





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 2168-2181.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.05.017
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Guoxin1,2( ), LI Yunhua1, SAI Yin1, GUO Wenhua1, ZHAO Yanhong2, ZHANG Manxin3, LIU Jiasen1,*(
), LI Yunhua1, SAI Yin1, GUO Wenhua1, ZHAO Yanhong2, ZHANG Manxin3, LIU Jiasen1,*( )
)
Received:2024-10-28
Online:2025-05-23
Published:2025-05-27
Contact:
LIU Jiasen
E-mail:a2432613041@163.com;jsliu588@163.com
CLC Number:
SUN Guoxin, LI Yunhua, SAI Yin, GUO Wenhua, ZHAO Yanhong, ZHANG Manxin, LIU Jiasen. Population Structure Analysis and Economic Traits Related Selection Signal Detection of Hu Sheep[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2168-2181.
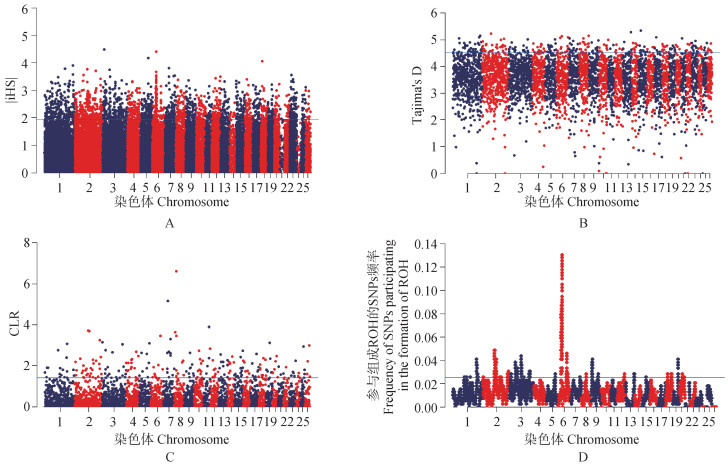
Fig. 4
Manhattan diagram of four selection signal results A. Manhattan map of standardized iHS values; B. Manhattan map of Tajima 's D value; C. Manhattan map of CLR values; D. Manhattan map of high-frequency SNPs. The blue line in the 4 Manhattan charts is the threshold line of the top 5% SNPs"
"
| 基因 Gene | 染色体 Chromosome | 检测方法 Test method | 相关性状 Related trait | 参考文献 Reference |
| ACAN | 18 | ROH、Tajima’s D | 骨骼发育 | [ |
| CSMD3 | 9 | iHS、ROH、Tajima’s D | 体尺 | [ |
| CCSER1 | 6 | iHS、ROH | 采食量 | [ |
| CAPN3 | 7 | iHS、CLR | 初生重 | [ |
| COL5A2 | 2 | iHS、ROH | 骨骼发育与皮肤发育 | [ |
| ERLEC1 | 3 | iHS、CLR、ROH | 初生重 | [ |
| FLVCR1 | 12 | iHS、ROH | 肌肉发育 | [ |
| FAM184B | 6 | iHS、ROH | 14月龄体重 | [ |
| GALNTL6 | 2 | iHS、CLR、ROH | 平均日增重 | [ |
| GPC6 | 10 | iHS、Tajima’s D | 体尺 | [ |
| HAPLN1 | 5 | iHS、CLR | 骨骼发育 | 无 |
| HAPLN3 | 18 | ROH、Tajima’s D | 骨骼发育 | 无 |
| IBSP | 6 | iHS、ROH、Tajima’s D | 眼肌面积 | [ |
| LAP3 | 6 | iHS、ROH | 初生重、采食量 | [ |
| LCORL | 6 | iHS、ROH | 体尺 | [ |
| MED28 | 6 | iHS、ROH | 宰前活重 | [ |
| MUSTN1 | 19 | ROH、Tajima’s D | 肌肉发育 | [ |
| PLIN1 | 18 | iHS、ROH | 饲料转化率 | [ |
| PDE9A | 1 | iHS、CLR | 肠胃发育 | [ |
| PDLIM5 | 6 | iHS、ROH | 肌肉发育 | [ |
| STRN3 | 18 | iHS、CLR | 肥尾发育 | [ |
| SUCLG2 | 19 | CLR、Tajima’s D | 能量代谢 | [ |
| SLC13A1 | 4 | iHS、Tajima’s D | 软骨发育 | [ |
Table 2
Candidate genes related to reproductive traits"
| 基因 Gene | 染色体 Chromosome | 检测方法 Test method | 相关性状 Related trait | 参考文献 Reference |
| SPP1 | 6 | iHS、ROH、Tajima’s D | 卵细胞发育与受精 | [ |
| CACNA1D | 19 | CLR、ROH | 受胎率 | [ |
| KCNN3 | 1 | iHS、ROH | 早产 | [ |
| ABHD2 | 18 | iHS、ROH、Tajima’s D | 精液品质 | [ |
| PPM1K | 6 | iHS、ROH | 引发多囊卵巢综合征 | [ |
| ADGRB3 | 9 | iHS、ROH | 胚胎发育 | [ |
| BMPR1B | 6 | iHS、ROH | 产羔数的主效基因 | [ |
| CDCA7 | 2 | iHS、CLR | 高排卵 | [ |
| COL4A3 | 2 | iHS、ROH | 繁殖相关生物过程 | [ |
| GPRIN3 | 6 | CLR、ROH | 产羔数 | [ |
| FSIP2 | 2 | CLR、ROH | 精子活力 | [ |
| HSD3B1 | 1 | iHS、Tajima’s D | 卵泡发育 | [ |
| HCRTR1 | 2 | iHS、ROH | 产羔数 | [ |
| MEPE | 6 | iHS、ROH、Tajima’s D | 产羔数 | [ |
| MAST4 | 16 | iHS、CLR | 产羔数 | [ |
| ROBO2 | 1 | iHS、Tajima’s D | 卵泡发育、母羊生产次数 | [ |
| SLIT2 | 6 | iHS、CLR | 卵泡发育 | [ |
| NDRG1 | 9 | iHS、CLR | 精子发生 | [ |
Table 3
Verification results of human homologous genes"
