





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 2685-2700.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.06.014
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
LUO Ruijie1( ), WANG Jiankui2, CAO Suying1,*(
), WANG Jiankui2, CAO Suying1,*( )
)
Received:2024-11-18
Online:2025-06-23
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
CAO Suying
E-mail:2587714111@qq.com;20137602@bua.edu.cn
CLC Number:
LUO Ruijie, WANG Jiankui, CAO Suying. Integrated Sequencing Analysis of lncRNA and mRNA Related to Ancestral-like Coarse in Aohan Fine Wool Sheep[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2685-2700.
Table 1
Descriptions of single character code in Cuffcompare software"
| 标记 Code | 软件中的描述 Description | 可能的lncRNA类型 Potential lncRNA type |
| = | Complete match of intron chain | |
| c | Contained | |
| j | Potentially novel isoform (fragment): at least one splice junction is shared with a reference transcript | |
| e | Single exon transfrag overlapping a reference exon and at least 10 bp of a reference intron, indicating a possible pre-mRNA fragment | |
| i | A transfrag falling entirely within a reference intron | intronic lncRNA[ |
| o | Generic exonic overlap with a reference intron | sense lncRNA[ |
| p | Possible polymerase run-on fragment (within 2 kb of a reference transcript) | |
| r | Repeat. Currently determined by looking at the soft-masked reference sequence and applied to transcripts where at least 50% of the bases are lower case | |
| u | Unknown, intergenic transcript | intergenic lncRNA[ |
| x | Exonic overlap with reference on the opposite strand | anti-sense lncRNA[ |
| s | An intron of the transfrag overlaps a reference intron on the opposite strand (likely due to read mapping errors) | |
| . | Tracking file only, indicates multiple classifications |
Table 2
Statistics of quality preprocessing results"
| 样本 Sample | 原始序列 Raw reads | 过滤后序列 Clean reads | Q30/% | GC含量/% GC content |
| 15180 | 90 832 836 | 89 431 798 | 97.06 | 50.00 |
| 15188 | 93 026 342 | 91 784 550 | 97.25 | 49.00 |
| 15190 | 92 599 986 | 91 039 240 | 96.85 | 49.50 |
| 15264 | 95 508 670 | 94 033 082 | 97.05 | 49.00 |
| 15268 | 88 211 386 | 86 928 822 | 97.17 | 48.50 |
| 15270 | 90 455 404 | 89 110 872 | 97.18 | 48.50 |
Table 3
Comparison of Reads with reference genome"
| 样本 Sample | 过滤后序列总数 Total clean reads | 比对到参考基因组上的Reads数 Total mapped reads | 在参考基因组上比对到多个位置的Reads数 Multiple mapped reads | 在参考基因组上比对到唯一位置的Reads数 Uniquely mapped reads |
