





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 3002-3013.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.06.042
• Clinical Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
KANG Huijie1( ), SHA Jichen1, YANG Tianyuan1, ZHANG Yuntong1, HOU Xiaoyu1, LI Siyao1, WANG Weiqian1, HOU Qingdian1, ZHANG Shuai1, YANG Haotian1,2, ZHAO Yuan1,*(
), SHA Jichen1, YANG Tianyuan1, ZHANG Yuntong1, HOU Xiaoyu1, LI Siyao1, WANG Weiqian1, HOU Qingdian1, ZHANG Shuai1, YANG Haotian1,2, ZHAO Yuan1,*( ), FAN Honggang1,*(
), FAN Honggang1,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-31
Online:2025-06-23
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
ZHAO Yuan, FAN Honggang
E-mail:hj_kang8436@163.com;16645266261@163.com;fanhonggang2002@163.com
CLC Number:
KANG Huijie, SHA Jichen, YANG Tianyuan, ZHANG Yuntong, HOU Xiaoyu, LI Siyao, WANG Weiqian, HOU Qingdian, ZHANG Shuai, YANG Haotian, ZHAO Yuan, FAN Honggang. Mechanistic Studies on the Inhibition of Malignant Biological Behavior of Canine Osteosarcoma Cells by Gambogenic Acid Regulated Glycogen Metabolism Pathway[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 3002-3013.
Table 1
Primer sequence"
| 基因 Gene | 序列(5′→3′) Sequence | |
| 上游引物Upstream primer | 下游引物Downstream primer | |
| ACTB(β-actin) | GGAACCACCATGTACCCTGG | TGCTGTCACCTTCTCCGTTC |
| SLC2A1(GLUT1) | AAGGAGGAGAGTCGGCAGAT | GACGTACGGACCACACAGTT |
| HK2 | GTAACAGACAACGGGCTCCA | GTCATCGAGTATGCCGTCGT |
| PYGL | ATCGCCAATGTGAAGCAGGA | TCCTCTGCCATTTCCACGTT |
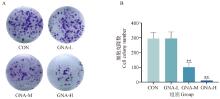
Fig. 2
Plot of the results of the plate cloning experiment and data analysis A. Plot of the results of the effect of GNA on the plate cloning of Mckinely canine OS cells; B. Analysis of the data from the plate cloning experiment. "*" indicates significant difference compared with the CON group, P < 0.05, and " **" indicates highly significant difference, P < 0.01"
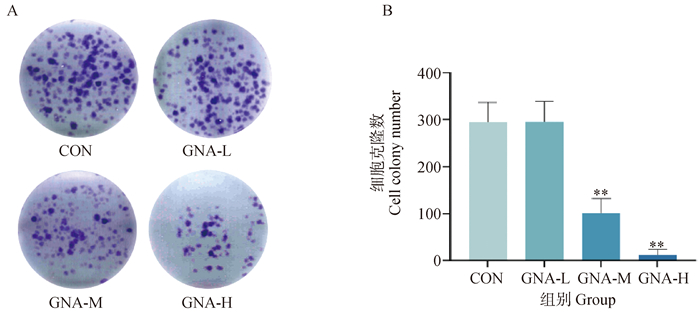
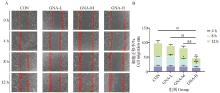
Fig. 3