| 结构域 Domain | 相关性状 Related trait | 基因 Gene |
| 骨骼Skeleton | 身高、胸高、腰臀围、 骨密度 | ACAN、ERLEC1、FLVCR1、FAM184B、GPC6、HAPLN1、HAPLN3、 IBSP、LAP3、LCORL、MED28、MUSTN1、PLIN1、PDE9A、PDLIM5、 ABHD2、CACNA1D、HCRTR1、KCNN3、MEPE、MAST4、ROBO2、 SLIT2、SPP1、NDRG1、COL4A4、ABCG2、DPY19L1、HTR1B、DNAJC18、 SND1、GPATCH3、STAB1、BRAF、 |
| 新陈代谢 Metabolism | 初生重、体重、 | ACAN、ERLEC1、GALNTL6、GPC6、HAPLN3、IBSP、LAP3、LCORL、 MUSTN1、PDLIM5、CACNA1D、HCRTR1、KCNN3、MAST4、ROBO2、 SLIT2、COL4A4、ABCG2、DPY19L1、HTR1B、DNAJC18、SND1、STAB1、 PRG4、TNIK、FABP3、KLF12、LINGO2 |
| 生殖Reproduction | 初情期 | ABHD2、CACNA1D、MAST4、COL4A4、STAB1、KLF12 |
| 免疫学 Immunology | 血细胞体积、血细胞比容、血红蛋白浓度 | WDHD1 FBLN1、GPATCH3、DOCK10、MSR1、TNIK、KLF12 |
| 1 | 王韵斐, 陈秋菊, 武翠香, 等. 巴美肉羊与湖羊杂交效果研究[J]. 现代畜牧科技, 2024 (12): 10- 13. |
| WANG Y F , CHEN Q J , WU C X , et al. Study on the hybridization effect of Bamei mutton sheep and Hu sheep[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry Science & Technology, 2024 (12): 10- 13. | |
| 2 | PAN Z Y , HE X Y , WANG X Y , et al. Selection signature in domesticated animals[J]. Yi Chuan, 2016, 38 (12): 1069- 1080. |
| 3 |
LIU D Y , CHEN Z L , ZHAO W , et al. Genome-wide selection signatures detection in Shanghai Holstein cattle population identified genes related to adaption, health and reproduction traits[J]. BMC Genomics, 2021, 22 (1): 747.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08042-x |
| 4 |
赵家豪, 刘贤, 张子敬, 等. 德南牛全基因组变异解析和功能基因挖掘[J]. 中国牛业科学, 2024, 50 (3): 1- 6.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9111.2024.03.001 |
|
ZHAO J H , LIU X , ZHANG Z J , et al. Whole-genome variation analysis and functional gene mining of Denan cattles[J]. China Cattle Science, 2024, 50 (3): 1- 6.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9111.2024.03.001 |
|
| 5 |
戴超辉, 崔乐康, 李辉, 等. 苏山猪和巴克夏猪全基因组ROH检测和选择信号分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (12): 5452- 5463.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.012 |
|
DAI C H , CUI L K , LI H , et al. Whole genome ROH detection and selection signal analysis in Sushan pigs and Berkshire pigs[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (12): 5452- 5463.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.012 |
|
| 6 |
吴平先, 王俊戈, 刁淑琪, 等. 基于填充测序数据的荣昌猪群体遗传结构和选择信号分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56 (1): 147- 158.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.01.014 |
|
WU P X , WANG J G , DIAO S Q , et al. Analysis of genetic architecture characteristics and selection signature by imputed whole genome sequencing data in Rongchang pigs[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56 (1): 147- 158.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.01.014 |
|
| 7 |
TU Y J , LIU Y F , ZHANG M , et al. Identifying signatures of selection related to CoMb development[J]. J Poult Sci, 2021, 58 (1): 5- 11.
doi: 10.2141/jpsa.0190104 |
| 8 |
LIU Z X , BAI C Y , SHI L L , et al. Detection of selection signatures in South African Mutton Merino sheep using whole-genome sequencing data[J]. Anim Genet, 2022, 53 (2): 224- 229.
