





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 2588-2598.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.06.030
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hao CHEN1( ), Ge HAO1(
), Ge HAO1( ), Jiayan PU1, Jie XIAO1, Changming XIONG1, Wei HE1, Yuhua ZHU1, Liwen XU1, Qing JIANG2,*(
), Jiayan PU1, Jie XIAO1, Changming XIONG1, Wei HE1, Yuhua ZHU1, Liwen XU1, Qing JIANG2,*( ), Guangyou YANG1,*(
), Guangyou YANG1,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-05
Online:2024-06-23
Published:2024-06-28
Contact:
Qing JIANG, Guangyou YANG
E-mail:chenhao2197@outlook.com;haoge@stu.sicau.edu.cn;jiangqing0904@126.com;guangyou1963@126.com
CLC Number:
Hao CHEN, Ge HAO, Jiayan PU, Jie XIAO, Changming XIONG, Wei HE, Yuhua ZHU, Liwen XU, Qing JIANG, Guangyou YANG. Evaluation of the Immune Protective Effect of Recombinant MIC2 from Eimeria intestinalis in Rabbits[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2588-2598.
Table 1
Immunization group"
| 组别 Group | 动物数量 Rabbits number | 免疫原及剂量 Immunogen and dosage | 免疫方式 Immunization route | 免疫次数 Immunization times | 攻虫 Challenge dosage |
| 未免疫未攻虫组 Unchallenged group | 8 | PBS 1 mL | 颈部皮下注射 | 2次,同等剂量,间隔14 d | 未感染 |
| 未免疫攻虫组 Challenged group | 8 | PBS 1 mL | 颈部皮下注射 | 2次,同等剂量,间隔14 d | 口服5×104孢子化卵囊 |
| pET-32a(+)组 pET-32a(+) vector group | 8 | 100 μg载体蛋白+1 mg皂素溶于无菌PBS 1 mL | 颈部皮下注射 | 2次,同等剂量,间隔14 d | 口服5×104孢子化卵囊 |
| rEiMIC2免疫组 rEiMIC2 immunized group | 8 | 100 μg rEiMIC2+ 1mg皂素溶于无菌PBS 1 mL | 颈部皮下注射 | 2次,同等剂量,间隔14 d | 口服5×104孢子化卵囊 |

Fig. 1
Alignment of amino acid sequences between EiMIC2 and other coccidia MIC2 A. EiMIC2 gene amplification results: M. MarkerIII DNA marker; 1. PCR product; B. Amino acid sequence alignment GenBank sequence number: E. intestinalis (OP805603); E. praecox (CDI78561.1); E. acervuline (XP_013250247.1); E. maxima (XP_013335154.1); E. necatrix (XP_013433151.1); E. brunetti (CDJ53405.1); E. mitis (XP_013349538.1); E. tenella (XP_013229200.1). Red box: B epitope"


Fig. 2
EiMIC2 Gene amplification, solubility analysis, protein purification and Western blot analysis A. rEiMIC2 solubility analysis and purification: M. Protein marker; 2-7. supernatant, 2, 4, 6, 8 mol-L-1 urea; 8. purified rEiMIC2; B. Western bolt: M. Protein marker; 9. Recognition reaction between rEiMIC2 and positive serum; 10. Recognition reaction between rEiMIC2 and negative serum"
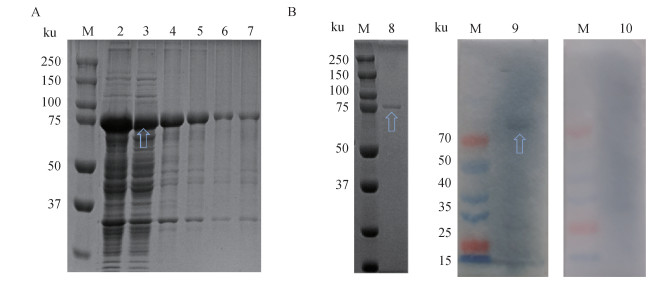
Table 5
Average weight gain rate, relative weight gain rate, oocyst reduction rate and feed-to-meat ratio of each group"
| 组别 Group | 攻虫前平均增重/g Average body weight gain before challenge | 攻虫后平均增重/g Average body weight gain after challenge | 相对增重率/% Relative weight gain | OPG/105 | 卵囊减少率/% Oocyst decrease ratio | 料肉比 Feed conversion ratio | 平均病变评分 Mean lesion scores | ACI |
| 未免疫未攻虫组 | 510.00±91.92a | 716.50±98.48a | — | — | — | 3.00∶1 | — | 200 |
| Unchallenged group | ||||||||
| 未免疫攻虫组 | 481.62±66.25a | 438.28±81.60b | 61.17 | 9.45±8.79a | — | 4.71∶1 | 2.03±1.39 | 88.37 |
| Challenged group | ||||||||
