





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (7): 2951-2962.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.07.015
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wanqing LI1( ), Yaqi ZENG1,2, Xinkui YAO1,2, Jianwen WANG1,2, Xinxin YUAN1, Chen MENG1, Yuanfang SUN1, Xuan PENG1, Jun MENG1,2,*(
), Yaqi ZENG1,2, Xinkui YAO1,2, Jianwen WANG1,2, Xinxin YUAN1, Chen MENG1, Yuanfang SUN1, Xuan PENG1, Jun MENG1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-12-25
Online:2024-07-23
Published:2024-07-24
Contact:
Jun MENG
E-mail:1085037205@qq.com;junm86@qq.com
CLC Number:
Wanqing LI, Yaqi ZENG, Xinkui YAO, Jianwen WANG, Xinxin YUAN, Chen MENG, Yuanfang SUN, Xuan PENG, Jun MENG. Comparative Analysis of Blood Transcriptome in Yili Horses Bred for Meat Performance[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2951-2962.
Table 1
Sequence information for qRT-PCR primers"
| 基因Gene | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequence | 片段长度/bp Amplicon length | 退火温度/℃ The annealing temperature |
| CTSH | S: GAACCCTACTTTCTGCCTGTGAC | 296 | 60 |
| A: TCCACAGCAACCAGGTCTTCA | |||
| SSTR1 | S: TGCCTGTGCTACGTGCTCATC | 179 | 60 |
| A: TGCTCTGCGAACACGTTGAC | |||
| APOA1 | S: AGGCCAGCGAGCATCTGAA | 148 | 60 |
| A: CACTGGGGAGTCAGCTGCTT | |||
| ITM2A | S: ATCATTGATGTGCCTGTCCCTAG | 244 | 60 |
| A: GAATCTCCTCCACAGCAACCAG | |||
| ENPP1 | S: CATCAGAGCTTTGCAGAGGGTG | 205 | 60 |
| A: CAGTCGAGCTGCTGGTCCATAT | |||
| ADCY5 | S: GTGTTTCCTGCTGCTGACCTT | 241 | 60 |
| A: CTGGCTGGCACTGATGTTGT | |||
| GAPDH | S: ATGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTAAACG | 154 | 60 |
| A: CATGGGTGGAATCATACTGAAACA |
Table 2
RNA-seq data quality inspection"
| 样品名称 Sample name | 有效数据 Clean reads | 总碱基数/bp Clean bases | Q20/% | Q30/% | GC含量/% GC content |
| HW_1 | 43 047 628 | 6.46G | 97.76 | 93.86 | 53.26 |
| HW_2 | 42 895 758 | 6.43G | 98.05 | 94.54 | 55.99 |
| HW_3 | 42 721 614 | 6.41G | 97.36 | 92.74 | 55.84 |
| HW_4 | 41 509 194 | 6.23G | 98.04 | 94.5 | 55.07 |
| HW_5 | 49 324 110 | 7.40G | 98.03 | 94.48 | 53.94 |
| HW_6 | 44 421 312 | 6.66G | 97.94 | 94.23 | 54.15 |
| LW_1 | 42 901 198 | 6.44G | 97.79 | 93.84 | 55.44 |
| LW_2 | 42 992 694 | 6.45G | 98.01 | 94.49 | 54.47 |
| LW_3 | 38 784 926 | 5.82G | 98.02 | 94.52 | 57.08 |
| LW_4 | 41 383 728 | 6.21G | 97.93 | 94.45 | 53.49 |
| LW_5 | 46 199 410 | 6.93G | 97.93 | 94.27 | 56.15 |
| LW_6 | 47 328 778 | 7.10G | 97.96 | 94.32 | 55.69 |
Table 3
Comparison between Reads and reference genomes"
| 样品名称 Sample name | 有效数据 Total reads | 有效数据比对占比 Total mapped | 未比对 Unsplice mapped | 唯一比对 Unique mapped | 多处比对 Multi mapped |
| HW_1 | 43 047 628 | 40 667 421(94.47%) | 21 706 035(50.42%) | 39 266 595(91.22%) | 1 400 826(3.25%) |
| HW_2 | 42 895 758 | 40 906 325(95.36%) | 21 879 648(51.01%) | 39 602 495(92.32%) | 1 303 830(3.04%) |
