUNES S , ROSA C , COUTO J , et al. Deciphering Babesia-vector interactions[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2017, 7, 429.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00429 |
| 9 |
WEI C Y , WANG X M , WANG Z S , et al. High prevalence of Babesia microti in small mammals in Beijing[J]. Infect Dis Poverty, 2020, 9 (1): 155.
doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00775-3 |
| 10 |
VANNIER E , KRAUSE P J . Human babesiosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2012, 366 (25): 2397- 2407.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1202018 |
| 11 |
HILDEBRANDT A , HUNFELD K P . Human babesiosis-a rare but potentially dangerous zoonosis[J]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr, 2014, 139 (18): 957- 962.
doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1369936 |
| 12 |
CAI Y C , WU F , HU W , et al. Molecular characterization of Babesia microti seroreactive antigen 5-1-1 and development of rapid detection methods for anti-B. microti antibodies in serum[J]. Acta Trop, 2018, 185, 371- 379.
doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.03.020 |
| 13 |
ALVAREZ J A , ROJAS C , FIGUEROA J V . An Overview of Current Knowledge on in vitro Babesia cultivation for production of live attenuated vaccines for bovine babesiosis in Mexico[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2020, 7, 364.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00364 |
| 14 |
STANDFAST N F , BOCK R E , WIECEK M M , et al. Overcoming constraints to meeting increased demand for Babesia bigemina vaccine in Australia[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2003, 115 (3): 213- 222.
doi: 10.1016/S0304-4017(03)00223-1 |
| 15 |
BANETH G . Antiprotozoal treatment of canine babesiosis[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2018, 254, 58- 63.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2018.03.001 |
| 16 |
GIMENEZ A M , FRANçOSO K S , ERSCHING J , et al. A recombinant multi-antigen vaccine formulation containing Babesia bovis merozoite surface antigens MSA-2a(1), MSA-2b and MSA-2c elicits invasion-inhibitory antibodies and IFN-γ producing cells[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2016, 9 (1): 577.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1862-1 |
| 17 |
BASTOS R G , ALZAN H F , RATHINASAMY V A , et al. Harnessing Mycobacterium bovis BCG trained immunity to control human and bovine babesiosis[J]. Vaccines (Basel), 2022, 10 (1): 123.
doi: 10.3390/vaccines10010123 |
| 18 |
AL-NAZAL H , LOW L M , KUMAR S , et al. A vaccine for human babesiosis: prospects and feasibility[J]. Trends Parasitol, 2022, 38 (10): 904- 918.
doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2022.07.005 |
| 19 | NGUYEN T T H , LEE J S , SHIM H . Construction of rabbit immune antibody libraries[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2023, 2702, 93- 106. |
| 20 |
FÖLDES K , ALIGHOLIPOUR FARZANI T , ERGüNAY K , et al. Differential growth characteristics of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in kidney cells of human and bovine origin[J]. Viruses, 2020, 12 (6): 685.
doi: 10.3390/v12060685 |
| 21 |
BEUGNET F , MOREAU Y . Babesiosis[J]. Rev Sci Tech, 2015, 34 (2): 627- 639.
doi: 10.20506/rst.34.2.2385 |
| 22 |
KUMAR B , MAHARANA B R , THAKRE B , et al. 18S rRNA gene-based piroplasmid PCR: An assay for rapid and precise molecular screening of Theileria and Babesia species in animals[J]. Acta Parasitol, 2022, 67 (4): 1697- 1707.
doi: 10.1007/s11686-022-00625-2 |
| 23 | 陈倩, 王静, 侯咏, 等. 鼠巴贝斯虫TaqMan探针荧光定量PCR方法的建立及应用[J]. 中国国境卫生检疫杂志, 2014, 37 (4): 221- 225. |
| CHEN Q , WANG J , HOU Y , et al. Establishment and application of a TaqMan probe fluorescence quantitative PCR method for Babesia microti[J]. Chinese Journal of Frontier Health and Quarantine, 2014, 37 (4): 221- 225. | |
| 24 |
TEAL A E , HABURA A , ENNIS J , et al. A new real-time PCR assay for improved detection of the parasite Babesia microti[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2012, 50 (3): 903- 908.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.05848-11 |
| 25 | 孙明. 牛巴贝斯虫TaqMan荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2020, 37 (10): 99-103, 20. |
| SUN M . Establishment of a TaqMan fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detection of Babesia bovis[J]. China Animal Health Inspection, 2020, 37 (10): 99-103, 20. | |
| 26 |
CAI Y C , YANG C L , SONG P , et al. The protective effects of BMSA1 and BMSA5-1-1 proteins against Babesia microti infection[J]. Parasites Hosts Dis, 2024, 62 (1): 53- 63.