| pET-32a(+)组 | 511.18±90.82a | 419.37±80.64b | 58.53 | 9.32±10.01a | -1.4 | 4.95∶1 | 2.67±0.75 | 91.83 |
| pET-32a(+) vector group | ||||||||
| rEiMIC2免疫组 | 471.87±82.97a | 530.00±90.18c | 73.97 | 2.83±3.22b | 69.98 | 3.98∶1 | 1.45±1.19 | 136.97 |
| rEiMIC2 immunization group | ||||||||
| 1 |
XIE Y , XIAO J , ZHOU X , et al. Global transcriptome landscape of the rabbit protozoan parasite Eimeria stiedae[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2021, 14 (1): 308.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04811-5 |
| 2 | PAKANDL M . Coccidia of rabbit: a review[J]. Folia Parasitol (Praha), 2013, 56 (3): 153- 166. |
| 3 | SHI T Y , TAO G R , BAO G L , et al. Stable transfection of Eimeria intestinalis and investigation of its life cycle, reproduction and immunogenicity[J]. Front Microbiol, 2016, 7, 807. |
| 4 | ABD EI-GHANY W A . Coccidiosis: a parasitic disease of significant importance in rabbits[J]. World Vet J, 2020, 10 (4): 499- 507. |
| 5 | 闫文朝, 王天奇, 索勋, 等. 家兔球虫病的研究进展[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2010, 40 (11): 1200- 1205. |
| YAN W C , WANG T Q , SUO X , et al. Advances in coccidiosis of domestic rabbits[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2010, 40 (11): 1200- 1205. | |
| 6 | 罗跃军, 任永军, 白鑫, 等. 斯氏艾美耳球虫重组表面抗原SAG13和SAG14对兔的免疫保护效果初步观察[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (3): 883- 893. |
| LUO Y J , REN Y J , BAI X , et al. Preliminary observation on the Immunoprotective effects of Recombinant surface antigens SAG13 and SAG14 of Eimeria stiedae in rabbits[J]. Acta Veterinaria Et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (3): 883- 893. | |
| 7 |
XIAO J , CHEN H , ZHENG R Y , et al. Recombinant GMA56 and ROP17 of Eimeria magna conferred protection against infection by homologous species[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 13, 1037949.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1037949 |
| 8 |
DUBOIS D J , SOLDATI-FAVRE D . Biogenesis and secretion of micronemes in Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Cell Microbiol, 2019, 21 (5): e13018.
doi: 10.1111/cmi.13018 |
| 9 |
OLAJIDE J S , QU Z G , YANG S L , et al. Eimeria proteins: order amidst disorder[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2022, 15 (1): 38.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05159-0 |
| 10 | 田秀玲, 汤新明, 秦梅, 等. 基于IFA技术检测微线体蛋白2在艾美耳属球虫的空间分布[J]. 寄生虫与医学昆虫学报, 2015, 21 (4): 240- 243. |
| TIAN X L , TANG X M , QIN M , et al. Analysis on the location of microneme 2 protein in sporozoites of Eimeria spp. by indirect immunofluorescence assay[J]. Acta Parasitology et Medica Entomologica Sinica, 2015, 21 (4): 240- 243. | |
| 11 |
FOROUTAN M , ZAKI L , GHAFFARIFAR F . Recent progress in microneme-based vaccines development against Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Clin Exp Vaccine Res, 2018, 7 (2): 93- 103.
doi: 10.7774/cevr.2018.7.2.93 |
| 12 |
YAN M , CUI X X , ZHAO Q P , et al. Molecular characterization and protective efficacy of the microneme 2 protein from Eimeria tenella[J]. Parasite, 2018, 25, 60.
