





畜牧兽医学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (12): 6013-6024.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.12.007
赵雨薇( ), 王卓, 张城瑞, 屠焰, 刁其玉, 崔凯*(
), 王卓, 张城瑞, 屠焰, 刁其玉, 崔凯*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-13
出版日期:2025-12-23
发布日期:2025-12-24
通讯作者:
崔凯
E-mail:zhaoyw0010@163.com;cuikai@caas.cn
作者简介:赵雨薇(2000-),女,安徽淮南人,硕士生,主要从事动物营养与饲料科学研究,E-mail:zhaoyw0010@163.com
基金资助:
ZHAO Yuwei( ), WANG Zhuo, ZHANG Chengrui, TU Yan, DIAO Qiyu, CUI Kai*(
), WANG Zhuo, ZHANG Chengrui, TU Yan, DIAO Qiyu, CUI Kai*( )
)
Received:2024-11-13
Online:2025-12-23
Published:2025-12-24
Contact:
CUI Kai
E-mail:zhaoyw0010@163.com;cuikai@caas.cn
摘要:
儿茶素类物质是一种从植物中提取的酚类活性物质,因其显著的抗氧化、抗炎、抗菌与抗肿瘤等生物特性,在保护肠道健康与稳态方面表现出优异特性,而稳定、健康的肠道环境是维持动物体的生长发育与机体健康的关键性因素。近年来,国内外的大量临床研究报道了儿茶素类物质缓解肠道损伤的作用机制,包括调节细胞间隙连接、激发炎症与氧化应激相关通路调节免疫功能以及调节肠道菌群的平衡等方面稳定肠道稳态,但在动物实际生产中的应用鲜有报道。本文综述了儿茶素类物质的生物学特性、修复肠道屏障的效果与机制,并展望儿茶素类物质于动物生产中应用的研究进展,为儿茶素类物质在养殖业中的合理利用提供参考。
中图分类号:
赵雨薇, 王卓, 张城瑞, 屠焰, 刁其玉, 崔凯. 儿茶素类物质调控动物肠道屏障功能的机制研究及应用进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(12): 6013-6024.
ZHAO Yuwei, WANG Zhuo, ZHANG Chengrui, TU Yan, DIAO Qiyu, CUI Kai. Mechanism Research and Application Progress of Catechins Regulating Animal Intestinal Barrier Function[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(12): 6013-6024.
表 1
八种常见的儿茶素类物质的结构"
| 名称 Name | 分子式 Molecular formula | 羟基数 Hydroxyl groups | 化学结构 Chemical structure |
| 儿茶素(+)-Catechin | C15H14O6 | 2 | 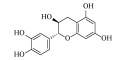 |
| 没食子儿茶素(+)-Gallocatechin | C15H14O7 | 3 | 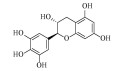 |
| 表儿茶素(-)-Epicatechin | C15H14O6 | 2 | 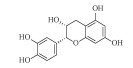 |
| 表没食子儿茶素(-)-Epigallocatechin | C15H14O7 | 3 | 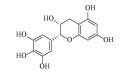 |
| 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate | C22H18O11 | 3 | 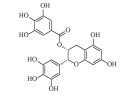 |
| 表儿茶素没食子酸酯 (-)-Epicatechin gallate | C22H18O10 | 2 | 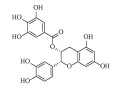 |
| 没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 (-)-Gallocatechin gallate | C22H18O11 | 3 | 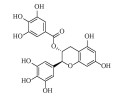 |
| 儿茶素没食子酸酯 (-)-Catechin gallate | C22H18O10 | 2 | 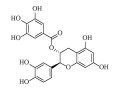 |
| 1 | 彭丽媛. 牛乳铁蛋白肽对肠粘膜屏障的保护作用及其机制研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2020. |
| PENG L Y. Research on protection and mechanism of bovine lactoferricin on intestinal barrier[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 2 |
CELEBIOGLU H , SVENSSON B . Dietary nutrients, proteomes, and adhesion of probiotic Lactobacilli to mucin and host epithelial cells[J]. Microorganisms, 2018, 6 (3): 90.