| 15180 | 89 431 798 | 76 136 143 (85.13%) | 7 542 762 (8.43%) | 68 593 381 (76.70%) |
| 15188 | 91 784 550 | 77 309 464 (84.23%) | 6 219 587 (6.78%) | 71 089 877 (77.45%) |
| 15190 | 91 039 240 | 75 357 994 (82.78%) | 5 924 476 (6.51%) | 69 433 518 (76.27%) |
| 15264 | 94 033 082 | 79 377 054 (84.41%) | 6 917 846 (7.36%) | 72 459 208 (77.06%) |
| 15268 | 86 928 822 | 71 416 612 (82.16%) | 5 356 182 (6.16%) | 66 060 430 (75.99%) |
| 15270 | 89 110 872 | 75 382 070 (84.59%) | 6 598 558 (7.40%) | 68 783 512 (77.19%) |
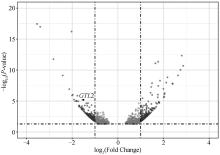
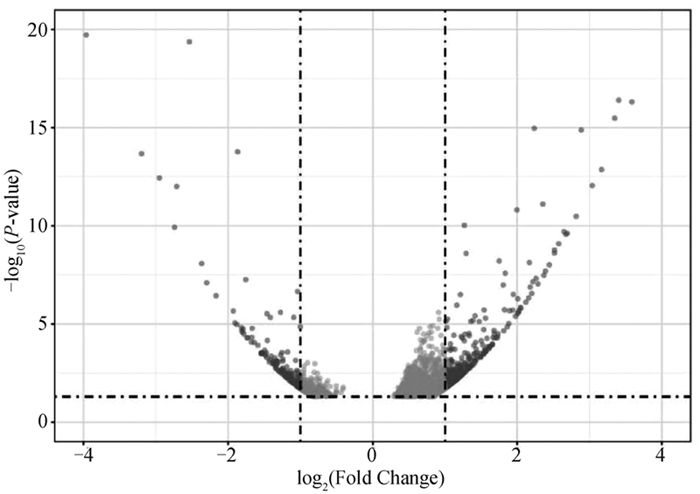
Fig. 3
Volcano plot of DE-lncRNAs and their target genes Each dot represents a significantly differentially expressed transcript (P < 0.05); The dark grey dots on the left represent downregulated transcripts, the dark grey dots on the right represent upregulated transcripts, and the light gray dots represent transcripts with significant but relatively small differences (|log2(Fold Change)| < 1); The black dot GTL2 is a key lncRNA for fine wool traits in a previous study"
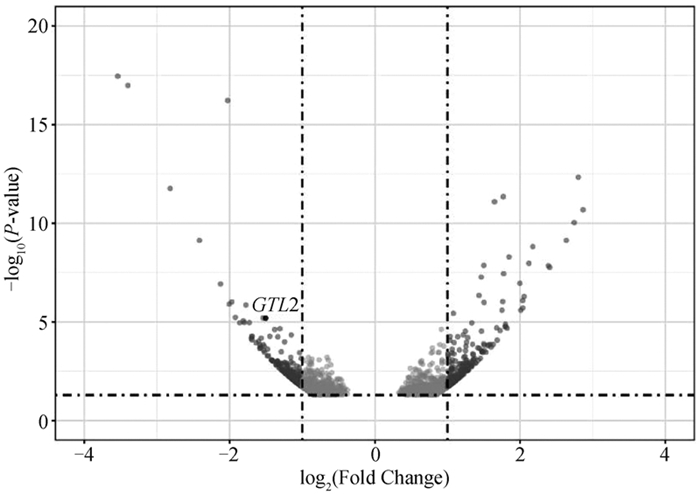
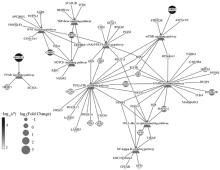
Fig. 6
DE-lncRNA target genes expression network The trianglular dots represents the differential signaling pathways, the circular dots represent differentially expressed genes; The size of the circular dots represent the relative difference multiple, and the color of the circular dots represent the significance of the difference"
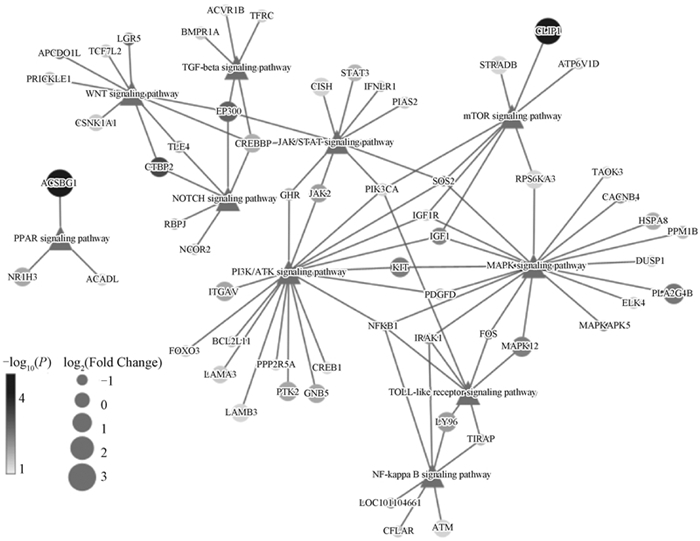
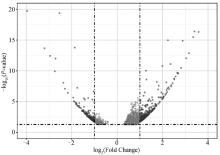
Fig. 8
Volcano plot of DEGs Each dot represents a significantly differentially expressed transcript (P < 0.05); The dark grey dots on the left represent downregulated transcripts, the dark grey dots on the right represent upregulated transcripts, and the light gray dots represent transcripts with significant but relatively small differences (|log2(Fold Change)| < 1)"
| 1 |
胡姗, 苗晓茸, 霍永智, 等. 羊绒、羊毛品质相关基因研究进展[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2024, 45 (1): 91- 96.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2024.01.014 |
|
HU S , MIAO X R , HUO Y Z , et al. Advances of genes related to cashmere and wool quality[J]. Journal Of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2024, 45 (1): 91- 96.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2024.01.014 |
|
| 2 |
PANTELEYEV A A . Functional anatomy of the hair follicle: The secondary hair germ[J]. Exp Dermatol, 2018, 27 (7): 701- 720.