Effect of GNA on the scratch healing behavior of Mckinely canine OS cells A. Plot of the results of the cell scratch experiment (40×, scale bar 200 μm); B. Analysis of the data of the cell scratch experiment. Compared with CON group, "*" indicates significant difference, P < 0.05; " **" indicates highly significant difference P < 0.01; " ***" indicates highly significant difference, P < 0.001; "##" indicates highly significant difference compared with CON group, P < 0.01; "$$" indicates highly significant difference compared with the low-dose group, P < 0.01; "&&" indicates highly significant difference compared with the medium-dose group, P < 0.01. The same as below"
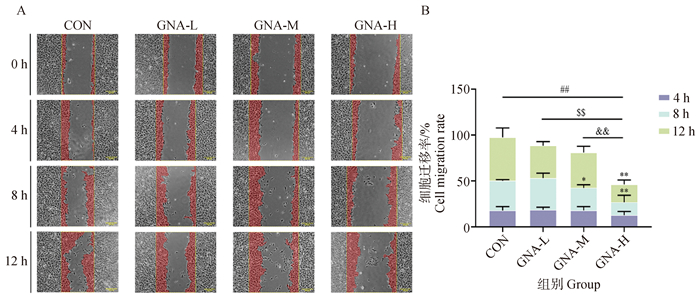
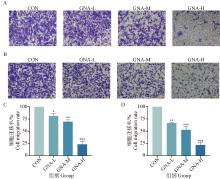
Fig. 4
Effect of GNA on migration and invasion behavior of Mckinely canine OS cells A. Graphs of the results of Transwell migration experiments; B. Graphs of the results of Transwell invasion experiments (200×, scale bar 50 μm); C. Analysis of Transwell migration data; D. Analysis of Transwell invasion data"

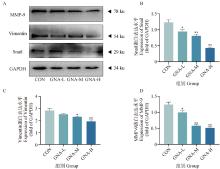
Fig. 5
Effect of GNA on the expression of proteins related to migration and invasion in Mckinely canine OS cells A. Graphs of Western blot experiment results; B. Data analysis of Snail expression results; C. Data analysis of Vimentin expression results; D. Data analysis of MMP-9 expression results"
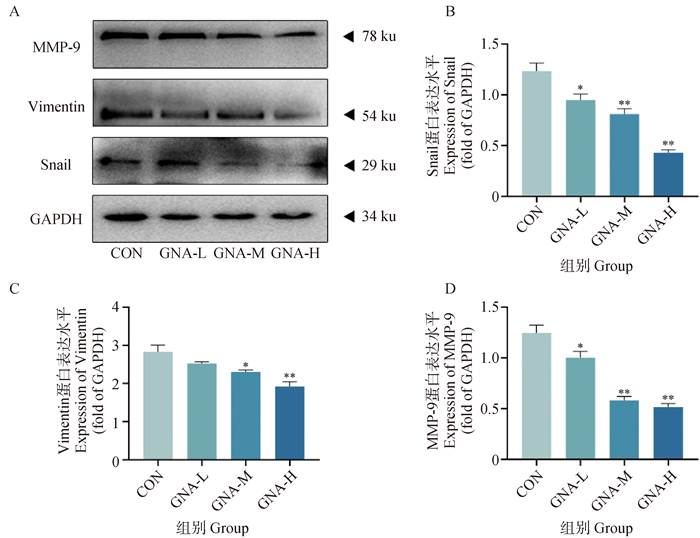
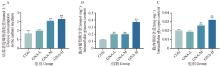
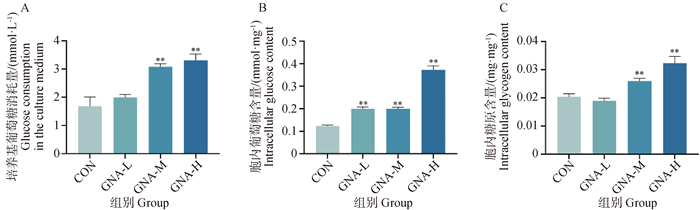
Fig. 7
Effect of GNA on glucose uptake and intracellular glycogen content levels in Mckinely canine OS cells A. Data analysis of medium glucose consumption; B. Data analysis of intracellular glucose content in canine OS cells; C. Data analysis of intracellular glycogen content in canine OS cells"
| 1 |
RAFALKO J M , KRUGLYAK K M , MCCLEARY-WHEELER A L , et al. Age at cancer diagnosis by breed, weight, sex, and cancer type in a cohort of more than 3, 000 dogs: Determining the optimal age to initiate cancer screening in canine patients[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18 (2): e0280795.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280795 |
| 2 |
ROMANUCCI M , DE MARIA R , MORELLO E M , et al. Editorial: Canine osteosarcoma as a model in comparative oncology: Advances and perspective[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2023, 10, 1141666.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1141666 |
| 3 |
BECK J , REN L , HUANG S , et al. Canine and murine models of osteosarcoma[J]. Vet Pathol, 2022, 59 (3): 399- 414.
