





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 442-454.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.01.040
• Clinical Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Yi( ), HOU Lulu, FANG Fei, GAO Linying, XIE Shumin, WANG Yu*(
), HOU Lulu, FANG Fei, GAO Linying, XIE Shumin, WANG Yu*( )
)
Received:2024-02-19
Online:2025-01-23
Published:2025-01-18
Contact:
WANG Yu
E-mail:wangyi@nefu.edu.cn;wangyu2013@nefu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
WANG Yi, HOU Lulu, FANG Fei, GAO Linying, XIE Shumin, WANG Yu. Fluoride Induced Small Intestine Oxidative Damage in Broilers via Autophagy and Ferroptosis[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 442-454.
Table 1
The primers used in the present study"
| 基因 Gene | 登录号 Accession No. | 正向序列(5′→3′) Forward sequence | 反向序列(5′→3′) Reverse sequence |
| β-actin | NM_205518.2 | CCGCTCTATGAAGGCTACGC | CTCTCGGCTGTGGTGGTGAA |
| ACSL4 | XM_046917350.1 | CCGTTGTTATCTTCTGCGAGACC | ACGCTCCACATTCATTGAGACCATAG |
| FTH1 | NM_205086.2 | AGAATGTGAACCAGTCGCTGTTAGAG | TGCTTGATGGCTTTCACCTGCTC |
| GPX4 | NM_204220.3 | GCTGTGGAAGTGGCTGAAGGAG | TTGGCCCTCACGGTTGATAAGAAAC |
| SLC7A11 | XM_040670527.2 | AACTGCTGGTTATTCGCCCTG | AAGCCAGCAACTACCAGTCCA |
| AKT | XM_046917866.1 | AGGAGGAAGAGATGATGGAT | GAATGGATGCCGTGAGTT |
| ATG5 | XM_046914043.1 | GGCACCGACCGATTTAGT | GCTGATGGGTTTGCTTTT |
| ATG12 | XM_046936147.1 | GGGACCCTCTATGAGTGTTTTGG | AAGACCACACCTCAGCAACTC |
| Beclin-1 | NM_001006332.1 | CGACTGGAGCAGGAAGAAG | TCTGAGCATAACGCATCTGG |
| mTOR | XM_417614.7 | GCTTATGGCACGGTGTTTCC | GCGATCATGCTCTGTTGCAG |
| p62 | XM_040682727.2 | GTTAATCCTCTGCGTGTGA | AAGAAGAATCGGTGTGCTAA |
| NQO1 | NM_001277620.2 | CGCACCCTGAGAAAACCTCT | TTCTTGAGGGGTCCGGTGAT |
| HO-1 | XM_046921508.1 | GTCGTTGGCAAGAAGCATCC | GGGCCTTTTGGGCGATTTTC |
| Nrf2 | XM_046943490.1 | CAGGGCAATGCTAGTGTGTACTCATC | AGGGTCTTTCTTTGGTGTGTTCATACG |
Table 2
The antibodies used in the present study"
| 抗体信息Antibody | 稀释率Dilution | 来源Source |
| β-actin | 1∶2 000 | Abclonal Technology, China |
| ALOX12 | 1∶500 | Boster, China |
| GPX4 | 1∶500 | Boster, China |
| NCOA4 | 1∶500 | Boster, China |
| FTH1 | 1∶500 | Boster, China |
| AKT | 1∶500 | Wanleibio, China |
| ATG12 | 1∶500 | Wanleibio, China |
| Beclin-1 | 1∶500 | Wanleibio, China |
| LC3 | 1∶500 | Wanleibio, China |
| mTOR | 1∶500 | Wanleibio, China |
| PI3K | 1∶500 | Wanleibio, China |
| P62 | 1∶500 | Wanleibio, China |
| Nrf2 | 1∶500 | Wanleibio, China |
| Keap1 | 1∶500 | Wanleibio, China |
| NQO1 | 1∶500 | Wanleibio, China |
| HO-1 | 1∶500 | Wanleibio, China |

Fig. 1
Effect of sodium fluoride on the morphological structure of intestinal villi in the broiler duodenum A. Control group (C); B. Low-fluoride group (L); C. Medium-fluoride group (M); D. High-fluoride group (H). The color pictures can be found by scanning the OSID code on the front page of the article"

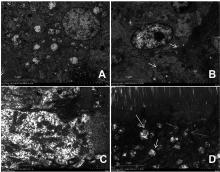
Fig. 2