doi: 10.1111/exd.13666 |
| 3 | 赵艳丽, 张世伟, 姜怀志. 辽宁绒山羊2品系皮肤毛囊结构及其活性变化规律的比较[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2009, 31 (6): 746-751, 758. |
| ZHAO Y L , ZHANG S W , JIANG H Z . Comparative study on hair follicles stucture and cycling between two strains of liaoning Cashmere goats[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2009, 31 (6): 746-751, 758. | |
| 4 |
YANG C H , XU J H , REN Q C , et al. Melatonin promotes secondary hair follicle development of early postnatal cashmere goat and improves cashmere quantity and quality by enhancing antioxidant capacity and suppressing apoptosis[J]. J Pineal Res, 2019, 67 (1): e12569.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.1256963 |
| 5 |
WANG M , DAI H , SHENG S , et al. Discovery and functional analysis of secondary hair follicle mirnas during annual cashmere growth[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (2): 1063.
doi: 10.3390/ijms24021063 |
| 6 | GOOT H . Evolution of the fleece of the sheep[J]. Nature, 1941, 148 (3759): 596- 597. |
| 7 | RYDER M L. The evolution of the fleece[Z]. New York: Scientific American, Incorporated, 1987, 256: 112-119. |
| 8 | MORTIMER S I , HATCHER S , FOGARTY N M , et al. Genetic parameters for wool traits, live weight, and ultrasound carcass traits in Merino sheep[J]. J Anim Sci, 2017, 95 (5): 1879- 1891. |
| 9 |
WANG J , HUA G , CHEN J , et al. Epigenetic mechanism of Gtl2-miRNAs causes the primitive sheep characteristics found in purebred Merino sheep[J]. Cell Biosci, 2023, 13 (1): 190.
doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01142-z |
| 10 |
JACKSON N , MADDOCKS I G , WATTS J E , et al. Evolution of the sheep coat: the impact of domestication on its structure and development[J]. Genet Res, 2020, 102, e4.
doi: 10.1017/S0016672320000063 |
| 11 | 王东梅, 李宝栋, 李海娟, 等. 培育敖汉细毛羊高繁品系及产肉性能的育种实践探索[J]. 畜牧业环境, 2023 (7): 5- 9. |
| WANG D M , LI B D , LI H J , et al. Exploration of breeding practice for cultivating high reproductive strains and meat production performance of Aohan fine wool sheep[J]. Animal Industry and Environment, 2023 (7): 5- 9. | |
| 12 |
GRAMMATIKAKIS I , LAL A . Significance of lncRNA abundance to function[J]. Mamm Genome, 2022, 33 (2): 271- 280.
doi: 10.1007/s00335-021-09901-4 |
| 13 |
DING Y , CHEN Y , YANG X , et al. An integrative analysis of the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competitive endogenous RNA network reveals potential mechanisms in the murine hair follicle cycle[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13, 931797.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.931797 |
| 14 |
ZHAO B , CHEN Y , HU S , et al. Systematic analysis of non-coding RNAs involved in the Angora rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) hair follicle cycle by RNA sequencing[J]. Front Genet, 2019, 10, 407.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00407 |
| 15 |
ZHANG Y , LI F , SHI Y , et al. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis of hair follicle morphogenesis reveals that lncRNA-H19 promotes dermal papilla cell proliferation through the Chi-miR-214-3p/beta-catenin axis in Cashmere goats[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (17): 10006.
