





畜牧兽医学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (8): 3872-3892.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.08.027
王琳玮1( ), 王靖1, 韩赛波1, 李涵川1, 王盼盼1, 郭刚2,*(
), 王靖1, 韩赛波1, 李涵川1, 王盼盼1, 郭刚2,*( ), 蒋林树1,*(
), 蒋林树1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-20
出版日期:2025-08-23
发布日期:2025-08-28
通讯作者:
郭刚,蒋林树
E-mail:wlw0710l@126.com;guogang2180@126.com;jls@bua.edu.com
作者简介:王琳玮(1999-),男,吉林长春人,硕士生,主要从事反刍动物营养与饲料活性物质开发与应用研究,E-mail: wlw0710l@126.com
基金资助:
WANG Linwei1( ), WANG Jing1, HAN Saibo1, LI Hanchuan1, WANG Panpan1, GUO Gang2,*(
), WANG Jing1, HAN Saibo1, LI Hanchuan1, WANG Panpan1, GUO Gang2,*( ), JIANG Linshu1,*(
), JIANG Linshu1,*( )
)
Received:2024-08-20
Online:2025-08-23
Published:2025-08-28
Contact:
GUO Gang, JIANG Linshu
E-mail:wlw0710l@126.com;guogang2180@126.com;jls@bua.edu.com
摘要:
旨在系统评估饲粮中添加植物精油(essential oils, EOs)对哺乳期犊牛血清免疫及生化指标的影响。通过荟萃分析(Meta分析)方法,对截至2024年4月已发表的537篇文献进行筛选,最终纳入17篇文献,涉及样本711例。采用随机效应模型(REM)计算合并统计量,并进行亚组分析、敏感性分析和发表偏倚分析。Meta分析结果显示:饲粮中添加EOs极显著提高了哺乳期犊牛血清中免疫球蛋白A(IgA)[标准化均数差(SMD)=0.66,95%置信区间(95%CI):0.23~1.08,P<0.002]、免疫球蛋白G(IgG)(SMD=0.70,95%CI:0.37~1.02,P<0.001)以及甘油三酯(TG)的浓度(SMD=0.51,95%CI:0.10~0.92,P=0.01);显著提高了血清中免疫球蛋白M(IgM)(SMD=0.49,95%CI:0.03~0.96,P=0.04)和总蛋白(TP)的浓度(SMD=0.45,95%CI:0.03~0.87,P=0.04),并显著降低了总胆固醇(TC)浓度(SMD=-0.59,95%CI:-1.07~-0.11,P=0.02)。亚组分析通过结合有效性与稳定性比较表明,短期饲喂(≤56 d)EOs的效果优于长期饲喂(>56 d);通过固体饲料添加EOs的效果优于通过液体饲料添加。敏感性分析和发表偏倚分析表明,研究结果具有稳定性和可靠性。综上所述,本研究采用Meta分析方法为EOs在犊牛生产中的应用奠定了理论基础,表明在饲粮中添加EOs可以有效改善哺乳期犊牛的血清免疫及生化指标。
中图分类号:
王琳玮, 王靖, 韩赛波, 李涵川, 王盼盼, 郭刚, 蒋林树. 植物精油对哺乳期犊牛血清免疫及生化指标影响的Meta分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(8): 3872-3892.
WANG Linwei, WANG Jing, HAN Saibo, LI Hanchuan, WANG Panpan, GUO Gang, JIANG Linshu. Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Essential Oils on Serum Immune and Biochemical Indicators in Suckling Calves[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3872-3892.
表 1
检索策略"
| 数据库Databases | 检索词Search word | 数目Number |
| Web of Science | ||
| #1 | TS=(calf OR calves) | 210 894 |
| #2 | TS=essential oils | 159 527 |
| #3 | #1 AND #2 | 339 |
| ScienceDirect | ||
| #1 | Title, abstract, keywords: calf OR calves | 29 449 |
| #2 | Title, abstract, keywords: “essential oils” | 8 274 |
| #3 | #1 AND #2 | 18 |
| PubMed | ||
| #1 | (calf [title/abstract]) OR (claves [title/abstract]) | 71 559 |
| #2 | essential oils [title/abstract] | 13 703 |
| #3 | #1 AND #2 | 29 |
| Scopus | ||
| #1 | TITLE-ABS-KEY (calf OR calves) | 108 403 |
| #2 | TITLE-ABS-KEY (“essential oils”) | 84 193 |
| #3 | #1 AND #2 | 122 |
| 知网CNKI | ||
| #1 | 犊牛 | 22 908 |
| #2 | 精油 | 15 710 |
| #3 | #1 AND #2 | 15 |
| 维普CQVIP | ||
| #1 | 犊牛 | 9 234 |
| #2 | 精油 | 8 198 |
| #3 | #1 AND #2 | 4 |
| 万方Wanfang | ||
| #1 | 犊牛 | 21 297 |
| #2 | 精油 | 14 389 |
| #3 | #1 AND #2 | 10 |
表 2
纳入研究的基本特征"
| 序号 No. | 作者 Author | 年份 Year | 国家 Country | 品种 Breed | 数量 N | 日龄 Days of age | 精油种类 Types of essential oils | 添加途径 Method of addition | 饲粮 Diets | 断奶日龄 Weaning ages | 持续时间 Duration | 结局指标5) Outcome indexes |
| 1 | Andrés等[ | 2024 | 西班牙 | 荷斯坦牛 | 16 | 3 | 牛至精油 | MR1) | MR | 70 | 42 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦ |
| 2 | Kara和Pirci[ | 2023 | 土耳其 | 荷斯坦牛 | 24 | 14 | 鼠尾草精油 | WM2) | WM+CS | 70 | 56 | ⑨⑩ |
| 3 | Nora等[ | 2024 | 巴西 | 荷斯坦牛 | 16 | 10 | 混合物精油 | MR | MR+CS | 70 | 60 | ①②③④⑥⑧ |
| 4 | Biyik等[ | 2023 | 土耳其 | 荷斯坦牛 | 40 | 4 | 迷迭香精油 | MR | MR+CS | 56 | 45 | ①④⑤⑥⑦⑨ |
| 5 | Coelho等[ | 2023 | 巴西 | 荷斯坦牛 | 40 | 1 | 桉树薄荷精油 | MR | MR+CS | 56 | 28 | ①④⑦ |
| 6 | Palhares Campolina等[ | 2021 | 巴西 | 荷斯坦牛 | 29 | 4 | 混合物精油 | MR | MR | 60 | 56 | ③④ |
| 7 | Asghari等[ | 2021 | 伊朗 | 荷斯坦牛 | 40 | 7 | 混合物精油 | WM | WM+CS | 42 | 35 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦ |
| 8 | Ebrahimi等[ | 2018 | 伊朗 | 瑞士褐牛 | 60 | 3 | 百里香/阿育魏实精油 | WM | WM+CS | NA | 60 | ①②③④⑤⑥ |
| 9 | Akbarian-Tefaghi等[ | 2018 | 伊朗 | 荷斯坦牛 | 22 | 3 | 混合物精油 | CS3) | WM+CS | 56 | 70 | ③④⑦ |
| 10 | Seirafy和Sobhanirad[ | 2017 | 伊朗 | 荷斯坦牛 | 48 | 3 | 百里香/牛至精油 | WM | WM+CS | NA | 63 | ③⑤⑥ |
