





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 2112-2122.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.05.012
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Qianhui1( ), ZHANG Yu1, ZHANG Taoni1, MO Meilan1,2,3,*(
), ZHANG Yu1, ZHANG Taoni1, MO Meilan1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-22
Online:2025-05-23
Published:2025-05-27
Contact:
MO Meilan
E-mail:2407211038@qq.com;momeilan@gxu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
WU Qianhui, ZHANG Yu, ZHANG Taoni, MO Meilan. Research Progress on Mechanism of Lipid Raft Involved in Coronavirus Infection and Its Application[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2112-2122.
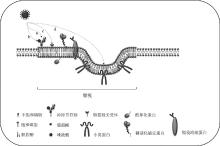
Fig. 1
Lipid rafts and their involvement in viral invasion a. Gangliosides in lipid rafts can be used as initial binding sites for virus invasion; b. Sialic acid in lipid rafts can be used as a virus auxiliary receptor; c. Lipid rafts can recruit lipid raft-related receptors; d. Caveolin in lipid rafts can be involved in virus entry"
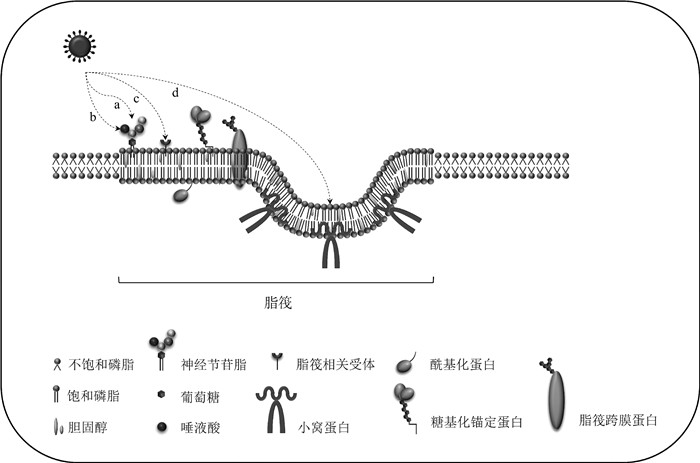
Table 1
Anti-coronavirus drugs targeting lipid rafts"
| 靶点 Target | 药物 Drug | 特性 Characteristic |
| 胆固醇 Cholesterol | 25-羟基胆固醇 25-hydroxycholesterol (25HC) | 1)抑制固醇调节元件结合蛋白2,刺激酰基辅酶A以减少膜脂筏;2)抑制氧化固醇结合蛋白或尼曼匹克C1前体蛋白来损害内体途径,导致病毒无法释放核酸;3)抑制固醇调节元件结合蛋白途径,增加聚糖对内糖苷酶的敏感性来糖基化,从而干扰病毒蛋白的前酰化 |
| α-环糊精 α-cyclodextrin | 单独或联合羟基酪醇与S蛋白及ACE2相互作用,降低SARS-CoV-2内吞作用效率 | |
| 甲基-β-环糊精 Methyl-β-cyclodextrin | 可在早期阶段阻断多种人类和动物病毒感染,包括SARS-CoV和SARS-CoV-2 | |
| 羟丙基-β-环糊精 Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin | 是用作SARS-CoV-2预防剂的候选药物 | |
| 羟基酪醇 Hydroxytyrosol | 具有抗病毒特性 | |
| 美伐他汀 Mevastatin | 消耗胆固醇,破坏脂筏 | |
| 菲利平 Filipin | 消耗胆固醇,破坏脂筏 | |
| 神经节苷脂 Ganglioside | 氯喹 Chloroquine | 已被证明在体外有效抑制SARS-CoV-2 |
| 羟氯喹 Hydroxychloroquine | 可识别呼吸道上皮细胞表达的神经节苷脂,并竞争性阻断SARS-CoV-2与这些细胞的结合 | |
| 鞘糖脂 Glycosphingolipid | 苯基棕榈酰胺吗啡丙醇(PPMP) DL-threo-1-phenyl-2- palmitoylamino-3- morpholino-1-propanol | 在体外,用PPMP(鞘糖脂合酶抑制剂)进行可逆处理,暂时破坏脂筏足以防止病毒感染细胞 |
| N-末端结构域 NTD | 阿奇霉素 Azithromycin | 与SARS-CoV-2蛋白NTD的神经节苷脂结合结构域相互作用阻断S蛋白与脂筏的结合;与羟氯喹在体外预防SARS-CoV-2感染具有协同作用 |
| 1 |
SIDDELL S , WEGE H , TER MEULEN V . The biology of coronaviruses[J]. J Gen Virol, 1983, 64 (4): 761- 776.
doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-761 |
| 2 |
ZHOU P , YANG X L , WANG X G , et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin[J]. Nature, 2020, 579 (7798): 270- 273.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7 |
| 3 |
FURUKAWA K , OHMI Y , HAMAMURA K , et al. Signaling domains of cancer-associated glycolipids[J]. Glycoconj, 2022, 39 (2): 145- 155.
doi: 10.1007/s10719-022-10051-1 |
| 4 |
WANG H Y , BHARTI D , LEVENTAL I . Membrane heterogeneity beyond the plasma membrane[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8, 580814.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.580814 |
| 5 |
PRALLE A , KELLER P , FLORIN E L , et al. Sphingolipid-cholesterol rafts diffuse as small entities in the plasma membrane of mammalian cells[J]. J Cell Biol, 2000, 148 (5): 997- 1008.
doi: 10.1083/jcb.148.5.997 |
| 6 | SAPOŃ K , MANŃKA R , JANAS T , et al. The role of lipid rafts in vesicle formation[J]. J Cell Biol, 2023, 136 (9): jcs260887. |
| 7 |
TRYBUS M , HRYNIEWICZ-JANKOWSKA A , WóJTOWICZ K , et al. EFR3A: a new raft domain organizing protein?[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2023, 28 (1): 86.
doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00497-y |
| 8 |
HIRANO K , KINOSHITA M , MATSUMORI N . Impact of sphingomyelin acyl chain heterogeneity upon properties of raft-like membranes[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr, 2022, 1864 (12): 184036.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2022.184036 |
| 9 |
LEVENTAL I , LYMAN E . Regulation of membrane protein structure and function by their lipid nano-environment[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2023, 24 (2): 107- 122.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00524-4 |
| 10 |
CONTRERAS F X , ERNST A M , HABERKANT P , et al. Molecular recognition of a single sphingolipid species by a protein 's transmembrane domain[J]. Nature, 2012, 481 (7382): 525- 529.
doi: 10.1038/nature10742 |
| 11 |
SAPOŃ K , JANAS T , SIKORSKI A F , et al. Polysialic acid chains exhibit enhanced affinity for ordered regions of membranes[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr, 2019, 1861 (1): 245- 255.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.07.008 |
| 12 |
CHOI K S , AIZAKI H , LAI M M C . Murine coronavirus requires lipid rafts for virus entry and cell-cell fusion but not for virus release[J]. J Virol, 2005, 79 (15): 9862- 9871.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.9862-9871.2005 |
| 13 |
SCHEIFFELE P , ROTH M G , SIMONS K . Interaction of influenza virus haemagglutinin with sphingolipid-cholesterol membrane domains via its transmembrane domain[J]. EMBO J, 1997, 16 (18): 5501- 5508.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.18.5501 |
| 14 |
PICKL W F , PIMENTEL-MUIÑOS F X , SEED B . Lipid rafts and pseudotyping[J]. J Virol, 2001, 75 (15): 7175- 7183.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.15.7175-7183.2001 |
| 15 |
BAVARI S , BOSIO C M , WIEGAND E , et al. Lipid raft microdomains: a gateway for compartmentalized trafficking of Ebola and Marburg viruses[J]. J Exp Med, 2002, 195 (5): 593- 602.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20011500 |
| 16 |
YANG Q , ZHANG Q , TANG J , et al. Lipid rafts both in cellular membrane and viral envelope are critical for PRRSV efficient infection[J]. Virology, 2015, 484, 170- 180.