doi: 10.1111/age.13173 |
| 9 | YAO Y X , PAN Z Y , DI R , et al. Whole genome sequencing reveals the effects of recent artificial selection on litter size of Bamei mutton sheep[J]. Animals (Basel), 2021, 11 (1): 157. |
| 10 | 常倩倩. 基于重测序技术筛选策勒黑羊多胎性状相关的基因及其功能研究[D]. 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学, 2022. |
| CHANG Q Q. Screening of genes related to multiple birth traits and theirfunctions in Qira black sheep based on resequencing technology[D]. Alaer: Tarim University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 11 |
祁军英, 裴全帮, 张文魁, 等. 全基因组选择信号鉴定高原型藏羊毛用性状候选基因及关联分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (12): 5511- 5526.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.017 |
|
QI J Y , PEI Q B , ZHANG W K , et al. Genome-wide selective signal identification and association analysis of candidate genes for Tibetan sheep wool traits[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (12): 5511- 5526.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.017 |
|
| 12 | ZHANG W T , JIN M L , LI T T , et al. Whole genome resequencing reveals selection signals related to wool color in sheep[J]. Animals (Basel), 2023, 13 (20): 3265. |
| 13 | 李晓龙. 基于全基因组重测序数据挖掘绵羊产奶和产羔性状的关键基因[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2022. |
| LI X L. Identification of candidate genes for milk production and litter sizetraits in sheep based on whole genome resequencing data[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 14 | LI R N , ZHAO Y H T , LIANG N M , et al. Genome-wide signal selection analysis revealing genes potentially related to sheep-milk-production traits[J]. Animals (Basel), 2023, 13 (10): 1654. |
| 15 | 施会彬. 基于全基因组重测序揭示盘欧羊选育群体遗传多样性与选择信号[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2023. |
| SHI H B. Whole genome resequencing reveals genetic diversity andselection signals in Panou sheep selection breedingpopulation[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 16 |
ZHAO L M , YUAN L F , LI F D , et al. Whole-genome resequencing of Hu sheep identifies candidate genes associated with agronomic traits[J]. J Genet Genomics, 2024, 51 (8): 866- 876.
doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2024.03.015 |
| 17 |
ZHANG D Y , ZHANG X X , LI F D , et al. Whole-genome resequencing identified candidate genes associated with the number of ribs in Hu sheep[J]. Genomics, 2021, 113 (4): 2077- 2084.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.05.004 |
| 18 | 谢锐. 基于湖羊重测序数据的全基因组选择信号检测及与繁殖性状相关候选基因鉴定[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2020. |
| XIE R. Genome-wide scan for selection signature and identification of candidate genes by using resequencing data of Hu sheep[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 19 |
PURCELL S , NEALE B , TODD-BROWN K , et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2007, 81 (3): 559- 575.