| 11 | Jeshari等[ | 2016 | 伊朗 | 荷斯坦牛 | 60 | 3 | 混合物精油 | CS | WM+CS | 56 | 56 | ①②④⑤⑥ |
| 12 | Soltan[ | 2009 | 埃及 | 荷斯坦牛 | 100 | 14 | 混合物精油 | MR | MR+CS | 56 | 56 | ①④ |
| 13 | 李娟花[ | 2021 | 中国 | 荷斯坦牛 | 72 | 3 | 混合物精油 | CS | WM+CS | NA | 28 | ①②③④⑤⑥ |
| 14 | 柏妍等[ | 2019 | 中国 | 荷斯坦牛 | 40 | 3 | 牛至精油 | CS | WM+CS | 42 | 70 | ①②③④⑤⑥ |
| 15 | 杨云燕[ | 2019 | 中国 | 荷斯坦牛 | 24 | 15 | 肉桂醛 | CS | AM4)+CS | 42 | 78 | ①②⑧⑨⑩ |
| 16 | 郭竟升[ | 2018 | 中国 | 荷斯坦牛 | 40 | 3 | 牛至精油 | CS | WM+CS | 42 | 70 | ①⑧⑨⑩ |
| 17 | 陈昊等[ | 2017 | 中国 | 荷斯坦牛 | 40 | 3 | 牛至精油 | CS | WM+CS | 42 | 70 | ①⑧⑨⑩ |

图 2
纳入文献的偏倚风险概览(A)和总结(B) 随机序列生成(选择偏倚):Random sequence generation (selection bias); 基线特征(选择偏倚):Baseline characteristics (selection bias); 分配隐藏(选择偏倚):Allocation concealment (selection bias); 动物随机安置(执行偏倚):Random housing (performance bias); 所有研究参与者和人员采用盲法(执行偏倚):Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias); 随机结果评估(检测偏倚):Random outcome assessment (detection bias); 结果评估的盲法(检测偏倚):Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias); 不完整的结果数据(失访偏倚):Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias); 选择性报告(报告偏倚):Selective reporting (reporting bias); 其他偏倚:Other bias“+”. 低偏倚风险;“?”. 偏倚风险不明;“-”. 高偏倚风险“+”. Low risk of bias; “?”. Unclear risk of bias; “-”. High risk of bias"

表 3
饲粮中添加植物精油对犊牛血清免疫指标影响的Meta分析"
| 异质性分析 Heterogeneity analysis | 项目 Item | 数量(n) Number | 随机效应模型REM | 异质性Heterogeneity | |||||
| 标准化均数差 SMD | 95%置信区间 95% CI | P值 P-value | 卡方(Q) Chi-squared | P值 P-value | I2/% | ||||
| Q检验Cochran′s Q test | IgA1) | 58 | 0.66 | 0.23, 1.08 | 0.002 | 3.71 | 0.29 | 19 | |
| 亚组分析-饲喂时长 Subgroup analysis-Feeding duration | ≤56 d | 58 | 0.70 | 0.29, 1.10 | <0.001 | 1.89 | 0.60 | 0 | |
| >56 d | 58 | 0.66 | 0.23, 1.08 | 0.002 | 3.71 | 0.29 | 19 | ||
| Q检验Cochran′s Q test | IgG2) | 98 | 0.70 | 0.37, 1.02 | <0.001 | 1.81 | 0.77 | 0 | |
| 亚组分析-饲喂时长 Subgroup analysis-Feeding duration | ≤56 d | 86 | 0.78 | 0.43, 1.14 | <0.001 | 1.01 | 0.80 | 0 | |
| >56 d | 52 | 0.58 | 0.19, 0.98 | 0.004 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加方式 Subgroup analysis-Method of types | LF3) | 46 | 0.94 | 0.36, 1.51 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.89 | 0 | |
| SF4) | 52 | 0.70 | 0.19, 0.98 | 0.004 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0 | ||
| Q检验Cochran′s Q test | IgM5) | 68 | 0.49 | 0.03, 0.96 | 0.04 | 4.91 | 0.18 | 39 | |
| 亚组分析-饲喂时长 Subgroup analysis-Feeding duration | ≤56 d | 68 | 0.37 | -0.16, 0.90 | 0.17 | 6.34 | 0.10 | 53 | |
| >56 d | 52 | 0.62 | 0.10, 1.13 | 0.02 | 3.28 | 0.19 | 39 | ||
表 4
饲粮中添加植物精油对犊牛血清生化指标影响的Meta分析"
| 异质性分析 Heterogeneity analysis | 项目 Item | 数量 N | 随机效应模型REM | 异质性Heterogeneity | |||||
| 标准化均数差SMD | 95%置信区间95% CI | P值P-value | 卡方(Q) Chi-squared | P值P-value | I2/% | ||||
| Q检验Cochran′s Q test | TP1) | 357 | 0.45 | 0.03, 0.87 | 0.04 | 58.84 | <0.001 | 80 | |
| 亚组分析-饲喂时长 Subgroup analysis-Feeding duration | ≤56 d | 289 | 0.44 | -0.02, 0.89 | 0.06 | 48.57 | <0.001 | 79 | |
| >56 d | 126 | 0.86 | 0.20, 1.52 | 0.01 | 23.07 | <0.001 | 78 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加方式 Subgroup analysis-Method of types | LF | 217 | 0.19 | -0.47, 0.84 | 0.58 | 35.03 | <0.001 | 83 | |
| SF | 140 | 0.73 | 0.18, 1.28 | 0.009 | 21.10 | <0.001 | 76 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加种类 Subgroup analysis-Method of addition | SEOs2) | 158 | 0.36 | -0.25, 0.97 | 0.25 | 38.11 | <0.001 | 82 | |
| BEOs3) | 199 | 0.50 | -0.03, 1.03 | 0.06 | 20.54 | 0.001 | 76 | ||
| Q检验Cochran′s Q test | ALB4) | 192 | -0.22 | -0.46, 0.22 | 0.07 | 2.11 | 0.95 | 0 | |
| 亚组分析-饲喂时长 Subgroup analysis-Feeding duration | ≤56 d | 118 | -0.17 | -0.47, 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.80 | 0.94 | 0 | |
| >56 d | 86 | -0.24 | -0.24, 0.13 | 0.21 | 1.60 | 0.66 | 0 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加方式 Subgroup analysis-Method of types | LF | 92 | -0.30 | -0.70, 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.99 | 0.80 | 0 | |