Electron microscopy of sodium fluoride on the ultrastructure of the intestinal villi of the broiler duodenum A. Control group (C); B. Low-fluoride group (L); C. Medium-fluoride group (M); D. High-fluoride group (H). Green arrows represent normal mitochondrial structure; red arrows represent mitochondrial cristae breaks, yellow arrows represent autophagosomes. The color pictures can be found by scanning the OSID code on the front page of the article"

| 1 |
ZUOH,CHENL,KONGM,et al.Toxic effects of fluoride on organisms[J].Life Sci,2018,198,18-24.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.02.001 |
| 2 | 邵奎东,张海涛.吉林省地方性氟中毒"十三五"防治进展及今后对策探讨[J].中国地方病防治,2023,38(1):1-7. |
| ZHAOK D,ZHANGH T.Progress in prevention and control of endemic fluorosis in Jilin Province during the 13th Five Year Plan period and future countermeasures[J].Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases,2023,38(1):1-7. | |
| 3 | 吕纬. 四方针铁矿及其铝氧化物复合体对氟离子的吸附性能与机理[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2021. |
| LV W. Adsorption performance and mechanisms of fluoride on the akaganeite and its aluminum oxide complex[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 4 |
OTTAPPILAKKILH,BABUS,BALASUBRAMANIANS,et al.Fluoride induced neurobehavioral impairments in experimental animals: a brief review[J].Biol Trace Elem Res,2023,201(3):1214-1236.
doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03242-2 |
| 5 |
RAHIMA,ESSAMADIA,EL AMIRIB.A comprehensive review on endemic and experimental fluorosis in sheep: Its diverse effects and prevention[J].Toxicology,2022,465,153025.
doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.153025 |
| 6 |
EFEU,DEDES,YVKSEKV,et al.Apoptotic and oxidative mechanisms in liver and kidney tissues of sheep with fluorosis[J].Biol Trace Elem Res,2021,199(1):136-141.
doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02121-y |
| 7 |
CHOUBISAS L,CHOUBISAD.Status of industrial fluoride pollution and its diverse adverse health effects in man and domestic animals in India[J].Environ Sci Pollut Res,2016,23(8):7244-7254.
doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6319-8 |
| 8 |
DENGY B,CUIH M,PENGX,et al.Effects of high dietary fluorine on erythrocytes and erythrocyte immune adherence function in broiler chickens[J].Biol Trace Elem Res,2013,155(2):247-252.
doi: 10.1007/s12011-013-9793-6 |
| 9 |
CHENG J,HUP C,XUZ C,et al.The beneficial or detrimental fluoride to gut microbiota depends on its dosages[J].Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,2021,209,111732.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111732 |
| 10 |
LUOQ,CUIH M,PENGX,et al.Intestinal IgA+ cell numbers as well as IgA, IgG, and IgM contents correlate with mucosal humoral immunity of broilers during supplementation with high fluorine in the diets[J].Biol Trace Elem Res,2013,154(1):62-72.
doi: 10.1007/s12011-013-9713-9 |
| 11 |
LIUJ,CUIH M,PENGX,et al.Dietary high fluorine induces apoptosis and alters Bcl-2, Bax, and caspase-3 protein expression in the cecal tonsil lymphocytes of broilers[J].Biol Trace Elem Res,2013,152(1):25-30.
doi: 10.1007/s12011-012-9595-2 |
| 12 |
LUOQ,CUIH M,PENGX,et al.Suppressive effects of dietary high fluorine on the intestinal development in broilers[J].Biol Trace Elem Res,2013,156(1-3):153-165.
