





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 5567-5574.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.021
• Animal Biotechnology and Reproduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
YAN Chao1,2( ), LIU Yonggang2, XIE Hao1, PENG Cuiting1, ZHANG Caiyong1, ZHAO Yulan1,3, QI Lin1, CHEN Zhilong1,3,4,5,*(
), LIU Yonggang2, XIE Hao1, PENG Cuiting1, ZHANG Caiyong1, ZHAO Yulan1,3, QI Lin1, CHEN Zhilong1,3,4,5,*( ), TANG Zhonglin1,3,4,5,*(
), TANG Zhonglin1,3,4,5,*( )
)
Received:2024-04-15
Online:2024-12-23
Published:2024-12-27
Contact:
CHEN Zhilong, TANG Zhonglin
E-mail:15170529593@163.com;chenzhilong@caas.cn;tangzhonglin@caas.cn
CLC Number:
YAN Chao, LIU Yonggang, XIE Hao, PENG Cuiting, ZHANG Caiyong, ZHAO Yulan, QI Lin, CHEN Zhilong, TANG Zhonglin. Detection of Gene Expression in Trace Cells of Early Porcine Embryo by Pre-amplified Quantitative PCR[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5567-5574.
Table 1
Information of primers"
| 基因 Gene | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primers sequence |
| EF1A1 | F: AATGCGGTGGGATCGACAAA |
| R: CACGCTCACGTTCAGCCTTT | |
| OCT4 | F: GTGTTCAGCCAAACGACCAT |
| R: TTGCCTCTCACTCGGTTCTC | |
| NANOG | F: GGTTTATGGGCCTGAAGAAA |
| R: GATCCATGGAGGAAGGAAGA | |
| SOX2 | F: ATGCACAACTCGGAGATCAG |
| R: TATAATCCGGGTGCTCCTTC | |
| HADAC1 | F: AGGGCACCAAGAGGAAAGTC |
| R: GAGGGCGATAGATTTCCATT | |
| HADAC2 | F: AGCCAGATGTCTTCAAAAAG |
| R: ACAGAGCCAAATCAGAACAG | |
| MBD3 | F: ACCTGAGCACCTTTGATTTCCG |
| R: CGAAGGCGTTCAGACCACTC | |
| HAT1 | F: ACGCCTCGCTCAAGAGTAGA |
| R: AGTCATCATCTGATTTCACA | |
| CBP | F: GCGTCCTCCAAGTATTACCC |
| R: GAGCAGGGTCTAAGAGAGTG | |
| DUXC | F: CAGCCAAGTCCAGTTCTGCA |
| R: AGTGCAGGTCTTCACTGGGT |

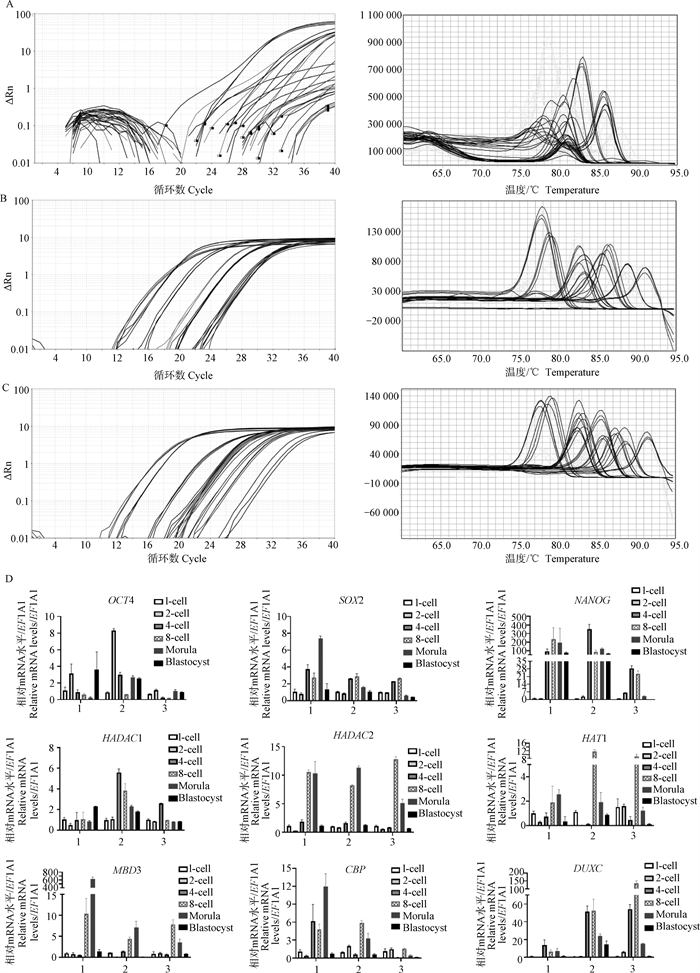
Fig. 2
The amplification and melt curve plots of qPCR using different concentration templates A. Amplification plot of qPCR using different cell numbers; B. Melt curve plot of qPCR using different cell numbers; C. Amplification plot of qPCR from samples wtih different dilution multiples; D. Melt curve plot from samples with different dilution multiples. 5. Dilute the sample 5 times; 100. Dilute the sample 100 times; 1 000. Dilute the sample 1 000 times; 20 000. Dilute the sample 20 000 times"


Fig. 3