| SF | 100 | -0.18 | -0.48, 0.13 | 0.26 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加种类 Subgroup analysis-Method of addition | SEOs | 88 | -0.30 | -0.73, 0.12 | 0.16 | 6.37 | 0.17 | 37 | |
| BEOs | 104 | -0.25 | -0.58, 0.07 | 0.13 | 1.58 | 0.66 | 0 | ||
| Q检验Cochran′s Q test | BUN5) | 221 | -0.15 | -0.58, 0.28 | 0.49 | 25.22 | 0.001 | 68 | |
| 亚组分析-饲喂时长 Subgroup analysis-Feeding duration | ≤56 d | 111 | -0.18 | -0.63, 0.28 | 0.44 | 7.68 | 0.10 | 48 | |
| >56 d | 121 | 0.03 | -0.75, 0.81 | 0.94 | 21.41 | <0.001 | 81 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加方式 Subgroup analysis-Method of types | LF | 142 | -0.26 | -0.83, 0.31 | 0.37 | 15.91 | 0.007 | 69 | |
| SF | 79 | 0.05 | -0.75, 0.86 | 0.90 | 9.13 | 0.01 | 78 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加种类 Subgroup analysis-Method of addition | SEOs | 100 | -0.19 | -1.03, 0.64 | 0.65 | 32.82 | <0.001 | 85 | |
| BEOs | 121 | 0.02 | -0.55, 0.39 | 0.95 | 16.80 | 0.005 | 70 | ||
| Q检验Cochran′s Q test | GLU6) | 330 | 0.14 | -0.26, 0.53 | 0.49 | 43.84 | <0.001 | 75 | |
| 亚组分析-饲喂时长 Subgroup analysis-Feeding duration | ≤56 d | 256 | 0.28 | -0.12, 0.68 | 0.17 | 25.88 | 0.001 | 69 | |
| >56 d | 85 | -0.08 | -1.03, 0.87 | 0.87 | 17.38 | <0.001 | 83 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加方式 Subgroup analysis-Method of types | LF | 231 | 0.31 | -0.21, 0.82 | 0.25 | 29.45 | <0.001 | 76 | |
| SF | 99 | -0.16 | -0.67, 0.36 | 0.56 | 7.78 | 0.05 | 61 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加种类 Subgroup analysis-Method of addition | SEOs | 106 | 0.53 | -0.28, 1.33 | 0.20 | 21.94 | <0.001 | 82 | |
| BEOs | 224 | 0.10 | -0.41, 0.62 | 0.70 | 33.55 | <0.001 | 79 | ||
| Q检验Cochran′s Q test | TG7) | 240 | 0.51 | 0.10, 0.92 | 0.01 | 20.25 | 0.005 | 65 | |
| 亚组分析-饲喂时长 Subgroup analysis-Feeding duration | ≤56 d | 136 | 0.57 | 0.27, 0.87 | <0.001 | 3.12 | 0.54 | 0 | |
| >56 d | 104 | 0.41 | -0.69, 1.52 | 0.46 | 16.78 | <0.001 | 88 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加方式 Subgroup analysis-Method of types | LF | 152 | 0.47 | -0.25, 1.19 | 0.20 | 18.48 | 0.001 | 78 | |
| SF | 88 | 0.57 | 023, 0.90 | <0.001 | 1.60 | 0.45 | 0 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加种类 Subgroup analysis-Method of addition | SEOs | 130 | 0.30 | -0.36, 0.96 | 0.37 | 30.00 | <0.001 | 80 | |
| BEOs | 110 | 0.24 | -0.38, 0.86 | 0.45 | 10.56 | 0.01 | 72 | ||
| Q检验Cochran′s Q test | TC8) | 246 | -0.59 | -1.07, -0.11 | 0.02 | 31.68 | <0.001 | 75 | |
| 亚组分析-饲喂时长 Subgroup analysis-Feeding duration | ≤56 d | 142 | 0.02 | -0.58, 0.63 | 0.94 | 19.12 | 0.002 | 74 | |
| >56 d | 110 | -1.13 | -1.75, -0.51 | <0.001 | 7.42 | 0.06 | 60 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加方式 Subgroup analysis-Method of types | LF | 158 | -0.56 | -1.21, 0.08 | 0.09 | 18.93 | 0.002 | 74 | |
| SF | 88 | -0.65 | -1.53, 0.24 | 0.15 | 12.67 | 0.002 | 84 | ||
| 亚组分析-添加种类 Subgroup analysis-Method of addition | SEOs | 130 | -1.04 | -1.60, -0.48 | <0.001 | 19.40 | 0.004 | 69 | |
| BEOs | 116 | -0.52 | -1.09, 0.05 | 0.07 | 11.79 | 0.02 | 66 | ||
| Q检验Cochran′s Q test | BHBA9) | 99 | 0.47 | -0.12, 1.06 | 0.12 | 11.24 | 0.02 | 64 | |
| 亚组分析-饲喂时长 Subgroup analysis-Feeding duration | ≤56 d | 99 | 0.30 | -0.20, 0.80 | 0.24 | 8.32 | 0.08 | 52 | |
| >56 d | 11 | 0.43 | -0.06, 0.92 | 0.01 | NA | NA | NA | ||
| 亚组分析-添加方式 Subgroup analysis-Method of types | LF | 88 | 0.31 | -0.32, 0.94 | 0.33 | 8.30 | 0.04 | 64 | |
| SF | 11 | 1.17 | 0.25, 2.09 | 0.01 | NA | NA | NA | ||
| 亚组分析-添加种类 Subgroup analysis-Method of addition | SEOs | 38 | 0.65 | -0.64, 1.95 | 0.32 | 4.30 | 0.04 | 77 | |
| BEOs | 61 | 0.33 | -0.35, 1.01 | 0.34 | 5.10 | 0.08 | 61 | ||
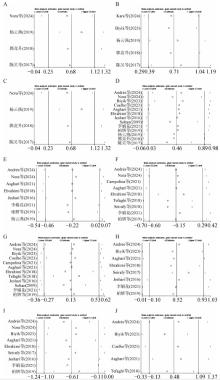
图 3
EOs对哺乳期犊牛血清免疫及生化指标影响的敏感性分析图 A. EOs对IgA浓度影响的敏感性分析;B. EOs对IgG浓度影响的敏感性分析;C. EOs对IgM浓度影响的敏感性分析;D. EOs对TP浓度影响的敏感性分析;E. EOs对ALB浓度影响的敏感性分析;F. EOs对BUN浓度影响的敏感性分析;G. EOs对GLU浓度影响的敏感性分析;H. EOs对TG浓度影响的敏感性分析;I. EOs对TC浓度影响的敏感性分析;J. EOs对BHBA浓度影响的敏感性分析;Lower CI Limit. 置信区间下限;Estimate. 估计值;Upper CI Limit. 置信区间上限"