| HW_3 | 42 721 614 | 40 343 393(94.43%) | 21 195 116(49.61%) | 38 947 985(91.17%) | 1 395 408(3.27%) |
| HW_4 | 41 509 194 | 39 685 953(95.61%) | 21 551 802(51.92%) | 38 402 846(92.52%) | 1 283 107(3.09%) |
| HW_5 | 49 324 110 | 46 657 915(94.59%) | 23 415 561(47.47%) | 44 904 565(91.04%) | 1 753 350(3.55%) |
| HW_6 | 44 421 312 | 41 947 291(94.43%) | 21 270 572(47.88%) | 40 545 723(91.28%) | 1 401 568(3.16%) |
| LW_1 | 42 901 198 | 40 815 273(95.14%) | 20 699 091(48.25%) | 39 346 774(91.71%) | 1 468 499(3.42%) |
| LW_2 | 42 992 694 | 40 845 397(95.01%) | 21 132 998(49.15%) | 39 490 684(91.85%) | 1 354 713(3.15%) |
| LW_3 | 38 784 926 | 36 540 202(94.21%) | 18 138 227(46.77%) | 35 206 863(90.77%) | 1 333 339(3.44%) |
| LW_4 | 41 383 728 | 39 309 987(94.99%) | 21 288 912(51.44%) | 37 975 268(91.76%) | 1 334 719(3.23%) |
| LW_5 | 46 199 410 | 43 935 460(95.10%) | 23 816 526(51.55%) | 42 427 868(91.84%) | 1 507 592(3.26%) |
| LW_6 | 47 328 778 | 45 111 705(95.32%) | 24 740 501(52.27%) | 43 491 387(91.89%) | 1 620 318(3.42%) |

Fig. 4
Volcano diagram of differentially expressed genes The horizontal axis represents the change in gene expression multiples in different samples, and the vertical axis represents the statistical significance of the difference at gene expression levels. The dots on the right side of the dotted line represent upregulated differentially expressed genes (up), the dots on the left side of the dotted line represent downregulated differentially expressed genes (down), and the dots in the middle of the two dotted lines represent genes (no) that do not meet the threshold screening"
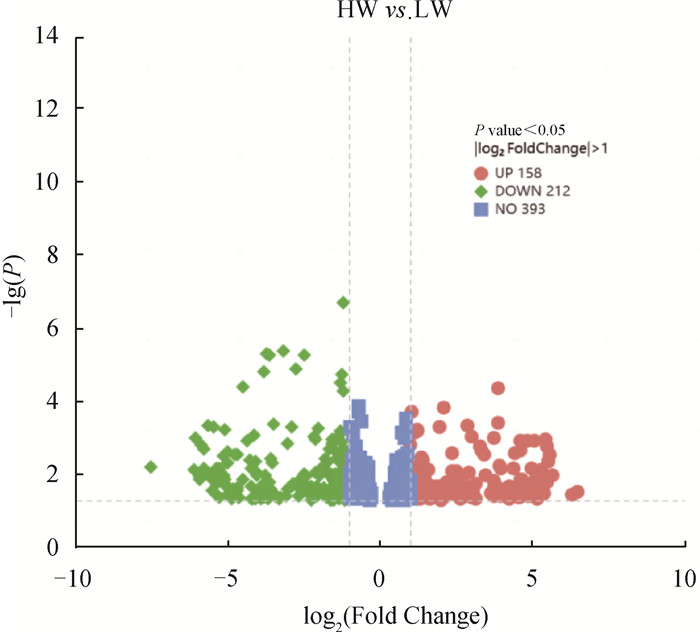

Fig. 6
KEGG enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes The horizontal axis represents the ratio of the number of differentially expressed genes annotated to the KEGG pathway to the total number of differentially expressed genes, the vertical axis represents the KEGG pathway, the size of the dots represents the number of genes annotated to the KEGG pathway, and the color from yellow to red represents the significance degree of enrichment"

| 1 | 王建文, 李林玲, 王镜力, 等. 伊犁马ACTN3基因外显子多态性研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2018, 49 (6): 1299- 1306. |
| WANG J W , LI L L , WANG J L , et al. Analysis on ACTN3 gene exon polymorphism of Yili horse[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2018, 49 (6): 1299- 1306. | |
| 2 | 彭宣, 王彤亮, 鲍奕柯, 等. 伊犁马体尺与心脏结构和功能参数的关联性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (11): 4615- 4624. |
| PENG X , WANG T L , BAO Y K , et al. Correlation analysis between body size and cardiac structural and functional parameters in Yili horses[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (11): 4615- 4624. | |