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms6030090 |
| 3 |
MEHANDRU S , COLOMBEL J F . The intestinal barrier, an arbitrator turned provocateur in IBD[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18 (2): 83- 84.
doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-00399-w |
| 4 |
MA T , VILLOT C , RENAUD D , et al. Linking perturbations to temporal changes in diversity, stability, and compositions of neonatal calf gut microbiota: prediction of diarrhea[J]. ISME J, 2020, 14 (9): 2223- 2235.
doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-0678-3 |
| 5 | 张天鹏. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, EGCG)通过AKT/PI3K和MAPKs信号通路诱导经缺氧再灌注处理的脐静脉内皮细胞凋亡[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2011. |
| ZHANG T P. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhances ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via AKT and MAPKN pathways[D]. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College, 2011. (in Chinese) | |
| 6 | 郭亚飞. 茶树鲜叶中儿茶素和氨基酸性状的遗传基础解析[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2023. |
| GUO Y F. Genetic basis analysis of catechins and amino acids traits in fresh leaves of Camellia sinensis[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 7 |
WU J , DENG X , SUN Y , et al. Aged oolong tea alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by modulating the gut microbiota and its metabolites[J]. Food Chem X, 2024, 21, 101102.
doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.101102 |
| 8 |
王浩磊, 刘梦燕, 龙泉, 等. 表儿茶素没食子酸酯对MAC-T和小鼠乳腺炎症与细胞焦亡及NF-κB通路和NLRP3炎性小体的抑制效应[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56 (1): 430- 441.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.01.039 |
|
WANG H L , LIU M Y , LONG Q , et al. Inhibition of epicatechin gallate on inflammation and pyroptosis as well as NF-κB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome in MAC-T cells and mouse mammary glands[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56 (1): 430- 441.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.01.039 |
|
| 9 |
KIM J M , HEO H J . The roles of catechins in regulation of systemic inflammation[J]. Food Sci Biotechnol, 2022, 31 (8): 957- 970.
doi: 10.1007/s10068-022-01069-0 |
| 10 |
LI M , QU R , LI P , et al. Green tea polyphenols reduced Porphyromonas gingivalis virulence and ameliorated aggravated gut inflammation by improving immunity and gut microbiota dysbiosis[J]. Food Biosci, 2024, 60, 104519.
doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104519 |
| 11 |
HUANG S , LI T , LI N , et al. Gut microbiota from green tea polyphenol-dosed mice improves intestinal epithelial homeostasis and ameliorates experimental colitis[J]. Microbiome, 2021, 9 (1): 184.
doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01115-9 |
| 12 | 李杰, 张志旭. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯对葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎的改善作用[J]. 食品工业科技, 2023, 44 (13): 390- 397. |
| LI J , ZHANG Z X . Improving effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44 (13): 390- 397. | |
| 13 |
SCHIRMER M , GARNER A , VLAMAKIS H , et al. Microbial genes and pathways in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2019, 17 (8): 497- 511.
doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0213-6 |
| 14 |
XIE L W , CAI S , ZHAO T S , et al. Green tea derivative (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) confers protection against ionizing radiation-induced intestinal epithelial cell death both in vitro and in vivo[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2020, 161, 175- 186.
doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.10.012 |
| 15 |
FATHIMA A , RAO J R . Selective toxicity of Catechin—a natural flavonoid towards bacteria[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2016, 100 (14): 6395- 6402.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7492-x |
| 16 |
KNEZEVIC S , GHAFOOR A , MEHRI S , et al. Catechin and other catechol-containing secondary metabolites: Bacterial biotransformation and regulation of carbohydrate metabolism[J]. PharmaNutrition, 2021, 17, 100273.