doi: 10.1177/03009858221083038 |
| 4 |
WILK S S , ZABIELSKA-KOCZYW S K A . Molecular mechanisms of canine osteosarcoma metastasis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (7): 3639.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22073639 |
| 5 |
SAMUELS S K , COOK M R , GREEN E , et al. Case report: Metastatic parosteal osteosarcoma in a dog[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2021, 8, 715908.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.715908 |
| 6 |
BREHM A , WILSON-ROBLES H , MILLER T , et al. Feasibility and safety of whole lung irradiation in the treatment of canine appendicular osteosarcoma[J]. Vet Comp Oncol, 2022, 20 (1): 20- 28.
doi: 10.1111/vco.12702 |
| 7 |
WEINMAN M A , RAMSEY S A , LEEPER H J , et al. Exosomal proteomic signatures correlate with drug resistance and carboplatin treatment outcome in a spontaneous model of canine osteosarcoma[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2021, 21 (1): 245.
doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01943-7 |
| 8 | JIA Z , ZHU X , ZHOU Y , et al. Polypeptides from traditional Chinese medicine: Comprehensive review of perspective towards cancer management[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 260 (Pt 1): 129423. |
| 9 |
YANG C , LI D , KO C N , et al. Active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine for enhancing the effect of tumor immunotherapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14, 1133050.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1133050 |
| 10 |
WANG Y , ZHANG X , WANG Y , et al. Application of immune checkpoint targets in the anti-tumor novel drugs and traditional Chinese medicine development[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2021, 11 (10): 2957- 2972.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.03.004 |
| 11 | 高慧敏, 彭代银, 王雷, 等. 藤黄化学成分和药理作用的研究进展及其质量标志物(Q-Marker)预测分析[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54 (8): 2668- 2685. |
| GAO H M , PENG D Y , WANG L , et al. Research progress on chemical composition and pharmacological effects of gamboge and predictive analysis on quality marker[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2023, 54 (8): 2668- 2685. | |
| 12 |
MI L , XING Z , ZHANG Y , et al. Unveiling gambogenic acid as a promising antitumor compound: A review[J]. Planta Med, 2024, 90 (5): 353- 367.
doi: 10.1055/a-2258-6663 |
| 13 |
LIU C , XU J , GUO C , et al. Gambogenic acid induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in colorectal cancer via the aurora A pathway[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9, 736350.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.736350 |
| 14 |
WANG M , TU Y , LIU C , et al. Gambogenic acid inhibits invasion and metastasis of melanoma through regulation of lncRNA MEG3[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2023, 46 (10): 1385- 1393.
doi: 10.1248/bpb.b23-00156 |
| 15 |
AN F , CHANG W , SONG J , et al. Reprogramming of glucose metabolism: Metabolic alterations in the progression of osteosarcoma[J]. J Bone Oncol, 2024, 44, 100521.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2024.100521 |
| 16 |
FU J Y , HUANG S J , WANG B L , et al. Lysine acetyltransferase 6A maintains CD4(+) T cell response via epigenetic reprogramming of glucose metabolism in autoimmunity[J]. Cell Metab, 2024, 36 (3): 557- 574.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.12.016 |
| 17 |
LIU J , CAO X . Glucose metabolism of TAMs in tumor chemoresistance and metastasis[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2023, 33 (11): 967- 978.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2023.03.008 |
| 18 |
DAUER P , LENGYEL E . New Roles for Glycogen in Tumor Progression[J]. Trends Cancer, 2019, 5 (7): 396- 399.
doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.05.003 |
| 19 |
FAVARO E , BENSAAD K , CHONG M G , et al. Glucose utilization via glycogen phosphorylase sustains proliferation and prevents premature senescence in cancer cells[J]. Cell Metab, 2012, 16 (6): 751- 764.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.10.017 |
| 20 |
LIU Q , LI J , ZHANG W , et al. Glycogen accumulation and phase separation drives liver tumor initiation[J]. Cell, 2021, 184 (22): 5559- 5576.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.10.001 |
| 21 |
YANG Y T , ENGLEBERG A I , YUZBASIYAN-GURKAN V . Establishment and Characterization of cell lines from canine metastatic osteosarcoma[J]. Cells, 2023, 13 (1): 25.
doi: 10.3390/cells13010025 |
| 22 |
CHEN X , ZHANG X , CAI H , et al. Targeting USP9x/SOX2 axis contributes to the anti-osteosarcoma effect of neogambogic acid[J]. Cancer Lett, 2020, 469, 277- 286.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.015 |
| 23 |
WEISS M C , EULO V , VAN TINE B A . Truly man's best friend: Canine cancers drive drug repurposing in osteosarcoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 28 (4): 571- 572.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3471 |
| 24 |
GIRI S , ALLEN K J H , PRABAHARAN C B , et al. Initial insights into the interaction of antibodies radiolabeled with lutetium-177 and actinium-225 with tumor microenvironment in experimental human and canine osteosarcoma[J]. Nucl Med Biol, 2024, 134-135, 108917.
doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2024.108917 |
| 25 | MASON N J . Comparative immunology and immunotherapy of canine osteosarcoma[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2020, 1258, 199- 221. |
| 26 |
胥辉豪, 刘江渝, 李启卷, 等. 己糖激酶2在犬乳腺肿瘤中的表达及预后研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (3): 1310- 1324.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.03.041 |
|
XU H H , LIU J Y , LI Q J , et al. Expression and prognosis of Hexokinase 2 in canine mammary tumors[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (3): 1310- 1324.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.03.041 |
|
| 27 |
CHEN B , HONG Y , GUI R , et al. N6-methyladenosine modification of circ_0003215 suppresses the pentose phosphate pathway and malignancy of colorectal cancer through the miR-663b/DLG4/G6PD axis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13 (9): 804.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05245-2 |
| 28 |
YANG E , WANG X , GONG Z , et al. Exosome-mediated metabolic reprogramming: the emerging role in tumor microenvironment remodeling and its influence on cancer progression[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020, 5 (1): 242.
doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00359-5 |
| 29 |
YOUNG L E A , CONROY L R , CLARKE H A , et al. In situ mass spectrometry imaging reveals heterogeneous glycogen stores in human normal and cancerous tissues[J]. EMBO Mol Med, 2022, 14 (11): e16029.
doi: 10.15252/emmm.202216029 |
| 30 |
REN L K , LU R S , FEI X B , et al. Unveiling the role of PYGB in pancreatic cancer: a novel diagnostic biomarker and gene therapy target[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2024, 150 (3): 127.
doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05644-2 |
| 31 |
JIANG L , LIU S , DENG T , et al. Analysis of the expression, function and signaling of glycogen phosphorylase isoforms in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2022, 24 (2): 244.
doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13364 |
| 32 |
ZOIS C E , HENDRIKS A M , HAIDER S , et al. Liver glycogen phosphorylase is upregulated in glioblastoma and provides a metabolic vulnerability to high dose radiation[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13 (6): 573.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05005-2 |
| 33 |
JI Q , LI H , CAI Z , et al. PYGL-mediated glucose metabolism reprogramming promotes EMT phenotype and metastasis of pancreatic cancer[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19 (6): 1894- 1909.
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.76756 |
| 34 |
CHEN Y F , ZHU J J , LI J , et al. O-GlcNAcylation increases PYGL activity by promoting phosphorylation[J]. Glycobiology, 2022, 32 (2): 101- 109.
doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwab114 |
| 35 | ZHAO X , WANG C , ZHAO L , et al. HBV DNA polymerase regulates tumor cell glycogen to enhance the malignancy of HCC cells[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2024, 8 (3): e0387. |
| 36 |
XU J , LIU X , LIU X , et al. Long noncoding RNA KCNMB2-AS1 promotes the development of esophageal cancer by modulating the miR-3194-3p/PYGL axis[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12 (1): 6687- 6702.
doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1973775 |
| [1] | ZHENG Yilei, SHEN Fengting, XIN Liang, YUAN Xiwang, LIN Lin, CAO Di, WU Jiusheng, SHI Fushan, WANG Huanan. Pathological and Immunohistochemical Analysis of A Case of Feline Nasal Malignant Neuroendocrine Neoplasm [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2948-2956. |
| [2] | LI Xueyuan, YANG Lifeng, ZHAO Deming. Pathologic Diagnosis and Analysis of Ovarian Tumors in Dogs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2393-2402. |
| [3] | Yi ZHANG, Jie XU, Xiaoyuan SONG, Shiwei ZHOU, Yumeng TENG, Xiaoli LIU, Guofu CHENG, Changqin GU, Wanpo ZHANG, Xueying HU. Clinico-histopathological Traits of Canine Mammary Tumors in Wuhan Area and Their Correlation with Benign and Malignant Tumors [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4121-4130. |
| [4] | Xiying XU, Yiheng WANG, Qianting OU, Linyuan HONG, Xujing LIU, Xianying LU, Kun JIA. Effects of Silencing PREX1 Expression on Proliferation and Invasiveness of CHMp [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3706-3713. |
| [5] | Yingxin TU, Xiangmei ZHOU, Deming ZHAO, Lifeng YANG. Canine Testicular Tumors: a Retrospective Pathological Study of 119 Cases [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3177-3184. |
| [6] | SHI Zefeng, LI Lingxu, GUO Yiwen, LIAO Yun, SUN Zhaoyu, WANG Lairong, YANG Deji, YAO Dawei. Detection of Microsatellite Instability in Marek's Disease Tumor based on High-resolution Melting [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 759-769. |
| [7] | DAI Yuexin, YANG Lifeng, ZHAO Deming, ZHOU Xiangmei. A Retrospective Pathological Study of Odontogenic Tumors in Dogs and Cats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4372-4378. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yan, LIU Jiayue, WU Meijin, ZHOU Jiahao, DIAO Hongxiu. Research Progress of Non-coding RNA as A Potential Biomarker for Canine Tumors [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2264-2271. |
| [9] | REN Xiaoli, FAN Yuying, HUANGFU Heping, LIU Yun, SHI Dongmei. Effect of GSK126 on Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition of Canine Mammary Tumor Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(4): 1721-1729. |
| [10] | XU Huihao, LIU Jiangyu, LI Qijuan, ZHENG Xiaobo, LIN Jiahao, JIN Yipeng, LIN Degui. Expression and Prognosis of Hexokinase 2 in Canine Mammary Tumors [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 1310-1324. |
| [11] | WU Juye, LU Baochun, ZHU Yufan, JIA Kun. The Effects of Thrombospondin 1 on the Biological Characteristics of Canine Mammary Tumor Cells in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(12): 4470-4481. |
| [12] | LI Yan, LAN Tingying, PANG Bo, YANG Xiaonong, HUANG Jian. Expression of NLRP3 Inflammasome Signal Associated Genes in Canine Mammary Tumors and Clinical Significance [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(4): 1252-1258. |
| [13] | DENG Zhaoyang, WANG Zheng, ZHANG Jiaren, HE Xijun, ZHENG Jiasan. Pathological and Immunohistochemical Analysis of Splenic Metastasis of Adrenal Cortical Carcinoma in a Cat [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(12): 3669-3674. |
| [14] | PAN Qidong, ZENG Xiancheng, YANG Bincai, LIU Qinghua, XU Quanming, CHEN Jilong. Analysis of Complete Genomic Sequences of Enzootic Nasal Tumor Virus 2 and Role of Its gag Gene in Tumorigenesis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(11): 3165-3174. |
| [15] | CHEN Mengyue, ZHANG Yuchen, LOU Jiangcheng, LUO Chuanzhen, ZHAO Hongli, LIU Xiaoli, HU Xueying. Histopathological Diagnosis and Immunohistochemical Analysis of 26 Cases of Canine Hair Follicle Tumors [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(5): 1407-1413. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||