The expression of different genes related to pluripotency and histone modification in pig embryos at different developmental stages of pig embryo using 3 qPCR methods A. The amplification and melt curves plot from traditional RT-qPCR; B. The amplification and melt curves plot from preamplifcation qPCR by cDNA; C. The amplification and melt curves plot from preamplifcation qPCR by samples; D. Results of the relative expression levels of different genes using 3 qPCR methods. 1. Traditional RT-qPCR; 2. Preamplifcation qPCR by cDNA; 3. Preamplifcation qPCR by samples"
| 1 |
ZHU W , BU G W , HU R F , et al. KLF4 facilitates chromatin accessibility remodeling in porcine early embryos[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2024, 67 (1): 96- 112.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-022-2349-9 |
| 2 |
BU G W , ZHU W , LIU X , et al. Coordination of zygotic genome activation entry and exit by H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in porcine early embryos[J]. Genome Res, 2022, 32 (8): 1487- 1501.
doi: 10.1101/gr.276207.121 |
| 3 |
HE T Y , PENG J Y , YANG S , et al. SINE-associated LncRNA SAWPA regulates porcine zygotic genome activation[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2024, 11 (2): 2307505.
doi: 10.1002/advs.202307505 |
| 4 |
GAO R N , LI Q C , QIU M Y , et al. Serum exosomal miR-192 serves as a potential detective biomarker for early pregnancy screening in sows[J]. Anim Biosci, 2023, 36 (9): 1336- 1349.
doi: 10.5713/ab.22.0422 |
| 5 |
ZOLINI A M , BLOCK J , RABAGLINO M B , et al. Genes associated with survival of female bovine blastocysts produced in vivo[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2020, 382 (3): 665- 678.
doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03257-y |
| 6 |
GROFF A F , RESETKOVA N , DIDOMENICO F , et al. RNA-seq as a tool for evaluating human embryo competence[J]. Genome Res, 2019, 29 (10): 1705- 1718.
doi: 10.1101/gr.252981.119 |
| 7 | LUO Q K , ZHANG H . Emergence of bias during the synthesis and amplification of cDNA for scRNA-seq[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2018, 1068, 149- 158. |
| 8 |
STÅHLBERG A , KUBISTA M . The workflow of single-cell expression profiling using quantitative real-time PCR[J]. Expert Rev Mol Diagn, 2014, 14 (3): 323- 331.