doi: 10.3347/PHD.23077 |
| 27 | 魏金龙, 周勇志, 龚海燕, 等. 田鼠巴贝斯虫感染对宿主凝血系统的影响[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2015, 45 (4): 390- 394. |
| WEI J L , ZHOU Y Z , GONG H Y , et al. Effects of Babesia microti infection on host coagulation system[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2015, 45 (4): 390- 394. | |
| 28 | 张世杰, 米荣升, 张晓丽, 等. 感染微小隐孢子虫绵羊的血常规及血清抗体动态变化[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2022, 30 (4): 163- 175. |
| ZHANG S J , MI R S , ZHANG X L , et al. Dynamic changes in blood routine and serum antibodies of sheep infected with Cryptosporidium parvum[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2022, 30 (4): 163- 175. | |
| 29 | 李月勤, 曹红梅, 张利卫, 等. 犬巴贝斯虫病的研究概况[J]. 现代牧业, 2019, 3 (4): 44- 46. |
| LI Y Q , CAO H M , ZHANG L W , et al. Research overview of canine babesiosis[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry, 2019, 3 (4): 44- 46. | |
| 30 |
CARIUS H J , LITTLE T J , EBERT D . Genetic variation in a host-parasite association: potential for coevolution and frequency-dependent selection[J]. Evolution, 2001, 55 (6): 1136- 1145.
doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2001.tb00633.x |
| 31 |
FRANK S A . Specific and non-specific defense against parasitic attack[J]. J Theor Biol, 2000, 202 (4): 283- 304.
doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1999.1054 |
| 32 |
HAMILTON W D , AXELROD R , TANESE R . Sexual reproduction as an adaptation to resist parasites (a review)[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1990, 87 (9): 3566- 3573.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3566 |
| 33 |
JIGGINS F M , KIM K W . Contrasting evolutionary patterns in Drosophila immune receptors[J]. J Mol Evol, 2006, 63 (6): 769- 780.
doi: 10.1007/s00239-006-0005-2 |
| 34 | 王婧, 周绪正, 李冰, 等. 抗巴贝斯虫药物的研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2013, 40 (4): 206- 211. |
| WANG J , ZHOU X Z , LI B , et al. Research progress on anti-Babesia drugs[J]. China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2013, 40 (4): 206- 211. | |
| 35 |
RIZK M A , EL-SAYED S A E , NASSIF M , et al. Assay methods for in vitro and in vivo anti-Babesia drug efficacy testing: Current progress, outlook, and challenges[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2020, 279, 109013.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2019.109013 |
| 36 | 郭宪国, 黄丽琴. 寄生虫与宿主的协同进化关系[J]. 国际医学寄生虫病杂志, 2009, 36 (1): 49- 54. |
| GUO X G , HUANG L Q . Co-evolution relationship between parasites and hosts[J]. International Journal of Medical Parasitic Diseases, 2009, 36 (1): 49- 54. | |
| 37 |
WEI N , DU Y , LU J , et al. A cysteine protease of Babesia microti and its interaction with tick cystatins[J]. Parasitol Res, 2020, 119 (9): 3013- 3022.
doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06818-w |
| 38 | 崔筱雨, 隋树丛, 苏炳娟, 等. 血常规检测技术在猪群健康监测中的应用[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2018 (2): 86- 88. |
| CUI X Y , SUI S C , SU B J , et al. Application of blood routine detection technology in swine herd health monitoring[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2018 (2): 86- 88. | |
| 39 | 王亚东, 韩旭东, 黄晓英. 血常规参数在重症疟疾中的诊断价值[J]. 南通大学学报(医学版), 2016, 36 (5): 464- 467. |
| WANG Y D , HAN X D , HUANG X Y . Diagnostic value of routine blood parameters in severe malaria[J]. Journal of Nantong University (Medical Sciences), 2016, 36 (5): 464- 467. | |
| 40 |
CHAUVIN A , MOREAU E , BONNET S , et al. Babesia and its hosts: adaptation to long-lasting interactions as a way to achieve efficient transmission[J]. Vet Res, 2009, 40 (2): 37.
doi: 10.1051/vetres/2009020 |
| 41 | 陈韶红, 蔡玉春, 陈家旭, 等. 田鼠巴贝虫(Babesia mocroti)的超微结构观察[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2013, 29 (11): 1072- 1075. |
| CHEN S H , CAI Y C , CHEN J X , et al. Ultrastructural observation of Babesia microti[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 2013, 29 (11): 1072- 1075. | |
| 42 |
IKE K , KOMATSU T , MURAKAMI T , et al. High susceptibility of Djungarian hamsters (Phodopus sungorus) to the infection with Babesia microti supported by hemodynamics[J]. J Vet Med Sci, 2005, 67 (5): 515- 520.
doi: 10.1292/jvms.67.515 |
| 43 |
NARURKAR R , MAMORSKA-DYGA A , AGARWAL A , et al. Babesiosis-associated immune thrombocytopenia[J]. Stem Cell Investig, 2017, 4, 1.