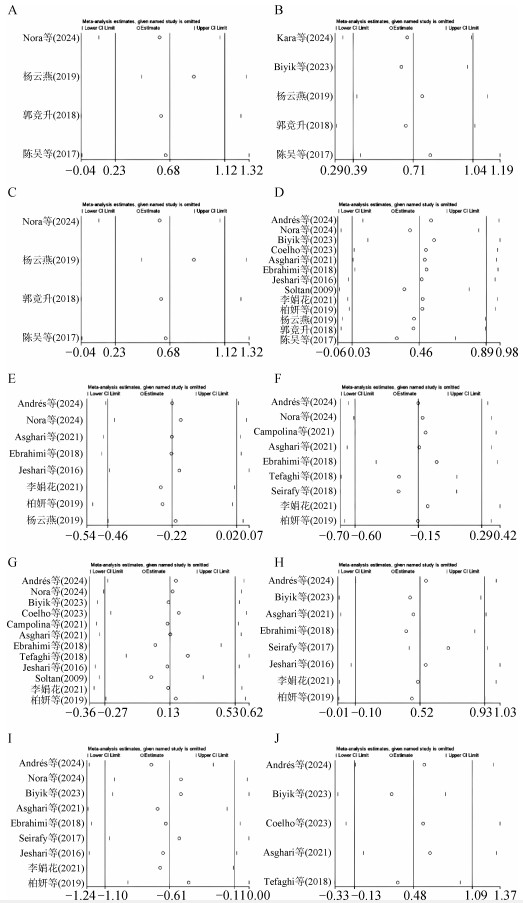
表 5
Meta分析Egger法检验结果"
| 结局指标 Outcome indexes | 偏倚检验(截距) Bias test (intercept) | |||
| 回归系数Coefficient | 标准误Std.err. | t值t-value | P值P-value | |
| 免疫球蛋白A浓度IgA concentration | 0.564 | 3.31 | 0.17 | 0.880 |
| 免疫球蛋白G浓度IgG concentration | 1.433 | 2.59 | 0.55 | 0.619 |
| 免疫球蛋白M浓度IgM concentration | -9.341 | 1.36 | -6.87 | 0.021 |
| 总蛋白浓度Total protein concentration | -0.253 | 2.90 | -0.09 | 0.932 |
| 白蛋白浓度Albumin concentration | -1.650 | 0.66 | -2.50 | 0.046 |
| 血清尿素氮浓度BUN concentration | 2.271 | 2.80 | 0.81 | 0.444 |
| 葡萄糖浓度Glucose concentration | -4.707 | 2.32 | -2.03 | 0.070 |
| 甘油三酯浓度Triglycerides concentration | -0.488 | 3.81 | -0.13 | 0.902 |
| 总胆固醇浓度Total cholesterol concentration | -1.985 | 2.99 | -0.66 | 0.528 |
| β-羟基丁酸浓度BHBA concentration | 3.016 | 5.15 | 0.59 | 0.599 |
| 1 |
BOLOURI P , SALAMI R , KOUHI S , et al. Applications of essential oils and plant extracts in different industries[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27 (24): 8999.
doi: 10.3390/molecules27248999 |
| 2 |
JI J , SHANKAR S , ROYON F , et al. Essential oils as natural antimicrobials applied in meat and meat products-a review[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2023, 63 (8): 993- 1009.
doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1957766 |
| 3 |
MATTÉ E H C , LUCIANO F B , EVANGELISTA A G . Essential oils and essential oil compounds in animal production as antimicrobials and anthelmintics: an updated review[J]. Anim Health Res Rev, 2023, 24 (1): 1- 11.
doi: 10.1017/S1466252322000093 |
| 4 | MEENU M , PADHAN B , PATEL M , et al. Antibacterial activity of essential oils from different parts of plants against Salmonella and Listeria spp[J]. Food chem, 2023, 404 (Pt B): 134723. |
| 5 |
CANESCHI A , BARDHI A , BARBAROSSA A , et al. Plant essential oils as a Tool in the control of bovine mastitis: An update[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28 (8): 3425.
doi: 10.3390/molecules28083425 |
| 6 |
ZHAO Q , ZHU L , WANG S , et al. Molecular mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effects of plant essential oils: A systematic review[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 301, 115829.
doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115829 |
| 7 |
BUNGAU S G , VESA C M , BUSTEA C , et al. Antioxidant and hypoglycemic potential of essential oils in diabetes mellitus and its complications[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (22): 16501.
doi: 10.3390/ijms242216501 |
| 8 |
AMAT S , MAGOSSI G , RAKIBUZZAMAN A , et al. Screening and selection of essential oils for an intranasal spray against bovine respiratory pathogens based on antimicrobial, antiviral, immunomodulatory, and antibiofilm activities[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2024, 11, 1360398.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1360398 |
| 9 |
TULLIO V , ROANA J , CAVALLO L , et al. Immune defences: a view from the side of the essential oils[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28 (1): 435.
doi: 10.3390/molecules28010435 |
| 10 |
MATERA R , LUCCHI E , VALGIMIGLI L . Plant essential oils as healthy functional ingredients of nutraceuticals and diet supplements: A review[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28 (2): 901.
doi: 10.3390/molecules28020901 |
| 11 |
ELBAZ A M , ASHMAWY E S , ALI S A M , et al. Effectiveness of probiotics and clove essential oils in improving growth performance, immuno-antioxidant status, ileum morphometric, and microbial community structure for heat-stressed broilers[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13 (1): 18846.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45868-9 |
| 12 |
GRAZUL M , KWIATKOWSKI P , HARTMAN K , et al. How to naturally support the immune system in inflammation-essential oils as immune boosters[J]. Biomedicines, 2023, 11 (9): 2381.
doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092381 |
| 13 | ALMUAYLI O , MARZOK M , HAMAD Y , et al. Supplementation with a combination of vitamin A, E, C and essential volatile oils improves growth performance and ameliorates antioxidant status in Holstein calves[J]. J Adv Vet Res, 2023, 13 (2): 288- 291. |
| 14 |
MARTÍN A , ANDRÉS S , ARTECHE-VILLASOL N , et al. Dietary administration of oregano essential oil to newborn dairy calves promotes long term effects on immunity parameters during the replacement phase[J]. Anim Sci Proc, 2022, 13 (3): 402.
doi: 10.1016/j.anscip.2022.07.139 |
| 15 |
LAKHANI N , KAMRA D N , LAKHANI P , et al. Immune status and haemato-biochemical profile of buffalo calves supplemented with phytogenic feed additives rich in tannins, saponins and essential oils[J]. Trop Anim Health Prod, 2019, 51 (3): 565- 573.
doi: 10.1007/s11250-018-1727-z |
| 16 | GADING B M W T , AGUS A , IRAWAN A , et al. Growth performance, hematological and mineral profile of post-weaning calves as influenced by inclusion of pelleted-concentrate supplement containing essential oils and probiotics[J]. Iran J Appl Anim Sci, 2020, 10 (3): 461- 468. |
| 17 |
DE SOUZA K A , COOKE R F , SCHUBACH K M , et al. Performance, health and physiological responses of newly weaned feedlot cattle supplemented with feed-grade antibiotics or alternative feed ingredientss[J]. Animal, 2018, 12 (12): 2521- 2528.
doi: 10.1017/S1751731118000551 |
| 18 |
OZKAYA S , ERBAS S , OZKAN O , et al. Effect of supplementing milk replacer with aromatic oregano (Oreganum onites L.) water on performance, immunity and general health profiles of Holstein calves[J]. Anim Prod Sci, 2018, 58 (10): 1892- 1900.
doi: 10.1071/AN16574 |
| 19 | PAPAKOSTIDIS C , GIANNOUDIS P V . Meta-analysis. What have we learned?[J]. Injury, 2023, 54 (Suppl 3): S30- S34. |
| 20 | SAUVANT D , LETOURNEAU-MONTMINY M P , SCHMIDELY P , et al. Review: Use and misuse of meta-analysis in Animal Science[J]. Animal, 2020, 14 (S2): s207- s222. |
| 21 |
PATRA A K . Meta-analyses of effects of phytochemicals on digestibility and rumen fermentation characteristics associated with methanogenesis[J]. J Sci Food Agric, 2010, 90 (15): 2700- 2708.
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4143 |
| 22 | 张冰, 康洁, 陈晓明. Meta分析多亚组标准差合并方法探讨[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2016, 16 (7): 851- 854. |
| ZHANG B , KANG J , CHEN X M . Methods to combine standard deviations of different subgroups in Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine, 2016, 16 (7): 851- 854. | |
| 23 | 许杨鹏, 喻亚宇, 付文杰, 等. Meta分析中缺失标准差换算与标准化均数差估计方法简介[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2016, 8 (12): 1412- 1415. |
| XU Y P , YU Y Y , FU W J , et al. Introduction of methods for estimating standardized mean different when missing standard deviation conversion in Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Cardiovascular Medicine, 2016, 8 (12): 1412- 1415. | |
| 24 | 陈匡阳, 马彬, 王亚楠, 等. SYRCLE动物实验偏倚风险评估工具简介[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2014, 14 (10): 1281- 1285. |
| CHEN K Y , MA B , WANG Y N , et al. SYRCLE's risk of bias tool for animal studies[J]. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine, 2014, 14 (10): 1281- 1285. | |
| 25 |
TUFANARU C , MUNN Z , STEPHENSON M , et al. Fixed or random effects meta-analysis? Common methodological issues in systematic reviews of effectiveness[J]. Int J Evid Based Healthc, 2015, 13 (3): 196- 207.
doi: 10.1097/XEB.0000000000000065 |
| 26 | 李秀鹏, 苏玉莹, 王悦同, 等. 低容量高强度间歇训练对肥胖或超重人群心血管疾病风险因子影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29 (12): 2590- 2604. |
| LI X P , SU Y Y , WANG Y T , et al. Effect of low-volume high-intensity interval training on cardiovascular risk factor in obese oroverweight populations: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29 (12): 2590- 2604. | |
| 27 | 周文杰, 林伟杰, 魏志鹏, 等. 循证视角下的偏倚识别: 基于Egger拓展模型的大数据元分析[J]. 情报学报, 2024, 43 (4): 491- 502. |
| ZHOU W J , LIN W J , WEI Z P , et al. Bias identification from an evidence-based perspective: a big data meta-analysis procedure based on Egger's extension model[J]. Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information, 2024, 43 (4): 491- 502. | |
| 28 |
ANDRÉS S , GINI C , CECILIANI F , et al. Essential oil supplementation in milk replacers: short- and long-term impacts on feed efficiency, the faecal microbiota and the plasma metabolome in dairy calves[J]. J Dev Orig Health Dis, 2024, 15, e5.
doi: 10.1017/S2040174424000084 |
| 29 | KARA K , PIRCI G . Immunity, rumen metagenomics, ruminal variables, and growth performance of calves fed milk with sage (Salvia officinalis) essential oil[J]. Trop Anim Health Prod, 2023, 56 (1): 27. |
| 30 |
NORA L , GIACOMELLI C M , DEOLINDO G L , et al. Inclusion of essential oils in a calf milk replacer and their effects on growth performance and the immune and oxidative systems[J]. Comp Clin Pathol, 2024, 33, 327- 335.
doi: 10.1007/s00580-024-03554-w |
| 31 |
BIYIK F , BIRICIK H , VRKMEZ E , et al. Effects of rosemary essential oil as a feed additive on performance, rumen fermentation, and blood parameters in preweaning Holstein calves[J]. Journal of the Hellenic Veterinary Medical Society, 2023, 74 (3): 6191- 6199.
doi: 10.12681/jhvms.31076 |
| 32 |
COELHO M G , DA SILVA A P , DE TOLEDO A F , et al. Essential oil blend supplementation in the milk replacer of dairy calves: Performance and health[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18 (10): e0291038.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291038 |
| 33 |
PALHARES CAMPOLINA J , GESTEIRA COELHO S , BELLI A L , et al. Effects of a blend of essential oils in milk replacer on performance, rumen fermentation, blood parameters, and health scores of dairy heifers[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16 (3): e0231068.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231068 |
| 34 |
ASGHARI M , ABDI-BENEMAR H , MAHERI-SIS N , et al. Effects of emulsified essential oils blend on performance, blood metabolites, oxidative status and intestinal microflora of suckling calves[J]. Anim Feed Sci Technol, 2021, 277, 114954.
doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2021.114954 |
| 35 | EBRAHIMI M A , SOBHANIRAD S , BAYAT A R . Effects of ajwain (Trachyspermum ammi) and thyme (Thymus vulgaris) oils on nutrients digestibility, blood parameters and growth performance of brown swiss neonatal calves[J]. Iran J Appl Anim Sci, 2018, 8 (3): 387- 395. |
| 36 |
AKBARIAN-TEFAGHI M , GHASEMI E , KHORVASH M . Performance, rumen fermentation and blood metabolites of dairy calves fed starter mixtures supplemented with herbal plants, essential oils or monensin[J]. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr(Berl), 2018, 102 (3): 630- 638.
doi: 10.1111/jpn.12842 |
| 37 | SEIRAFY H , SOBHANIRAD S . Effects of oregano (Origanum vulgare) and thyme (Thymus vulgaris) oils on growth performance and blood parameters in Holstein suckling calves[J]. Iran J Appl Anim Sci, 2017, 7 (4): 585- 593. |
| 38 |
JESHARI M , RIASI A , MAHDAVI A H , et al. Effect of essential oils and distillation residues blends on growth performance and blood metabolites of Holstein calves weaned gradually or abruptly[J]. Livest Sci, 2016, 185, 117- 122.
doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2015.12.011 |
| 39 |
SOLTAN M A . Effect of essential oils supplementation on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, health condition of Holstein male calves during pre- and post-weaning periods[J]. Pak J Nutr, 2009, 8 (5): 642- 652.
doi: 10.3923/pjn.2009.642.652 |
| 40 | 李娟花. 乳化处理精油对犊牛生长性能、血液代谢物及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2021 (20): 37- 40. |
| LI J H . Effects of emulsified essential oil on growth performance, blood metabolites and intestinal microflora of calves[J]. China Feed, 2021 (20): 37- 40. | |
| 41 | 柏妍, 郎侠, 王彩莲, 等. 饲粮中添加牛至精油和莫能菌素对荷斯坦犊牛血清生化指标、消化酶活性及瘤胃微生物区系的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2019, 50 (12): 2458- 2469. |
| BAI Y , LANG X , WANG C L , et al. Effects of oregano essential oil and monensin in diet on serum biochemical parameters, digestive enzyme activities and ruminal microflora of Holstein calves[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2019, 50 (12): 2458- 2469. | |
| 42 | 杨云燕. 肉桂醛对犊牛生长性能、健康及瘤胃发酵相关指标的影响[D]. 西宁: 广西大学, 2019. |
| YANG Y Y. Effects of addition of cinnamaldehyde on growth performance, healthy and rumen fermentation relaed parameter of calves[D]. Xining: Guangxi University, 2019. (in Chinese) | |
| 43 | 郭竟升. 牛至精油对荷斯坦犊牛生长性能的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2018. |
| GUO J S. The effects of oregano essential oil on the growth performance of Holstein calf[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese) | |
| 44 | 陈昊, 刘婷, 吴建平, 等. 牛至精油对新生犊牛生长发育和血液免疫的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2017, 34 (10): 2141- 2148. |
| CHEN H , LIU T , WU J P , et al. Effects of oregano essential oil on growth and hematogenic immunity ofnewborn calves[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34 (10): 2141- 2148. | |
| 45 | 那立冬, 张世栋, 董书伟, 等. 产后患子宫内膜炎对奶牛血清和子宫黏液中免疫球蛋白质量浓度的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2017, 26 (4): 503- 508. |
| NA L D , ZHANG S D , DONG S W , et al. Effects of dairy cows with endometritis on immunoglobulin mass concentration in serum and uterus mucus of postpartum[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2017, 26 (4): 503- 508. | |
| 46 |
LIN S , KE C , LIU L , et al. Genome-wide association studies for immunoglobulin concentrations in colostrum and serum in Chinese Holstein[J]. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23 (1): 41.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08250-5 |
| 47 |
HOU K , TONG J , ZHANG H , et al. Microbiome and metabolic changes in milk in response to artemisinin supplementation in dairy cows[J]. AMB Express, 2020, 10 (1): 154.
doi: 10.1186/s13568-020-01080-w |
| 48 |
BRENES A , ROURA E . Essential oils in poultry nutrition: Main effects and modes of action[J]. Anim Feed Sci Technol, 2010, 158 (1-2): 1- 14.
doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2010.03.007 |
| 49 |
DE LAVOR É M , FERNANDES A W C , DE ANDRADE TELES R B , et al. Essential oils and their major compounds in the treatment of chronic inflammation: A review of antioxidant potential in preclinical studies and molecular mechanisms[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018, 2018, 6468593.
doi: 10.1155/2018/6468593 |
| 50 | 周洋, 彭艳, 周小秋. 植物精油对动物生长和免疫力的影响及其作用机制[J]. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30 (1): 37- 43. |
| ZHOU Y , PENG Y , ZHOU X Q . Effects of essential oil on animal's growth and immunity and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2018, 30 (1): 37- 43. | |
| 51 | 宋淑珍, 宫旭胤, 吴建平. 牛至精油对蒙古羊生长性能、血清免疫指标和粪便寄生虫的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34 (11): 7210- 7219. |
| SONG S Z , GONG X Y , WU J P . Effects of oregano essential oil on growth performance, serum immune indices and fecal parasites of mongolian sheep[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34 (11): 7210- 7219. | |
| 52 | 张瑞, 周维强, 马越, 等. 牛至精油和初乳复合物对机会猪生长性能、血清抗氧化和免疫指标的影响[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2022, 49 (4): 1314- 1321. |
| ZHANG R , ZHOU W Q , MA Y , et al. Effects of oregano essential oil and colostrum complex on growth performance, serum indicators related antioxidant and immune in opportunity piglets[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 49 (4): 1314- 1321. | |
| 53 |
LIU T , CHEN H , BAI Y , et al. Calf starter containing a blend of essential oils and prebiotics affects the growth performance of Holstein calves[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2020, 103 (3): 2315- 2323.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-16647 |
| 54 |
NKRUMAH J D , SHERMAN E L , LI C , et al. Primary genome scan to identify putative quantitative trait loci for feedlot growth rate, feed intake, and feed efficiency of beef cattle[J]. J Anim Sci, 2007, 85 (12): 3170- 3181.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0234 |
| 55 | 贾泽统. 苜蓿与燕麦干草不同配比对奶牛生产性能的影响[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2018. |
| JIA Z T. Effects of different proportion of alfalfaand oat hayon production performance of dairy cows[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese) | |
| 56 | 朱晓艳, 赵诚, 史莹华, 等. 苜蓿青贮料替代苜蓿青干草对奶牛生产性能及乳品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25 (5): 156- 164. |
| ZHU X Y , ZHAO C , SHI Y H , et al. Effect of replacing alfalfa hay with alfalfa silage on production performance and milk quality in dairy cows[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25 (5): 156- 164. | |
| 57 | 张巧娥, 曹守勤, 周玉香, 等. 甘草提取物对宁夏滩羊血液生化指标的影响[J]. 饲料研究, 2009 (10): 51- 52. |
| ZHANG Q E , CAO S Q , ZHOU Y X , et al. Effects of licorice extract on blood biochemical parameters of Ningxia Tan sheep[J]. Feed Research, 2009 (10): 51- 52. | |
| 58 |
TYLER J W , PARISH S M , BESSER T E , et al. Detection of low serum immunoglobulin concentrations in clinically ill calves[J]. J Vet Intern Med, 1999, 13 (1): 40- 43.