doi: 10.1007/s12011-013-9845-y |
| 13 |
CHENS Y,XUEY J,SHENY T,et al.Effects of different selenium sources on duodenum and jejunum tight junction network and growth performance of broilers in a model of fluorine-induced chronic oxidative stress[J].Poult Sci,2022,101(3):101664.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101664 |
| 14 |
ZHAOW P,WANGH W,LIUJ,et al.Mitochondrial respiratory chain complex abnormal expressions and fusion disorder are involved in fluoride-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in ovarian granulosa cells[J].Chemosphere,2019,215,619-625.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.043 |
| 15 |
JUH,CHENS Y,XUEY J,et al.The role of Nrf2 pathway in alleviating fluorine-induced apoptosis by different selenium sources in the chicken duodenum and jejunum[J].Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,2021,224,112708.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112708 |
| 16 | 胡流芳,王迎,任汝静,等.Keap1-Nrf2/ARE信号通路的抗氧化应激作用及其调控机制[J].国际药学研究杂志,2016,43(1):146-152, 166. |
| HUL F,WANGY,RENR J,et al.Anti-oxidative stress actions and regulation mechanisms of Keap1-Nrf2/ARE signal pathway[J].Journal of International Pharmaceutical Research,2016,43(1):146-152, 166. | |
| 17 |
SUNY,ZHENGY F,WANGC X,et al.Glutathione depletion induces ferroptosis, autophagy, and premature cell senescence in retinal pigment epithelial cells[J].Cell Death Dis,2018,9(7):753.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0794-4 |
| 18 |
ZHAOY F,LIY Y,WANGJ M,et al.Fluoride induces apoptosis and autophagy through the IL-17 signaling pathway in mice hepatocytes[J].Arch Toxicol,2018,92(11):3277-3289.
doi: 10.1007/s00204-018-2305-x |
| 19 |
TANGH Y,HOUH Q,SONGL,et al.The role of mTORC1/TFEB axis mediated lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy impairment in fluoride neurotoxicity and the intervention effects of resveratrol[J].J Hazard Mater,2024,467,133634.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.133634 |
| 20 |
JIANGJ Z,RUANY B,LIUX H,et al.Ferritinophagy is critical for deoxynivalenol-induced liver injury in mice[J].J Agric Food Chem,2024,72(12):6660-6671.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c00556 |
| 21 |
DIXONS J,LEMBERGK M,LAMPRECHTM R,et al.Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death[J].Cell,2012,149(5):1060-1072.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042 |
| 22 | 岑怡,王甜甜,高兴杰,等.铁死亡调控机制及其在肠道疾病中的研究进展[J].生命的化学,2022,42(11):2071-2078. |
| CENY,WANGT T,GAOX J,et al.Regulatory mechanism and research progress of ferroptosis in intestinal diseases[J].Chemistry of Life,2022,42(11):2071-2078. | |
| 23 | 王浩,肖金龙,沈珏,等.细胞死亡的新方式——铁死亡与铜死亡[J].畜牧兽医学报,2024,55(2):461-470. |
| WANGH,XIAOJ L,SHENJ,et al.New ways of cell death—ferroptosis and cuproptosis[J].Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2024,55(2):461-470. | |
| 24 |
LIX,YANGJ,SHIE B,et al.Riboflavin alleviates fluoride-induced ferroptosis by IL-17A-independent system Xc-/GPX4 pathway and iron metabolism in testicular Leydig cells[J].Environ Pollut,2024,344,123332.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123332 |
| 25 |
ZHANGY,FANGY M,ZHAOS,et al.Fluoride resistance capacity in mammalian cells involves global gene expression changes associate with ferroptosis[J].Chem Biol Interact,2023,381,110555.
doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110555 |
| 26 |
SONGC,HEPINGH F,SHENY S,et al.AMPK/p38/Nrf2 activation as a protective feedback to restrain oxidative stress and inflammation in microglia stimulated with sodium fluoride[J].Chemosphere,2020,244,125495.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125495 |
| 27 | 毕翻,万珑,温建霞,等.氟对仔鼠生长发育、学习记忆及血清氧化应激水平的影响[J].中华地方病学杂志,2020,39(4):243-247. |
| BIF,WANL,WENJ X,et al.Effects of fluoride on growth and development, learning and memory, and oxidative stress in serum of offspring rat[J].Chinese Journal of Endemiology,2020,39(4):243-247. | |
| 28 | 辛涛,许娟,刘红岗.Nrf2/HO-1通路在Erastin诱导的非小细胞肺癌A549细胞铁死亡中的作用[J].山西医科大学学报,2023,54(7):879-884. |
| XINT,XUJ,LIUH G.Role of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in Erastin-induced ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells[J].Journal of Shanxi Medical University,2023,54(7):879-884. | |
| 29 | TANGZ,LAIC C,LUOJ,et al.Mangiferin prevents the impairment of mitochondrial dynamics and an increase in oxidative stress caused by excessive fluoride in SH-SY5Y cells[J].J Biochem Mol Toxicol,2021,35(4):e22705. |
| 30 | XUZ R,HANX,OUD M,et al.Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy for tumor therapy[J].Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,2020,104(2):575-587. |
| 31 | ZHANGJ H,ZHUY C,SHIY,et al.Fluoride-induced autophagy via the regulation of phosphorylation of mammalian targets of rapamycin in mice leydig cells[J].J Agric Food Chem,2017,65(40):8966-8976. |
| 32 | 孔志伟,姚婷婷.自噬相关基因Beclin1和LC3与子宫内膜异位症的研究进展[J].医学综述,2019,25(21):4166-4173. |
| KONGZ W,YAOT T.Research on endometriosis and autophagy associated gene beclin1 and LC3[J].Medical Recapitulate,2019,25(21):4166-4173. | |
| 33 | MIZUSHIMAN.Methods for monitoring autophagy[J].Int J Biochem Cell Biol,2004,36(12):2491-2502. |
| 34 | KABEYAY,MIZUSHIMAN,UENOT,et al.LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing[J].EMBO J,2000,19(21):5720-5728. |
| 35 | 刘世玉,冯学召,古丽妮尕尔·司马义,等.p62敲除对细胞自噬的影响及其对泛素化修饰蛋白募集的作用[J].新疆医科大学学报,2023,46(9):1119-1123, 1131. |
| LIUS Y,FENGX Z,GULINIGAERS,et al.Effect of p62 knockout on cellular autophagy and its role in recruitment of ubiquitination-modified proteins[J].Journal of Xinjiang Medical University,2023,46(9):1119-1123, 1131. | |
| 36 | 吕晓希,胡卓伟.自噬流的检测方法[J].药学学报,2016,51(1):45-51. |
| LVX X,HUZ W.New methods to detect autophagic flux[J].Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica,2016,51(1):45-51. | |
| 37 | XUW J,HUZ Y,ZHANGJ J,et al.Cross-talk between autophagy and ferroptosis contributes to the liver injury induced by fluoride via the mtROS-dependent pathway[J].Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,2023,250,114490. |
| 38 | 李昕,李平,熊秋宏.自噬和铁死亡的相互联系[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2021,43(1):144-151. |
| LIX,LIP,XIONGQ H.The crosstalk between autophagy and ferroptosis[J].Chinese Journal of Cell Biology,2021,43(1):144-151. | |
| 39 | 李敏,杨前,刘亚轩,等.镉通过诱导自噬促进肾小管上皮细胞铁死亡的研究[J].陆军军医大学学报,2022,44(17):1705-1711. |
| LIM,YANGQ,LIUY X,et al.Cadmium promotes ferroptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells by inducing autophagy[J].Journal of Army Medical University,2022,44(17):1705-1711. | |
| 40 | MANCIASJ D,WANGX X,GYGIS P,et al.Quantitative proteomics identifies NCOA4 as the cargo receptor mediating ferritinophagy[J].Nature,2014,509(7498):105-109. |
| 41 | HOUW,XIEY C,SONGX X,et al.Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin[J].Autophagy,2016,12(8):1425-1428. |
| 42 | GAOM F,MONIANP,PANQ H,et al.Ferroptosis is an autophagic cell death process[J].Cell Res,2016,26(9):1021-1032. |
| 43 | SONGX H,LONGD X.Nrf2 and ferroptosis: a new research direction for neurodegenerative diseases[J].Front Neurosci,2020,14,267. |
| 44 | 刘恒,段晓峰.铁自噬及相关基因NCOA4、FTH1在口腔鳞癌中的研究进展[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2023,21(1):87-91. |
| LIUH,DUANX F.Research progress of ferritinophagy and related genes FTH1 and NCOA4 in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J].China Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,2023,21(1):87-91. | |
| 45 | DINGK Y,LIUC B,LIL,et al.Acyl-CoA synthase ACSL4: an essential target in ferroptosis and fatty acid metabolism[J].Chin Med J (Engl),2023,136(21):2521-2537. |