| 3 |
李涛涛, 聂清清, 王芊与, 等. 基于SWOT分析伊犁马产业发展策略探索[J]. 农业技术与装备, 2023, (5): 54- 56.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-887X.2023.05.020 |
|
LI T T , NIE Q Q , WANG Q Y , et al. Research on the development strategy of Yili horse industry based on SWOT analysis[J]. Agricultural Technology & Equipment, 2023, (5): 54- 56.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-887X.2023.05.020 |
|
| 4 | 孟军. 昭苏马场伊犁马杂交改良效果初步研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2010. |
| MENG J. A primary study on improved effect of Yili horse by hybridized in Zhaosu stud[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2010. (in Chinese) | |
| 5 |
吐尔逊江·吾木尔艾力, 喀尔肯·马木尔汗, 团勇, 等. 伊犁马青年种公马体尺体重相关性研究[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2022, 42 (1): 72- 75.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3887.2022.01.016 |
|
TUERXUNJIANG·WUMUERAILI , KAERKEN·MAMUERHAN , TUAN Y , et al. Study on correlation between body size and weight of young Ili stallion[J]. China Herbivore Science, 2022, 42 (1): 72- 75.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3887.2022.01.016 |
|
| 6 | 闫睛. 伊犁马HSL、DGAT1和LPL基因多态性及其与肉质性状相关性研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2020. |
| YAN Q. The correlation analysis research between HSL, DGAT1 and LPL gene polymorphism with meat quality traits in Yili horse[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 7 |
STANISŁAWCZYK R , ŻUREK J , RUDY M , et al. Influence of horse age on carcass tissue composition and horsemeat quality: exploring nutritional and health benefits for gourmets[J]. Appl Sci, 2023, 13 (20): 11293.
doi: 10.3390/app132011293 |
| 8 |
杨红, 徐明华. 1961—2010年世界马肉生产与效率分析[J]. 经济研究导刊, 2012, (29): 31- 33.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-291X.2012.29.015 |
|
YANG H , XU M H . The horse meat production in the world and its efficiency analysis during the year 1961—2010[J]. Economic Research Guide, 2012, (29): 31- 33.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-291X.2012.29.015 |
|
| 9 | 孙燕勇, 马凤英, 郭丽丽, 等. 动物血液转录组测序的应用研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2023, 50 (2): 460- 468. |
| SUN Y Y , MA F Y , GUO L L , et al. Advances on the application of animal blood transcriptome[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 50 (2): 460- 468. | |
| 10 |
ZHENG X D , CHENG J , QIN W J , et al. Whole transcriptome analysis identifies the taxonomic status of a new Chinese native cattle breed and reveals genes related to body size[J]. Front Genet, 2020, 11, 562855.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.562855 |
| 11 |
ROPKA-MOLIK K , STEFANIUK-SZMUKIER M , ŻUKOWSKI K , et al. Transcriptome profiling of Arabian horse blood during training regimens[J]. BMC Genet, 2017, 18 (1): 31.