doi: 10.3390/ijms231710006 |
| 16 |
ZHU N , LIN E , ZHANG H , et al. LncRNA H19 overexpression activates Wnt signaling to maintain the hair follicle regeneration potential of dermal papilla cells[J]. Front Genet, 2020, 11, 694.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00694 |
| 17 |
LIN B J , LIN G Y , ZHU J Y , et al. LncRNA-PCAT1 maintains characteristics of dermal papilla cells and promotes hair follicle regeneration by regulating miR-329/Wnt10b axis[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2020, 394 (1): 112031.
doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112031.3321/j.issn:0253-9772.2008.11.002 |
| 18 |
ZHU Y B , WANG Z Y , YIN R H , et al. A lncRNA-H19 transcript from secondary hair follicle of Liaoning cashmere goat: Identification, regulatory network and expression regulated potentially by its promoter methylation[J]. Gene, 2018, 641, 78- 85.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.10.028 |
| 19 | 赵帅. 细毛羊次级毛囊形态发生诱导期转录组差异表达分析[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2015. |
| ZHAO S. Transcriptomic difference analysis in the skin of fine-wool sheep during secondary follicle initiation[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese) | |
| 20 |
COCK P J , FIELDS C J , GOTO N , et al. The Sanger FASTQ file format for sequences with quality scores, and the Solexa/Illumina FASTQ variants[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2010, 38 (6): 1767- 1771.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1137 |
| 21 |
HANSEN K D , BRENNER S E , DUDOIT S . Biases in Illumina transcriptome sequencing caused by random hexamer priming[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2010, 38 (12): e131.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq224 |
| 22 |
LANGMEAD B , SALZBERG S L . Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2[J]. Nat Methods, 2012, 9 (4): 357- 359.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923 |
| 23 |
KIM D , PERTEA G , TRAPNELL C , et al. TopHat2: accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions[J]. Genome Biol, 2013, 14 (4): R36.
doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-4-r36 |
| 24 |
TRAPNELL C , ROBERTS A , GOFF L , et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks[J]. Nat Protoc, 2012, 7 (3): 562- 578.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.016 |
| 25 |
PACHTER L , TRAPNELL C , WILLIAMS B A , et al. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2010, 28 (5): 511- 515.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.1621 |
| 26 |
LIU X , ZHAO J , XUE L , et al. A comparison of transcriptome analysis methods with reference genome[J]. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23 (1): 232.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08465-0 |
| 27 | KONG L , ZHANG Y , YE Z Q , et al. CPC: assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2007, 35 (Web Server issue): W345- W349. |
| 28 |
SUN L , LUO H , BU D , et al. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2013, 41 (17): e166.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt646 |
| 29 |
VITALE R , BUGNON L A , FENOY E L , et al. Evaluating large language models for annotating proteins[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2024, 25 (3): bbae177.
doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae177 |
| 30 |
LI A , ZHOU H , XIONG S , et al. PLEKv2: predicting lncRNAs and mRNAs based on intrinsic sequence features and the coding-net model[J]. BMC Genomics, 2024, 25 (1): 710- 756.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10630-6 |
| 31 |
CHAN S N , PEK J W . Stable intronic sequence RNAs (sisRNAs): an expanding universe[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2019, 44 (3): 258- 272.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2018.09.016 |
| 32 |
WANG W , MIN L , QIU X , et al. Biological function of long non-coding RNA (LncRNA) xist[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9, 645647.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.645647 |
| 33 |
RANSOHOFF J D , WEI Y , KHAVARI P A . The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2018, 19 (3): 143- 157.
doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.104 |
| 34 | SALAMA S R . The complexity of the mammalian transcriptome[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2022, 1363, 11- 22. |
| 35 |
LIU S , WANG Z , ZHU R , et al. Three differential expression analysis methods for RNA sequencing: limma, EdgeR, DESeq2[J]. J Vis Exp, 2021 (175)
doi: 10.3791/62528 |
| 36 |
SHANNON P , MARKIEL A , OZIER O , et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks[J]. Genome Res, 2003, 13 (11): 2498- 2504.
doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303 |
| 37 |
LIN X , ZHU L , HE J . Morphogenesis, growth cycle and molecular regulation of hair follicles[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10, 899095.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.899095 |
| 38 | 秦志云, 姜怀志. 羊胎儿期皮肤毛囊发育及调控机制的研究概述[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2023, 50 (2): 638- 646. |
| QIN Z Y , JIANG H Z . An overview of research on skin hair follicle development and regulatory mechanism in sheep during the fetal period[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 50 (2): 638- 646. | |
| 39 |
LORZ C , GARCIA-ESCUDERO R , SEGRELLES C , et al. A functional role of RB-dependent pathway in the control of quiescence in adult epidermal stem cells revealed by genomic profiling[J]. Stem Cell Rev Rep, 2010, 6 (2): 162- 177.
doi: 10.1007/s12015-010-9139-0 |
| 40 |
GRECO V , CHEN T , RENDL M , et al. A two-step mechanism for stem cell activation during hair regeneration[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2009, 4 (2): 155- 169.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.12.009 |
| 41 |
MVLLER-RÖVER S , TOKURA Y , WELKER P , et al. E- and P-cadherin expression during murine hair follicle morphogenesis and cycling[J]. Exp Dermatol, 1999, 8 (4): 237- 246.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1999.tb00377.x |
| 42 |
DEMARS J , CANO M , DROUILHET L , et al. Genome-wide identification of the mutation underlying fleece variation and discriminating ancestral hairy species from modern woolly sheep[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2017, 34 (7): 1722- 1729.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx114 |
| 43 |
LV F H , CAO Y H , LIU G J , et al. Whole-genome resequencing of worldwide wild and domestic sheep elucidates genetic diversity, introgression, and agronomically important loci[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2022, 39 (2): msab353.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab353 |
| 44 | 常永芳, 包鹏甲, 褚敏, 等. LncRNA在哺乳动物毛囊发育调控中的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2019, 35 (8): 205- 212. |
| CHANG Y F , BAO P J , CHU M , et al. Research progress on the regulation of lncRNA in the development of mammalian hair follicle[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2019, 35 (8): 205- 212. | |
| 45 |
ZHANG L , WANG J , CAI G , et al. Imprinted Dlk1-Gtl2 cluster miRNAs are potential epigenetic regulators of lamb fur quality[J]. BMC Genomics, 2023, 24 (1): 632.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09741-3 |
| 46 |
FAN Y , REN C , DENG K , et al. The regulation of lncRNA GTL2 expression by DNA methylation during sheep skeletal muscle development[J]. Genomics, 2022, 114 (5): 110453.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110453 |
| 47 |
CHEN Q , BAO J , ZHANG H , et al. LncRNA GTL2 regulates myoblast proliferation and differentiation via the PKA-CREB pathway in Duolang sheep[J]. Zool Res, 2024, 45 (6): 1261- 1275.
doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.125 |
| 48 |
LUO J , ZHANG Y , GUO Y , et al. TRIM28 regulates Igf2-H19 and Dlk1-Gtl2 imprinting by distinct mechanisms during sheep fibroblast proliferation[J]. Gene, 2017, 637, 152- 160.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.09.048 |
| 49 | 封洋. 毛囊发生过程及调控方式的研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2022, 58 (9): 26- 32. |
| FENG Y . Advances in mammalian hair follicle genesis and its regulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2022, 58 (9): 26- 32. | |
| 50 |
LIU Z , HU X , LIANG Y , et al. Glucocorticoid signaling and regulatory T cells cooperate to maintain the hair-follicle stem-cell niche[J]. Nat Immunol, 2022, 23 (7): 1086- 1097.
doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01244-9 |
| 51 |
SAXENA N , MOK K W , RENDL M . An updated classification of hair follicle morphogenesis[J]. Exp Dermatol, 2019, 28 (4): 332- 344.