doi: 10.1051/parasite/2018061 |
| 13 | ZHANG Z C , LIU L R , HUANG J W , et al. The molecular characterization and immune protection of microneme 2 of Eimeria acervulina[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2006, 215, 96- 105. |
| 14 |
XIAO J , HE W , XIONG C M , et al. Protective efficacy of recombinant proteins AMA1 and IMP1 in rabbits infected with Eimeria intestinalis[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2023, 320, 109985.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2023.109985 |
| 15 |
WEI W R , SHEN N X , XIAO J , et al. Expression analysis and serodiagnostic potential of microneme proteins 1 and 3 in Eimeria stiedai[J]. Genes (Basel), 2020, 11 (7): 725.
doi: 10.3390/genes11070725 |
| 16 |
BORTOLUZZI C , PARAS K L , APPLEGATE T J , et al. Comparison between McMaster and Mini-FLOTAC methods for the enumeration of Eimeria maxima oocysts in poultry excreta[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2018, 254, 21- 25.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2018.02.039 |
| 17 |
JOHNSON J , REID W M . Anticoccidial drugs: lesion scoring techniques in battery and floor-pen experiments with chickens[J]. Exp Parasitol, 1970, 28 (1): 30- 36.
doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90063-9 |
| 18 |
SHEN N X , WEI W R , CHEN Y H , et al. An antibody persistent and protective two rSsCLP-based subunit cocktail vaccine against Sarcoptes scabiei in a rabbit model[J]. Vaccines (Basel), 2020, 8 (1): 129.
doi: 10.3390/vaccines8010129 |
| 19 |
FANG S F , GU X L , EL-ASHRAM S , et al. Immune protection provided by a precocious line trivalent vaccine against rabbit Eimeria[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2019, 275, 108927.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2019.108927 |
| 20 |
SOUTTER F , WERLING D , NOLAN M , et al. A novel whole yeast-based subunit oral vaccine against Eimeria tenella in Chickens[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13, 809711.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.809711 |
| 21 |
LIU Q , CHEN Z T , SHI W Y , et al. Preparation and initial application of monoclonal antibodies that recognize Eimeria tenella microneme proteins 1 and 2[J]. Parasitol Res, 2014, 113 (11): 4151- 4161.
doi: 10.1007/s00436-014-4087-2 |
| 22 |
BROSSIER F , DAVID SIBLEY L . Toxoplasma gondii: microneme protein MIC2[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2005, 37 (11): 2266- 2272.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.06.006 |
| 23 |
BANDINI G , LEON D R , HOPPE C M , et al. O-Fucosylation of thrombospondin-like repeats is required for processing of microneme protein 2 and for efficient host cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites[J]. J Biol Chem, 2019, 294 (6): 1967- 1983.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005179 |
| 24 |
SASAI K , FETTERER R H , LILLEHOJ H , et al. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the Eimeria tenella Microneme protein MIC2[J]. J Parasitol, 2008, 94 (6): 1432- 1434.
doi: 10.1645/GE-1558.1 |
| 25 | CARRUTHERS V B, TOMLEY F M. Microneme proteins in apicomplexans[M]//BURLEIGH B A, SOLDATI-FAVRE D. Molecular Mechanisms of Parasite Invasion. New York: Springer, 2008: 33-45. |
| 26 |
HOAN T D , ZHANG Z C , HUANG J W , et al. Identification and immunogenicity of microneme protein 2 (EbMIC2) of Eimeria brunetti[J]. Exp Parasitol, 2016, 162, 7- 17.
doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2015.12.015 |
| 27 |
HUANG J W , ZHANG Z C , LI M H , et al. Eimeria maxima microneme protein 2 delivered as DNA vaccine and recombinant protein induces immunity against experimental homogenous challenge[J]. Parasitol Int, 2015, 64 (5): 408- 416.
doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2015.06.002 |
| 28 | AKPO Y , KPODÉKON M T , DJAGO Y , et al. Vaccination of rabbits against coccidiosis using precocious lines of Eimeria magna and Eimeria media in Benin[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2012, 184 (1): 73- 76. |
| 29 | SADEK BACHENE M , TEMIM S , AINBAZIZ H , et al. A vaccination trial with a precocious line of Eimeria magna in Algerian local rabbits Oryctolagus cuniculus[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2018, 261, 73- 76. |
| 30 | PAKANDL M , SEWALD B , DROUET-VIARD F . Invasion of the intestinal tract by sporozoites of Eimeria coecicola and Eimeria intestinalis in naive and immune rabbits[J]. Parasitol Res, 2006, 98 (4): 310- 316. |
| 31 | DROUET-VIARD F , LICOIS D , PROVÔT F , et al. The invasion of the rabbit intestinal tract by Eimeria intestinalis sporozoites[J]. Parasitol Res, 1994, 80 (8): 706- 707. |
| 32 | YUAN X , LIU J , HU X F , et al. Alterations in the jejunal microbiota and fecal metabolite profiles of rabbits infected with Eimeria intestinalis[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2022, 15 (1): 231. |
| 33 | LU C Y , YAN Y Q , JIAN F C , et al. Coccidia-Microbiota interactions and their effects on the host[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11, 751481. |
| 34 | CHAPMAN H D . Milestones in avian coccidiosis research: a review[J]. Poult Sci, 2014, 93 (3): 501- 511. |
| 35 | DONG X J , ABDELNABI G H , LEE S H , et al. Enhanced egress of intracellular Eimeria tenella sporozoites by splenic lymphocytes from coccidian-infected chickens[J]. Infect Immun, 2011, 79 (8): 3465- 3470. |
| 36 | SONG X K , HUANG X M , YAN R F , et al. Efficacy of chimeric DNA vaccines encoding Eimeria tenella 5401 and chicken IFN-γ or IL-2 against coccidiosis in chickens[J]. Exp Parasitol, 2015, 156, 19- 25. |
| 37 | HOAN T D , THAO D T , GADAHI J A , et al. Analysis of humoral immune response and cytokines in chickens vaccinated with Eimeria brunetti apical membrane antigen-1 (EbAMA1) DNA vaccine[J]. Exp Parasitol, 2014, 144, 65- 72. |
| 38 | ARENDT M , ELISSA J , SCHMIDT N , et al. Investigating the role of interleukin 10 on Eimeria intestinal pathogenesis in broiler chickens[J]. Vet Immunol Immunopathol, 2019, 218, 109934. |
| 39 | GAZZINELLI-GUIMARÃES A C , GAZZINELLI-GUIMARÃES P H , NOGUEIRA D S , et al. IgG induced by vaccination with Ascaris suum extracts is protective against infection[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9, 2535. |
| 40 | XIONG L , CHEN L , CHEN Y X , et al. Evaluation of the immunoprotective effects of eight recombinant proteins from Baylisascaris schroederi in mice model[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2023, 16 (1): 254. |
| 41 | ZHAO P F , LI Y C , ZHOU Y Q , et al. In vivo immunoprotective comparison between recombinant protein and DNA vaccine of Eimeria tenella surface antigen 4[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2020, 278, 109032. |
| 42 | ZHANG Z C , LIU X C , YANG X C , et al. The molecular characterization and immunity identification of microneme 3 of Eimeria acervulina[J]. J Eukaryot Microbiol, 2016, 63 (6): 709- 721. |
| 43 | CHEN H , PU J Y , XIAO J , et al. Evaluation of the immune protective effects of rEmMIC2 and rEmMIC3 from Eimeria magna in rabbits[J]. Parasitol Res, 2023, 122 (2): 661- 669. |
| [1] | WU Wenying, XIA Qing, HU Mengjie, ZHAO Yixuan, WANG Chen, ZHANG Yuhao, HAO Chengwu, HE Sun, GUO Aizhen, CHEN Jianguo, CHEN Yingyu. Establishment of Rabbit Challenge Model of Mycoplasma bovis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1268-1277. |