doi: 10.1016/j.phanu.2021.100273 |
| 17 |
BRAICU C , LADOMERY M R , CHEDEA V S , et al. The relationship between the structure and biological actions of green tea catechins[J]. Food Chem, 2013, 141 (3): 3282- 3289.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.05.122 |
| 18 |
GRZESIK M , NAPARLO K , BARTOSZ G , et al. Antioxidant properties of catechins: Comparison with other antioxidants[J]. Food Chem, 2018, 241, 480- 492.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.117 |
| 19 |
PEREIRA-CARO G , MORENO-ROJAS J M , BRINDANI N , et al. Bioavailability of black tea theaflavins: Absorption, metabolism, and colonic catabolism[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2017, 65 (26): 5365- 5374.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b01707 |
| 20 | 张印. 柑橘原花青素积累及ABA代谢的调控机制研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2022. |
| ZHANG Y. Research on the regulation mechanism of proanthocyanidin accumulation and ABA metabolism in citrus[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 21 |
DUDEK M K , GLIŃSKI V B , DAVEY M H , et al. Trimeric and Tetrameric A-Type Procyanidins from Peanut Skins[J]. J Nat Prod, 2017, 80 (2): 415- 426.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00946 |
| 22 |
姜美涵, 魏金涛, 呙于明, 等. 植物精油对产气荚膜梭菌感染肉仔鸡肠道损伤、肠道菌群CAZy谱和eggNOG通路的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (6): 2448- 2457.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.06.023 |
|
JIANG M H , WEI J T , GUO Y M , et al. Effects of essential oils on gut lesions, carbohydrate active enzymes spectrum and eggNOG pathways of intestinal flora in broilers challenged with Clostridium perfringens[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (6): 2448- 2457.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.06.023 |
|
| 23 |
韩露露, 韩德平, 赵启南, 等. miRNA介导应激幼畜肠道损伤的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (3): 877- 888.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.03.003 |
|
HAN L L , HAN D P , ZHAO Q N , et al. Research progress of intestinal injury in young farm animals under stress mediated by miRNA[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (3): 877- 888.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.03.003 |
|
| 24 |
SHYER A E , HUYCKE T R , LEE C , et al. Bending gradients: How the intestinal stem cell gets its home[J]. Cell, 2015, 161 (3): 569- 580.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.041 |
| 25 | 谢黎伟. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG)对小鼠放射性肠损伤的防护作用及机制研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2021. |
| XIE L W. The study on the radioprotection effect and mechanism of EGCG on radiation induced intestinal injury[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 26 |
LI Y , MA S , ZHANG Y , et al. (-)-Epicatechin mitigates radiation-induced intestinal injury and promotes intestinal regeneration via suppressing oxidative stress[J]. Free Radic Res, 2019, 53 (8): 851- 864.
doi: 10.1080/10715762.2019.1635692 |
| 27 | 黄玮玮, 马涛, 李志华, 等. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯通过抑制凋亡减轻脓毒症肠道损伤的研究[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2024, 33 (4): 529- 535. |
| HUANG W W , MA T , LI Z H , et al. Epigallocatechin gallate attenuates intestinal injury in sepsis by inhibiting apoptosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 33 (4): 529- 535. | |
| 28 |
OTANI T , FURUSE M . Tight junction structure and function revisited[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2020, 30 (10): 805- 817.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.08.004 |
| 29 |
KOSIŃSKA A , ANDLAUER W . Modulation of tight junction integrity by food components[J]. Food Res Int, 2013, 54 (1): 951- 960.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.12.038 |
| 30 |
CONTRERAS T C , RICCIARDI E , CREMONINI E , et al. (-)-Epicatechin in the prevention of tumor necrosis alpha-induced loss of Caco-2 cell barrier integrity[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2015, 573, 84- 91.
doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.01.024 |
| 31 |
DEY P , SASAKI G Y , WEI P , et al. Green tea extract prevents obesity in male mice by alleviating gut dysbiosis in association with improved intestinal barrier function that limits endotoxin translocation and adipose inflammation[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2019, 67, 78- 89.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.01.017 |
| 32 | 刘肃宇. 肠源硒蛋白在儿茶素EGCG预防DSS诱导小鼠结肠炎中的作用研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2023. |
| LIU S Y. Roles of colonic selenoproteins on the prevention of DSS induced mouse colitis by green tea EGCG[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 33 |
DEY P , OLMSTEAD B D , SASAKI G Y , et al. Epigallocatechin gallate but not catechin prevents nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice similar to green tea extract while differentially affecting the gut microbiota[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2020, 84, 108455.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108455 |
| 34 |
JOHANSSON M E V , SJÖVALL H , HANSSON G C . The gastrointestinal mucus system in health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 10 (6): 352- 361.
doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.35 |
| 35 |
GROSCHWITZ K R , HOGAN S P . Intestinal barrier function: Molecular regulation and disease pathogenesis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2009, 124 (1): 3- 20.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.038 |
| 36 |
COX K E , LIU S , LWIN T M , et al. The mucin family of proteins: Candidates as potential biomarkers for colon cancer[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15 (5): 1491.
doi: 10.3390/cancers15051491 |
| 37 | 冀凤杰. 抗菌肽对断奶仔猪肠道功能的调控作用及机制研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2022. |
| JI F J. Regulation and mechanism of antimicrobial peptides on intestinal function of weaned piglets[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 38 |
WU M , WU Y , LI J , et al. The dynamic changes of gut microbiota in Muc2 deficient mice[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19 (9): 2809.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19092809 |
| 39 |
VAN DER SLUIS M , DE KONING B A E , DE BRUIJN A C J M , et al. Muc2-deficient mice spontaneously develop colitis, indicating that MUC2 is critical for colonic protection[J]. Gastroenterology, 2006, 131 (1): 117- 129.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.04.020 |
| 40 |
VOLSTATOVA T , MARCHICA A , HRONCOVA Z , et al. Effects of chlorogenic acid, epicatechin gallate, and quercetin on mucin expression and secretion in the Caco-2/HT29-MTX cell model[J]. Food Sci Nutr, 2019, 7 (2): 492- 498.
doi: 10.1002/fsn3.818 |
| 41 |
GEORGIADES P , PUDNEY P D A , ROGERS S , et al. Tea derived galloylated polyphenols cross-link purified gastrointestinal mucins[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9 (8): e105302.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105302 |
| 42 |
JIA W , XIE G , JIA W . Bile acid-microbiota crosstalk in gastrointestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 15 (2): 111- 128.
doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.119 |
| 43 |
VAVASSORI P , MENCARELLI A , RENGA B , et al. The bile acid receptor FXR is a modulator of intestinal innate immunity[J]. J Immunol, 2009, 183 (10): 6251- 6261.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803978 |
| 44 |
GADALETA R M , VAN ERPECUM K J , OLDENBURG B , et al. Farnesoid X receptor activation inhibits inflammation and preserves the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Gut, 2011, 60 (4): 463- 472.
doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.212159 |
| 45 | ANNABA F , KUMAR P , DUDEJA A K , et al. Green tea catechin EGCG inhibits ileal apical sodium bile acid transporter ASBT[J]. Am J Physiol-Gastr L, 2010, 298 (3): G467- G473. |
| 46 |
WANG Y , YU Y , DING L , et al. Matcha green tea targets the gut-liver axis to alleviate obesity and metabolic disorders induced by a high-fat diet[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9, 931060.
doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.931060 |
| 47 |
LOMBARDO BEDRAN T B , FEGHALI K , ZHAO L , et al. Green tea extract and its major constituent, epigallocatechin-3-gallate, induce epithelial beta-defensin secretion and prevent beta-defensin degradation by P orphyromonas gingivalis[J]. J Periodontal Res, 2014, 49 (5): 615- 623.
doi: 10.1111/jre.12142 |
| 48 |
WAN M L Y , LING K H , WANG M F , et al. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate improves epithelial barrier function by inducing the production of antimicrobial peptide pBD-1 and pBD-2 in monolayers of porcine intestinal epithelial IPEC-J2 cells[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2016, 60 (5): 1048- 1058.
doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500992 |
| 49 |
TURNER J R . Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2009, 9 (11): 799- 809.
doi: 10.1038/nri2653 |
| 50 | 王文文. 发酵豆粕对断奶仔猪肠道屏障的保护作用及机理研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2023. |
| WANG W W. Protective effect and mechanism of fermented soybean meal on gut barrier in weaned piglets[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 51 |
SIDHU D , VASUNDHARA M , DEY P . The intestinal-level metabolic benefits of green tea catechins: Mechanistic insights from pre-clinical and clinical studies[J]. Phytomed, 2024, 123, 155207.
doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155207 |
| 52 |
LIU Z , BRUINS M E , NI L , et al. Green and black tea phenolics: Bioavailability, transformation by colonic microbiota, and modulation of colonic microbiota[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2018, 66 (32): 8469- 8477.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02233 |
| 53 |
LEE H C , JENNER A M , LOW C S , et al. Effect of tea phenolics and their aromatic fecal bacterial metabolites on intestinal microbiota[J]. Res Microbiol, 2006, 157 (9): 876- 884.
doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2006.07.004 |
| 54 |
RENZETTI A , BETTS J W , FUKUMOTO K , et al. Antibacterial green tea catechins from a molecular perspective: mechanisms of action and structure-activity relationships[J]. Food Funct, 2020, 11 (11): 9370- 9396.
doi: 10.1039/D0FO02054K |
| 55 |
LIANG W , FERNANDES A P , HOLMGREN A , et al. Bacterial thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase as mediators for epigallocatechin 3-gallate-induced antimicrobial action[J]. FEBS J, 2016, 283 (3): 446- 458.
doi: 10.1111/febs.13587 |
| 56 |
TABASCO R , SÁNCHEZ-PATÁN F , MONAGAS M , et al. Effect of grape polyphenols on lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria growth: Resistance and metabolism[J]. Food Microbiol, 2011, 28 (7): 1345- 1352.
doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2011.06.005 |
| 57 |
LI Q , VAN HERREWEGHEN F , ONYANGO S O , et al. In vitro microbial metabolism of (+)-catechin reveals fast and slow converters with individual-specific microbial and metabolite markers[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70 (34): 10405- 10416.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c00551 |
| 58 |
ZHANG X , ZHU X , SUN Y , et al. Fermentation in vitro of EGCG, GCG and EGCG3"Me isolated from Oolong tea by human intestinal microbiota[J]. Food Res Int, 2013, 54 (2): 1589- 1595.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2013.10.005 |
| 59 |
SUN H , CHEN Y , CHENG M , et al. The modulatory effect of polyphenols from green tea, oolong tea and black tea on human intestinal microbiota in vitro[J]. J Food Sci Technol, 2018, 55 (1): 399- 407.
doi: 10.1007/s13197-017-2951-7 |
| 60 |
CHEN W , ZHU X , LU Q , et al. C-ring cleavage metabolites of catechin and epicatechin enhanced antioxidant activities through intestinal microbiota[J]. Food Res Int, 2020, 135, 109271.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109271 |
| 61 |
XIE J , SUN N , HUANG H , et al. Catabolism of polyphenols released from mung bean coat and its effects on gut microbiota during in vitro simulated digestion and colonic fermentation[J]. Food Chem, 2022, 396, 133719.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133719 |
| 62 |
CHENG M , ZHANG X , ZHU J , et al. A metagenomics approach to the intestinal microbiome structure and function in high fat diet-induced obesity mice fed with oolong tea polyphenols[J]. Food Funct, 2018, 9 (2): 1079- 1087.