doi: 10.1086/519795 |
| 20 |
WANG J , ZHANG Z . GAPIT Version 3:Boosting Power and Accuracy for Genomic Association and Prediction[J]. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2021, 19 (4): 629- 640.
doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2021.08.005 |
| 21 |
VOIGHT B F , KUDARAVALLI S , WEN X Q , et al. A map of recent positive selection in the huangenome[J]. PLoS Biol, 2006, 4 (3): 72.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040072 |
| 22 |
陶伟, 侯黎明, 王彬彬, 等. 利用全基因组选择信号方法鉴别影响猪肉滴水损失的候选基因[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (5): 1373- 1383.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.05.006 |
|
TAO W , HOU L M , WANG B B , et al. Identification of candidate genes affecting drip loss in pork by genome-wide selection signal method[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (5): 1373- 1383.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.05.006 |
|
| 23 |
BROWNING B L , BROWNING S R . Genotype imputation with millions of reference samples[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2016, 98 (1): 116- 126.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.11.020 |
| 24 |
SZPIECH Z A , HERNANDEZ R D . Selscan: an efficient multithreaded program to perform EHH-based scans for positive selection[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2014, 31 (10): 2824- 2827.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu211 |
| 25 |
PAVLIDIS P , ŽIVKOVIC D , STAMATAKIS A , et al. SweeD: likelihood-based detection of selective sweeps in thousands of genomes[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2013, 30 (9): 2224- 2234.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst112 |
| 26 |
LENCZ T , LAMBERT C , DEROSSE P , et al. MALHOTRA.Runs of homozygosity reveal highly penetrant recessive loci in schizophrenia[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2007, 104 (50): 19942- 19947.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710021104 |
| 27 |
BAO J J , XIONG J K , HUANG J P , et al. Genetic diversity, selection signatures, and genome-wide association study identify candidate genes related to litter size in Hu sheep[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (17): 9397.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25179397 |
| 28 | 张彦威, 于丽娟, 徐新明, 等. 选择信号分析及其对绵羊功能基因的挖掘进展[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2023, 50 (12): 4935- 4946. |
| ZHANG Y W , YU L J , XU X M , et al. Advance on selection signal analysis and its exploration for functional genes in sheep[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 50 (12): 4935- 4946. | |
| 29 |
潘章源, 狄冉, 刘秋月, 等. 绵羊多羔主效基因BMPR1B的研究进展[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2015, 36 (5): 1- 6.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2015.05.001 |
|
PAN Z Y , DI R , LIU Q Y , et al. Advances in ovine prolificacy gene BMPR1B[J]. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2015, 36 (5): 1- 6.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2015.05.001 |
|
| 30 |
MANZARI Z , MEHRABANI-YEGANEH H , NEJATI-JAVAREMI A , et al. Detecting selection signatures in three Iranian sheep breeds[J]. Anim Genet, 2019, 50 (3): 298- 302.
doi: 10.1111/age.12772 |
| 31 |
LIN Y , LU Z K , GUO T T , et al. Key genes and metabolites that regulate wool fibre diameter identified by combined transcriptome and metabolome analysis[J]. Genomics, 2024, 116 (5): 110886.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2024.110886 |
| 32 |
YANG J , LI X , CAO Y H , et al. Comparative mRNA and miRNA expression in European mouflon (Ovis musimon) and sheep (Ovis aries) provides novel insights into the genetic mechanisms for female reproductive success[J]. Heredity, 2019, 122 (2): 172- 186.
doi: 10.1038/s41437-018-0090-1 |
| 33 |
ORTEGA M S , DENICOL A C , COLE J B , et al. Use of single nucleotide polymorphisms in candidate genes associated with daughter pregnancy rate for prediction of genetic merit for reproduction in Holstein cows[J]. Anim Genet, 2016, 47 (3): 288- 297.
doi: 10.1111/age.12420 |
| 34 |
DAY L J , SCHAA K L , RYCKMAN K K , et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the KCNN3 gene associate with preterm birth[J]. Reprod Sci, 2011, 18 (3): 286- 295.