doi: 10.1586/14737159.2014.901154 |
| 9 |
KRONEIS T , JONASSON E , ANDERSSON D , et al. Global preamplification simplifies targeted mRNA quantification[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7, 45219.
doi: 10.1038/srep45219 |
| 10 | SEKOVANIĆ A , DOROTIĆ A , JURASOVIĆ J , et al. Pre-amplification as a method for improvement of quantitative RT-PCR analysis of circulating miRNAs[J]. Biochem Med (Zagreb), 2021, 31 (1): 010901. |
| 11 |
XIAO Y , SOSA F , DE ARMAS L R , et al. An improved method for specific-target preamplification PCR analysis of single blastocysts useful for embryo sexing and high-throughput gene expression analysis[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2021, 104 (3): 3722- 3735.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-19497 |
| 12 |
MOGHADDASZADEH-AHRABI S , FARAJNIA S , RAHIMI-MIANJI G , et al. A short and simple improved-primer extension preamplification (I-PEP) procedure for whole genome amplification (WGA) of bovine cells[J]. Anim Biotechnol, 2012, 23 (1): 24- 42.
doi: 10.1080/10495398.2011.630907 |
| 13 |
SUN S Q , ABOELENAIN M , ARIAD D , et al. Identifying risk variants for embryo aneuploidy using ultra-low coverage whole-genome sequencing from preimplantation genetic testing[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2023, 110 (12): 2092- 2102.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2023.11.002 |
| 14 |
ANDERSSON D , AKRAP N , SVEC D , et al. Properties of targeted preamplification in DNA and cDNA quantification[J]. Expert Rev Mol Diagn, 2015, 15 (8): 1085- 1100.
doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1057124 |
| 15 | YUAN Y , SPATE L D , REDEL B K , et al. Quadrupling efficiency in production of genetically modified pigs through improved oocyte maturation[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2017, 114 (29): E5796- E5804. |
| 16 |
YOSHIOKA K , SUZUKI C , TANAKA A , et al. Birth of piglets derived from porcine zygotes cultured in a chemically defined medium[J]. Biol Reprod, 2002, 66 (1): 112- 119.
doi: 10.1095/biolreprod66.1.112 |
| 17 |
ZHOU F , WANG R , YUAN P , et al. Reconstituting the transcriptome and DNA methylome landscapes of human implantation[J]. Nature, 2019, 572 (7771): 660- 664.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1500-0 |
| 18 |
WU Y , XU X C , QI M J , et al. N6-methyladenosine regulates maternal RNA maintenance in oocytes and timely RNA decay during mouse maternal-to-zygotic transition[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2022, 24 (6): 917- 927.
doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-00915-x |
| 19 |
XU R M , ZHU Q S , ZHAO Y Y , et al. Unreprogrammed H3K9me3 prevents minor zygotic genome activation and lineage commitment in SCNT embryos[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14 (1): 4807.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40496-3 |
| 20 |
LAVAGI I , KREBS S , SIMMET K , et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals developmental heterogeneity of blastomeres during major genome activation in bovine embryos[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8 (1): 4071.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22248-2 |
| 21 |
KOLODZIEJCZYK A A , LÖNNBERG T . Global and targeted approaches to single-cell transcriptome characterization[J]. Brief Funct Genomics, 2018, 17 (4): 209- 219.
doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elx025 |
| 22 |
KORENKOVÁ V , SCOTT J , NOVOSADOVÁ V , et al. Pre-amplification in the context of high-throughput qPCR gene expression experiment[J]. BMC Mol Biol, 2015, 16, 5.
doi: 10.1186/s12867-015-0033-9 |
| 23 |
HERNÁNDEZ-ARTEAGA S , LÓPEZ-REVILLA R . Ultrasensitive quantitation of human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncogene sequences by nested real time PCR[J]. Infect Agent Cancer, 2010, 5, 9.