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.06.005 |
| 17 |
CHAZAL N , GERLIER D . Virus entry, assembly, budding, and membrane rafts[J]. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev, 2003, 67 (2): 226- 237.
doi: 10.1128/MMBR.67.2.226-237.2003 |
| 18 |
MAÑES S , DEL REAL G , MARTÍNEZ-A C . Pathogens: raft hijackers[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2003, 3 (7): 557- 568.
doi: 10.1038/nri1129 |
| 19 | ONO A , FREED E O . Role of lipid rafts in virus replication[J]. Adv Virus Res, 2005, 64, 311- 358. |
| 20 |
VERMA D K , GUPTA D , LAL S K . Host lipid rafts play a major role in binding and endocytosis of influenza a virus[J]. Viruses, 2018, 10 (11): 650.
doi: 10.3390/v10110650 |
| 21 | AZZAZ F , YAHI N , DI SCALA C , et al. Ganglioside binding domains in proteins: physiological and pathological mechanisms[J]. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol, 2022, 128, 289- 324. |
| 22 |
FANTINI J , YAHI N , AZZAZ F , et al. Structural dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 variants: a health monitoring strategy for anticipating Covid-19 outbreaks[J]. J Infect, 2021, 83 (2): 197- 206.
doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.06.001 |
| 23 |
SUZUKI Y . [Variation of influenza viruses and their recognition of the receptor sialo-sugar chains][J]. Yakugaku Zasshi, 1993, 113 (8): 556- 578.
doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.113.8_556 |
| 24 |
MARKWELL M A , SVENNERHOLM L , PAULSON J C . Specific gangliosides function as host cell receptors for Sendai virus[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1981, 78 (9): 5406- 5410.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5406 |
| 25 |
CAMPANERO-RHODES M A , SMITH A , CHAI W G , et al. N-glycolyl GM1 ganglioside as a receptor for simian virus 40[J]. J Virol, 2007, 81 (23): 12846- 12858.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.01311-07 |
| 26 |
MAGINNIS M S . Virus-receptor interactions: the key to cellular invasion[J]. J Mol Biol, 2018, 430 (17): 2590- 2611.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.06.024 |
| 27 |
ROLSMA M D , KUHLENSCHMIDT T B , GELBERG H B , et al. Structure and function of a ganglioside receptor for porcine rotavirus[J]. J Virol, 1998, 72 (11): 9079- 9091.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.9079-9091.1998 |
| 28 |
HAMMACHE D , YAHI N , MARESCA M , et al. Human erythrocyte glycosphingolipids as alternative cofactors for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) entry: evidence for CD4-induced interactions between HIV-1 gp120 and reconstituted membrane microdomains of glycosphingolipids (Gb3 and GM3)[J]. J Virol, 1999, 73 (6): 5244- 5248.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.6.5244-5248.1999 |
| 29 |
FANTINI J , CHAHINIAN H , YAHI N . Convergent evolution dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 and HIV surface envelope glycoproteins driven by host cell surface receptors and lipid rafts: lessons for the future[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (3): 1923.
doi: 10.3390/ijms24031923 |
| 30 |
CHAN J F W , KOK K H , ZHU Z , et al. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2020, 9 (1): 221- 236.
doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902 |
| 31 | 鲁丹, 方一泰, 罗德炎, 等. 外泌体参与新冠病毒感染的机制及其应用的研究进展[J]. 病毒学报, 2024, 40 (1): 160- 168. |
| LU D , FANG Y T , LUO D Y , et al. Research progress on the functions of exosomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection, diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis[J]. Chinese Journal of Virology, 2024, 40 (1): 160- 168. | |
| 32 |
LI X W , ZHU W H , FAN M Y , et al. Dependence of SARS-CoV-2 infection on cholesterol-rich lipid raft and endosomal acidification[J]. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2021, 19, 1933- 1943.
doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.04.001 |
| 33 |
KHATTAB E S A E H , RAGAB A , ABOL-FTOUH M A , et al. Therapeutic strategies for Covid-19 based on molecular docking and dynamic studies to the ACE-2 receptors, Furin, and viral spike proteins[J]. J Biomol Struct Dyn, 2022, 40 (23): 13291- 13309.
doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1989036 |
| 34 | 孙亚娟, 张达, 汤傲星, 等. α属冠状病毒入侵宿主所需宿主因子研究进展[J]. 病毒学报, 2024, 40 (1): 215- 224. |
| SUN Y J , ZHANG D , TANG A X , et al. Research progress on host factor required of alpha-coronavirus invasion[J]. Chinese Journal of Virology, 2024, 40 (1): 215- 224. | |
| 35 |
FANTINI J , AZZAZ F , CHAHINIAN H , et al. Electrostatic surface potential as a key parameter in virus transmission and evolution: how to manage future virus pandemics in the post-COVID-19 era[J]. Viruses, 2023, 15 (2): 284.