doi: 10.1177/1933719110391277 |
| 35 |
GHOREISHIFAR S M , ERIKSSON S , JOHANSSON A M , et al. Signatures of selection reveal candidate genes involved in economic traits and cold acclimation in five Swedish cattle breeds[J]. Genet Sel Evol, 2020, 52 (1): 52.
doi: 10.1186/s12711-020-00571-5 |
| 36 |
AN B , XIA J , CHANG T , et al. Genome-wide association study reveals candidate genes associated with body measurement traits in Chinese Wagyu beef cattle[J]. Anim Genet, 2019, 50 (4): 386- 390.
doi: 10.1111/age.12805 |
| 37 |
NEBENDAHl C , GRS S , ALBRECHT E , et al. Early postnatal feed restriction reduces liver connective tissue levels and affects H3K9 acetylation state of regulated genes associated with protein metabolism in low birth weight pigs[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2016, 29, 41- 55.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.10.017 |
| 38 |
WEI C H , WANG H H , LIU G , et al. Genome-wide analysis reveals population structure and selection in Chinese indigenous sheep breeds[J]. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16 (1): 194.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1384-9 |
| 39 | RAMLJAK J , PEHAR M , CERANAC D , et al. Genomic characterization of local croatian sheep breeds-effective population size[J]. Animals (Basel), 2024, 14 (13): 1928. |
| 40 | HITIT M , KAYA A , MEMILI E . Sperm long non-coding RNAs as markers for ram fertility[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2024, 11 (10): 1337939. |
| 41 |
POKHAREL K , PEIPPO J , HONKATUKIA M , et al. Integrated ovarian mRNA and miRNA transcriptome profiling characterizes the genetic basis of prolificacy traits in sheep (Ovis aries)[J]. BMC genomics, 2018, 19 (1): 104.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4400-4 |
| 42 | YURCHENKO A A , DENISKOVA T E , YUDIN N S , et al. High-density genotyping reveals signatures of selection related to acclimation and economically important traits in 15 local sheep breeds from Russia[J]. BMC Genomics, 2019, 20 (3): 294. |
| 43 |
RAMOS Z , GARRICK D J , BLAIR H T , et al. Genomic regions associated with wool, growth and reproduction traits in Uruguayan Merino sheep[J]. Genes, 2023, 14 (1): 167.
doi: 10.3390/genes14010167 |
| 44 | MA Z , WANG W , ZHANG D , et al. Polymorphisms of PLIN1 and MOGAT1 genes and their association with feed efficiency in Hu sheep[J]. Gene, 2024, 897 (1): 148072. |
| 45 |
JIANG Y , LI X J , LIU J L , et al. Genome-wide detection of genetic structure and runs of homozygosity analysis in Anhui indigenous and Western commercial pig breeds using PorcineSNPs80k data[J]. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23 (1): 373.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08583-9 |
| 46 |
YANG B G , YUAN Y , ZUOH D K , et al. Genome-wide selection signal analysis of Australian Boer goat reveals artificial selection imprinting on candidate genes related to muscle development[J]. Anim Genet, 2021, 52 (4): 550- 555.
doi: 10.1111/age.13092 |
| 47 | MU L S , YE Z H , HU J H , et al. PPM1K-regulated impaired catabolism of branched-chain amino acids orchestrates polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. EBioMedicine, 2023, 89 (1): 104492. |
| 48 |
LIN T , HE X Y , WANG X Y , et al. Litter size of sheep (Ovis aries): Inbreeding depression and homozygous regions[J]. Genes, 2021, 12 (1): 109.
doi: 10.3390/genes12010109 |
| 49 |
MA X F , LIU A J , TIAN S J . A meta-analysis of mRNA expression profiling studies in sheep with different FecB genotypes[J]. Anim Genet, 2023, 54 (3): 225- 238.
doi: 10.1111/age.13304 |
| 50 | 常成, 张茜, 贺小云, 等. 绵羊甲状腺miR-370-3p靶向COL4A3基因调控繁殖力性状的初步研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2023, 28 (9): 108- 116. |
| CHANG C , ZHANG Q , HE X Y , et al. Preliminary study on the regulation of fertility traits by miR-370-3p targeting COL4A3 gene in sheep thyroid gland[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2023, 28 (9): 108- 116. | |
| 51 |
ZHU M T , ZHANG H M , YANG H , et al. Polymorphisms and association of GRM1, GNAQ and HCRTR1 genes with seasonal reproduction and litter size in three sheep breeds[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2022, 57 (5): 532- 540.