| [2] | CHEN Mengjuan, LIU Yuqing, WANG Zhitong, WEN Jiale, XU Huifen, YU Guangqing, LI Ming. Construction of Eukaryotic Expression Vector, Expression Pattern of BMP15 Gene, and Its Expression in Ovary of New Zealand White Rabbit [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 562-575. |
| [3] | ZHANG Qianwen, LIU Yumei, SHI Lihui, LIANG Wenjun, LI Mengyun, WANG Yuqin, ZHANG Ziqiang. Pathological Observation and Drug Sensitivity Analysis of Salmonella Infection in Female Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3510-3518. |
| [4] | ZHENG Ruoyu, REN Yongjun, XIAO Jie, BAI Xin, PU Jiayan, CHEN Hao, YANG Guangyou. Evaluation of the Immunoprotective Effect of Recombinant Protein of Eimeria stiedae 3-Phosphoglyceraldehyde Dehydrogenase on Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2581-2595. |
| [5] | LI Yujuan, ZHANG Yuanming, ZHANG Beiyu, LI Fuchang, LIU Lei. Effects of Dietary Lysine Supplementation on Hair Production Performance and Hair Follicle Development of Angora Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 2013-2019. |
| [6] | HUANG Cuirui, HAO Guiying, ZHOU Yu, TIAN Yan, YANG Fusheng, TANG Li, YANG Guangyou, XIE Yue, HE Ran, XU Jing, GU Xiaobin. Recombinant Arginine Kinase of Psoroptes ovis Induces Cutaneous Eosinophil Recruitment in Rabbit [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 2186-2194. |
| [7] | YUAN Sheng, LI Anqi, Lü Wenke, YANG Lulu, ZHOU Feng, HUANG Liangzong, BAI Aiquan, WEN Feng, HUANG Shujian, GUO Jinyue. Analysis of Variation in Major Virulence-related Genes of a Strain of Pseudorabies Virus and Its Pathogenicity to Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 2195-2199. |
| [8] | WANG Jianing, ZHANG Ziqiang, KONG Dejing, FENG Caicai, ZHANG Feike, LIU Yumei. Isolation and Identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5198-5206. |
| [9] | CAI Jiawei, ZHANG Chen, JIN Rongshuai, BAO Zhiyuan, ZHANG Xiyu, WANG Fan, ZHAI Pin, ZHAO Bohao, CHEN Yang, TANG Xianwei, WU Xinsheng. Analysis of Testicular Tissue Morphology and Semen Transcriptome of Male Rabbits under Heat Stress [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4653-4663. |
| [10] | YANG Anqi, LI Jiacheng, SONG Ying, CHEN Xin, JIN Rongshuai, ZHAO Bohao, WU Xinsheng, CHEN Yang. Effects of CYP19A1 on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Rabbit Ovary Granulosa Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4209-4219. |
| [11] | WU Diange, XIA Miao, YAN An, JIANG Haotian, FAN Jiaqi, ZHOU Siyuan, WEI Xu, LIU Shudong, CHEN Baojiang. Effects of Carvacrol on Growth Performance, Nutrient Apparent Digestibility, Intestinal Morphology, Short-chain Fatty Acids Content and Intestinal Flora in Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4233-4246. |
| [12] | XIAO Jie, LUO Yuejun, CHEN Hao, PU Jiayan, HE Wei, XIONG Changming, HAO Ge, REN Yongjun, YANG Guangyou. Screening of PCR-detection Targets of Eimeria stiedae, E. intestinalis, and E. magna in Rabbits and Establishment of the Single and Multiplex Direct PCR Methods [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4327-4337. |
| [13] | ZHENG Ruoyu, XIAO Jie, BAI Xin, CHEN Hao, PU Jiayan, REN Yongjun, YANG Guangyou. Evaluation of the Immunoprotective Effect of Recombinant Protein of Eimeria magna 3-Phosphoglyceraldehyde Dehydrogenase on Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4338-4349. |
| [14] | ZHANG Xiyu, ZHAI Pin, WANG Fan, DAI Yingying, ZHAO Bohao, CHEN Yang, WU Xinsheng. Expression and Function of KRT 16 in Hair Follicle Development of Angora Rabbit [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(1): 157-167. |
| [15] | SANG Lei, CHEN Dongjin, SUN Shikun, GAO Chengfang, WANG Jinxiang, CHEN Yanfeng, XIE Xiping. Cloning and Expression of GnIH Gene and Its Effect on Reproductive Hormones Secretion of Young Male Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(1): 201-212. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||