doi: 10.1111/j.1939-1676.1999.tb02163.x |
| 59 |
DONOVAN G A , DOHOO I R , MONTGOMERY D M , et al. Associations between passive immunity and morbidity and mortality in dairy heifers in Florida, USA[J]. Prev Vet Med, 1998, 34 (1): 31- 46.
doi: 10.1016/S0167-5877(97)00060-3 |
| 60 |
WHITAKER D A , EAYRES H F , AITCHISON K , et al. No effect of a dietary zinc proteinate on clinical mastitis, infection rate, recovery rate and somatic cell count in dairy cows[J]. Vet J, 1997, 153 (2): 197- 203.
doi: 10.1016/S1090-0233(97)80040-8 |
| 61 |
STANLEY C C , WILLIAMS C C , JENNY B F , et al. Effects of feeding milk replacer once versus twice daily on glucose metabolism in Holstein and Jersey calves[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2002, 85 (9): 2335- 2343.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(02)74313-0 |
| 62 | GVMVS R , EROL HS , IMIK H , et al. The effects of the supplementation of lamb rations with oregano essential oil on the performance, some blood parameters and antioxidant metabolism in meat and liver tissues[J]. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg, 2017, 23 (3): 395- 401. |
| 63 |
BLOME R M , DRACKLEY J K , MCKEITH F K , et al. Growth, nutrient utilization, and body composition of dairy calves fed milk replacers containing different amounts of protein[J]. J Anim Sci, 2003, 81 (6): 1641- 1655.
doi: 10.2527/2003.8161641x |
| 64 |
ÜNAL A , KOCABAČLI N . Effect of different dosages of oregano oil on performance and some blood parameters in lambs[J]. Ankara Vniv Vet Fak Derg, 2014, 61, 199- 204.
doi: 10.1501/Vetfak_0000002629 |
| 65 |
TASSOUL M D , SHAVER R D . Effect of a mixture of supplemental dietary plant essential oils on performance of periparturient and early lactation dairy cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2009, 92 (4): 1734- 1740.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2008-1760 |
| 66 | 计徐, 朱洪龙, 夏伦志, 等. 复合植物精油对断奶仔猪生长性能、器官指数、养分表观消化率、血清生化和抗氧化指标及肠道形态结构的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35 (7): 4266- 4275. |
| JI X , ZHU H L , XIA L Z , et al. Effects of plant essential oil compounds on growth performance, organ indexes, nutrient apparent digestibility, serum biochemical and antioxidant indexes and intestinal morphology of weaned piglets[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35 (7): 4266- 4275. | |
| 67 |
HU X , WANG Y , SHEIKHAHMADI A , et al. Effects of dietary energy level on appetite and central adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in broilers[J]. J Anim Sci, 2019, 97 (11): 4488- 4495.
doi: 10.1093/jas/skz312 |
| 68 |
CHAVES A V , STANFORD K , DUGAN M E R , et al. Effects of cinnamaldehyde, garlic and juniper berry essential oils on rumen fermentation, blood metabolites, growth performance, and carcass characteristics of growing lambs[J]. Livest Sci, 2008, 117 (2-3): 215- 224.
doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2007.12.013 |
| 69 | 柏妍. 牛至精油替代莫能菌素对荷斯坦奶公牛瘤胃功能和生长性能的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2020. |
| BAI Y. Effects of oregano essential oil as potential alternative for monensin on ruminal function and growth performance of young Holstein dairy bulls[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 70 |
OH J , WALL E H , BRAVO D M , et al. Host-mediated effects of phytonutrients in ruminants: A review[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2017, 100 (7): 5974- 5983.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-12341 |
| 71 | 刘立山, 周瑞, 吴建平, 等. 日粮中添加牛至精油对牛肉脂肪酸以及血液生化指标的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2019 (13): 47- 51. |
| LIU L S , ZHOU R , WU J P , et al. Effects of fatty acids in beef and blood biochemical index by adding oregano oil into ration[J]. China Feed, 2019 (13): 47- 51. | |
| 72 |
SILVA A S , CORTINHAS C S , ACEDO T S , et al. Effects of essential oils supplementation, associated or not with amylase, on dry matter intake, productive performance, and nitrogen metabolism of dairy cows[J]. Anim Feed Sci Technol, 2023, 297, 115575.
doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2023.115575 |
| 73 |
HONG J , STEINER T , AUFY A , et al. Effects of supplemental essential oil on growth performance, lipid metabolites and immunity, intestinal characteristics, microbiota and carcass traits in broilers[J]. Livest Sci, 2012, 144 (3): 253- 262.
doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2011.12.008 |
| 74 |
SU G , ZHOU X , WANG Y , et al. Dietary supplementation of plant essential oil improves growth performance, intestinal morphology and health in weaned pigs[J]. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr(Berl), 2020, 104 (2): 579- 589.
doi: 10.1111/jpn.13271 |
| 75 |
OETZEL G R . Monitoring and testing dairy herds for metabolic disease[J]. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract, 2004, 20 (3): 651- 674.
doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2004.06.006 |
| 76 | 郑全芳, 陈培荣. 混合植物精油对绵羊生长性能、养分消化、瘤胃发酵及血液指标的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2021 (14): 53- 56. |
| ZHENG Q F , CHEN P R . Effects of mixed plant essential oils on growth performance, nutrient digestion, rumen fermentation and blood indices of sheep[J]. China Feed, 2021 (14): 53- 56. | |
| 77 | HILDEBRAND C , HOLLENBACH J , SEEGER B , et al. β-hydroxybutyrate effects on bovine caruncular epithelial cells: A model for investigating the peri-implantation period disruption in Ketotic dairy cows[J]. Animals(Basel), 2023, 13 (18): 2950. |
| 78 |
YOUSSEF M , EL-ASHKER M . Significance of insulin resistance and oxidative stress in dairy cattle with subclinical ketosis during the transition period[J]. Trop Anim Health Prod, 2017, 49 (2): 239- 244.