doi: 10.1111/rda.14091 |
| 52 |
PURUHITA , NOOR R R , MARGAWATI E T , et al. Association of the single nucleotide polymorphism in CAPN3 gene with growth performance in Merino and Garut (MEGA) backcross sheep[J]. J Genet Eng Biotechnol, 2023, 21 (1): 77.
doi: 10.1186/s43141-023-00524-7 |
| 53 |
LIU D H , LI X , WANG L , et al. Genome-wide association studies of body size traits in Tibetan sheep[J]. BMC Genomics, 2024, 25 (1): 739.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10633-3 |
| 54 | 付玉, 张博, 凌遥, 等. 骨骼肌生长发育调控基因MUSTN1的研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2022, 58 (5): 1- 4. |
| FU Y , ZHANG B , LING Y , et al. Advances in MUSTN1 genes in the regulation of skeletal muscle growth and development[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2022, 58 (5): 1- 4. | |
| 55 | CHEN Z Y , WANG G X , WANG W M , et al. PDE9A polymorphism and association analysis with growth performance and gastrointestinal weight of Hu sheep[J]. Gene, 2024, 900 (1): 148137. |
| 56 |
BAKHTIARIZADEH M R . Deciphering the role of alternative splicing as a potential regulator in fat-tail development of sheep: a comprehensive RNA-seq based study[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14 (1): 2361.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52855-1 |
| 57 |
SERRANITO B , CAVALAZZI M , VIDAL P , et al. Local adaptations of Mediterranean sheep and goats through an integrative approach[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 21363.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00682-z |
| 58 | ZHAO X , ONTERU S K , PIRIPI S , et al. In a shake of a lamb 's tail: using genomics to unravel a cause of chondrodysplasia in Texel sheep[J]. Anim Genet, 2012, 43 (1): 9- 18. |
| 59 |
TAO L , HE X E , JIANG Y T , et al. Genome-wide analyses reveal genetic convergence of prolificacy between goats and sheep[J]. Genes, 2021, 12 (4): 480.
doi: 10.3390/genes12040480 |
| 60 |
ZHU M T , ZHANG H M , YANG H , et al. Polymorphisms and association of GRM1, GNAQ and HCRTR1 genes with seasonal reproduction and litter size in three sheep breeds[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2022, 57 (5): 532- 540.
doi: 10.1111/rda.14091 |
| 61 | AKHMET N , ZHU L , SONG J , et al. Exploring the sheep MAST4 gene variants and their associations with litter size[J]. Animals (Basel), 2024, 14 (4): 591. |
| 62 | ZANG S Q , YANG X R , YE J F , et al. Quantitative phosphoproteomics explain cryopreservation-induced reductions in ram sperm motility[J]. J Proteomics, 2024, 298 (1): 105153. |
| 63 | QU Y H , JIAN L Y , CE L , et al. Identification of candidate genes in regulation of spermatogenesis in sheep testis following dietary vitamin E supplementation[J]. Anim Reprod Sci, 2019, 205 (1): 52- 61. |
| 64 | WANG J , CHEN H , ZENG X . Identification of hub genes associated with follicle development in multiple births sheep by WGCNA[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2022, 9 (1): 1057282. |
| 65 |
DICKINSON R E , HRYHORSKYJ L , TREMEWAN H , et al. Involvement of the SLIT/ROBO pathway in follicle development in the fetal ovary[J]. Reproduction, 2010, 139 (2): 395- 407.