doi: 10.3390/v15020284 |
| 36 |
WANG H L , YANG P , LIU K T , et al. SARS coronavirus entry into host cells through a novel clathrin-and caveolae-independent endocytic pathway[J]. Cell Res, 2008, 18 (2): 290- 301.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2008.15 |
| 37 |
CARONI P . New EMBO memberserreview: actin cytoskeleton regulation through modulation of PI(4, 5)P(2) rafts[J]. EMBO J, 2001, 20 (16): 4332- 4336.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.16.4332 |
| 38 |
CUI J , LI F , SHI Z L . Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2019, 17 (3): 181- 192.
doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0118-9 |
| 39 |
LEDNICKY J A , TAGLIAMONTE M S , WHITE S K , et al. Independent infections of porcine deltacoronavirus among Haitian children[J]. Nature, 2021, 600 (7887): 133- 137.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04111-z |
| 40 |
SEYRAN M , TAKAYAMA K , UVERSKY V N , et al. The structural basis of accelerated host cell entry by SARS-CoV-2[J]. FEBS J, 2021, 288 (17): 5010- 5020.
doi: 10.1111/febs.15651 |
| 41 |
SUN X L . The role of cell surface sialic acids for SARS-CoV-2 infection[J]. Glycobiology, 2021, 31 (10): 1245- 1253.
doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwab032 |
| 42 |
FANTINI J , CHAHINIAN H , YAHI N . Leveraging coronavirus binding to gangliosides for innovative vaccine and therapeutic strategies against COVID-19[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021, 538, 132- 136.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.015 |
| 43 |
BAKILLAH A , HEJJI F A , ALMASAUD A , et al. Lipid raft integrity and cellular cholesterol homeostasis are critical for SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14 (16): 3417.
doi: 10.3390/nu14163417 |
| 44 |
FANTINI J , CHAHINIAN H , YAHI N . A vaccine strategy based on the identification of an annular ganglioside binding motif in monkeypox virus protein E8L[J]. Viruses, 2022, 14 (11): 2531.
doi: 10.3390/v14112531 |
| 45 |
DARWISH S , LIU L P , ROBINSON T O , et al. COVID-19 plasma extracellular vesicles increase the density of lipid rafts in human small airway epithelial cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (2): 1654.
doi: 10.3390/ijms24021654 |
| 46 |
LAN J , GE J , YU J , et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor[J]. Nature, 2020, 581 (7807): 215- 220.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5 |
| 47 |
PALACIOS-RÁPALO S N , DE JESÚS-GONZÁLEZ L A , CORDERO-RIVERA C D , et al. Cholesterol-rich lipid rafts as platforms for SARS-CoV-2 entry[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12, 796855.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.796855 |
| 48 |
FANTINI J , DI SCALA C , CHAHINIAN H , et al. Structural and molecular modelling studies reveal a new mechanism of action of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine against SARS-CoV-2 infection[J]. Int J Antimicrob Agents, 2020, 55 (5): 105960.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105960 |
| 49 |
PAK A J , YU A , KE Z L , et al. Cooperative multivalent receptor binding promotes exposure of the SARS-CoV-2 fusion machinery core[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13 (1): 1002.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28654-5 |
| 50 |
THORP E B , GALLAGHER T M . Requirements for CEACAMs and cholesterol during murine coronavirus cell entry[J]. J Virol, 2004, 78 (6): 2682- 2692.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.6.2682-2692.2004 |
| 51 |
LU Y N , LIU D X , TAM J P . Lipid rafts are involved in SARS-CoV entry into Vero E6 cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2008, 369 (2): 344- 349.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.02.023 |
| 52 |
JEFFERS S A , TUSELL S M , GILLIM-ROSS L , et al. CD209L (L-SIGN) is a receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2004, 101 (44): 15748- 15753.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403812101 |
| 53 |
GUO H C , HUANG M , YUAN Q , et al. The important role of lipid raft-mediated attachment in the infection of cultured cells by coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus beaudette strain[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12 (1): e0170123.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170123 |
| 54 |
LORIZATE M , KRÄUSSLICH H G . Role of lipids in virus replication[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2011, 3 (10): a004820.
doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a004820 |
| 55 |
WEI X N , SHE G L , WU T T , et al. PEDV enters cells through clathrin-, caveolae-, and lipid raft-mediated endocytosis and traffics via the endo-/lysosome pathway[J]. Vet Res, 2020, 51 (1): 10.
doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-0739-7 |
| 56 | PRATELLI A , COLAO V . Role of the lipid rafts in the life cycle of canine coronavirus[J]. J Gen Virol, 2015, 96 (Pt 2): 331- 337. |
| 57 |
GRAHAM D R M , CHERTOVA E , HILBURN J M , et al. Cholesterol depletion of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and simian immunodeficiency virus withβ-cyclodextrin inactivates and permeabilizes the virions: evidence for virion-associated lipid rafts[J]. J Virol, 2003, 77 (15): 8237- 8248.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.15.8237-8248.2003 |
| 58 |
SVIRIDOV D , MILLER Y I , BALLOUT R A , et al. Targeting lipid rafts-a potential therapy for COVID-19[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11, 574508.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574508 |
| 59 |
ALBONI S , SECCO V , PAPOTTI B , et al. Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin depletes membrane cholesterol and inhibits SARS-CoV-2 entry into HEK293T-ACEhi cells[J]. Pathogens, 2023, 12 (5): 647.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens12050647 |
| 60 |
MAO S J , REN J , XU Y , et al. Studies in the antiviral molecular mechanisms of 25-hydroxycholesterol: disturbing cholesterol homeostasis and post-translational modification of proteins[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2022, 926, 175033.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175033 |
| 61 | PAOLACCI S , KIANI A K , SHREE P , et al. Scoping review on the role and interactions of hydroxytyrosol and alpha-cyclodextrin in lipid-raft-mediated endocytosis of SARS-CoV-2 and bioinformatic molecular docking studies[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2021, 25 (1 Suppl): 90- 100. |
| 62 |
WANG Y Y , ZHANG Y Y , ZHANG C C , et al. Cholesterol-rich lipid rafts in the cellular membrane play an essential role in avian reovirus replication[J]. Front Microbiol, 2020, 11, 597794.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.597794 |
| 63 |
WANG N , HAN S L , LIU R , et al. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as ACE2 blockers to inhibit viropexis of 2019-nCoV Spike pseudotyped virus[J]. Phytomedicine, 2020, 79, 153333.
doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153333 |
| 64 |
WANG M L , CAO R Y , ZHANG L K , et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro[J]. Cell Res, 2020, 30 (3): 269- 271.
doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0 |
| 65 |
WANG S B , LI W Y , HUI H , et al. Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses by depleting membrane cholesterol[J]. EMBO J, 2020, 39 (21): e106057.
doi: 10.15252/embj.2020106057 |
| 66 |
FANTINI J , CHAHINIAN H , YAHI N . Synergistic antiviral effect of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in combination against SARS-CoV-2:what molecular dynamics studies of virus-host interactions reveal[J]. Int J Antimicrob Agents, 2020, 56 (2): 106020.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106020 |
| 67 |
ANDREANI J , LE BIDEAU M , DUFLOT I , et al. In vitro testing of combined hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on SARS-CoV-2 shows synergistic effect[J]. Microb Pathog, 2020, 145, 104228.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104228 |
| 68 |
DAS T , MUKHOPADHYAY C . Identification of possible binding modes of SARS-CoV-2 spike N-terminal domain for ganglioside GM1[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 2023, 812, 140260.
doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2022.140260 |
| 69 |
GUÉRIN P , YAHI N , AZZAZ F , et al. Structural dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: a 2-year retrospective analysis of SARS-CoV-2 variants (from alpha to omicron) reveals an early divergence between conserved and variable epitopes[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27 (12): 3851.
doi: 10.3390/molecules27123851 |
| 70 |
HU J , PENG P , CAO X X , et al. Increased immune escape of the new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern Omicron[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2022, 19 (2): 293- 295.
doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00836-z |
| 71 |
MOULANA A , DUPIC T , PHILLIPS A M , et al. Compensatory epistasis maintains ACE2 affinity in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA. 1[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13 (1): 7011.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34506-z |
| [1] | CAO Liyan, KONG Xiangyu, YUAN Cong, DUAN Yueyue, MA Guoxiang, SHI Lei, ZHANG Yu, WAN Ying, LI Xiangtong, WANG Yating, DU Yu, ZHENG Haixue, WANG Qi. Identifcation of a Novel Linear B-cell Epitope in the Nucleocapsid Protein of Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1854-1864. |
| [2] | JIANG Huihua, ZHAO Long, GUO Kangkang. Effect of HE Gene Receptor Binding Domain Variation on Bovine Coronavirus Infection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1336-1343. |
| [3] | ZHAO Long, LIN Jingyi, DOU Wei, XU Tingxuan, GU Qingyun, GAO Haihui, LI Shengqing, GUO Kangkang. In vitro Screening of Tibetan Medicine with Inhibitory Effects on Bovine Coronavirus Replication [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 826-838. |
| [4] | ZENG Miaomiao, YANG Xiaoman, ZHANG Xin, LIU Dakai, SHI Hongyan, ZHANG Jiyu, ZHANG Liaoyuan, CHEN Jianfei, FENG Tingshuai, LI Xiuwen, SHI Da, FENG Li. Establishment and Preliminary Application of an Indirect ELISA for Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus N Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 319-326. |
| [5] | Wangqing BAN MA, Xi CHEN, Yi YUE, Yurong SU, Hua YUE, Cheng TANG. Isolation, Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics of a Bovine Respiratory Coronavirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3094-3104. |
| [6] | Jing LI, Yuanxu ZHANG, Zezhao WANG, Yan CHEN, Lingyang XU, Lupei ZHANG, Xue GAO, Huijiang GAO, Junya LI, Bo ZHU, Peng GUO. Research Progress in Machine Learning Genomic Selection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2281-2292. |
| [7] | Ying CHEN, Dayong CHEN, Riga WU, Chunjuan QIU, Lihong FAN, Meirong BAO, Yuan YUE, Hongyan LIANG, Jiaxin ZHANG, Jianhui TIAN, Lei AN, Liqin WANG. Influence of Meat Sheep Varieties on the Scale Application of in vitro Embryo Production Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2451-2459. |
| [8] | HUANG Jin, LI Siyuan, MAO Li, CAI Xuhang, XIE Lingling, WANG Fu, ZHOU Hua, LI Jizong, LI Bin. Eukaryotic Expression of Bovine Coronavirus S1 Protein and Establishment and Application of Indirect ELISA [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2050-2060. |
| [9] | HU Zeqi, LI Runcheng, TAN Zuming, XIE Xiuyan, WANG Jiangping, QIN Lejuan, LI Rong, GE Meng. Establishment and Preliminary Application of PEDV, PoRVA and PDCoV TaqMan Triple RT-qPCR Assay [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2267-2272. |
| [10] | QIU Meiyu, ZHANG Xuemei, ZHANG Ning, LIU Mingjun. Approach and Application of Prime Editing System [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1345-1355. |
| [11] | LIU Qiang, NIU Xiaoxia, FANG Min, LIU Yanling, GAO Hui, CHEN Jixiang, JIAHUA Cairang, ZHANG Sinong, LI Yong. Research Progress of Bovine Coronavirus Spike Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 944-956. |
| [12] | YU Qisheng, ZHU Qing, ZHOU Qun, SONG Xin, ZHANG Jiaqi, CHEN Taoyun, XU Lin, ZHANG Chaohui, ZHANG Bin. Expression of BCoV Spike Protein by Baculovirus Expression System and Its Immunogenicity in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 640-648. |
| [13] | LI Siyuan, FU Xincheng, YUAN Xuesong, MAO Li, CAI Xuhang, SUN Xinru, HUANG Jin, XIE Lingling, WANG Fu, ZHOU Hua, ZHANG Qi, LI Jizong, LI Bin. Detection of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Pathogens and Evolution Analysis of Bovine Coronavirus in Langfang, Hebei [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 649-659. |
| [14] | LÜ Daiyue, CHEN Yanfei, ZHAI Tianshu, CAO Shengbo, XUE Qinghong. Research Progress and Application of Emerging Virus Detection Methods and Sequencing Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5398-5411. |
| [15] | HUANG Deru, CHANG Yirui, DING Ziyan, ZHANG Yashan, CHEN Aolei. Progress on Application of Animal Intestinal Organoids [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5431-5439. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||