doi: 10.21037/sci.2017.01.02 |
| 44 |
GODDARD A , LEISEWITZ A L , KRISTENSEN A T , et al. Platelet indices in dogs with Babesia rossi infection[J]. Vet Clin Pathol, 2015, 44 (4): 493- 497.
doi: 10.1111/vcp.12306 |
| 45 |
GODDARD A , LEISEWITZ A L , KRISTENSEN A T , et al. Platelet activation and platelet-leukocyte interaction in dogs naturally infected with Babesia rossi[J]. Vet J, 2015, 205 (3): 387- 392.
doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.05.008 |
| 46 | AYDOGAN A , AKKUCUK S , ARICA S , et al. The analysis of mean platelet volume and platelet distribution width levels in appendicitis[J]. Indian J Surg, 2015, 77 (Suppl 2): 495- 500. |
| 47 |
SCHWARTZ D , SHARKEY L , ARMSTRONG P J , et al. Platelet volume and plateletcrit in dogs with presumed primary immune-mediated thrombocytopenia[J]. J Vet Intern Med, 2014, 28 (5): 1575- 1579.
doi: 10.1111/jvim.12405 |
| 48 |
VAN ROOYEN L J , HOOIJBERG E H , SCHOEMAN J P , et al. Thromboelastographic platelet mapping in dogs with complicated Babesia rossi infection[J]. Vet Clin Pathol, 2019, 48 (1): 11- 18.
doi: 10.1111/vcp.12689 |
| 49 |
LUO Y , JIA H , TERKAWI M A , et al. Identification and characterization of a novel secreted antigen 1 of Babesia microti and evaluation of its potential use in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunochromatographic test[J]. Parasitol Int, 2011, 60 (2): 119- 125.
doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2010.11.001 |
| 50 | LI M , AO Y , GUO J , et al. Surface antigen 1 is a crucial secreted protein that mediates Babesia microti invasion into host cells[J]. Front Microbiol, 2019, 10, 3046. |
| 51 |
LEVIN A E , WILLIAMSON P C , BLOCH E M , et al. Serologic screening of United States blood donors for Babesia microti using an investigational enzyme immunoassay[J]. Transfusion, 2016, 56 (7): 1866- 1874.
doi: 10.1111/trf.13618 |
| 52 |
WU J , CAO J , ZHOU Y , et al. Evaluation on Infectivity of Babesia microti to domestic animals and ticks outside the ixodes genus[J]. Front Microbiol, 2017, 8, 1915.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01915 |
| 53 |
BLOCH E M , LEVIN A E , WILLIAMSON P C , et al. A prospective evaluation of chronic Babesia microti infection in seroreactive blood donors[J]. Transfusion, 2016, 56 (7): 1875- 1882.
doi: 10.1111/trf.13617 |
| 54 |
AGUILAR-DELFIN I , HOMER M J , WETTSTEIN P J , et al. Innate resistance to Babesia infection is influenced by genetic background and gender[J]. Infect Immun, 2001, 69 (12): 7955- 7958.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.12.7955-7958.2001 |
| 55 |
SCHLOSSER J , DäHNERT L , DREMSEK P , et al. Different outcomes of experimental hepatitis E virus infection in diverse mouse strains, wistar rats, and rabbits[J]. Viruses, 2018, 11 (1): 1.
doi: 10.3390/v11010001 |
| 56 |
WHITE N J . Determinants of relapse periodicity in Plasmodium vivax malaria[J]. Malar J, 2011, 10, 297.
doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-297 |
| 57 |
KRAUSE P J , GEWURZ B E , HILL D , et al. Persistent and relapsing babesiosis in immunocompromised patients[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2008, 46 (3): 370- 376.