doi: 10.1186/s12863-017-0499-1 |
| 12 |
GRIFFITHS J I , WALLET P , PFLIEGER L T , et al. Circulating immune cell phenotype dynamics reflect the strength of tumor-immune cell interactions in patients during immunotherapy[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117 (27): 16072- 16082.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1918937117 |
| 13 |
DE LIMA V A , HANSEN M , SPANGGAARD I , et al. Immune cell profiling of peripheral blood as signature for response during checkpoint inhibition across cancer types[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11, 558248.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.558248 |
| 14 |
SANGLARD L P , NASCIMENTO M , MORIEL P , et al. Impact of energy restriction during late gestation on the muscle and blood transcriptome of beef calves after preconditioning[J]. BMC Genomics, 2018, 19 (1): 702.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5089-8 |
| 15 | YU H W , RAZA S H A , PAN Y T , et al. Integrative analysis of blood transcriptomics and metabolomics reveals molecular regulation of backfat thickness in Qinchuan cattle[J]. Animals (Basel), 2023, 13 (6): 1060. |
| 16 | 韩信嵘. 基于转录组测序分析中国西门塔尔牛和安格斯牛脂肪沉积相关基因的差异表达[D]. 通辽: 内蒙古民族大学, 2021. |
| HAN X R. Analysis of differentially expressed genes related to fat deposition in simmental and angus based on transcriptome sequencing[D]. Tongliao: Inner Mongolia Minzu University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 17 | 李娜. miRNA、mRNA调控新疆褐牛和哈萨克牛肉质成脂性状分子机制研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2020. |
| LI N. Study on molecular mechanism of miRNA and mRNA regulating the meaty fat-forming traits of Xinjiang brown cattle and Kazakh cattle[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 18 |
李兰会, 张志胜, 孙丰梅, 等. 钙蛋白酶嫩化肉类机理[J]. 生命的化学, 2003, 23 (3): 212- 214.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1336.2003.03.019 |
|
LI L H , ZHANG Z S , SUN F M , et al. Theory of calpains in meat tenderness and its developing[J]. Chemistry of Life, 2003, 23 (3): 212- 214.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1336.2003.03.019 |
|
| 19 |
CHEEDIPUDI S M , ASGHAR S , MARIAN A J . Genetic ablation of the DNA damage response pathway attenuates lamin-associated dilated cardiomyopathy in mice[J]. JACC Basic Transl Sci, 2022, 7 (12): 1232- 1245.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.06.015 |
| 20 |
TRIANTAFYLLOU A , RUGGLES N . Lysosomal and cytoskeletal events in epithelial salivary tumours as assessed by imunohistochemistry for CD63 and HSP27[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2022, 229, 153691.
doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153691 |
| 21 | 黄建文. 天府肉羊CTSL、CTSH和CTSF基因克隆及其在部分组织器官中的表达分析[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2014. |
| HUANG J W. Cloning, sequence analysis and partial tissue expression of CTSL, CTSH and CTSF gene in Tianfu goat[D]. Ya'an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese) | |
| 22 | 傅楚涵. CTSHD和COSTD的制备方法及其减肥功能的研究[D]. 广州: 广东药科大学, 2018. |
| FU C H. Study on the preparation of CTSHD and COSTD and their anti-obesity effect[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2018. (in Chinese) | |
| 23 |
FONTANESI L , SPERONI C , BUTTAZZONI L , et al. Association between polymorphisms in cathepsin and cystatin genes with meat production and carcass traits in Italian Duroc pigs: confirmation of the effects of a cathepsin L (CTSL) gene marker[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2012, 39 (1): 109- 115.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-0715-4 |
| 24 |
HEO Y , YOON E , JEON Y E , et al. Cryo-EM structure of the human somatostatin receptor 2 complex with its agonist somatostatin delineates the ligand-binding specificity[J]. eLife, 2022, 11, e76823.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.76823 |
| 25 |
NESPECA M , GIORGETTI C , NOBILE S , et al. Does whole-body hypothermia in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy affect surfactant disaturated-phosphatidylcholine kinetics?[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11 (4): e0153328.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153328 |
| 26 |
JIN Q J , SUN J J , FANG X T , et al. Molecular characterization and polymorphisms of the caprine Somatostatin (SST) and SST Receptor 1 (SSTR1) genes that are linked with growth traits[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2011, 38 (5): 3129- 3135.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-9983-7 |
| 27 | 赵芳芳. IGF1、SSTR1、GSKIP、CAPN4和FTO基因的遗传变异与绵羊生长和胴体性状关联性研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2018. |
| ZHAO F F. Variation of IGFl, SSTRI, GSKIP, CAPN4 and FTO genes associated with ovine growth and carcass traits[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese) | |
| 28 |
TURAL U , IOSIFESCU D V . Adiponectin in anorexia nervosa and its modifiers: A meta-regression study[J]. Int J Eat Disorder, 2022, 55 (10): 1279- 1290.