doi: 10.1111/exd.13913 |
| 52 |
ZHAO B , LI J , ZHANG X , et al. Exosomal miRNA-181a-5p from the cells of the hair follicle dermal papilla promotes the hair follicle growth and development via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2022, 207, 110- 120.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.177 |
| 53 |
HE M , LV X , CAO X , et al. SOX18 promotes the proliferation of dermal papilla cells via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (23): 16672.
doi: 10.3390/ijms242316672 |
| 54 |
ZHOU H , HUANG S , LV X , et al. Effect of CUX1 on the proliferation of Hu sheep dermal papilla cells and on the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Genes, 2023, 14 (2): 423.
doi: 10.3390/genes14020423 |
| 55 |
LIU S , LEASK A . CCN2 modulates hair follicle cycling in mice[J]. Mol Biol Cell, 2013, 24 (24): 3939- 3944.
doi: 10.1091/mbc.e13-08-0472 |
| 56 |
XIAO S , WANG J , CHEN Q , et al. The mechanism of activated platelet-rich plasma supernatant promotion of hair growth by cultured dermal papilla cells[J]. J Cosmet Dermatol, 2019, 18 (6): 1711- 1716.
doi: 10.1111/jocd.12919 |
| 57 |
NISSIMOV J N , DAS C A . Hair curvature: a natural dialectic and review[J]. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc, 2014, 89 (3): 723- 766.
doi: 10.1111/brv.12081 |
| 58 |
LU Q , GAO Y , FAN Z , et al. Amphiregulin promotes hair regeneration of skin-derived precursors via the PI3K and MAPK pathways[J]. Cell Proli, 2021, 54 (9): e13106.
doi: 10.1111/cpr.13106 |
| 59 |
RAMOT Y , BERTOLINI M , BOBOLJOVA M , et al. PPAR-gamma signalling as a key mediator of human hair follicle physiology and pathology[J]. Exp Dermatol, 2020, 29 (3): 312- 321.
doi: 10.1111/exd.14062 |
| 60 |
WANG E , HAREL S , CHRISTIANO A M . JAK-STAT signaling jump starts the hair cycle[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2016, 136 (11): 2131- 2132.
doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.08.029 |
| 61 |
HAREL S , HIGGINS C A , CERISE J E , et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of JAK-STAT signaling promotes hair growth[J]. Sci Adv, 2015, 1 (9): e1500973.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500973 |
| 62 |
LIU G , CHENG G , ZHANG Y , et al. Pyridoxine regulates hair follicle development via the PI3K/Akt, Wnt and Notch signalling pathways in rex rabbits[J]. Anim Nutr, 2021, 7 (4): 1162- 1172.
doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2021.09.003 |
| 63 |
CHEN Y , FAN Z , WANG X , et al. PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is essential for de novo hair follicle regeneration[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11 (1): 144.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01650-6 |
| 64 |
RISHIKAYSH P , DEV K , DIAZ D , et al. Signaling involved in hair follicle morphogenesis and development[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15 (1): 1647- 1670.
doi: 10.3390/ijms15011647 |
| 65 |
TU W , CAO Y W , SUN M , et al. mTOR signaling in hair follicle and hair diseases: recent progress[J]. Front Med, 2023, 10, 1209439.
doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1209439 |
| 66 |
LI C , FENG C , MA G , et al. Time-course RNA-seq analysis reveals stage-specific and melatonin-triggered gene expression patterns during the hair follicle growth cycle in Capra hircus[J]. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23 (1): 140.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08331-z |
| 67 | XIONG L , ZHEVLAKOVA I , WEST X Z , et al. TLR2 regulates hair follicle cycle and regeneration via BMP signaling[J]. Elife, 2024, 12, 1- 26. |
| [1] | GU Bo, WANG Anqi, YU Xinmiao, GUO Juntong, YANG Yi, DENG Yijie, JIANG Huaizhi. Construction of Ovarian ceRNA Networks and Screening of Key miRNA in Two Different Breeds of Sheep Based on Whole Transcription Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2765-2777. |
| [2] | WU Qiong, LI Lingdan, YUAN Hui, BIN Chen, DENG Ke, LI Wei, YE Shiyi, LI Guopan, SHEN Qingchun, XIONG Tao. Prokaryotic Expression of PoIFN-α 8s and Identification of Its Activity in vitro and in vivo [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2413-2423. |
| [3] | HUANG Cheng, YANG Zhiyuan, LIN Jian, CHENG Huimin, WANG Mi, MAO Huilin, WANG Guoliang, LIU Guiming, ZHAO Jicheng, LIU Yuehuan. Construction and Efficacy Evaluation of mRNA Vaccines against H9 Subtype Avian Influenza Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1843-1853. |
| [4] | CHEN Qiong, MAO Shuaixiang, WU Longfei, YANG Chuang, SUN Baoli. lncRNA Expression Characteristics in Semitendinosus Muscle of Leiqiong Cattle and Lufeng Cattle and Its ceRNA Network Analysis in Skeletal Muscle Development and Fat Deposition [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1203-1215. |
| [5] | YANG Yang, LI Liangyuan, WAN Pengcheng, LU Shouliang, LIU Changbin, YANG Hua, WANG Limin, DAI Rong, ZHOU Ping. Screening and Analysis of Core Genes and Key lncRNAs for Seasonal Estrus Traits in Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1264-1277. |
| [6] | LU Na, GAO Yu, ZHAO Jiawei, SU Di, CHEN Jialei, LUO Zhongli. Construction and Characterization of Transcription Vectors for Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus mRNA Vaccines [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 803-813. |
| [7] | ZHOU Xianshan, HUANG Shihui, NIU Xi, RAN Xueqin, WANG Jiafu. Differential Expression Study of Structural Variation in the Ubiquitin Ligase 2 Gene of Xiang Pigs with Wrinkled Skin [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 136-146. |
| [8] | Yan ZHANG, Meijin WU, Jiahao ZHOU, Hongxiu DIAO. The Effect of Doxorubicin Treatment on the Differential Expression of lncRNAs in Canine Mammary Tumor CHMp Cell Line [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2716-2726. |
| [9] | ZHOU Yang, WU Weizi, CAO Weisheng, WANG Fuguang, XU Xiuqiong, ZHONG Wenxia, WU Liyang, YE Jian, LU Shousheng. A Whole Genome Sequencing Method for African Swine Fever Virus based on Nanopore Sequencing Technology was Established [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2080-2089. |
| [10] | LIU Weiye, HUANG Xuewei. Research Progress of Non-coding RNA in Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Infection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1488-1498. |
| [11] | CAO Yuzhu, XING Yuxin, MA Chenglin, GUAN Hongbo, JIA Qihui, KANG Xiangtao, TIAN Yadong, LI Zhuanjian, LIU Xiaojun, LI Hong. Biological Characterization of Chicken FGF6 Gene and Association of Its Polymorphisms with Economic Traits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1536-1550. |
| [12] | YANG Yang, YU Qian, LIU Yucheng, YANG Hua, ZHAO Zhuo, WANG Limin, ZHOU Ping, YANG Qingyong, DAI Rong. Identification and Tissue Expression Analysis of the Sheep MYL Gene Family [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1551-1564. |
| [13] | TIAN Rui, XU Sixiang, XIE Feng, LIU Guangjin, WANG Gang, LI Qingxia, DAI Lei, XIE Guoxin, ZHANG Qiongwen, LU Yajing, WANG Guangwen, WANG Jinxiu, ZHANG Wei. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Genome of Clostridium perfringens Isolated from Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1707-1715. |
| [14] | Huan WANG, Taoyu CHEN, Hui WU, Yong MENG, Shiyuan LI, Hejie QIAN, Shihua NIU, Churiga MAN, Qiaoling CHEN, Hongyan GAO, Li DU, Fengyang WANG, Si CHEN. Polymorphism Analysis of the ATG16L2 Gene Promoter Region in Hainan Black Goat [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 4980-4991. |
| [15] | Xiaokun LIN, Mengmeng DU, Lisheng ZHOU, Zhengang HUANG, Di WANG, Donghui ZHOU, Xinxin CAO, Jianning HE, Jinshan ZHAO, Hegang LI. Genome-Wide Association Study of Wool Economic Traits in Aohan Fine Wool Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4346-4359. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||