doi: 10.1530/REP-09-0182 |
| 66 | SMITCHGER J A , TAYLOR J B , MOUSEL M R , et al. Genome-wide associations with longevity and reproductive traits in U.S. rangeland ewes[J]. Front Genet, 2024, 15 (1): 1398123. |
| [1] | WANG Qinqian, GAO Zhendong, LU Ying, MA Ruoshan, DENG Weidong, HE Xiaoming. Research Progress of Whole Genome Resequencing in Chinese Indigenous Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2026-2037. |
| [2] | LI Xiaowei, TIAN Wei, LIU Yuan, LI Huixia. Study on the Difference of m6A Methylation Modification in Ovarian Granulosa Cells of Hu Sheep under Heat Stress [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1712-1721. |
| [3] | HUANG Yani, TANG Xi, LI Jingquan, WEI Jiacheng, WU Zhenfang, LI Xinyun, XIAO Shijun, ZHANG Zhiyan. Large-scale Population Analysis of Potential Causal Genes for Daily Weight Gain and Age at 100 kg in Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1100-1109. |
| [4] | JIA Wanli, WANG Jiying, LI Jingxuan, WANG Yanping, GENG Liying, ZHANG Chuansheng, ZHAO Xueyan. Identification of Key Genes Affecting Drip Loss in Laiwu Pigs Based on Transcriptome Sequencing Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1134-1146. |
| [5] | LU Xiu, ZHANG Ming'ai, KONG Min, ZHANG Jing, WANG Binghan, HOU Zhongyi, TENG Xingyi, JIANG Yajing, FAN Wenlei, WANG Baowei. Screening for Candidate Genes Related to Egg Production in Wulong Geese Based on Transcriptome and Proteome Analyses [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 232-245. |
| [6] | LI Wei, WU Xilong, ZHAO Xingrui, XU Lanjiao, YANG Xiaobin, SONG Xiaozhen. Effects of Chinese Medicine Jianpisiwei Formulas on Growth Performance, Rumen Fermentation and Microbiota Composition of Weaned Hu Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 466-478. |
| [7] | Tana AN, Haige HAN, Togtokh MONGKE, Baoyindeligeer MONGKEJARGAL, Wenbo LI, Manglai DUGARJAVIIN. A Review of the Genetic Characteristics of Different Coat Colors in Domestic Horses [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3297-3308. |
| [8] | Mingliang HE, Xiaoyang LÜ, Yongqing JIANG, Zhenghai SONG, Yeqing WANG, Huiguo YANG, Shanhe WANG, Wei SUN. Function Analysis of SOX18 in Hu Sheep Hair Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells Based on Transcriptome Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2409-2420. |
| [9] | WANG Yaxin, WANG Jing, TIAN Xuekai, YANG Gongshe, YU Taiyong. Application of Multi-omics Technology in the Study of Important Economic Traits of Livestock and Poultry [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1842-1853. |
| [10] | CAO Yuzhu, XING Yuxin, MA Chenglin, GUAN Hongbo, JIA Qihui, KANG Xiangtao, TIAN Yadong, LI Zhuanjian, LIU Xiaojun, LI Hong. Biological Characterization of Chicken FGF6 Gene and Association of Its Polymorphisms with Economic Traits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1536-1550. |
| [11] | DAI Chaohui, CUI Lekang, LI Hui, ZHAO Weimin, FU Yanfeng, LI Bixia, WANG Xuemin, LIAO Chao, CHEN Yanyu, BAO Wenbin, CHENG Jinhua. Whole Genome ROH Detection and Selection Signal Analysis in Sushan Pigs and Berkshire Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5452-5463. |
| [12] | QI Junying, PEI Quanbang, ZHANG Wenkui, XU Teng, ZUO Mingxing, HAN Buying, LI Xue, LIU Dehui, WANG Song, ZHOU Baicheng, ZHAO Kai, TIAN Dehong. Genome-wide Selective Signal Identification and Association Analysis of Candidate Genes for Tibetan Sheep Wool Traits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5511-5526. |
| [13] | Xiaokun LIN, Mengmeng DU, Lisheng ZHOU, Zhengang HUANG, Di WANG, Donghui ZHOU, Xinxin CAO, Jianning HE, Jinshan ZHAO, Hegang LI. Genome-Wide Association Study of Wool Economic Traits in Aohan Fine Wool Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4346-4359. |
| [14] | Liwa ZHANG, Yaojing YUE, Xuejiao AN, Jianye LI, Bohui YANG, Zhenfei XU, Jinxia ZHANG, Zhiguang GENG, Yanli GUO, Rui ZHANG. Comparative Analysis of the Contents of Amino Acids, Fatty Acids and Volatile Flavor Compounds in the Muscles of Hu Sheep and Their Different Hybrid Combinations [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4428-4442. |
| [15] | TANG Xinxin, ZHENG Jumei, LUO Na, YING Fan, ZHU Dan, LI Sen, LIU Dawei, AN Bingxing, WEN Jie, ZHAO Guiping, LI Hegang. Genetic Mechanism of Broiler Leg Disease Based on Genome-Wide Association Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 99-109. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||