doi: 10.1186/1750-9378-5-9 |
| 24 |
XIAO Y , SOSA F , DE ARMAS L R , et al. An improved method for specific-target preamplification PCR analysis of single blastocysts useful for embryo sexing and high-throughput gene expression analysis[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2021, 104 (3): 3722- 3735.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-19497 |
| 25 |
ANDERSSON D , AKRAP N , SVEC D , et al. Properties of targeted preamplification in DNA and cDNA quantification[J]. Expert Rev Mol Diagn, 2015, 15 (8): 1085- 1100.
doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1057124 |
| 26 |
JANNAMAN E A , XIAO Y , HANSEN P J . Actions of colony-stimulating factor 3 on the maturing oocyte and developing embryo in cattle[J]. J Anim Sci, 2020, 98 (4): skaa115.
doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa115 |
| 27 |
WU K L , FAN D D , ZHAO H , et al. Dynamics of histone acetylation during human early embryogenesis[J]. Cell Discov, 2023, 9 (1): 29.
doi: 10.1038/s41421-022-00514-y |
| 28 |
YANG G , ZHANG L F , LIU W Q , et al. Dux-mediated corrections of aberrant H3K9ac during 2-cell genome activation optimize efficiency of somatic cell nuclear transfer[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28 (1): 150- 163.e5.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.09.006 |
| 29 |
LI L J , LAI F N , HU X Y , et al. Multifaceted SOX2-chromatin interaction underpins pluripotency progression in early embryos[J]. Science, 2023, 382 (6676): eadi5516.
doi: 10.1126/science.adi5516 |
| 30 |
STIRPARO G G , KUROWSKI A , YANAGIDA A , et al. OCT4 induces embryonic pluripotency via STAT3 signaling and metabolic mechanisms[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2021, 118 (3): e2008890118.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008890118 |
| 31 |
LAI F N , LI L J , HU X Y , et al. NR5A2 connects zygotic genome activation to the first lineage segregation in totipotent embryos[J]. Cell Res, 2023, 33 (12): 952- 966.
doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00887-z |
| 32 |
LI X , ZOU C , LI M X , et al. Transcriptome analysis of in vitro fertilization and parthenogenesis activation during early embryonic development in pigs[J]. Genes (Basel), 2021, 12 (10): 1461.
doi: 10.3390/genes12101461 |
| 33 |
WEI Q Q , LI R Q , ZHONG L , et al. Lineage specification revealed by single-cell gene expression analysis in porcine preimplantation embryos[J]. Biol Reprod, 2018, 99 (2): 283- 292.
doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy062 |
| 34 |
KONG Q R , YANG X , ZHANG H , et al. Lineage specification and pluripotency revealed by transcriptome analysis from oocyte to blastocyst in pig[J]. FASEB J, 2020, 34 (1): 691- 705.
doi: 10.1096/fj.201901818RR |
| 35 |
LEE M , CHOI K H , OH J N , et al. SOX2 plays a crucial role in cell proliferation and lineage segregation during porcine pre-implantation embryo development[J]. Cell Prolif, 2021, 54 (8): e13097.
doi: 10.1111/cpr.13097 |
| 36 |
DE MACEDO M P , GLANZNER W G , GUTIERREZ K , et al. Simultaneous inhibition of histone deacetylases and RNA synthesis enables totipotency reprogramming in pig SCNT embryos[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (22): 14142.