doi: 10.1039/C7FO01570D |
| 63 |
HUO J , WU Z , SUN W , et al. Protective Effects of Natural Polysaccharides on Intestinal Barrier Injury: A Review[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70 (3): 711- 735.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c05966 |
| 64 |
LEE Y , KAMADA N , MOON J J . Oral nanomedicine for modulating immunity, intestinal barrier functions, and gut microbiome[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2021, 179, 114021.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.114021 |
| 65 |
SUZUKI J I , OGAWA M , FUTAMATSU H , et al. Tea catechins improve left ventricular dysfunction, suppress myocardial inflammation and fibrosis, and alter cytokine expression in rat autoimmune myocarditis[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2007, 9 (2): 152- 159.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2006.05.007 |
| 66 | 王鹏. AhR/IL-22/Stat3信号通路在肠道菌群调节抗菌肽分泌中的作用与机制研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2019. |
| WANG P. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor/L-22/Stat3 signaling pathway is inyolved in the modulation of intestinal mucosa antimicrobial molecules by commensal microbiota in mice[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2019. (in Chinese) | |
| 67 |
LI M , YAN Q , CHEN C , et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate mitigates cadmium-induced intestinal damage through modulation of the microbiota-tryptophan-aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway[J]. Eco Toxicol Environ Saf, 2024, 280, 116520.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116520 |
| 68 |
PORATH D , RIEGGER C , DREWE J , et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate impairs chemokine production in human colon epithelial cell lines[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2005, 315 (3): 1172- 1180.
doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.090167 |
| 69 | OANH N C , THU C T T , HONG N T , et al. Growth performance, meat quality, and blood characteristics of finisher crossbred pigs fed diets supplemented with different levels of green tea (Camellia sinensis) by-products[J]. Vet World, 2023, 16 (1): 27- 34. |
| 70 | 肖勇. 儿茶素对妊娠母猪繁殖性能、抗氧化力和免疫功能的影响研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2014. |
| XIAO Y. Effects of catechins on the reproductive performance, antioxidant and immune function in pregnant sows[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese) | |
| 71 | 楼芳芳, 刘禹熙, 陈雨诗, 等. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯对金华猪生产性能、肉品质、肠道菌群及抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2023, 59 (8): 345- 351. |
| LOU F F , LIU Y X , CHEN Y S , et al. Effects of epigallocatechin gallate on performance, meat quality, intestinal flora and antioxidant capacity of Jinhua pigs[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2023, 59 (8): 345- 351. | |
| 72 | 陈雨诗, 刘禹熙, 杨童寓丹, 等. 饲粮中添加甜菜碱和表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯对育肥猪生长性能、肉品质、血清生化和抗氧化指标的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2024, 36 (3): 1525- 1536. |
| CHEN Y S , LIU Y X , YANG T Y D , et al. Effects of dietary betaine and epigallocatechin gallate on growth performance, meat quality, serum biochemical and antioxidant indices of finishing pigs[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2024, 36 (3): 1525- 1536. | |
| 73 |
JUSTINO A B , CARRILLO M S P , BITTAR V P , et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate-synthesized gold nanoparticles modulate reactive oxygen species and antioxidant parameters in brain and heart tissues using a chicken embryo model[J]. Mater Chem Phys, 2024, 322, 129557.
doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2024.129557 |
| 74 |
MADKOUR M , ABDEL-FATTAH S A , ALI S I , et al. Impact of in ovo feeding of grape pomace extract on the growth performance, antioxidant status, and immune response of hatched broilers[J]. Poult Sci, 2024, 103 (8): 103914.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103914 |
| 75 |
张帆帆, 曾艳兵, 方绍培, 等. 鸭坦布苏病毒病的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2021, 52 (6): 1489- 1497.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.06.005 |
|
ZHANG F F , ZENG Y B , FANG S P , et al. Research progress in duck tembusu virus disease[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52 (6): 1489- 1497.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.06.005 |
|
| 76 |
ZHU Y Q , GU X X , ZHANG M , et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate exhibits antiviral effects against the duck Tembusu virus via blocking virus entry and upregulating type I interferons[J]. Poult Sci, 2021, 100 (4): 100989.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.01.012 |
| 77 |
ZHONG R Z , FANG Y , QIN G X , et al. Tea catechins protect goat skeletal muscle against H2O2-induced oxidative stress by modulating expression of phase 2 antioxidant enzymes[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2015, 63 (36): 7921- 7928.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b00816 |
| 78 |
ZHU X , LI A , SUN N , et al. Green tea catechin prevents oxidative stress-regulated autophagy and apoptosis signaling, and inhibits tenderness in postmortem bovine longissimus thoracis et lumborum muscle[J]. Food Chem X, 2023, 19, 100758.
doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100758 |
| 79 | 马骁. 表儿茶素对LPS诱导的奶牛乳腺炎的调控及其分子机制[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2022. |
| MA X. Inhibitory effect and underlying molecular mechanism of epicatechin on LPS induced bovine mastitis[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 80 |
ZHUANG X , CHEN Z , SUN X , et al. Fermentation quality of herbal tea residue and its application in fattening cattle under heat stress[J]. BMC Vet Res, 2021, 17 (1): 348.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-03061-y |
| [1] | 陈婷, 崔亚东, 兰伟, 孔祥峰. 氨基葡萄糖的功能及其在动物生产中的应用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(4): 1518-1526. |
| [2] | 张燕敏, 刘帅, 滕战伟, 谢红兵, 夏小静, 贺永惠, 常美楠. 功能性寡糖缓解犊牛腹泻的机理研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(3): 979-994. |
| [3] | 王卓, 赵雨薇, 屠焰, 刁其玉, 崔凯. β-防御素的生物学特性及其在调控动物肠道屏障中的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(3): 995-1005. |
| [4] | 张萱, 杨雪, 李新科, 郑楠, 孟璐. 丁酸钠对幼鼠回肠发育、炎症因子及物理屏障功能的调控作用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(3): 1278-1289. |
| [5] | 王雨珊, 刘旺景. 植物源性黄酮类化合物介导微生物保护肠道屏障的机制[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(12): 5998-6012. |
| [6] | 张鹤馨, 曲悠扬, 陈若瑄, 何欢, 唐琦超, 尹柏双, 王奔, 冯秀晶. 绿原酸通过抑制NF-κB/NLRP3通路介导的细胞焦亡改善慢性应激致大鼠肠道损伤[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(12): 6502-6512. |
| [7] | 白慧涛, 孙健, 解伟纯, 王雪莹, 王晓娜, 唐丽杰. 粪菌移植改善仔猪断奶早期肠道屏障功能的作用机制研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(11): 5379-5388. |
| [8] | 季小禹, 王永伟, 邱妍, 张才. 甘草多糖的生理功能及其在畜禽生产中的应用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(6): 2379-2387. |
| [9] | 李亚霖, 甄士博, 曹林, 孙逢雪, 王利华. 植物乳杆菌及其后生元对育成期母貂生长性能、免疫功能及肠道健康的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(6): 2530-2539. |
| [10] | 刘泽青, 耿怡雯, 朱龙龙, 马超, 陈国顺, 王晶. 发酵中草药饲料添加剂在畜禽生产中的研究应用进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(10): 4250-4262. |
| [11] | 牟湘钰, 徐云若, 胡静怡, 周欣妍, 朱勇文. 家禽支链氨基酸营养需要研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(1): 31-38. |
| [12] | 谢旖, 邹郦睿, 陶冉, 刘莎, 王江萍, 文利新, 邬静, 王吉. 单宁酸对低剂量T-2毒素诱导小鼠结肠黏膜损伤与菌群失调的保护效应[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(8): 3582-3594. |
| [13] | 曹秀芸, 刘吉文, 汤智辉, 郑紫怡, 闫丽萍, 宋素泉. 一株鸭腺病毒3型的分离、鉴定及致病性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(5): 2050-2061. |
| [14] | 汪倩, 王建梅, 安柯颖, 夏兆飞. 增益素对溃疡性结肠炎犬免疫功能、肠道屏障和肠道菌群的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(3): 1261-1272. |
| [15] | 刘慧娟, 王超, 周斌斌, 张佳琦, 王恬, 庄苏. 饲粮中添加芦丁对肉鸡回肠形态、免疫、抗氧化及屏障功能的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(2): 630-641. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