doi: 10.1086/525852 |
| 58 | HEMMER R M , FERRICK D A , CONRAD P A . Role of T cells and cytokines in fatal and resolving experimental babesiosis: protection in TNFRp55-/- mice infected with the human Babesia WA1 parasite[J]. J Parasitol, 2000, 86 (4): 736- 742. |
| 59 |
CLAWSON M L , PACIORKOWSKI N , RAJAN T V , et al. Cellular immunity, but not gamma interferon, is essential for resolution of Babesia microti infection in BALB/c mice[J]. Infect Immun, 2002, 70 (9): 5304- 5306.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.9.5304-5306.2002 |
| 60 |
RAUF U , SULEMAN M , ABID A , et al. Humoral and cell-mediated immune response validation in calves after a live attenuated vaccine of Babesia bigemina[J]. Pathogens, 2020, 9 (11): 936.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens9110936 |
| [1] | LIU Feng, LI Kun, ZHANG Xingze, MA Xueqing, SUN Pu, LI Fengjuan, CAO Yimei, BAI Xingwen, FU Yuanfang, YUAN Hong, OUYANG Yifan, LIU Zaixin, LU Zengjun, LI Pinghua. Construction and Expression of IgA Antibodies against Foot-and-mouth Disease Virus and Analysis of Its Antiviral Activity [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3985-3991. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xinyu, DAI Pengxiu, ZHANG Fan, ZHANG Xinke. The Relationship between Cat Periodontal Disease and Oral Flora and Its Prevention and Treatment [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 4065-4073. |
| [3] | SHU Jingchao, ZHANG Han, PENG Zhifeng, QIAO Hongxing. Isolation, Identification and Virulence Gene Analysis of Porcine Pathogenic Lactococcus garvieae [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3399-3407. |
| [4] | JIANG Yanping, LIU Wei, GONG Haoyang, CAI Limeng, LI Jiaxuan, CUI Wen, ZHOU Han, HAN Jianchun, TANG Lijie. Preparation of Monoclonal Antibodies to IBDV and Establishment of a Double Antibody Sandwich ELISA Method for Detection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3433-3441. |
| [5] | WANG Feiyan, LIU Chaofan, ZHANG Ya'nan, ZHOU Xiaotian, REN Jing, YUAN Chen, LI Tanqing, SONG Qinye. Preparation of Monoclonal Antibody to Porcine IL-15 and Establishment of Double Antibody Sandwich ELISA Method [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3442-3452. |
| [6] | ZHANG Xiaoling, HE Xinglin, ZHANG Mengdi, LI Pengfei, SUN Yumei, MA Hailong, ZHU Hongmei, ZHANG Mengjia, LI Wentao. Preparation of E2 Protein Nanoparticles from Classical Swine Fever Virus and the Immunogenicity Study in Rabbit [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2301-2311. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yu, CHENG Fanyu, YU Zhaorong, SHAO Ying, WEI Ningbo, CHEN Fangfang, WANG Zhenyu, SONG Xiangjun, TU Jian, QI Kezong*. Preparation, Identification, and Preliminary Application of Monoclonal Antibodies against Fowl Adenovirus Serotype 4 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2364-2371. |
| [8] | CAO Liyan, KONG Xiangyu, YUAN Cong, DUAN Yueyue, MA Guoxiang, SHI Lei, ZHANG Yu, WAN Ying, LI Xiangtong, WANG Yating, DU Yu, ZHENG Haixue, WANG Qi. Identifcation of a Novel Linear B-cell Epitope in the Nucleocapsid Protein of Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1854-1864. |
| [9] | MA Xiaoli, LI Duan, ZENG Daoping, LIU Yanling, WANG Xiaomin, PENG Guoliang, SONG Changxu, WANG Lei, XU Zheng. Establishment of a Fully Automated Chemiluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay for Detecting Antibodies against African Swine Fever Virus p72 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1355-1365. |
| [10] | ZHAO Long, LIN Jingyi, DOU Wei, XU Tingxuan, GU Qingyun, GAO Haihui, LI Shengqing, GUO Kangkang. In vitro Screening of Tibetan Medicine with Inhibitory Effects on Bovine Coronavirus Replication [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 826-838. |
| [11] | LI Fan, SUN Haifeng, SUN Meng, GAO Yanxiao, SUN Yangyang, ZHANG Lujie, BAI Juan, JIANG Ping. Preparation and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Porcine IL-1β Monoclonal Antibody [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 890-899. |
| [12] | SUN Xinru, WU Wenqing, LUO Yajuan, XIE Rui, PENG Changjiang, HUA Lin, WU Bin, PENG Zhong. Preparation of Monoclonal Antibodies against MltA Protein of Lawsonia intracellularis and Establishment of Blocking ELISA Antibody Detection Method [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5660-5669. |
| [13] | SONG Hongyan, CHEN Fuyou, JIA Chenyu, HUANG Yuzhou, LAI Yufang, ZHOU Qi, HUANG Lidong, CHEN Jilong, LI Xunliang. Expression of FtsZ Protein of Mycoplasma synoviae and Establishment of an Indirect ELISA Method for Antibody Detection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5732-5742. |
| [14] | CAO Qiuxia, YAN Kexin, CHENG Zhenkong, BIAN Xianyu, WANG Chuanhong, LI Sufen, ZHANG Xuehan, FAN Baochao, GUO Rongli, YANG Shanshan, WANG Xiaodu, LI Bin. Expression and Biological Activity Analysis of Porcine CCL25 Recombinant Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5864-5874. |
| [15] | CAO Hengzhi, MA Qianyue, JIANG Yanping, CUI Wen, LI Jiaxuan, QIAO Xinyuan. Preparation of Monoclonal Antibody against Bovine Kobuvirus and Establishment of Double Antibody Sandwich ELISA Method [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 5084-5094. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||