doi: 10.3390/ijms232214142 |
| [1] | HU Zeqi, LI Runcheng, TAN Zuming, XIE Xiuyan, WANG Jiangping, QIN Lejuan, LI Rong, GE Meng. Establishment and Preliminary Application of PEDV, PoRVA and PDCoV TaqMan Triple RT-qPCR Assay [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2267-2272. |
| [2] | YANG Yang, YU Qian, LIU Yucheng, YANG Hua, ZHAO Zhuo, WANG Limin, ZHOU Ping, YANG Qingyong, DAI Rong. Identification and Tissue Expression Analysis of the Sheep MYL Gene Family [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1551-1564. |
| [3] | DONG Xinyi, LI Jinqun, CHEN Qinxi, LIAO Ming, CAO Weisheng. Establishment of Blood Nucleic Acid Screening Technology for Subgroup J Avian Leukosis Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1115-1126. |
| [4] | KANG Jia, DUAN Xiangru, YIN Xuejiao, YANG Ruochen, LI Taichun, SHAN Xinyu, CHEN Meijing, ZHANG Yingjie, LIU Yueqin. Effects of Cysteine and Methionine on Secondary Hair Follicle Growth and Hair Dermal Papilla Cell Proliferation in vitro in Cashmere Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 515-527. |
| [5] | Qingzhen SHI, Hongyang XU, Yan ZHANG, Yi ZHANG, Yachun WANG, Jianyong HAN, Li JIANG. Detection and Comparative Analysis of Genomic Genetic Variations in Trace Cells Using Different Methods [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4311-4324. |
| [6] | CHEN Cancan, JIANG Jing, SUN Xiaoyan, REN Hangxing, LI Jie. Expression of AGRP Gene in Goat Tissue and Its Action Mechanism on Melanin Production [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(4): 1441-1451. |
| [7] | ZHAI Gang, GU Wenyuan, LIU Tao, LIU Ying, ZHANG Shuai, FAN Jinghui, ZUO Yuzhu. Establishment of TaqMan Detection Method of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Analysis of Genetic Variation based on S Gene [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(2): 847-854. |
| [8] | JI Zhengyu, NI Mengru, ZHANG Zhaobo, ZHAO Gan, HUANG Zan, LI Pinghua, HUANG Ruihua, HOU Liming. Research on Adipogenic Capacity and Gene Expression Pattern of in Vitro FAPs Cells Derived from Longissimus Dorsi Muscle of Suhuai Pig [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4126-4142. |
| [9] | SANG Lei, CHEN Dongjin, SUN Shikun, GAO Chengfang, WANG Jinxiang, CHEN Yanfeng, XIE Xiping. Cloning and Expression of GnIH Gene and Its Effect on Reproductive Hormones Secretion of Young Male Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(1): 201-212. |
| [10] | ZHOU Shiwei, WU Tingjie, WANG Qian, CAI Bei, HAN Saizheng, WU Yanhu, WANG Xiaolong, CHEN Yulin. Establishment of the Efficient Method to Detect the FecB Mutation and the Construction of the Prolific Tan Sheep Population [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 2920-2929. |
| [11] | LUORENG Zhuoma, WANG Jinpeng, JIAO Peng, LI Yanxia, DONG Yiwen, WEI Dawei, WNAG Xingping. Construction of Dairy Cow Mastitis Model and Analysis of mRNA Transcription Level of Inflammation Related Cytokine Genes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(8): 2763-2772. |
| [12] | YU Yongtao, MAO Yanni, ZHAO Qingmei, LI Jinrong, BAI Xiaonan, XUE Jiaqi, ZHANG Haodong. Expression Pattern Analysis of Related Genes in SWN Gene Cluster of Alternaria oxytropis Mutated by Ethyl Methylate [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(4): 1241-1251. |
| [13] | LI Yan, LAN Tingying, PANG Bo, YANG Xiaonong, HUANG Jian. Expression of NLRP3 Inflammasome Signal Associated Genes in Canine Mammary Tumors and Clinical Significance [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(4): 1252-1258. |
| [14] | LIU Yue, XUE Xianglan, LI Xiaobo, JIANG Lin, PU Yabin, HE Xiaohong, MA Yuehui, ZHAO Qianjun. Research Progress of the Relationship between Chromatin Accessibility and Animal Embryo Development [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(3): 680-687. |
| [15] | MIN Xingyu, YANG Lixue, YU Hailing, HU Yulei, YANG Manzhen, YANG Luyu, LI Jian, XIONG Xianrong. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Cattle-yak PPP1R11 Gene in Testis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(2): 481-492. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||