| 46 | CHUB,KONN,CHEND L,et al.ALOX12 is required for p53-mediated tumour suppression through a distinct ferroptosis pathway[J].Nat Cell Biol,2019,21(5):579-591. |
| [1] | LI Yuanfang, WU Ran, LI Shuaihao, WEI Qianran, WANG Yadong, WANG Dandan, LI Zhi, LI Guoxi, LIU Qiaoming. The Role of G3BP1 in the Proliferation and Differentiation of Chicken Intramuscular Preadipocytes and Identification of Its Molecular Markers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 159-167. |
| [2] | YIN Qiong, GAO Mingchao, YAO Xiumei, LIU Kunyu, LIU Wei, JIE Hongwei, LI Hua, YE Fei. Correlation Analysis between Melanin Content in Breast Muscle and PMEL17 Gene of Muchuan Black-bone Chickens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 168-177. |
| [3] | WU Shuang, YIN Na, YU Mohan, PING Yuyu, BAI Hao, CHEN Shihao, CHANG Guobin. The Effect of TRIM39.2 Overexpression on the Transcriptional Expression of Chicken Macrophages [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 178-188. |
| [4] | Shuo YANG, Min HUO, Zixuan SU, Yuxiang SHI. Research Progress on the Impact of Mitochondrial Quality Control on Oxidative Stress in Livestock and Poultry [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3769-3776. |
| [5] | Hongyu FU, Yue LI, Han CUI, Jiuzhi LI, Wanxue XU, Xi WANG, Ruifeng FAN. The Mechanism of Long-Chain acyl-CoA Synthetase 4-mediated Ferroptosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3792-3801. |
| [6] | Xiangchen LI, Linnan WANG, Zhengqing YU, Li ZHANG, Chenchen YANG, Liangli SONG. Quercetin Inhibits Autophagy to Restore LTA-induced Tight Junction Function in Mammary Alveolar Cells-large T Antigen [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3887-3896. |
| [7] | Zijin YUAN, Wanxin WANG, Ya XING, Jiahui LI, Ying XUE, Jing GE, Minmeng ZHAO, Long LIU, Daoqing GONG, Tuoyu GENG. HDLBP Is Involved in Goose Fatty Liver Formation by Regulating the Level of Oxidative Stress and the Expression of Inflammatory Factors [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3897-3913. |
| [8] | Jiqiao ZHANG, Yingjie CAI, Yuxiao LI, Chang CAO, Tao LI, Xiuyu BAO, Jianqin ZHANG. Comparative Analysis of Growth Performance, Immune, Intestinal Morphology, and Cecal Microbiota of Lueyang Black-bone Chickens under Different Rearing Systems [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4001-4011. |
| [9] | Xinman LIU, Hongyuan ZHOU, Rui SANG, Bingjie GE, Kexin YAN, Wei WANG, Minghong YU, Xiaotong LIU, Qian QIU, Xuemei ZHANG. Effect of Taraxasterol on Oxidative Stress in Liver Tissue of Broilers with AFB1 Induced Liver Injury [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4141-4152. |
| [10] | Ming LOU, Haoyu LUO, Fang MU, Hui LI, Ning WANG. Advances in the Study of Chicken Insulin Signaling Pathway [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3288-3296. |
| [11] | Yi WANG, Juan GAO, Yuemin HU, Yuefei YANG, Bojun FAN, Huiming JU. Effect of Transient Serum Starvation on Metabolism and Autophagy of Porcine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3408-3417. |
| [12] | Xinyu CAO, Jiawei CAI, Zhiyuan BAO, Shuyu YAO, Yunpeng LI, Yang CHEN, Xinsheng WU, Bohao ZHAO. The Function Analysis of ATG14 Regulates the Autophagy Process in Rabbit Hair Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3472-3481. |
| [13] | Li ZHANG, Mengmeng YU, Ying WANG, Suyan WANG, Zhuangzhuang XU, Peng LIU, Yuntong CHEN, Xiaole QI, Liuan LI, Yulong GAO. Analysis of Cellular Receptor chNHE1 Expression in Chicken Tissues Infected with Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroup J [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3631-3639. |
| [14] | Xiaolong HUANG, Xihui SHENG, Jingwei YUAN. Research Progress of Environmental Adaptability in Chickens from Perspective of Omics Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2809-2824. |
| [15] | Yaxuan MENG, Yan LIU, Jing WANG, Guoshun CHEN, Tao FENG. Research Progress in the Effect of Oxidative Stress on Ovarian Function in Female Livestock [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2825-2835. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||