doi: 10.1002/eat.23753 |
| 29 |
RANA M N , NEELAND I J . Adipose tissue inflammation and cardiovascular disease: an update[J]. Curr Diabetes Rep, 2022, 22 (1): 27- 37.
doi: 10.1007/s11892-021-01446-9 |
| 30 |
GAN L , YAN J , LIU Z J , et al. Adiponectin prevents reduction of lipid-induced mitochondrial biogenesis via AMPK/ACC2 pathway in chicken adipocyte[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2015, 116 (6): 1090- 1100.
doi: 10.1002/jcb.25064 |
| 31 |
YAN J , YANG H , GAN L , et al. Adiponectin-impaired adipocyte differentiation negatively regulates fat deposition in chicken[J]. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr, 2014, 98 (3): 530- 537.
doi: 10.1111/jpn.12107 |
| 32 |
MOREIRA G C M , BOSCHIERO C , CESAR A S M , et al. A genome-wide association study reveals novel genomic regions and positional candidate genes for fat deposition in broiler chickens[J]. BMC Genomics, 2018, 19 (1): 374.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4779-6 |
| 33 |
WANG Z G , WANG L , ZHANG Z Z , et al. Apolipoprotein A-Ⅳ involves in glucose and lipid metabolism of rat[J]. Nutr Metab (Lond), 2019, 16, 41.
doi: 10.1186/s12986-019-0367-2 |
| 34 |
KIRCHNER J , BEVAN M J . Itm2a is induced during thymocyte selection and T cell activation and causes downregulation of Cd8 when overexpressed in Cd4+Cd8+ double positive thymocytes[J]. J Exp Med, 1999, 190 (2): 217- 228.
doi: 10.1084/jem.190.2.217 |
| 35 |
BARBER T D , BARBER M C , TOMESCU O , et al. Identification of target genes Regulated by PAX3 and PAX3-FKHR in embryogenesis and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma[J]. Genomics, 2002, 79 (3): 278- 284.
doi: 10.1006/geno.2002.6703 |
| 36 |
VAN DEN PLAS D , MERREGAERT J . Constitutive overexpression of the integral membrane protein ITM2A enhances myogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells[J]. Cell Biol Int, 2004, 28 (3): 199- 207.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2003.11.019 |
| 37 |
LIU G Y , GE C R , ZHANG X , et al. Isolation, sequence identification and tissue expression distribution of three novel porcine genes--RAB14, S35A3 and ITM2A[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2008, 35 (2): 201- 206.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-007-9071-9 |
| 38 |
TUKIAINEN T , PIRINEN M , SARIN A P , et al. Chromosome X-wide association study identifies loci for fasting insulin and height and evidence for incomplete dosage compensation[J]. PLoS Genet, 2014, 10 (2): e1004127.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004127 |
| 39 |
TUCKERMANN J P , PITTOIS K , PARTRIDGE N C , et al. Collagenase-3 (MMP-13) and integral membrane protein 2A (ITM2A) are marker genes of chondrogenic/osteoblastic cells in bone formation: sequential temporal, and spatial expression of ITM2A, alkaline phosphatase, MMP-13, and osteocalcin in the mouse[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2000, 15 (7): 1257- 1265.
doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.7.1257 |
| [1] | WU Yongjie, XU Yinghuan, LIU Tengfei, MA Lin, CHEN Hong, XU Yongping. Effect of Scrotal Hyperthermia on Structure and Function of Blood-testis Barrier in Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2973-2982. |
| [2] | XU Shiyuan, ZHANG Liuguang, LIU Songqi, WU Kaihui, WANG Chao, WANG Dong, PANG Yunwei. Study on the Effects and Mechanism of ART3 in Regulating Spermatogenesis in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2995-3010. |
| [3] | Mingliang HE, Xiaoyang LÜ, Yongqing JIANG, Zhenghai SONG, Yeqing WANG, Huiguo YANG, Shanhe WANG, Wei SUN. Function Analysis of SOX18 in Hu Sheep Hair Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells Based on Transcriptome Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2409-2420. |
| [4] | Kaihui WU, Liuguang ZHANG, Chao WANG, Shiyuan XU, Songqi LIU, Kaimin YUAN, Dong WANG, Yunwei PANG. Study on the Mechanism of Melatonin Relieving Testicular Damage in Mice Induced Busulfan [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2486-2497. |
| [5] | SUN Wenli, WANG Haoqi, ZE Licuo, GAO Yufan, ZHANG Feifan, ZHANG Jian, DUAN Mengqi, SHANG Peng, QIANG Bayangzong. Polymorphism of Pro-Inflammatory Factors (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) in Tibetan Pigs and Its Association Analysis with Immune Traits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1958-1969. |
| [6] | CHEN Zhe, QU Xiaolu, GUO Binbin, SUN Xuefeng, YAN Leyan. Study on Candidate Genes for Green Light Affecting Early Development of Goose Embryo Heart Based on Transcriptome Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1978-1988. |
| [7] | ZHANG Ying, SONG Chunlian, ZHANG Ying, SHEN Hong, SHU Xianghua, YANG Honggui. Study on the Damage of Blood-brain Barrier by Tight Junction Protein Mediated by MMP-9 in Pseudorabies Virus-infected Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2186-2194. |
| [8] | XU Junjie, ZHANG Lutong, WANG Jinjie, CHEN Xiaochen, HE Weixian, CAI Chuanjiang, CHU Guiyan, YANG Gongshe. Exploring the Effect of Epimedium on Estrus of Gilts Based on Multiomics and Network Pharmacology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1615-1628. |
| [9] | WANG Xin, NIE Tong, LI Aqun, MA Jun. Hesperidin Alleviates High-fat-diet Induced Hepatic Oxidative Stress in Mice via Oxidative Phosphorylation Pathway [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1302-1313. |
| [10] | GAO Yawei, PENG Di, SUN Zhaoyang, YAN Ziyue, CUI Kai, MA Zefang. Mining the Molecular Mechanism of Exogenous Melatonin Affecting the Development of Mink Ovary Based on Transcriptome Data [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 607-618. |
| [11] | LIU Yili, TANG Jiao, MIN Qi, YANG Lu, WANG Zening, HU Lian, ZHAO Di, JIANG Mingfeng. Mining Key Candidate Genes of Development and Metabolism in Yak Abomasum Based on Transcriptome Data [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 153-168. |
| [12] | YU Zhou, YANG Baigao, ZHANG Hang, XU Xi, ZHANG Peipei, FENG Xiaoyi, CAO Jianhua, NIU Yifan, DU Weihua, HAO Haisheng, ZHU Huabin, ABULIZI·Wusiman, ZHAO Xueming. Research Progress of Estrus Markers in Dairy Buffalo [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(9): 3623-3630. |
| [13] | HU Ting, ZHANG Yonghong, HOU Xiaolin, YAO Hua, CUI Defeng, PAN Zaozao, ZHANG Lingyu, ZHANG Jiaxi, WU Qiong. The Effects of Bisphenol A on Inflammation and Amino Acid Metabolism Pathways in Porcine Testis Sertoli Cells Based on Transcriptome Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 2858-2871. |
| [14] | LIU Hang, WANG Huanhuan, GE Ying, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Weiwu, WEI Yinghui, LI Qinghai, FAN Jinghui, ZHANG Xuedong. Screening of Candidate Genes of Skin Color of Black-Bone Chicken Based on Transcriptome and Proteome [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2320-2329. |
| [15] | BAI Lu, WANG Mengjie, MA Xiaochun, HE Zhengxiao, KONG Fuli, LIU Dawei, YING Fan, ZHU Dan, ZHAO Guiping, WEN Jie, LIU Ranran. Study of the Alteration of Wooden Breast Histological and Molecular Regulatory Pathways in Chickens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 1915-1926. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||