doi: 10.1007/s11250-016-1211-6 |
| 79 | 刁其玉. 营养调控技术在犊牛培育中的应用[J]. 饲料工业, 2020, 41 (7): 1- 7. |
| DIAO Q Y . The application of nutrition regulation technology in calf rearing[J]. Feed Industry, 2020, 41 (7): 1- 7. | |
| 80 | 屠焰. 代乳品酸度及调控对哺乳期犊牛生长性能、血气指标和胃肠道发育的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2011. |
| TU Y. Effect of milk replacer acidity and acidity adjusting on growth performance, blood gas parameters and gastrointestinal tract development in pre-ruminant calves[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2011. (in Chinese) | |
| 81 |
WU J , GUO J , LIU T , et al. Feeding a calf starter containing monensin alone or in combination with an oregano, and cobalt blend to Holstein calves[J]. J Anim Sci, 2020, 98 (7): skaa214.
doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa214 |
| 82 |
CALSAMIGLIA S , BUSQUET M , CARDOZO P W , et al. Invited review: Essential oils as modifiers of rumen microbial fermentation[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2007, 90 (6): 2580- 2595.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2006-644 |
| 83 |
VAN DEN BOSSCHE T , GOOSSENS K , AMPE B , et al. Effect of supplementing an α-amylase enzyme or a blend of essential oil components on the performance, nutrient digestibility, and nitrogen balance of dairy cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2024, 107 (7): 4509- 4523.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2023-24073 |
| 84 |
VAN GASTELEN S , YÁÑEZ-RUIZ D , KHELIL-ARFA H , et al. Effect of a blend of cinnamaldehyde, eugenol, and Capsicum oleoresin on methane emission and lactation performance of Holstein-Friesian dairy cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2024, 107 (2): 857- 869.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2023-23406 |
| 85 |
VITTORAZZI P C Jr , TAKIYA C S , NUNES A T , et al. Feeding encapsulated pepper to dairy cows during the hot season improves performance without affecting core and skin temperature[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2022, 105 (12): 9542- 9551.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2022-22078 |
| 86 |
NUSSBAUMER-STREIT B , KLERINGS I , DOBRESCU A I , et al. Excluding non-English publications from evidence-syntheses did not change conclusions: a meta-epidemiological study[J]. J Clin Epidemiol, 2020, 118, 42- 54.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.10.011 |
| [1] | 包小平, 崔俊伟, 赵玉龙, 郭成, 陈明, 毕研亮. 产后不同挤奶时间对初乳品质及不同品质初乳对新生犊牛被动免疫转移的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(8): 3861-3871. |
| [2] | 熊平文, 徐川辉, 艾高祥, 季华员, 胡艳, 陈将, 宋琼莉, 宋文静, 韦启鹏, 陈小连, 邹志恒, 陈和洪. 金荞麦茎叶粉对赣南藏香母猪养分表观消化率、血清生化指标及粪微生物区系的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(7): 3290-3304. |
| [3] | 孔祥鹤, 苏欣雨, 钟一铭, 卢赵梓暄, 廖献茂, 张哲, 张旭, 高萌萌, 周玉龙, 樊祜卿. 黑龙江省地区犊牛腹泻源致病性大肠杆菌流行情况调查、毒力基因及耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(7): 3390-3398. |
| [4] | 张燕敏, 刘帅, 滕战伟, 谢红兵, 夏小静, 贺永惠, 常美楠. 功能性寡糖缓解犊牛腹泻的机理研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(3): 979-994. |
| [5] | 张雨, 王琪茹, 师鑫潮, 郭子明, 何欣, 张铁, 赵兴华. 厚朴酚固体分散体对犊牛生长性能、血清抗氧化能力和肠道微生物的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(2): 943-952. |
| [6] | 沈鹏, 王艺, 任炜杰, 杨永春, 宋厚辉, 王志亮. 牛结节性皮肤病免疫抗体监测的Meta分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(8): 3649-3658. |
| [7] | 田思瑾, 赵佳琪, 王晓明, 王丽平, 黄金虎. 我国猪链球菌对常用抗菌药物耐药性的Meta分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(7): 3163-3176. |
| [8] | 王玮, 王景松, 郭亚男, 高乐, 王玲玲, 陈灿, 王健霖, 王建东, 马科, 李继东. 宁夏部分地区犊牛腹泻样本大肠杆菌分离菌株的毒力因子检测与分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(7): 3261-3266. |
| [9] | 苏传琛, 焦静娅, 王永帅, 罗朋娜, 昌兴海, 黄艳群. 导入25%洛岛红鸡血缘对河南斗鸡相关指标的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(3): 1007-1018. |
| [10] | 易鹏飞, 孙磊, 马亚楠, 马雪连, 李娜, 孙亚伟, 钟旗, 姚刚. 健康安格斯犊牛与IBRV感染犊牛鼻腔菌群变化比较[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(3): 1147-1158. |
| [11] | 高辉, 方敏, 姜玲玲, 马耀玉, 刘强, 张刚, 牛小霞, 王璞, 李勇, 张思浓. 中国2012—2022年羊群中蓝舌病毒流行的Meta分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(2): 706-717. |
| [12] | 杨作斌, 史晋成, 马紫薇, 陈如龙, 舒展, 李鑫, 王金泉, 钟旗, 马雪连, 姚刚. 粪菌移植治疗犊牛无特异病原性腹泻和细菌性腹泻的疗效及其肠道菌群变化[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(10): 4720-4734. |
| [13] | 郑先瑞, 卓明雪, 纪金丽, 蒋维虎, 邓在双, 张吉成, 田雅莉, 丁月云, 张晓东, 殷宗俊. 皖南黑猪不同生长阶段血清免疫指标及肠道菌群的特征分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(9): 3770-3783. |
| [14] | 付曦瑶, 陈丽红, 陈小丽, 孙伟丽, 郭肖兰. 11~17周龄雌性雉鸡蛋白质适宜需要量研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(7): 2910-2923. |
| [15] | 陈烨馨, 谢梦圆, 李文豪, 张志丹, 王晓丹, 陈柯佳, 刘平平, 周伟光, 王建龙, 徐晓静. 牛轮状病毒和志贺菌阳性犊牛腹泻粪便样本中肠道菌群的分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(4): 1624-1631. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
